This article explains a simple pure sine wave inverter circuit using Arduino, which could be upgraded to achieve any desired power output as per the user's preference
Circuit Operation
In the last article I will explained how to generate sine wave pulse width modulation or SPWM though Arduino, we are going to use the same Arduino board to make the proposed simple pure sine wave inverter circuit.The design is actually extremely straightforward, as shown in the following figure.
You just have to program the arduino board with the SPWM code as explained in the previous article, and hook it up with some of the external devices.
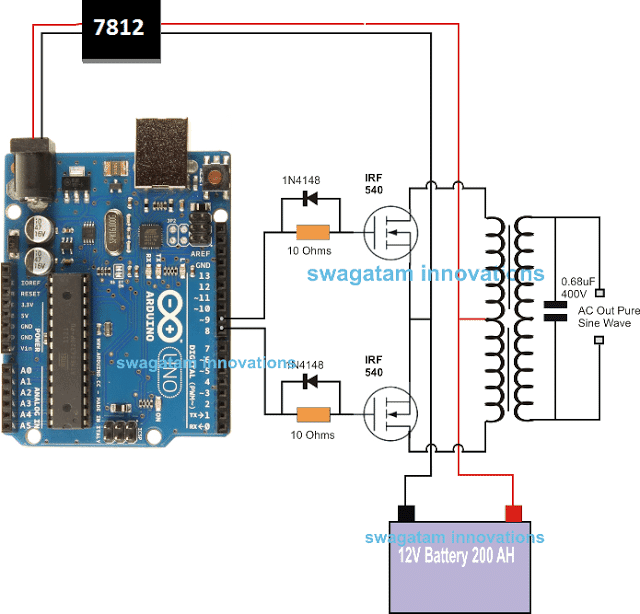
Pin#8 and pin#9 generate the SPWMs alternately and switch the relevant mosfets with the same SPWM pattern.
The mosfst in turn induce the transformer with high current SPWM waveform using the battery power, causing the secondary of the trafo to generate an identical waveform but at the mains AC level.
The proposed Arduino inverter circuit could be upgraded to any preferred higher wattage level, simply by upgrading the mosfets and the trafo rating accordingly, alternatively you can also convert this into a full bridge or an H-bridge sine wave inverter
Powering the Arduino Board
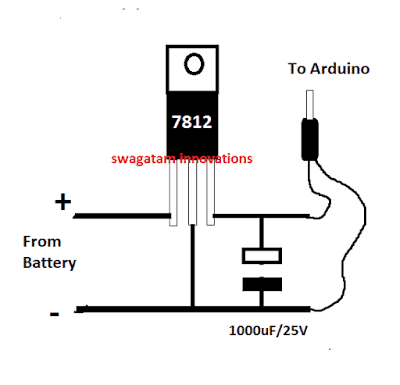
In the diagram the Arduino board could be seen supplied from a 7812 IC circuit, this could be built by wiring a standard 7812 IC in the following manner. The IC will ensure that the input to the Arduino never exceeds the 12V mark, although this might not be absolutely critical, unless the battery is rated over 18V.
If you have any questions regarding the above SPWM inverter circuit using a programmed Arduino, please feel free to ask them through your valuable comments.
Waveform Images for Arduino SPWM
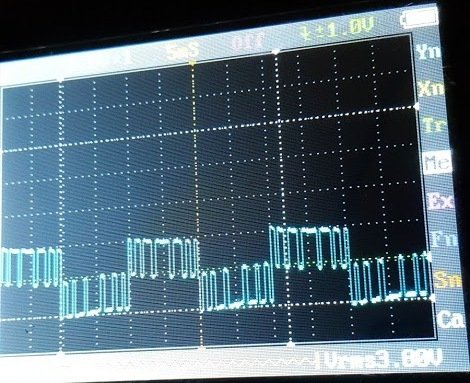
Image of SPWM waveform as obtained from the above Arduino inverter design (Tested and Submitted By Mr. Ainsworth Lynch)
UPDATE:
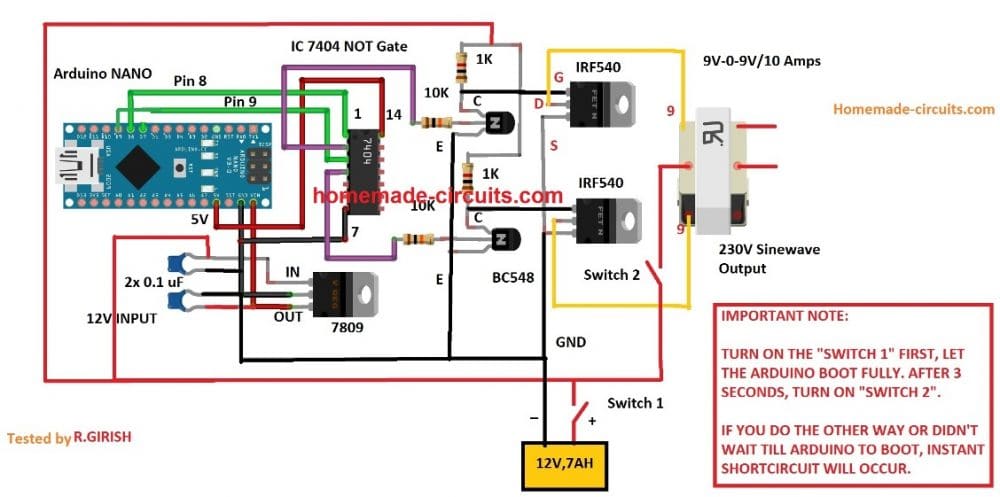
Using BJT Buffer Stage as Level Shifter
Since an Arduino board will produce a 5V output, it may not be an ideal value for driving mosfets directly.
Therefore an intermediate BJT level shifter stage may be required for raising the gate level to 12V so that the mosfets are able to operate correctly without causing unnecessary heating up of the devices,. The updated diagram (recommended) can be witnessed below:
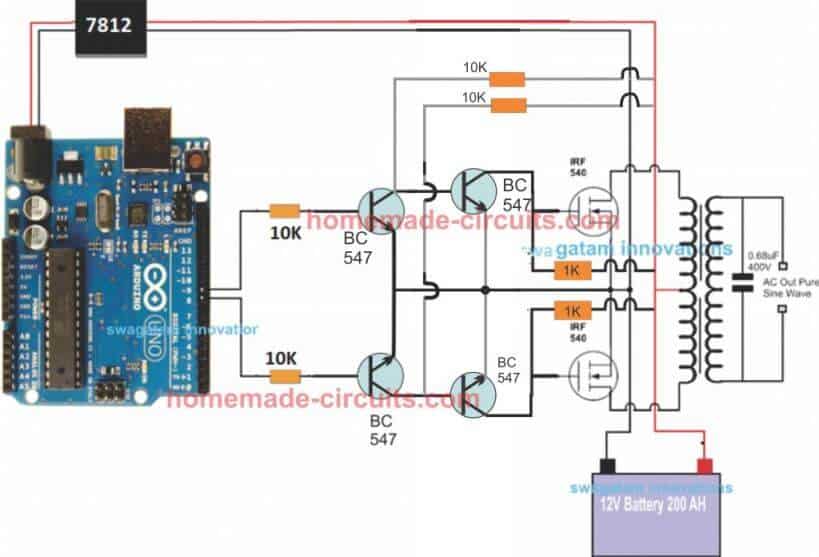
For the full Program Code please visit the following link: Arduino SPWM Generator Circuit
Video Clip
Parts List
All resistors are 1/4 watt, 5% CFR
- 10K = 4
- 1K = 2
- BC547 = 4nos
- Mosfets IRF540 = 2nos
- Arduino UNO = 1
- Transformer = 9-0-9V/220V/120V current as per requirement.
- Battery = 12V, Ah value as per requirement
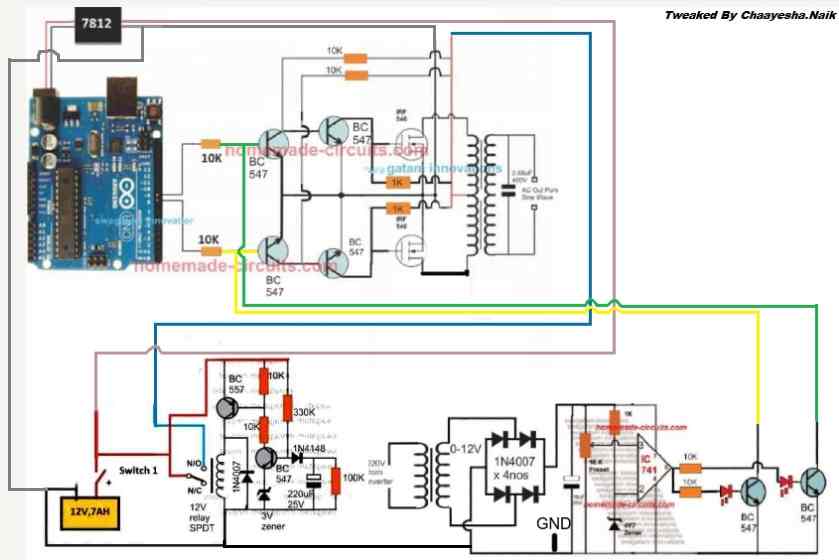
Delay Effect
To ensure that the mosfet stages initiate with a delay during the Arduino booting or start up, you may modify left side BC547 transistors into delay ON stages, as shown below. This will safeguard the mosfets and prevent them from burning during power switch ON Arduino booting.
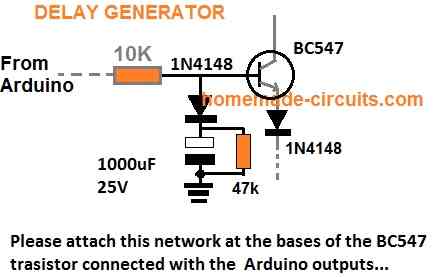
FOR INCREASING THE DELAY YOU CAN INCREASE THE 10K VALUE TO 100K
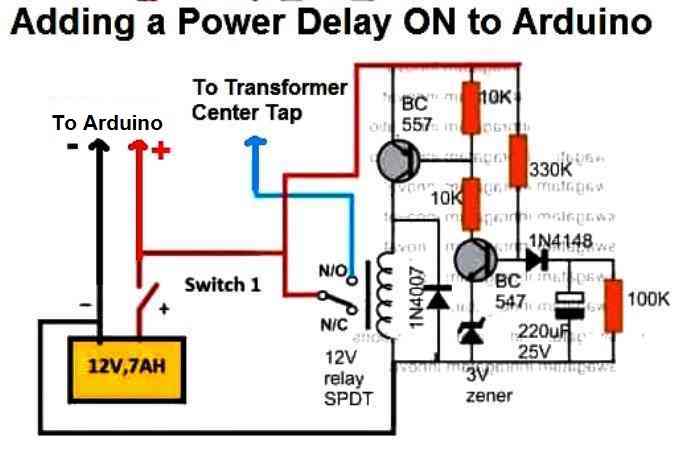
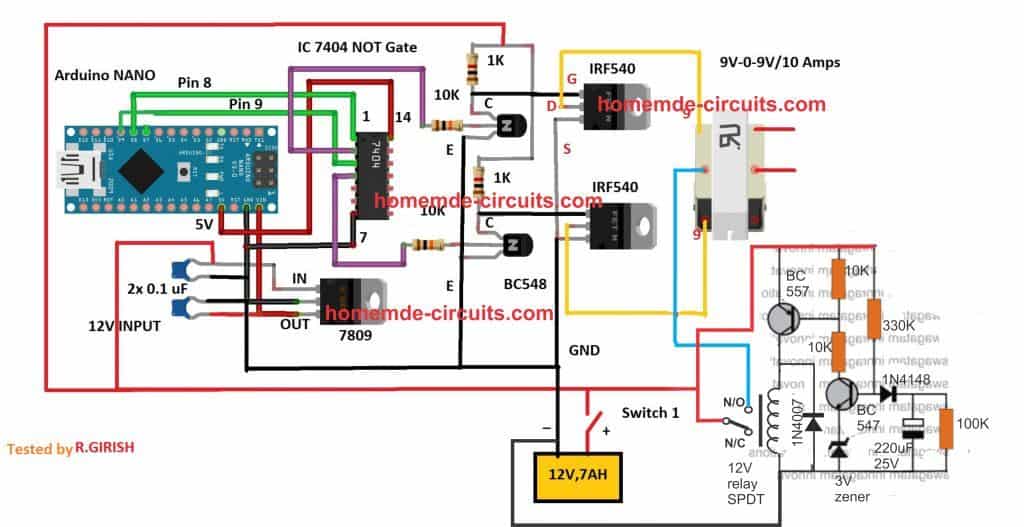
A More Reliable Delay ON Timer
If you are not comfortable with the response of the above passive delay ON timer circuit, you can employ the following configuration using BJTs and a relay. This design is extremely reliable and will effectively protect your Arduino and the inverter from burning due to a malfunctioning delay effect.
Just add this to the above inverter configuration.
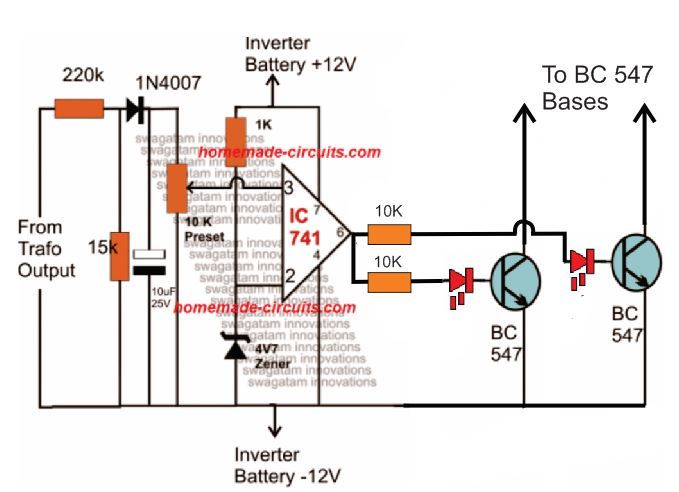
Adding an Automatic Voltage Regulator
Just like any other inverter the output from this design can rise to unsafe limits when the battery is fully charged.
To control this an automatic voltage regulator could be employed as shown below.
The BC547 collectors should be connected to the bases of the left side BC547 pair, which are connected to the Arduino via 10K resistors.
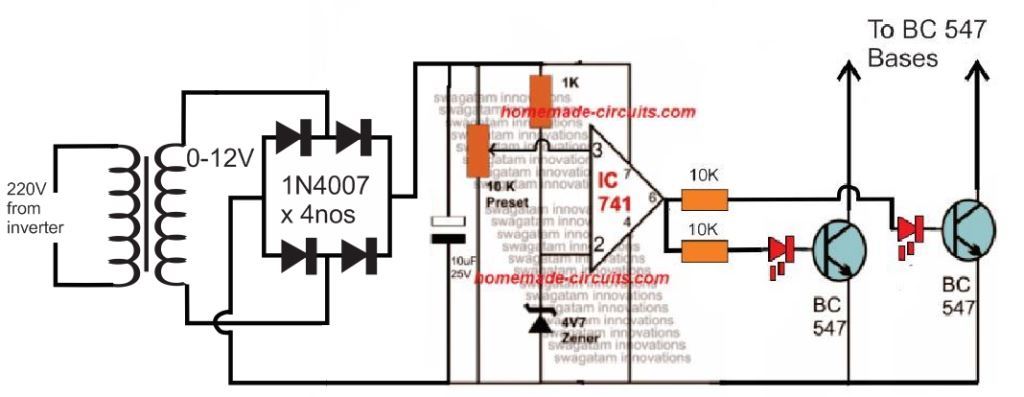
For an isolated version of voltage correction circuit we can modify the above circuit with a transformer, as shown below:
How to Setup
To set up the automatic voltage correction circuit, feed a stable 230V or 110V as per your inverter specs to the input side of the circuit.
Next, adjust the 10k preset carefully such that the red LEDs just light up. That's all, seal the preset and connect the circuit with the above Arduino board for implementing the intended automatic output voltage regulation.
The Complete Circuit Diagram
The complete diagram using the automatic voltage regulator and the delay ON timer would look like this:
Using CMOS Buffer
Another design for the above Arduino sinewave inverter circuit can be seen below, the CMOS IC is used as an aided buffer for the BJT stage
Important:
In order to avoid an accidental switch ON prior to Arduino booting, a simple delay ON timer circuit may be included in the above design, as shown below:
Hey I built this circuit today after some years now, I keep getting one Fet blown, not sure if its because I am using Irfz44n Fets, I did not build the delay on circuit, Instead switched pin 9 and 10 to input on boot up and added a delay then switch them to output when the arduino is fully booted after 2 seconds but I still have the same fet shorting on each leg, the software method is a standard practice, I I still get output from the inverter with one fet blown 30v.
Would irf740 work better thats the only other thing I have.
Hi, In my experiment I used IRF540 and did not have any such issues. But i don’t think the IRFZ44N can be the problem, unless the MOSFET has some internal defect. You can isolate the power supply input to the transformer center-tap and the Arduino, and then switch ON the Arduino first, and then after about 5 seconds switch ON the supply to the transformer and check the results.
irf740 may not be suitable because it is rated at 400V and your transformer may be rated at just 12-0-12V.
I added a software delay but when I read the article I realize the delay should just be for one Fet I delayed them both which is probably my issue.
also I used the modified spwm code that Mr Atton made im not sure if you tested that without issue also, if not I would just use your code.
Please initially check with a manual delay, by isolating the transformer center tap and the Arduino, and please use only the code supplied by me, because it is the tested one.
Hi swagatam. Trust you good?. I have designed the above circuit which is working perfectly fine. But my problem is the feedback circuit which I have designed just as it is but it is still not working. Please try and solve my problem for me. Thanks
Thank you Jonathan,
I hope you have built and implemented the following feedback circuit:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/Arduino-regulation.jpg
I would suggest you to test this circuit stage separately using a variac.
In this circuit, can you please test how much voltage do you get across the 10uF capacitor.
Remember, this DC voltage across the 10uF is the direct interpretation of the AC 220V that comes from the inverter output. When the inverter output voltage rises, this DCV also rises. As soon as this corresponding DC voltage at pin#3 of the 741 IC goes above the pin#2 zener vooltage, the output pin#6 of the IC turns high causing the BC547 to conduct and ground the MOSFET gates, shutting down the inverter.
So please verify the above stage separately and let me know.
Hi Swagatam,
As you know, sinewave PWM (SPWM) could be generated at different high frequencies (though much higher than 50 Hz). Since I don’t have Arduino board (though I design the hardware and firmware of my controllers using AVR MCUs, as ATmega8 and ATmega32) I wonder if you measured the PWM frequency which is generated by the offered Arduino firmware above. Thank you.
For instance, let us assume that the SPWM frequency is around 16 KHz. Naturally, it needs to be filtered to generate the 50Hz pure sinewave output at the transformer secondary. I read many articles on how to build a pure sinewave inverter, but none of them shows how the SPWM filtration is done. The only device which is supposed to do it in their circuits is the inverter power transformer since there is no explicit filter. But to let the transformer act as a filter, its mutual coupling coefficient (K) shouldn’t be made close 1 (as in mains stabilizers for example). The more K is made lower than 1, the higher the leakage inductance between the MOSFETs and the load is. And this leakage inductance does the filtering (shunted also by the iron losses at the high frequencies). But the more (K) is made lower than 1, the lower the transformer efficiency is. In practice, separating the coils of the primary and secondary, instead of winding them on the same coil, lowers (K). The optimum distance between the two coils is usually determined by trial and error. But if by adding a small capacitor (<1uF) at the transformer output (not loaded), the output voltage is acceptable (its high frequency ripple is hardly noticeable), the transformer is ok.
Thank you Kerim, for the valuable information.
Each 50 Hz half cycle is chopped into 7 pillars, or 7 pieces, so each 20 millisecond cycle accompanies 14 PWM peaks.
I know this may look a little higher to handle for an iron core transformer, but in my experiment it worked perfectly well, without any buzzing or heating up of the transformer.
Yes, adding a high voltage capacitor at the output side of the transformer helps to smoothen the SPWM cycles into pure a sinewave like frequency.
If I understood you well, the PWM of the Arduino program (above) is 700 Hz only. At this relatively low frequency, I expect the ripple of the sinewave output is not small. So, I wonder how it looks on your scope screen in your experiment. Please let me know if the output ripple could be made small even at this very low PWM frequency and without an external LC filter. Thank you.
But, even with such a high ripple, the generated output is much better than of a square wave or quasi-sinewave.
For instance, among your many published articles about the pure sinewave inverters, which one its PWM frequency is highest?
Thank you Kerim, for calculating the frequency.
According to my knowledge the only way to reduce the ripple is either by using a capacitor at the transformer output or by increasing the pwm frequency and using a ferrite core transformer.
In the above Arduino concept I used a 3uf capacitor at the output which produced a relatively good sinewave, however if this capacitor value is increased that might further help to improve the sine waveform quality and reduce the ripples proportionately, although that would also incur some power wastage. The above sinewave inverter project uses the maximum frequency for the pwm among all the published articles.
I asked about the SPWM frequency because lately I wrote a code for ATmega8 to generate the SPWM at 15.625 KHz (8000 KHz / 512). (For instance, since about 40 years ago, I used to write my CPU/MCU codes in assembly language only). This code can be used for a push-pull inverter which I designed its hardware too. Its push-pull transformer could be driven by two sets of N-MOSFET which, in turn, are driven by discrete circuits using BJT; NPN & PNP for fast turn on-off with dead time.
By simulating the code and its hardware, the results were as expected. I set K=0.99 in the transformer model. I hope soon I will have the time to test it in real.
In case we will find a way to let you receive files from me, I don’t mind sharing my design here (code and circuit).
MCUs existed 40 years ago? I did not know that. Thanks for sharing the info.
Sure, please feel free to share the codes anyway you like, through email or directly through comments using online free upload sites.
I appreciate your kind efforts.
Sorry for not being clearer. You are right, 40 years ago, MCUs didn’t exist, only CPUs did (as Z80).
I had to say on my precious post:
“In the last 40 years, I used to write first my CPU codes (for Z80), then my MCU codes (for C51 and AVR families).in assembly language only”.
OK, got it, thanks for the clarification.
Few suggestions:
– Can the delay circuit be realized mainly in the software? I think the Arduino microcontroller ensures that on power on, all I/O pins are set to the input direction and in the high-Z mode by the microcontroller electronics. Software must explicitly configure pins for output or PWM. Suppose the Arduino pins that drive BC547 transistors are pulled to the ground with 100k or stronger resistors. Would it be enough to ensure that the MOSFET stages initiate with a delay during the Arduino booting or start-up? MOSFETS will be active once the Arduino application reconfigures the pins driving BC547 transistors.
– The automatic voltage regulator can be realized mostly in the software. Arduino has 6 ADC inputs and is capable of performing tens of thousands of ADC conversions a second. A simple voltage divider with a diode and capacitor as a half-wave rectifier can be connected to the Arduino ADC pin. Arduino ADC pins have about 100k input impedance, so a half-wave rectifier should be good enough. After every SPWM cycle, Arduino can read the output voltage and decide what to do next.
Thank you for your valuable suggestions, it would be indeed very nice if the delay feature and the automatic voltage control are added within the Arduino. Please let us know if you have the necessary programming codes for that.
Yes, if the Arduino pins that drive BC547 transistors are pulled to the ground with 100k or stronger resistors, that would be enough to ensure that the MOSFET stages initiate with a delay during the Arduino booting or start-up.
Would I only need to pull one side to ground or both bc547
both the BJTs….
how can I make closed loop single phase inverter using Arduino
Please go through the above article, everything is explained in it.
Hello sir I want to control inverter out put by varying the the duty cycle values of arduino by push button from 0 to 100% duty cycle at increment or decrement by 1%.
I want to make 0 to 10 volt pure sinwave inverter at 400 Hz frequency and the ac voltage can be controlled by microcontroller at +/- 1% duty cycle variation so that 10 volt AC change accordingly.
Thanks and regards.
Please suggest me the code and circuit.
Hello RK, I wish I could solve your query, however my Arduino coding skills are not good enough, therefore it can be difficult for me to help you with this question.
thanks for reply.
So the CMOS based circuit seams like an inherently better circuit as circuit loading does not affect the arduino outputs? however, I notice there is no feedback mechanism like it the upper circuit. Is it not possible or just not needed because of the buffer?
There’s no loading with the transistorized circuit also due to the presence of the 10K resistors. 10K is quite a high value and will absolutely not cause any loading on the Arduino.
Yes, feedback might not be necessary since the Arduino generates a fixed PWM.
then which circuit would you choose? I am planning to build a low powered 12V, 500ma, to 120V variable frequency inverter.
Also, I have started trying to source components for the CMOS version but find that at Digikey many items are either obsolete or require purchasing large quantities, I’m not willing to pay $3000 to use only 2 transistors. Can you suggest alternate parts?
The transistorized version of the above Arduino inverter is the most efficient one and is a tested design. I would recommened this design. The 10K resistor associated with the Arduino outputs can be even raised to 100K to reduce loading.
I did not quite understand what you meant by “I’m not willing to pay $3000 to use only 2 transistors. Can you suggest alternate parts?” Kindly elaborate
BC547 is listed as obsolete on Digikey. https://www.digikey.com/en/products/detail/onsemi/BC547/976363#product-details-substitutes
BC548 is also obsolete in bulk, but i I buy 6662 of them they are only .05 each. ($333.10) , https://www.digikey.com/en/products/detail/rochester-electronics-llc/BC548/11545848
i forget which one only had a $3000 option. i’ll have to take better notes in my searching
That’s super strange because BC547 is the most standard type of BJT and one of the most used general purpose transistor…. how on earth this transistor can become obsolete??
You can try 2N2222 or any other equivalent transistor, they all will work.
couple more questions about the Voltage regulator circuit.
1) what is a 4V7 zener? 4V, 7V 4.7V? or other?
2) there are 2 led’s shown in series with the gates on BC547. are they required? this will be in a box and used remotely. do they have a troubleshooting purpose?
1) 4V7 = 4.7V
2) Yes they are required, since the LEDs prevent the leakage or the offset voltage from 741 output to reach the base of the BC547 transistors, thus preventing false switching of the transistors..
are they just standard 12V(forward Voltage) Red LED’s?
They are standard 3.3 V, 20 mA LEDs.
one more question about the voltage regulator, is this what you mean by IC741?
https://www.digikey.com/en/products/detail/texas-instruments/TPIC74100QPWPRQ1/1531097
if so, is there a through hole substitute?
741 is an IC, not a voltage regulator, if you are not familiar with 741 IC then I am afraid you should not try this circuit, chances are you might not succeed.
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/IC-741-and-LM393-comparison-compressed.jpg
Sorry, I did not recognize the Op-Amp symbol. The regulator I found is Also an IC. Searching on Both digikey and Mouser for IC741 resulted in nothing, so I went the hard way (drilling down) and had to choose a category. Voltage Regulator was just a guess. The wiring for the OP-Amp seams straight forward (other than the LED’s,) and i plan to use a socket so as to not damage the Chip when soldering, so i’ll take my chances. I’m just an electrician with electronics hobby experience not an electronics engineer. Sorry for the dumb questions, but I need this Arduino controlled inverter for one of my other hobbys (Astrophotography) .
No problem, you can go ahead and build this project. The op amp output voltage control might not be necessary since the Arduino is generating a calculated fixed PWM, so the output voltage should be pretty constant.
sir, how to construct a 450w 12vdc-230vac solar inverter?
Aqil,
Please provide detailed information regarding the inverter and the load, if possible I will try to help.
A 12V solar panel and 12V battery supply to a 350W water filter. All i need is 500W (inverter sizing) inverter circuit diagram with code
If you divide 350 by 12, it gives 30 amps, so your transformer must be rated at 6-0-6 30 amps or 32 amps. Please get this transformer then I will tell you how to proceed.
i dont find for step up transformer. i just found for step down transformer…
Step down transformer will do but it must rated at 6-0-6V 32 amps on one side and 220V on the other side.
Okay now proceed to the next step sir
Did you get the transformer?
Yes
Please build the circuit which is explained above using that transformer. You will also need a 12V 300 Ah battery for the 350 watt output
Hello sir, thank you for the Arduino sine wave circuit, can the circuit also be used for 24V DC?
Thank you Emmanuel,
24 V can be also used. For that you will need a 12-0-12V transformer and the +24V will need to be fed on its center tap. The Arduino must be fed with 12 V through a 7812 IC.
Hi…. I really love the first topology. Believe it’s the pull-push topology. However, despite reading, I can’t figure out the use of the diode connected in parallel to the 10 ohm resistor. I thought it should rather face the other direction to prevent current from going back into the arduino.
Glad you liked the post. The diodes make sure that the when the Arduino outputs are 0 logic or during the switch OFF periods the internal capacitance of the MOSFETs can discharge very quickly through the diodes, causing minimum heating of the MOSFETs.
Thank you for this simple circuit. I have tried it and it is currently working. I need help, please, with a circuit to charge batteries from solar cells. by using arduino and igbt
Sorry, I don’t have an Arduino, IGBT based solar charger with me right now.
Hi Swagatam
I discovered that by connecting an LC circuit to the output of the square inverter circuit the square wave gets filtered into a pure sine wave. I have used an 30A 20-0 transformer ‘s secondary as the inductor and a 2.5MFD capacitor so can you conform that it is a pure sine wave inverter ?
Thank you,
Chaayesha.Naik
Hi Chaayesha,
That is correct and possible, but the results will not not too accurate and efficient. It will not be pure sine wave. Initially try only with a capacitor, if the results are not good then add an Inductor also.
Hi Swagatam
I really want to try doing this, if not with a single IGBT can it be done with an H – bridge arrangement also can you write a code for it please
Hi Chaayesha,
Unfortunately my Arduino coding skills are not good, so it will not be possible for me to write a new code. Also adding a H-bridge can be quite difficult with this Arduino circuit.
Hi Swagatam
I need some help in building a pure sinewave inverter using a single IGBT with the UNO board what i want to do is convert the square wave 240v to dc using FBR then switching it with the IGBT in a sine wave there by converting the squarewave inverter to sinewave because i have some majour issues with the MOSFET blowing up so i will use a square wave inverter board with this circuit so can you please write a program for me
Thank you
Regards,
Chaayesha.Naik
Hi Chaayesha,
Using a single IGBT will not produce a push pull AC output which means the output will not have negative AC cycles, there will be only positive cycles above the zero crossing line.
Also the full bridge concept can be quite complex to design, instead you can use the following concept using 12V battery and a transformer:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/single-IGBT-sine-wave-inverter-circuit.jpg
Thanks for the replies, I really appreciate your good works. Please can you help me with a circuit diagram of mppt charge controller?
Hillary, you can try exploring one of these articles:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/?s=MPPT+homemade
Good day Mr swag. I made the inverter as drawn, I used irfp150 MOSFET and the MOSFET gets too hot, what should I do about it?
Hi Hillary, the MOSFETs should not get too hot. Even at full output load the MOSFETs should become little hot, up to around 80 to 100 degrees Celsius. I have tested this circuit, I did not find mosfets getting too hot even with a load connected. Something might be wrong with your circuit.
You can try adding large heatsinks to the MOSFETs and check if that helps to solve the issue.
Good evening sir, thanks for your time and teachings. More grease to your elbow. My question is, how do I add a feedback to an Arduino based inverter with a center tapped transformer?
Thank you Hillary,
Adding a feedback to the Arduino will require additional coding and reprogramming of the Arduino board, which I am not sure how to do. That is why I added a feedback through a external op amp circuit.
I did build your cct and it works great .. Thanks.
I just need to add the over Voltage stage.
With a square wave osc the duty cycle can be varied and the output Voltage can be regulated.
With a Sine wave osc the duty cycle cannot be changed and regulating the output Voltage becomes more complicated.
QUESTION:
Is it possible to have more than one Sinewave array , where the sharp turn at the top of the Sine
is still round but a little more flat thus putting more current into the Transformer.
I think this will work , BUT I dont know how to create the Sine values for more flatter top and keep the freq at 50 Hz.
Can you help with creating these values.
Sounds great! The flat top sinewave can be perhaps created by increasing the microsecond delay 2000 to 3000. This 1000 microsecond increase in delay can be subsequently compensated by reducing the other delays proportionately
Sir please what is the name of that your oscilloscope
It is DSO138
Do have to program the Arduino nano
Yes the Arduinos need to be programmed with the following code:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/arduino-spwm-generator-circuit/
Thank you for this posting about sinewave inverters. This is a subject I am particularly interested in. I have been involved in designing and building inverters for about 40 years now, where the power outputs are anything from 50 watts to 5KW. I have usually based the batteries on either 24 or 48 volts and have had very good results. I was wondering about your timer circuit to switch on the inverter after the Arduino had booted. The FETs on the output could easily be referenced to 0v via 4k7 resistors with collector tied transistors deriving their power from the 12v + line. The gates of the FETs could then be driven from the emitters of the transistors with a 1K resistor. In this way the output FETs would not conduct until the previous sections had received pulses from the Arduino chip. The timing circuit would not then be needed.
I would be very keen to know what you think about this modification as this has been the basis of most of my inverter designs over the years. I have supplied thousands of inverter systems over the years and many of them are working very well still.
Kind regards
Thank you for asking this interesting question.
An emitter follower driver cannot be used here for the FETs, because the output from the Arduino is 5 V. So if an emitter follower is used, the FET gates would finally get a voltage of around 5 – 0.6 = 4.4 V, which will not drive the FETs optimally, causing a lot of heating on the FETs.
Moreover, we are not sure how the Arduino outputs would respond during the booting phase, that is why a timer is used to ensure a 100% safety to the FETs.
My challenge is that for pure sine wave inverter the transformer input is wind half the battery voltage for example a 24v inverter system 3.5kw the transformer input is wind to handle 12v – 14v for pure sine wave inverter my question is how will the control circuitry divide the 24v from the battery so that the transformer will receive 12v to 14v and also how to determine the transformer input wire guage .
Thank you for replying
It is done by the SPWM waveform, whose average value would be around 12V DC.
Hi
Great article, but nowhere do you seem to mention the power rating, ie how many watts can this circuit drive, I couldn’t find a spec for the transformer – that would have told me too.
Hi, thanks! The power rating will depend on 3 items: The transformer, the battery and the MOSFETs, you can customize or upgrade these three items appropriately to get any desired power from the inverter.
More on this can be studied here:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/how-to-calculate-and-match-inverter/
Super , great article also
Glad it helped!
Hi
I have a doubt that dose the Automatic Voltage Regulator also increases the voltage when the voltage drops below the set voltage ?
Regards
Hi,
No that will not happen. Voltage regulator will keep the output voltage constant only as long as the output RMS is above the minimum threshold, such as 220V. If the output is over loaded and the voltage drops below 220V, then the automatic regulator will not be able to do anything.
Hi swagatham can you check if the schematic is correct so that i can start building the inverter
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/Arduino-sine-wave-inverter-with-delay-ON-timer-and-automatic-volatge-correction.jpg
Thankyou
Regards
Hi Chaayesha,
Your diagram is correct. I have made a small improvement in the diagram by connecting all the GND lines together, which is very important.
Please do not build the whole circuit at once, otherwise it may have errors and problems.
Build each stage separately, check them separately, if they all work satisfactorily, only then integrate them into one.
Hi
Thanks a lot as you said i will build each stage separately and if i have any dobuts while building the inverter i will ask. Also you can share the schematic to anyone if they want to check it or also you can post it on the site. Again thanks a LOTTT!! because no one else would reply on other sites
Regards
You are most welcome! Let me know if you have any further issues! I am always glad to help!
Hi swagatham i am not able to post the schematic link in the website it constantly refreshes so can i send you the file trough E-mail ?
Hi Chaayesha,
Your comments were going into the trash folder because of the “https” in your link. Always remove the https while posting a link.
But no issues I have restored your comment from the trash folder and have answered it. Please check your previous comment for the reply.
Hi
Swagatham Thanks for the reply!. the thing which i cannot understand is the collector from the bc547 in the automatic voltage regulator circuit must connect to the right side or left side of the 10k resistor near the UNO.Also i had questions regarding that if we can use 4MFD fan capasitors (2 in parallel) and if we can use a 10-0-10 transformer instead of a 9-0-9 transformer. And can we add a (IRF9630)P-channel mosfet before the N channel mosfet so that the gate of the n channel mosfet gets pulled up when gate of the P channel mosfet gets pulled down and the 1k ressistor is pulled down of the n channel mosfet.Also will the UNO get burnt if the BC547 from the automatic voltage regulator circuit sends an voltage back to it while trying to regulate the voltage ??
Regards
Hi Chaayesha,
I have already answered to all your questions. Please refer to your previous comment.
Sorry i sent it 2 times. and also i am preparing a diagram with all the circuits and after its done i will share it with you and you just verify if its ok .
Regards
Sure, no problems! Let me know if you any further doubts.
Hi swagatham,
I am designing a puresine wave inverter using irf3205 so can you send me the circuit diagram for it with the delay circuit and Automatic Voltage Regulator circuit
Thank you!
Regards
Hi Chaayesha,
I think you can build the inverter design which is explained in the above article. It has all the facilities that you intend to have in your inverter design. Let me know if you have any further doubts or queries…I will try to solve it for you quickly.
Hi
i am not able to properly under stand how to connect both the delay circuit and Automatic Voltage Regulator circuit together so can you please draw the schematic with both the delay circuit and Automatic Voltage Regulator circuit connected to the circuit in the 4th picture. I am realy sorry for the inconvenence
regards
Drawing all the stages can make the diagram too big to accommodate in the page. Please tell me what you cannot understand, I will try to sort it for you. I would recommend that you first build the basic Arduino inverter circuit with the delay ON feature. Once you build it successfully then I will show you add the automatic output voltage control to the circuit.
For the delay ON timer you can add the following circuit with the Arduino and the battery.
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/Arduino-power-delay-ON-circuit.jpg
Hi
Thankyou for your reply , i can understand that Drawing all the stages can make the diagram too big to accommodate in the page.So the part that i cannont understand properly is that the collector from the bc547 in the Automatic Voltage Regulator circuit will connect before the 10k (next to the UNO left side) to the mosfets or after the 10k to the mosfet (right side after the UNO) but also the collector from the bc547 in the Automatic Voltage Regulator circuit will supply a voltage to the mosfets and the UNO so will the UNO burn if it gets a reverse voltage ?. And thankyou for the delay part i understood it. and also will a 10-0-10 transformer work in the place of a 9-0-9 transformer also can i use a 4MFD fan capasitor (2 MFD caps in parallel). and I think that if we add a low power (IRF9630) P channel mosfet before the N channel mosfet the delay circuit is not requierd right ?? also if you use a logic level p channel mosfet before the n channel mosfets then the transistor circuit is not requierd ?? correct me if i am wrong thank you .
Regards
The collectors of the BC547 transistors of the Automatic Voltage Regulator circuit will connect after the 10K resistors which are associated with the Arduino output (with the bases of the left side BC547 transistors of the inverter).
The Automatic voltage regulator will not supply any voltage, instead it will ground the base voltage of the inverter BC547 transistors to initiate the shut down process.
It is protected with a 220K resistor and diode so there’s no question of any burning unless you make a wrong connection. If you are not confident then you can use the transformer version of the circuit. Any transformer between 3-0-3V and 12-0-12V will work (500 mA).
I can’t figure out how a P-channel mosfet can avoid the delay circuit? According to me it is better to add the delay circuit for maximum safety.
very interesting. can we convert DC to AC 11w tube using hybrid transformer?
expecting your valuable guidance.
Yes that’s possible. Yu can try the following circuit:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/electronic-ballast-circuit-for-uv-germicidal-lamps/
Hi Swagatam
I am Designing the H bridge converter, I required Sinusoidal at high frequency (3kHz). Can you guide me on How should I change the Arduino code to obtain High Frequency at Output?
Regards
Hi Leo,
you can probably try the following circuit for the H bridge design, but make sure the battery and transformer are 12V rated.
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/arduino-H-bridge.jpg.webp
Changing the code can be plenty of hard work and a lot of thinking. Basically you will have to replace each of the microsecond delays with smaller delays such that they together add up to produce 3000 Hz for each channel.
Hello Swagatam. You have great circuits and great explanations to teach folks about the circuits. Here’s my idea: 55 gal blue drum full of 400 pounds of water is my gravity battery. Pull it up to some height with a block and tackle. My goal is to run a 5000 btu ac for 1 hour. 5000btuas/3412btusper kw is about 1400 watts, and running this contraption would give some cool air for an hour. Then make someone else crank the drum back to to run it again. At first I looked into a 3phase PMA alternator that puts out 12V 3phase at 150 rpm, and has a three phase rectifier, but the spec for the alternator says I need more rpm to get more watts. I have a 1500 watt 12V inverter. Lets say my blue drum spins a Big Pulley like a bike wheel, which turns the PMA or even a 100 amp car alternator and its putting out 24V. Seems like that would put out twice the volts modified sine wave, which would make my window unit very unhappy. So I need a clever linkage to spin the alternator at whatever rpm it takes to keep 12V going into the inverter. Plan B would be to make it completely electronic, but since this proj seems to be mostly mechanical, and just uses a car alternator and a harbor freight inverter, do you know how to make a governor to run the alternator at the right speed? Hope you write back.
Thanks Bob! Your concept looks interesting.
If you are looking for a circuit to limit the speed and the voltage output of an alternator, then yes that can be done through a simple shunt regulator circuit. Is the alternator a 3 phase alternator or a single phase alternator?
Hello Swagatam.
I wish to thank you for all the circuits you make available for free on your site. They are very educational to a amateur radio operator like me. My call is KE4WCE.
My question is where in the code for the Arduino Pure Sine Wave Inverter Circuit would I need to change from 50Hz (cycles) to 60Hz and replace it with what number.
Or if you don’t mind me asking the math formula and a example so I may able to do it myself.
Thank You 73’s
Thank you very much Amos,
In the Arduino code explained above we have used the total delay on each channel as 10 ms, since each 50 Hz AC half cycle requires 10ms to complete. For a 60 Hz cycle the completion time of half cycle becomes 12 ms. So you will have to adjust the microsecond time (in brackets) on each channel of the code in such a way that it produces a delay of 12 ms or 12000 microseconds.
Thank you For the fast reply. I am going to have a go at it and see if I can duplicate your circuit. Again Thank you for your time and patience.
73’s
I am glad to help!
HI,
I Build the first most simple’s project on the page. After programming my arduino I founded that my irf540 is heating up and when i checked the frequency on my arduino ouput it was around 500 hz . I am most certain thats why the mosfets heat up. I cannot see what i am doing wrong. Advise please
Regards
Peter
MOSFETs can work with frequencies up to MHz and GHz, so frequency can never be a problem, I have tested the design thoroughly and had no such problems. My MOSFETs also heated up a a little but it was because of the 100 watt load at the output of the transformer. If your MOSFETs are heating up due to an output load then it is normal, simply put a heatsink on it.
And one more thing…. instead of using high voltage capacitors at transformer output for waveform smoothing. can we use low voltage capacitors at the transformer input??? voltage and power handling will be easier… what say??
I don’t think that might be possible, because at the input side everything is PWM based and digital which cannot be transformed into an analogue sine wave….the transformation may be possible only at the output side of the transformer.
Hiii Swagatam, The delay circuit is introduced as a safety. But What I say is instead of introducing a circuit why dont we use aurduino digital output signal to switch the DC supply to inverter circuit. mainly for three reasons, 1) Human error is eliminated. 2) circuit is simplified 3) Delay circuit malfunction hazard is also eliminated. Whats your say in this??
Thanks Vivek,
My Arduino knowledge is not good, so I won’t be able to suggest on this modification. If you think this is something feasible then surely it can be implemented and tried in this design.
Best Swagatam
I may be understanding the circuit diagram wrong but I simulated the circuit and it does not seem to work.
I don’t understand how the positive terminal can be connected directly to the base of the mosfet. What is the reason for the BJT level shifters? Also a positive voltage is applied again directly (resistor in series… so voltage division?) to the bjt. I would like to build this circuit but cannot seem to understand its working principle.
Would it be possible to communicate by email for me to better understand the circuit please?
Kindest Regards Christiaan
Christiaan, level shifters are necessary to enable the mosfets gates to get 12V supply so that they can conduct optimally. If we connect the mosfets directly with the Arduino, the gates will be be able to get only 5V which may not be sufficient for the mosfets to switch ON perfectly.
The first BC547 inverts the Arduino PWM so it cannot be directly used with the mosfets otherwise the mosfets gates would be switched with inverse PWM signals. The second BC547 corrects this issue and makes the PWM same as the Arduino output, but at 12V level
The circuit is fully tested so you can build it and test it for getting the required results, simulation is not required.
Thank you for the response.
That makes sense but wont the voltage to the mosfet be 13.3V since this is more the operating voltage of a 12V battery? Is this still a suitable value?
Then lastly do you have a inverter circuit that does not use a transformer but still steps up from 12V to 230V?
Sincerely Christiaan
Most mosfet gates are designed to work with upto 20V, so 13V is quite OK.
Making an 12V to 230V inverter without a transformer is almost impossible, as far as I know.
Thanks for the replies Swagatam.
This is definitely one of the only sites where you get replies.
What is the wattage of this inberter?
It’s my pleasure Tiaan.
Hello
Can you show the charging circuit?
All the best
J K BARIK
Sure, you can get the desired battery charger circuit from these two articles:
Lead Acid Battery Charger Circuits
Op amp Battery Charger Circuit with Auto Cut Off
Hello sir , can you please tell me how the feedback circuit works and why you connect them in the gate of the Mosfet but not in the arduino .
Lalawmpuia, where do you think the feedback can be connected with the Arduino? It will require special coding for that. Connecting the feedback to MOSFET gates is an universal option which can configured easily without any coding by anybody and with any inverter.
Sir can you please explain how the BC547 collector is connected to the base/gate of the BJT/Mosfet . Since I have a hard time understanding that . Since the emmiter side is connected to ground and does that simply pull down ?
The BC547 collector will pull down the mosfet gate while it is ON, and when it is OFF the mosfet gate will get the switching voltage through the 1K resistor.
How does the feedback works? since the feedback ( bc547) emmiter is connected to the base of the bc547( arduino output ) will it just pull down from bc547 base to ground . Please explain the worling of this feedback . Also I tried your Circuit and code as well but I have burn out 10 mosfet ( 5 times irfz44n and 5 times irf3205 ) in just under 10 seconds . It was too hot to even touch .
When the input voltage to the op amp circuit exceeds the set limit the op amp output and the BC547 conduct and grounds the Arduino BC547 bases causing the mosfets to shut off. As soon as the mosfets are turned off the voltage begins to drop which reverts the opamp output causing the mosfets to switch ON again, and this process continues which keeps the output voltage within the desired range.
Your mosfets may be burning due to some fault in your design, or may be the mosfets are not good quality.
You can in the video the circuit works perfectly even while the circuit is built without any PCB.
Thank you so much .
Hello sir , I have a question about the transformer , if I use a 6-0-6 transformer rated at 3A , at ideal mode , what will be the rated watt of the output ? Since 3A is the highest rated transformer I can buy from our state .
Hello Fanai, it will be 6 x 3 = 18 watts for each half cycle of AC output, that means for one full AC cycle it can be around 36 watts
Hello sir , how are you ?
I have one question regarding the feedback , my circuit is exactly same as your circuit , and the transformer I used is from an old ups , and the question is , the output Voltage decrease to 140V from 210V when connected a load . Will the feedback you posted work in this situation to give 220V constant even when connected to a load ( 60W incandescent lamb) ?
Hello Fanai, no, the feedback cannot boost a low voltage happening due to over load or low wattage transformer/battery, it can only prevent an over voltage. To correct the voltage drop you must ensure that the transformer, battery and the mosfets are appropriately rated as per the load requirement.
k. well the solution i have now will have to do till i have more time. seems the best way forward will be to build an inverter that doesnt have over voltage protection. when i have time i’ll pull the transformer out of the old inverter, check it to make sure it meets the specs of the Arduino. i’ll also grab the heat sinks for the mosfets. then i’ll have another 1000 questions for you. thank you for your help.
Sure, no problem, all the best to you!
this may be off topic, i’m looking at building this inverter but perhaps its better to tell you what my problem is first because you may have a better solution. i have a 300 watt inverter thats doing just fine. but its connected to lithium ion batterys instead of lead acid. the ion batterys are 4p so top voltage is 16.4. the inverter has i high voltage cut off at 15.5. i’m working around the problem by placing a buck inverter between the batterys and the inverter, the buck inverter is set to output at 14.9 volts. this works but seems wasteful. is there a more efficient way to lower the voltage to the inverter ?? or should i build this inverter you describe ?? one last note, i have an old modified sine wave inverter that took 3 months to destroy my refigerator, is made by a company called “trip” (good quaility), its 3000 watts 12 volts, its very heavy, do you think i can strip the transformer and mofets and heat sinks from the trip inverter ? is it worth the effort? so the big question i have for you is this, if you were in my situation what would you do ?
Using a buck converter between the battery and the inverter can be indeed quite wasteful, but unfortunately there’s no other more efficient way than a buck converter, except if one Li-Ion cell is reduced, and a 3S combination is used with a 12.6V output supply.
The transformer winding rating must match the PWM average of the Arduino in the above explained concept. The average voltage at the collector of the first BC547 transistor will be the value that must match the half winding specs of the transformer.
So definitely you can salvage the transformer from your 3000 watt inverter but the criteria are it must be a center tap transformer and winding data must complement the Arduino PWM rate. For the mosfets However I would recommend using new MOSFETs, unless you are entirely sure that the mosfets from the old inverter are perfectly intact and good.
Hi Mr
i have built a small circuit using Bc547 & Bc557 as BJT Buffer stage to drive the Mosfets (i’m using IRFZ46)
when i check the ouput of the buffer stage connected to Arduino uploaded with Spwm Code
on DSO138 oscilloscope the output is same as the pattern of the wave in the picture on the page
But on the Drain of the Mosfet its square wave
Why?
My circuit using readymade oscillator SG3524 is working fine
But using the Arduino the output is connected to lamp & is flashing
any idea?
thanks for ur Help
I need another circuit which i didnt know how to contact the page
a small Solid state relay using mosfets which have Com positive or negative 12V
NC NO so i can select which source to use power of
2 12v dc inputs & 1 output \]
Thanks
You must do exactly as shown in the above schematics because it is a tested design, I cannot suggest about any other configuration.
if i connect the oscilloscope to the Drain of the Mosfet should i see the same signal as the arduino output ?
i will test it with 2 npn transistors instead of the buffer stage i have used
thanks for help
Drain waveform should be exactly as its gate waveform.
any suggestions why i get square waveform on the drain when the gate is the same as the waveform in ur pic ?
That is actually not possible. The ON/OFF switching of the drain is dependent on the ON/OFF switching of its gate, and has to be exactly similar. Not sure why it is not happening for your mosfet…
It’s interesting how people solve a problem based on their background. You designed a delay circuit to insure there are no shoot-through conditions at startup. Being a software engineer, I would have done this in software by driving the relay with transistor and an output from the Arduino :-).
Great article, thanks for publishing!
Thank you for the feedback, I completely agree, this could have been solved through a code modification also.
Hi swag, which pin of the arduino do I connect the delay generator to
Hi Nimel, the pin8 and pin9 go to the first BC547 via 10k, this BC547 base is configured with the delay timer network, so it is the pin8 nd pin9 which go to the delay network
Sir, can you please share the transformar specification, required for this project.
Thanks.
Partha, the transformer voltage can be 6-0-6V for a 12V battery. Transformer current will depend on the load wattage. If the load wattage is 200 watt then dividing this by 6 becomes 33 amps and so on.
Hello Sir,
Thanks for the article,i would love to know more on the programming aspect.Please can you explain in detail how the avr side of the above circuit works to protect the circuit,like when the LED lights up,what does it mean,and can i implement it on all other inverter circuit?
Hello Patrick, yes you can use the concept universally with any inverter circuit. More details can be learned from the following artcle:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/load-independentoutput-corrected/
thanks for the good circuit .
Kindly tell if we want to vary the frequency or if we wants the the output at 1 kHz
Thank you for liking the post!
Yes you an change the frequency to any desired value, simply by altering the “microsecond” values in the code.
As you can see, the above applications works with 50 Hz frequency, therefore the microsecond delays in the code across both the channels are adjusted accordingly to a 20 ms value.
For 1kHz, this total delay for the entire code will need to be adjusted to 1 ms.
Hi,
If you are going to use 1kHz, then you will probably need to design or obtain a transformer suitable for the job.
The 50/60Hz transformers used here will not provide the performance at 1 kHz.
The impedance of the transformer is lower at 50/60Hz than at 1 kHz.
In fact it will be 1000/50 = 20 time higher.at 1 kHz.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrical_impedance
It’s around 700 Hz, which is not too bad for an iron core transformer according to me…in my experiment everything worked fine.
Excellent article.
What would need to change to cater for a 24v battery?
Thank you, no changes will be required, except the transformer and the battery. The transformer can be a 12-0-12V for the primary side
здравствуйте. а можно как-то реализовать между переходами мертвую точку или
dead line
dead time already introduced at the end of the codes for each channel
digitalWrite(8, LOW);
//……
digitalWrite(9, LOW);
}
//————————————-//
Thanks for quick reply on my previous comments. I want to know one more thing how output frequency calculated. For some spacial applicatoin i want to lower the frequency about 10Hz to 15Hz. Please help.
It will depend on the specific oscillator circuit, and the RC parts used in the oscillator. The frequency can be changed by changing the RC values of the oscillator.
Thanks for the reply, but think there is some confusion, The frequency shoud be depends on arduino code coz SPWM is generated by arduino itself…?
Yes, for the above Arduino, the frequency is dependent on the delay (microsecond) set for each of the PWM blocks. You can modify them accordingly to ensure the waveform delay coincides with the frequency timing or the Hz rate
Hi, Nice projects is this, I want to make this same project with 110V DC source, can i replace 12V DC source with 110V? Second thing in place of saperate Power On delay circuit, we can also use Arduino itself for the same.
Hi, thanks, for 110V DC input you will need a 110V transformer connected with the MOSFETs.
you can use the same power for the Arduino and the delay circuit
Good day Sir
I am in the first stage of building the inverter with the AVR(not the isolated version)
I want to know if I connect the collectors of the BC547 in the AVR to the bases of the BC547 outputs of the Arduino,won’t it interfere with the output signal of Arduino?
Thank you
Dean
Hi Dean, it will interfere, but due to the transformer inductance and capacitive filter at the output, the waveform will be leveled of, and we might not see the interference happening at the 220V side.
Thank you for your quick response,I really appreciate it.I will keep you updated on the progress of the project.I noted in Mr Atton’s code,he used pin 9 and 10 on the Arduino.Maybe some people building this project used pin 8 and 9 like on the drawing.Maybe just make a note on that.
Thanks for the feedback, appreciate it!
Hello sir,How to communicate and control conventional inverters from Arduino Micro controllers? I want to turn on/off the inverter through Arduino .please tell me how i can do this ?
Hello Arijit, the above explained circuit is switching the inverter ON/OFF 50 times per second, and with PWM
yes ,i saw ,but i will do same thing in grid tied inverter?
Sorry, presently we do not have an Arduino based GTI circuit
Hello Sir,
I need to clear all my basics of circuit designing. Can you please recommend anything on this?
That would be very helpful.
Thank You & Regards,
Mudit
Hello Mudit, you can read the following article;
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/electronic-basics-explained/
Thank you so much. Much appreciated, As a matter of fact, I am kind of your Junior, dipIETE batch 2012-2015.
You are welcome Mudit, Glad to know you are also an dipIETE holder!
Hi Swagatam,
Please assist me with the following:
Please refer to your cct for the Arduino Pure Sine Wave Inverter.
I would like to combine the Arduino cct with the Seven Simple Inverter cct’s ie. UNIVERSAL PUSH PULL MOSFET MODULE WHICH WILL INTERFACE WITH ANY DESIRED OSCILLATOR CIRCUIT
Will it be possible to interface the Arduino with the Push Pull cct by connecting the two 2nd BC548’s collectors to Push Pull cct at the gate of the 1st IRF9540 and IRF540?
I would really like to do this as I like the additional features of the Push Pull Inverter. Especially the transformer with no center tap and the automatic switching between mains and battery. However I would like to keep the Arduino features as well.
Your assistance will be much appreciated.
Regards
Jan
Hi Jan, yes it is possible to interface it with the above Arduino output. But initially try the full bridge without the charger section. You can use the following module, replace the 220 V output points with 0-6V / 220V transformer, and feed the 310V points with 12V battery. Once the working is confirmed then you try adding the battery charger section to see how it responds
Yes the BJT stages will be required, to ensure that the Bridge MOSFETs get the required 12 V for the biasing
Hi Swagatam,
Ref. All P-Channel IRF9540
I hate to admit that I have been defeated by the Mosfet’s virus. To date I have destroyed about 25 of these devices. My project https://www.homemade-circuits.com/arduino-pure-sine-wave-inverter-circuit/ has been very successful so far. All the modules work very well except for the final stage which is the Mosfet Full Bridge.
I have decided that it is not feasible to continue with the Mosfet Bridge. Instead I want to rather use TIP3055 (BDY29 is not available in my country) BJT’s as per your https://www.homemade-circuits.com/modified-sine-wave-inverter-circuit-2/ BJT concept as in https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/02/InverterOutputStage-1.png. The problem is that the transformer I use does not have a center tap. Do you have any suggestions as to how I can overcome this problem and drive 0-6V transformer with BJT’s instead of Mosfets?
Perhaps I will have beter luck with the BJT’s than with the Mosfet’s.
Your assistance as always will be much appreciated.
Regards
Jan
Hi Jan, I am sorry to hear that. The following link shows two H bridge based circuits for motor control, which can be also applied for inverter.
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/full-bridge-bidirectional-motor/
The first diagram employs the same P-channel, N-channel MOSFET topology which you found problematic, and the second one is a BJT based design which is probably a more convenient one, but not as efficient as using MOSFET
Thank you Swagatam
I really appreciate your feedback
Regards
Jan
You are welcome Jan!
Hello Sir,
Can I please have the flowchart for the programming code used in the arduino to have sine wave from this inverter circuit.
Hello Haritha, I think you can create it yourself by understanding how the SPWMs get converted to pure sinewave when induced with an inductive load like a transformer. It is simple, the varying PWM width correspondingly create a varying exponential curve for the sinewave. So thinner pwms cause the low amplitude rising and falling section of the sine, while the thicker PWMs correspond to the peak section of the sine wave curve
Hello Swagatam .. yeah okay – so before I get going… I have sent you a “request email” to your address..?? I do not know, whether you read those emails or not.?? I just wanted to submit a few circuits, for people to build what I consider to be really smart – plain and straight forward, little UPS circuits. So I am not a real fan of Arduino, for almost obvious reasons. I use microchip PIC’s in which the processor is just a chip.. with of course a V-regulator. (I could say to you… look here… here is a 12V PIC chip.. YES a small PCB with circuits to make up a 12V PIC chip). The driver chips are very plain. I have made up a few circuits, which I can deposit here in time.. I find that after about 2 years of examining the math of whatever is needed, I still believe that I am learning. I do electronics as a hobby-practical, and really am busy with a massive – project, which I have been working on for now – close to 20 years… Whatever I will give here is results / experiments / findings – from my project. I need to ask you – if you are interested..?? cause this is quite an involved system… with a program with which we will use to create to programs for the PIC chips.
So please Sir.. try to revue what I have written in your … LAV…… email address and let me know…
Thank You…!!
Hello Spencer, I appreciate your efforts, however when I checked your email, your contribution appeared to be a promotional article, having external links. Moreover, the codes are not free, the readers have to pay a huge amount for the codes, which the readers will not like. I would have published if it was completely free and did not have those external links. I hope you will understand and bear with me!
good morning sir ,
can u send me the code by mail please ?
best regards
Hello, I am stuck with the 2nd diagram and use an 8v (2 pin) power source and notice that the frequency is much higher than 50Hz (150Hz-200Hz) and the voltage drop when plugged. You can update the full circuit diagram including: “Delay Effect” + “Automatic Voltage Regulator”.
Thank you.
Hello, please use an oscilloscope to check the frequency
I couldn’t find the code to throw in arduino, can you help? thank you. for contact;
The link for the code is furnished in the article itself.
Hi Swagatam
Can I use a ferrite core transformer instead of iron core??
yes you can
Hello, I have 5v DC power and want to increase to 220v sine wave, the power is only 10w-20w, how can I edit the above circuit, or have any circuit that meets the above requirements, please. Thank you very much.
Simply replace the shown transformer with a 3-0-3V / 5 amp /220 V transformer
Thanks you. Can I use Transistor C1815 and IRF530N to replace Bc547 and IRF540 in battery powered circuits (3.8v-5v)?
I tried it with the 5v source, the transformer 6-0-6 / 220v, the noise appeared softly, increasing the power to 12v, the sound was even clearer, was this normal ?, or I had to change the Mosfet?\
Thanks you very much.
There will be a slight buzzing noise which is normal with all inverters. By the way 5V will not work with a 6V transformer, it must be a 3-0-3Vv transformer.
Sorry for bothering you so much, but I’m trying to learn from your circuit.
If I want to use the 6-0-6 / 220v transformer, is there any way to adjust the output voltage into a 220v sine wave with the above circuit and 5v DC input source? You can instruct me to adjust the output voltage arbitrarily with a transformer and arbitrary DC input source, thank you very much.
Sorry, it is not possible to get 220V from a 6V transformer and 5V supply and PWM switching. The transformer primary value should be equal to the average DC present at the Arduino output pins to be able to get 220V equivalent at the secondary
Thank you for patiently answering my questions, I would like to ask one more question of how to calculate the capacitor after the AC 220v power source (DC 5v, DC 7.4v ..). As in your circuit of DC12v source, transformer 9-0-9 it is 0.68uF.
Thanks you very much.
Thank you, sorry i don’t have the formula for calculating capacitor filter with AC frequency..in the video demo I have used 3uF/400V
Hello my friend thanks for the post. Here is my problem if you could help.
I have built a similar circuit now the problem is output voltage regulation, when I connect a load the voltage drops, so somehow the pwm duty must increase accordingly to maintain the desired voltage.
Hello Friend, sorry I can’t suggest the code because my Ardino programming knowledge is not good.
Hi,
In order to implement the full bridge inverter circuit using 4 N mosfets, could I use two voltages:
a) One voltage for the load eg. 24V
b) Another voltage 30V for the nand gate ?
thus avoiding the complications of the precharge circuit ?
Hi, the 30V must be across the gate/source of the high side MOSFETs, not across gate and ground…if you can implement this then it may work. By the way NAND gates would burn at 30 V
Hey Thanks for your Valuable information
I need help with Multiple SPWM generation using Arduino.
If you could help me with it?
Thanks Zain, sorry my knowledge of Arduino coding is not good so can’t help in this regard
Hi! Swagatam, hope your goodself is enjoying good health. First of all i would like to appreciate your work that i have gone through your website, its amazing.
Actually i am working on the voltage regulation and voltage control of Self-excited Induction Generator. First i am using AC/DC (rectifier) from output of generator then i want to supply this DC to the SPWM based inverter to get regulated AC voltage. So i wanted to ask that whether i can use your above explained circuit and its code or not because you are feeding the inverter by 12V battery while in my case its upto 220-480v DC. Kindly guide me on this i would be grateful.
Thanks.
Regards,
Zain Ul Abideen, Founder, ZUPGEN.
Thanks Zain, you will nee a full bridge design for your requirement. You can try the following circuit:
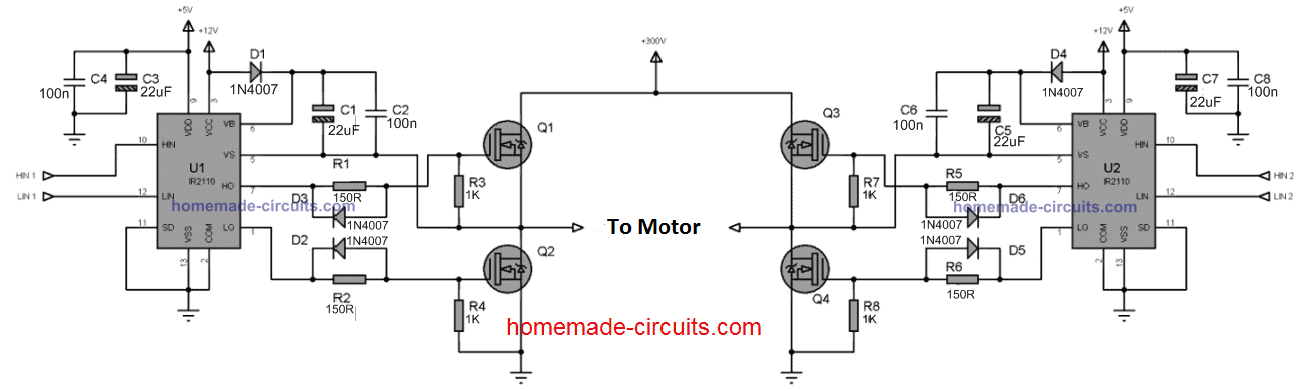
Join the HIN with LIN of the opposite ICs, and feed the Arduino SPWM to these HIN/LIN paired outputs.
thanks for all very good ideas
i will ask you ,can i drive relay of delay using arduino itself using some programming without any additional capacitors or transistors?
Thanks for your greate ideas ….
But i will ask if i can drive the relay of delay using same arduino ?
Sorry I have no idea about it!
Hi Swagatam,
I have tried to put some more MOSFETs together to sum up to about 1500W. Please could you help me verify the correctness of the parallel connection? Find a screenshot in the following link:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1HY1qj8fi9PRGXQcikYCbFhNuPbHkxVFm/view?usp=sharing
Thanks a lot,
Jackson
Hi Jackson,
That looks OK to me, you can go ahead with it!
I connected the transistors and mosfets correctly as per the circuit provided.or maybe I should use all the three batteries to give 36v.then regulate it to 12v for driver circuit instead of using one battery out of the three to supply the components.then supply the original 36v to the trafo middle wire .can this idea help sir.i am now stuck abit.
Thank you sir for assistance.i am yet to assemble the entire circuit.i will TextBack to clarify the outcome of the circuit.i wanted to use it to simply power light bulbs and television at rural home.thanks.
No problem, wish you all the best!
Hello sir.i assembled the circuit but no success.there is a spark of shot when I connect the 36v from the +ve end of the third battery to the transformer middle wire.out of the three batteries I used one to supply the driver components.then I connected the other two batteries to give 36-38v .so I supply the trafo with the +ve end of the third battery.simply by attaching the +36v with it.but a huge spark is observed at the contact.please help.i used the second code in the article.
Hello Yususf, if you connect everything at a time and check, then you are bound to have problems. The correct way is to check any circuit step wise.
In this case first you must begin by checking the Arduino output waveform, and frequency, and confirm it. Then connect the BC547 stages and check the waveform and frequency across the collectors. Then connect the MOSFET and the transformer, and switch ON the Arduino first, and then after a 10/20 seconds switch ON the battery on the transformer center tap through a fuse.
In this way you won’t burn anything and get successful results, and also will know how things are proceeding across all the stages.
Thank you sir.i hope a 3-5A fuse will be fine .for the waveform across the collectors of BC547.is there any other method to verify a waveform other than an oscillocope.i will check the voltage across the collector and emitter of each BC547 to ascertain proper switching.then will see the results.for the frequency,I lack a frequency meter but I think the code surely is a 50hz through the two pins.i used the second code with arrays ,hope it’s ok for the same purpose.
Yusuf, without an oscilloscope and frequency meter it would a trial and error method. so a small scope is the recommended option if you do not wish to lose more devices. You can cheaply purchase a DS0138 Dso138 2.4″ Handheld Pocket-Size Digital Oscilloscope for just $25 online for the testing
Hello sir.i connected the BJTs all two pairs without mosfets and measured at collectors.still one channel reads 9.5v and 9.5v while other only 0.75v amd 2.45v.i wonder what problem.i will try to check and tell you again.
Hello Yusuf, the BJT first stage will invert the Arduino PWM ON time and therefore will show 30% duty cycle…the second stage will invert the first BJT stage 30 % PWM back to 70% replicating the Arduino output, which will be used for switching the MOSFETs.
Hello sir.i disconnected the mosfets from the BJTs and measured the transistors after switching the arduino.i first put meter at DCV and obtained 0.55 and 9.75 for one channel.then the other channel read only 0.03 and 1.55.very low indeed.i then put meter at ACV and first channel read 0.5v and 20.4v.the other channel only read 0.00 and 2.5v.i thought problem was code so itried to interchange the pins 9 and 10 but still the problem remained for the same second channel.so is it the transistors with problem or what.the first channel seems to be ok.(0.55v and 20.4v at ACV.)(0.5v and9.75v at DCV).
Hello Yusuf, as per my reading the DC level which is average DC of the PWM will be 70% of the supply level. For Arduino output this should be around 3.2V for 5V supply, 8.4V for 12V supply, and for 36V this could be around 25.2V DC
Ok sir.so I got 9.70v across collector but I supplied the driver with 13 v.is this approximate.then should the value be the same for all BJTs or can vary from first pair to second pair.here am confused.but the other Chanel still has problems as I said.produces low values .only 1.45v reading instead of 9.7v. then you said 36v supply should produce average of 25.2 v according to the code.but you said earlier that maximum supply for BJTs is 12v DC.did you mean 36v of transformer centre tap.please clarify this point sir.
Yusuf, if you can get 3.2V at the Arduino output, the other values across 12V and 36 V will automatically adjust to the appropriate MS values
Sorry sir.i did not understand.you mean I should get around 25.2v across the collectors of BJTs or what did you mean.excuse me sir.but I supplied the BJTs with around 13v from battery.please clarify.
I guess you meant 36vdc supply should read around 25.2v at the mosfets stage.across drain and source.for(24v 0 24v trafo)
Yes that’s right, I was actually pointing out the duty cycles relevant to the various voltage levels used in your design.
Morning sir.so how do I measure the 3.2v from Arduino output.however one channel produces low values while the other seems ok.my connection is pretty perfect.one channel reads 7.1v and 9.65v at collectors.the other only 0.5v and 1.55v.anyway guide me on how to measure the 3.2v.from which points.i saw in comments you used 1N 4148 diodes across output and you got 3.2v.please assist.
Hi Yusuf, you simply have to connect the positive prod of the DC voltmeter with the Arduino output, and the black prod with the ground terminal or the negative terminal of the Arduino.
Please delete the code and upload it afresh and then check the response again
Yusuf, if you separately measure the Arduino outputs it will show the RMS for the half cycles, so this average should be around 1.75V
I apploaded the second code again .I connected both output pins one at a time as you said and both read 2.38v .I used a multimeter.the code is the same without alteration.
The total delay of the code is 14 millisecond, or 7 millisecond per half cycle. One full code cycle is supposed to be at the rate of 50 Hz, or 20 millisecond. So 14ms is 70% of 20ms, or 7ms is 70% of 10ms (half cycle half code).
Since Arduino works with 5V, 70% of 5V is 3.5V for full code.
PLease measure by connecting 1N4148 diodes from the two outputs and join their cathodes together and then check the output from cathode to ground
Ok.you mean I should connect anode of diodes to the outputs and join the cathode of diodes together.then measure cathode intersection point with respect to ground.hope it’s that way.
yes that’s correct!
Ok sir.i connected diode cathode end with respect to ground and read 3.25v with multimeter.hope it’s fine.hope I can connect the BJTs now to next step.
I got 3.25v with the diode connection.i will integrate the other circuit(BJTs one pair at a time and measure the value.hope it should be around 8.5-9v at collector and emitter.thank you
OK great!
Hello sir.problem comes when I connect the second pair of BJTs.with one pair both BJTs read same reasonable value.after second pair one channel has low values.voltage at Arduino output is same for both pins(3.25v)
Both the channel codes are identical so the PWM timing should be also identical, I think an oscilloscope will solve the problem quickly
Hello sir .the circuit now works very fine I tested with18w bulb and it glew bright.problem is I only used one pair of BJTs .so is there a problem for that.for the spark it is no longer.i used a 1000mf 25v cap to stabilize the battery power.i will measure output voltage and let you know.my question is can it survive with one BJT stage..
Yusuf, you must connect exactly as shown in the second diagram along with the delay generator. If you use only the first BJT stage, it will produce 30% power at the transformer output, meaning your voltage will not be 220V, it will be 90V
Thanks sir.i will check on that and try to rectify by adding the second buffer stage.is it a must for the feedback circuit.moreover,what about the battery charging circuit you recommended,I hope it works accurate with no problem.i am yet to assemble the battery charger meanwhile.
Hi Yusuf, the problem has occurred because you couldn’t implement it correctly, and you are doing it without proper tools and understanding. All my circuits will work perfectly without problems provided you do them with proper understanding and knowledge…you may find the battery charger also very difficult to build if you do it without understanding the details…so please make sure you learn and understand the stages and the concepts perfectly before trying them because all circuits will require some serious adjustments and tweaking for getting the desired results.
Hello sir.hope u fine.i have faced a problem concerning the voltage level across the BJTs.the voltage drops to 3.5 volts and realized that batteries are low.once I contact the +36 volts to the transformer center.the bulb glows quite bright then becomes dim immediately.i did not use a fuse but I did not expect that to be the reason of that.please help.i am yet to recharge the batteries are try it again.
Bulb getting dim immediately indicates low battery or wrongly matched battery and load, also you have not mentioned the battery Ah, and load’s V, I specs..use an oscilloscope to confirm the response accurately.
Hello sir.the problem of dimming was probably due to low battery since the bulb now works fine after charging them.challenge is that my output is high becoz I am now using a 6v 0 6v trafo.around 40A from UPS.my battery are two in parallel so 7+7=14Ah 12v supply to transformer.my output is 261v but batteries are full 13v.please give some solution for that.
Hello Yusuf, you an reduce the microseconds values slightly to reduce the output voltage proportionately…you can experiment this with some trial and error
Hello sir.i tested the code even before doing the reduction of on time proportionally as you said.i mean I tested the circuit again and the bulb flickered brightly.i think the wave was just noise that made bulb to flicker throught.please help.i will test with high voltage capacitor at the output to filter the noise.
Hello Yusuf, as you can see in the video, the working is perfect, no flickering of light and the waveform is pure sine…so please check your design correctly with an oscilloscope.
Hello sir.i am stuck with a very confusing problem that I once encountered earlier.when I attach my +ve 12v to the trafo center tap there is a spark.i tried to double-check my circuit which was working at first.but still the spark is there.this happens even before I power the arduino.spark is there when i contact the center tap.so it’s like the Arduino is fine but problem is on the power or drive stage.please any help sir.my mosfets is IRF3205.my trafo is 8v 0 8v.
Hello Yusuf, it means your MOSFETs are shorted and damaged. You are saying the Arduino output is fine, how did you confirm this?
Hello sir.about the Arduino output,I checked the rms voltage at the BJTs and they both read same value(8.5v).which I hop is fine.problem comes when I connect the mosfets to ground and to the gates input.if I release the ground terminal of mosfets,no spark but if I place the ground terminal,spark is just observed.once again,this happen even b4 powering the circuit.i will try to purchase suitable mosfets.that can handle higher voltage and also place some caps to reduce voltage spikes.then give feedback.thanks
Hello Yusuf, the Arduino output must be confirmed with an oscilloscope, anyway in your case the problem is definitely a shorted MOSFETs, you can change them and see the response.
Hello sir.i looked some spare of mosfets that i had and tried the circuit and observed some little sparking still.however after powering Arduino and closing the circuit the spark is very small and bulb lights normal brightness.the transformer is also buzzing throught with noise.in summary the bulb lights good but there is still some sparking observed.any help is appreciated sir.
Yusuf, connect an ammeter in series with the battery positive. If the meter reading matches the approximate load current, then your inverter may be working fine, otherwise it may still have problems.
Ok sir.so I connect +ve of meter to -ve of battery and -ve of meter to +ve of battery.then I should measure the current while the circuit is in operation with load and match.according to that ,it means that if there is no load connected the meter should also read zero or very low current in mA when circuit is operating with no load at output.
Ammeter should be in series with the positive line of the battery. Meter positive will connect with battery positive, meter negative will connect with inverter positive.
Hello sir.i was looking to charge my inverter batteries with 50w solar panel I have.i would like to know if it is practical to use the inverter while batteries are in charging mode.i mean using batteries while they are charging through solar.thanks
Yusuf, if the charging rate of your panel is more than the discharge rate by the inverter then you can use it for charging the battery and operating the inverter both simultaneously
Hello sir.i wanted to know if I can charge my batteries using a transformer connected at output of inverter.i have not tried that but it seems impossible for me.please assist if a 12v or 15v trafo at output can also charge batteries simultaneously.
Yusuf, if you are referring to the inverter battery charging by the same inverter output so that the inverter keeps working forever, then that’s impossible.
Hello sir.sorry for any inconvenience.suppose I power Arduino using power bank.as usual the circuit will start working.the Arduino output pins deliver 5v 50mA.i ask if connecting a BJT transistor amplifier and coupling a mosfet with around 5A rating will amplify the current from 5v output to around 2A.then connect this with a DC booster module to give around 14.5v 3A.and work as charger.if it can please assist some approach for that.thanks.
No that will not happen, transistors work like switches only they cannot generate current by themselves.
Hello sir.the issue of sparking of the circuit is persisting and seems to be a tricky challenge to me.the spark is very serious when batteries are fully charged and it can’t stay even a second becomes hot.fuses get blown when I try to place.i wrote another program of square wave by switching high and low just for testing the BJTs and they both produced 11.7v which looks fine(one pair).but still the spark is there.at first I used the same square wave and it worked very fine.now the bulb lights with spark then becomes dim at that moment.i am getting confused here.perhaps I should use IRF540n mosfet instead of IRF3205.please help.
Hi Yusuf, I have already given you the solution in the previous comments. Your inverter MOSFETs are burned. If you don’t change them, your transformer and the battery also will get permanently damaged. You can any, IRF340 or IRF3205 both will work
Lastly.there is observation that I like you clarify it for me.i used a normal led and connected +ve of led to battery +ve and -ve to mosfet drain and it lit bright.then I grounded the mosfet gates and led lit but very dim and not clearly.if I release the gates from ground.the led lits very bright again.any clarification from this.
The best way to check is remove MOSFETs from the transformer and then connect the battery to transformer, if there’s no spark or heavy drain then the MOSFETs are faulty otherwise the transformer can be faulty.
Hello sir.is it possible to use both irf540 and irf3205 combined .I want to add two in parallel but I have extra 3205 with me.then another querry is suppose my solar panel is 50w,it means I can connect a 40w load at inverter and run it continuously throughout using the panel.thanks
Hello yususf, yes you connect the mentioned MOSFETs in parallel. If the output from the panel is consistently 50 watts then you can connect 40 watt load with it
Hello sir.can I charge my lead acid battery using solar panel.then if possible ,i wanted to Know the size of panel required to charge a 75ah battery lead acid.my value was 0.2x75x12v=180w/200w panel.is this correct sir.
Hello Yusuf, you can calculate the parameters using the steps explained in the following article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/how-to-calculate-and-match-solar-panel/
Hi, tank you sir for this very educative work! I am about to build this inverter and have the following questions:
1 – in the IRF540 datasheet, i saw that the Gate-Source threshold voltage 4V max. why then do we need level shift to 12V? I thought the IRF540 is one of those MOSFETs suitable to be used with Arduino or other microcontrollers without worrying about level shifts.
Thanks
Thanks Jackson, 4V is the threshold gate voltage. In simple terms it is the minimum level required to just turn ON the MOSFET. Therefore at least 9V should be considered to enable the MOSFET to work with proper efficiency.
For this reason I use IRL540’s instead of IRF540’s. IRL540’s have a 5v max drive voltage, perfectly matched to the Arduino.
That sounds great, thanks for the feedback!
Hello sir , How are you , I have one question again about the transformer .
From where I am now , I cannot buy 6-0-6 transformer . The one I found is only 3A rated . So Can I just use a 12-0-12 rated at 5 amp .
Or can you suggest any website where I can buy 6-0-6 rated at 8amps. Since I want to light a 60W using this inverter circuit . Hope you can help .
Hello Fanai,
You can use 12-0-12V transformer, but then the output will be less than 200V with a 12V battery. I think you can buy a 6-0-6 5 amp or 10 amp transformer from any online store or get it made to order
Will an old ups transformer works in your circuit . Since In my old ups transformer , I can choose different voltage in the output side ( primary ) . But when I used this mosfet burns so quickly .
Yes any transfromer will work rated at 6-0-6 or 9-0-9. Remember to add reverse diodes across drain/source of each mosfets, and also connect the 12V supply to the Arduino via a 100 ohms resistor and connect a 1000 uF capacitor right across the arduino supply pins.
Switch ON the Arduino first and then switch ON the transformer supply after around 10 seconds.
Hi Swagatam,
Thanks a lot for the answer, it’s now understood.
Using a pair of IRF540 as in the diagram should result to about 250W with a 12 volt battery(considering efficiency losses are out), correct?
What kind of transformer is the best recommended to be use here?, what should be the power rating?
About the automatic voltage regulator, does it also regulate in case of reduced voltage due to high loads?.
Thanks in advance.
Jackson
Thanks Jackson, Yes that’s correct.
The transformer wattage must be slightly higher than the desired full wattage output from the inverter.
The automatic voltage correction will not increase the voltage drop due to overload, it will stabilize the output only as long as the output load is within the range and the battery voltage is not below the minimum lower value (11V for 12V battery)
Hello Sir,
Thanks a lot for the response. I’ll keep you regarding the progress of my work!
Regards
Wish you all the best Jackson
Hello sir.can PNP transistors be used in replace of NPN transistor.i have BC557 transistors with me .
Hi Yusuf, PNP will work if the MOSfets are also P channel, otherwise not.
Hello sir.you said the Arduino average voltage x/5v should correspond 24/36v of trafo/battery.so from which points will I measure the voltage(around 3.2v) roughly from output of arduino.then what about voltage btwn the collectors and emitter of each transistor.what should I get roughly.please help sir.
Hello Yusuf, if you adjust the Arduino output, the transistor and the transformer will also get adjusted to the same RMS automatically
Hello sir.so I obtained these values.(first channel at pin 9 transistors,,,at DCV I got 0.55v and 9.71v .at ACV I got 0.5vac and 20.5vac .then second channel pin 10,,,at DCV I got 0.04v and 1.45v.at ACV I got 0.00vac and 2.5vac .so how can I proceed sir .any assistance sir.even if I interchange the channel pins,the problem is still in the same transistors.its like code has no problem.but one channel has very low values.thank.
Helpful
hi sir, do you have the program code for the first circuit ?
My transformer has two wire in the primary coil and two wire in the secondary coil. Can i use this kind of transformer for making inverter? Thank you.
You can try the first circuit from this article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/5kva-transformerless-inverter-circuit/
Connect the MOSFeT top line with the IC positive…and connect the transformer 12V side with “AC OUT” points.
Thank you for this comment. I will try this out.
sir,
have you tried the feedback circuit? does the automatic voltage correction works ? I am making this project ..need this information badly
Salman, I have not tested the feedback circuit, but I am sure it will work without any doubts.
Hello Swagatam, I wish to integrate some other functions to the arduino, like attaching an LCD and automatic battery charging. Do you think this will affect the PWM output?
Hello Ubaka, the output will remain unaffected as long as the inverter program code is not changed.
Ok, from your program, the pins used are 9 and 10 the software is correct. Now lets attach LCD for charger, temp and power consumption. how will this affect the Output
I have made this inverter and it seems to be working fine. But when I connect a led blub to it, the bulb flickers. Any suggestion will be appreciated.
Thanks for your time
Please try a philips LED bulb and see the response. I did not try it in this circuit but I tried it in another circuit shown below where the bulb illuminated without any problems. This circuit output is crude compared to the above Arduino circuit:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/1500-watt-pwm-sinewave-inverter-circuit/
I appreciate your time, I forgot to mention. I am using an UPS transformer, I have not connected the capacitor at the output (waiting for delivery). The bulbs are of Havel, Philips and EverReady etc, this only happens with 18 watts bulb or higher, lower wattage works fine. My whole purpose to make this inverter is to run my 3D printer with it (way too many power cuts in my area). I tired checking the output voltage with a multi-meter (cheap multi-meter) and it blew my meter, but the bulb were still glowing.
If you need any help with 3D printing you can let me know, my email id is rahul.das2904@gmail.com
Can you tell me the voltage and current specifications of the transformer? If only higher watt LED bulbs are flickering it could be due to lack of power or current from the transformer!
I have changed the transformer and it fixed the issue, now I am using 12-0-12 5 Amp transformer. Bulbs are doing good, but when I checked a table fan, it barely moves. Could you please tell me how many watts does it produce.
Appreciate the time.
To get a correct 240V output, a 9-0-9V transformer recommended. With 12V transformer the wattage will be less than 60 watts and the voltage may be less than 220V. Check the output voltage, if it’s dropping when the fan is connected then you may need a 10 amp transformer, or may be the present transformer is not a genuine 5 amps
Hello sir,
Nice to talk you again. Yah i tested with 12-0-12 transformer and it gives around 175v to 180v which is not so good for many home appliances.
Problem is that 9-0-9v transformer is only available in 100 watts in our market. And i need to build a 1kva rated inverter.
Now my question is can i use 6v-0-6v transformer (available in any wattage) in replacement of 9-0-9v ? Is the output voltage goes over 240v ? Please explain pros and cons.
It’s urgent please reply asap.
Hello Sourav,
You can use 6-0-6v transformer, but you will have to adjust the off time in the code so that the average or the duty cycle for the transformer primary becomes around 7V.
Or you can simply increase the dead-time between the two channels.
Increase the microsecond value at the second last line of the first channel code, and also for the second channel code.
Increase it from 500 to 1500 or randomly to any value until the voltage at the collector of the transistor show 7V
Hello sir,
Ok i understood. Then the test points will from the first pairs and 2nd pairs of BC547 collectors individually to the negative terminal. Is that right or i made some mistakes ? Total 4 test points to check the voltage of 7v.
If i use 6-0-6 transformer will it take any effect in the high voltage output side ? Means the voltage goes over 240v. Is this will happen ?
Thank you.
Hi saurav,
You can check across any BC547 transistor for both the channels. Connect the positive probe of meter with collector, and negative probe at the emitter.
If 7V average is maintained for a 13V battery then the output will be always below 240V so it will always safe.
Hello sir,
I understood. Now there are 4 test points to check the voltage of 7v at the 4 nos of BC547 collectors respectively one by one. Am i right ? Please explain.
Thank you.
Hi Saurav, Yes, they must all show approximately 7V. Make sure the collector 10K are connected with 12V
Good afternoon sir,
Thank you so much. I will notify you when i have built this circuit. Yesterday ordered 12-6-0-6-12v 5Amps transformer. 6-0-6v will in use.
Thanks you.
OK great, thanks!
Hi sir,
First of all wish you a very happy Diwali , god bless you !
So, just a minutes ago i have done this circuit. But still some problems i faced with it.
You told me to check the collector voltages at rated with 7v but i got 0.73v. Yes exactly this. Also you told me to rewrite the code to replace the microsecond value from 500 to 1500 at any random point so i chosse 800 and 1200 in a separate time individually. Output voltage from transformer is like in a fraction of second very high(340v) then low (10v) and then 0v , 5v, 15v, 0v respectively showing.
Just remembering that i am using 6-0-6v / 5Amps transformer and 7.5AH battery.
Thank you Saurav, regarding the code modification I suggested to change the second last line of the two channels of the code.
Check the collector with a DC voltmeter it should show the average value of the pwm ON time.
Do not connect the transformer while checking the voltage.
Thanks for your time sir, I will check. I am not able to get a 9v transformer online. I have a few transformers with me, I will check with those and let you know. Thanks again for your time.
No Problem Rahul, wish you all the best!
Good day sir, how do I implement high voltage and low voltage batery cut off as well as charging unit. Thanks.
Good day Leeman, You can use the following circuits for charging the battery
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/opamp-low-high-battery-charger/
Hi sir,
I’m desiging an UPS and we have a DC boost converter (15A, max 37V output), 12V 12A battery, 15-0-15V transformer and lots of IRF3710 mosfets with BC547s for the inverter.
I want to use your inverter design but I have some questions;
Can we use IRF3710 instead of IRF540?
What should be the input voltage of inverter for using 15 0 15V transformer for the 230V output?
I didn’t design boost converter myself, bought as module. Realized that it has constant current output. Will it be a problem?
Hi Atakan,
What is the purpose of the boost converter in your application?
You can use the mentioned MOSFET instead of IRf540
For 15-0-15V the RMS from the Arduino stage should be also 15V. Therefore you may have to use a 20V DC input supply voltage and adjust the Arduino L/H PWM output microseconds to get around 15V RMS.
Hi Mr. Swagatam,
Thank you for your reply.
I’m planning to use the DC-DC boost converter to get 20V DC input from battery, because my battery is 12V.
Is there any other way to get 20V output from a 12V battery instead of a boost converter?
Hi Atakan, I don’t think that would be too beneficial. That would reduce the efficiency cost wise and with the output power also. Instead you can use the 12V battery with a 9-0-9 transformer. In that case the Arduino circuit can be directly implemented without any modifications in the code.
Hi Swagatam, first of all I want to thank you for sharing this project with us. I need some help because I want to make a full-bridge inverter (H-bridge) to convert 12V DC to 6V AC. I will use arduino to control the MOSFET’s in order to obtain the AC signal but my question is how can I decrease the voltage from 12V to 6V and how to obtain a SIN PURE signal from the square wave which I will get as the result of H-bridge circuit ? Thanks in advance
Thanks Omer, do you want to have 12V as the peak and 6V as the RMS at the output? In that case you will have to dimension (by calculating the LOW/HIGH microseconds) the SPWMs such that it produces the mentioned voltage across the full bridge outputs with the desired RMS.
A full bridge version is discussed in this article, which could be modified as described above:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/arduino-full-bridge-h-bridge-sinewave-inverter-circuit/
I examine the link above and it was really helpful, thank you. So in my case (12V DC as input and 6V AC as output) can I use the same components over there (I mean the MOSFETs types etc.) on condition to change the dimensions of SPWN only ? Is it possible to obtain the signal which is required by behaving as I mentioned above ?
Yes that’s right, but you will need a 12-0-12V / 6V transformer.
Hi Swagatam, I couldn’t find any resource related with calculating the dimension of SPWM produced by Arduino in order to have a 6V AC signal (using 4 n-channel MOSFET, H-bridge inverter), could you help me please? Another point I would like to make is that I supply my H-bridge inverter with 12V DC, I also used your arduino code to produce SPWM but I have a 0.5V Pure Sine Wave in the output (without using a transformer, I used a RC filter only). I think that obtained output is too low, isn’t it ? Do you have any advice ?
Hi Omer, please refer to the conversation between Mr. Serd and me below, you will be able to learn how to adjust the HIGH microsecond timing in the code to get 6V RMS or an average 6v at the output of an Hbridge.
I am not sure what an RC filter result maybe but If you measure the RMS at the collector of the BC547 with 12V as the input then it should show 8.4V.
Hello Swatagam,
How to make the switching frequency from the PWM to be 10 kHz?
Hello Nik, you will have to adjust the “microseconds” on each channel such that they add up to give 0.00005 seconds on each channel.
Hello Swagatam,
I realise that this is a lot to ask, but can you please help me troubleshoot my circuit?
What I’m basically trying to do is shown by this circuit below:
https://drive.google.com/open?id=1Gn6HU8BsW_9DnAlsc72Wo1VqynnC18rl
However, since I’m using my laptop to power up the arduino, few changes has been made to the circuit as below:
https://drive.google.com/open?id=14E2pTDyYGi4bvW-Y5h8MuSi4tathpzso
The signals measured are as below:
Arduino – https://drive.google.com/open?id=1sTQ4Jj0mZyl_bhtqHUtIiANN2sEJjHJK
Transistor – https://drive.google.com/open?id=1MHrwUHCjRse1RBysXNS1wbehh_f-jB04
MOSFET – https://drive.google.com/open?id=1ghb5ARqfiFTMA1cAA72aJjHrN48Uynng
Transformer – https://drive.google.com/open?id=1p4cRx6Ovbqk0dIgXArTDV8Yuwt28v6lm
The signals from the arduino and transistor seems to be right. The signal starts to be unreadable after the MOSFET. I’m not sure what is the problem as I have checked the circuit several times. Please do recommend any solution to make the circuit working. Thank you in advance
Hi Nick,
May I know why you used a single BJT buffer? It should two BJTs as indicated in the above article. For single BJT buffer you will have to invert the entire Arduino code, meaning swap all the LOW and HIGH with each other.
Hi Sawagatm, I have made this circuit on PCB it works 100% correctly. The output of the circuit is 230V and fixed 50 Hz and pure sine wave. Thanks for your sharing, now i want to change the frequency of the circuit from 25 to 75 Hz simply making a VFD. Can this code be modified by using the analog read pin of arduino and a variable. The circuit should be pure sinewave like this. I will be very thankful for your guidance.
Hi Muhammad, I am glad you could make it successfully, however I have no idea how to use the analogue read pin to get an adjustable frequency. I hope one of the visitors here would be able to throw some light on this and help you out with the details.
Thanks for your reply, please share this issue on your wall or mention that visitor. This idea will lead this circuit to a pure sine wave variable frequency drive.
sure, I will, however I think the best place would be to put this question in Arduino.cc forums, one of the experts there would be able to provide some hints….
Hi can you please give specification of the components I want to o this project please.
Hi, I’ll try to update it soon!!
good evening Sir, please I will need you to help with, a circuit diagram, function and working operation of a “WEBSERVER BASED INTERACTIVE PURE SINE WAVE INVERTER “
Hi Abraham, I don’t think I know about this inverter concept, so would be difficult for me to suggest much on this topic?
Hello Swagatam!
I like your idea, I will use it for my same project, which I started few years ago, but never finished it. I`m a little bit confused about choosing the perfect transformer ratio. I`m trying to calculate the RMS value of that signal that you posted. With voltage of 12V, I calculated two values: uRMS= 10,03Vrms and uRMS= 7,09Vrms.
>Data of signal: t1= 10ms, t2= 10ms, T= 20ms. The signal in ON for 7000us= 7ms and OFF for 3000us= 3ms on positive side of signal, the same data is for negative side of signal too.
>First of all duty cycle: D= t1/T= 10ms/20ms= 0,35= 35%
>Positive side of signal: Upeak1^2= Vp^2×t1/T= 12^2×0,01/0,02= 50,4 – the negative side of signal is the same as positive signal, so the value is also 50,4
>Finally uRMS value: 1. uRMS= sqrt(50,4+50,4)= 10,03Vrms
OR 2. uRMS= sqrt(50,4)= 7,09Vrms (I think that one is correct – choosing just one value, because signal is the same, at positive and negative side)
>Am I thinking right? Which one is correct? Thanks for your response.
Greetings to you. Engineer Serđ.
Thank you Serd,
I am glad you liked the idea. If you have carefully calculated them they should be right, due to lack of of time I won’t be able to confirm them at the moment. In my free time I may check them and let you know.
Thank you for you quick reply. Please check them for me and let me know, I think the correct value is 7,09Vrms. I`m very interested in that thing, it`s great project.
Greetings to you. Serđ.
Hi Serd,
according to me the total ON time of one PWM cycle is 14mS, so duty cycle should be 14/20 = 0.7 or 70%, and 70% of the 12V will be the RMS, that’s 8.4V
Let me know if I am right?
Hi Swagatam,
I see, that you calculated the whole period, so 20ms. Pulses are ON 7ms on positive side and 7ms on negative side, together 14ms.
>Then duty cycle is: D= t/T= 14/20= 0,7= 70%
>70% of 12V is RMS value: Vrms= 12V×0,7= 8,4V
>That seems to be ok. If I choose classic equation for sinusoidal waveform at home outlet it is: Vrms= Vp/sqrt(2)= 325V/sqrt(2)= 230V.
So in that case for inverter: Vrms= Vp/sqrt(2)= 12/sqrt(2)= 8,5V
I think that you are right. The best transformer ratio in that case would be 9-0-9V.
I used equations for different timing in positive and negative side of signal. That could be a problem…
There are big voltage differences too, about 17% – when the battery is empty, voltage is about 10,8V and when it`s full about 13V. If the battery charges there is around 14-15V with smart acu charger. There are also some voltage loses on MOSFETS. I still think that 9-0-9V transformer is the best choice in that case.
I didn`t make the circuit yet to measure that values, can you measure it to prove our theory of 8,5V RMS on primary of transformer?
Greetings, Serđ.
Hi Serd, you are right with your assessments.
I confirmed it through the Arduino output by connecting 1N4148 diodes across the two outputs and then connecting the common end of the diodes with the DC voltmeter, and it read 3.2V which is close to the actual average value 3.5V for 5V. Because 70% of 5V is 3.5V. The 0.3V drop is probably due to the diode fwd voltage drop.
Here’s the image: https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/PWM-RMS.jpg
Yes the battery voltage may vary a lot, and that’s why I have added the opamp voltage regulator circuit. So at full charge you may except an over voltage of 280V which will be regulated at 220V by this circuit, until the battery actually drops to a 220V equivalent value
I checked all variants of sketches for that circuit and I think, that circuit using IC4093 driver and H-bridge is the best. I also looked for ICL7667 dual power MOSFET driver but it`s mean to run 2 N-channel MOSFETS directly, or if you replace P- channel with N-channel in circuit and connect two N- channels together to ICL7667 driver pin and vice versa. Let me know, if I`m right. In case of H-bridge you don`t need center tapped transformer. It`s really hard to get high power center tapped transformers (I looked for 9-0-9V 100W and above. I just found one 150W but it`s expensive as devil :D) and there is problem, that there are two coils which could not be the same (trasformer is in saturation). I`m little confused with 1 coil transformer for H-bridge. Our calculations were 8,4V rms, so in that case you could use 9V/230V – 1 coil transformer right?
Greetings, Serđ.
Yes that’s right, an H-bridge helps you to get rid of the inefficient center tap transformer. However for driving 4 n channel mosfets you will need a special driver IC, there are many excellent variants you can find online.
An example design can be seen in the second diagram below given article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/5kva-transformerless-inverter-circuit/
Hello Sir, Good Afternoon. I have some questions about the power rating of this circuit.
1. If i use 5x IRF3205 MOSFETs (approx 200W rated power each) in both sides parallel means total of 10 MOSFETs will in use then what will be the wattage of this circuit or inverter ? Can i use more MOSFETs to increase the wattage of this circuit?
2. With the above if i use 1000W 9-0-9 transformer then will this circuit work fine and what will the output wattage of the transformer?
3. It is the most important question to me. How can i calculate the wattage of any inverter circuit by adding or removing MOSFETs ?
Like if this circuit use 4 MOSFETs and the wattage will 400W then if i add 2 MOSFETs extra the changes of wattage is 600 means this circuit will handle extra 200W.
Hi Sourav, IRF3205 has a maximum tolerable wattage of 110 x 55 = 6050 watts, 200w is the maximum power it can handle without a heatsink. The MOSFET will handle 6kv as long as the case temperature of the device does not exceed 50 degrees Celsius.
You can multiply the ID with the VDDS to get the max wattage of any mosfet, provided it’s kept cool during the operation.
Hello Sir, thank you for giving your time. I understood. So the IRF3205 MOSFET can handle the maximum power of 200w.
My question was that in this about circuit there 2 MOSFETs are used. So if i use IRF3205 by replacing them what will the maximum power of this circuit?
Afterall how can someone calculate the maximum power of this circuit with the following 2 MOSFETs ?
If i add more MOSFETs in parallel will the power increase?
Please give a mathematical example so that i can understand.
Hi Sourav, 200 watt is without cooling, with cooling it is 6000 watts.
MOSFETs are only like switches, they do not decide the power output. The power is decided by the transformer and the battery.
If you parallel them you just have to add the power of the mosfets together to get the maximum tolerable capacity of the devices.
You can read this article for more info:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/how-to-calculate-and-match-inverter/
Hello Sir, I understood all that you had told. I read the article it’s worthy to a designer who is newbie in this field.
But till now one question is hammering in my mind.
When using 1500W transformer could the two MOSFETs handle 1000W home appliances or i have to use more in parallel ? Please explain thoroughly the use of the more number of the MOSFETs.
Adding more MOSFETs does it increase the output wattage ?
Hello Sourav,
There’s no need to add more MOSFEts if a single pair can handle the full load. The only advantage of using MOSFeTs in parallel is low resistance for the current and therefore less heat on the MOSFET.
For example you can use a single pair of IRF3205 for 6000 watt load, but it will create lot of heat on the MOSFETs, however if you add many IRF540 in parallel that will be create less heat, but both options will work.
As already mentioned MOSFETs do not increase output power, they only work like switches just like our home ON/OFF buttons, which must be rated accordingly. In our homes we have bigger switches for appliances like fridge and geysers, and smaller switches for lights and fans.
For 1500watt transformer you must select 1500 watt MOSFETs to handle 1000 watt load, a single large pair will work or many smaller MOSFETs in parallel will also work
Also i forgot to ask that if my transformer is 1500W rated and i want to run a 1000w appliance are the two MOSFETs ok or if i have to add more then how many FETs i have to use in total?
This portion is annoying me what is the necessity of adding more number of MOSFETs ?
Hello Sir, Good Morning. Again many many thanks to you. You are awesome.
I can’t find this problem anywhere or any article. I didn’t understand how do people calculate those MOSFET’s number to use in inverters cause in many circuit diagram i saw 10 pairs used in parallel , somewhere in H-Bridge usually 2 pairs are used but there 4 pairs were used. So i asked near local markets the designers say “it improves performance …… It produces more power….. etc “. There was no perfect answer i received. Now i can tell people the actual reason of adding more MOSFETs.
I’m building this circuit when it will be done i will contact you through your mail id. Please help me out for further problems.
Have a good day sir.
Glad it helped Sourav,
Always check 3 things in MOSFET datasheet:
ID (current), VDDS (voltage), RDSon (resistance).
ID x VDDS = maximum watts mosfet can handle when mounted on proper heatsink.
Lower RDSon means lower heat. Parallel MOSFETs will mean reducing RDSon therefore lower heat and higher efficiency.
I want spwm inverter with bipolar using arduino code sir
Bipolar is not so familiar to me, however I think the above design could be transformed into bipolar through external NOT gates
Hi Swagatam,
From your previous answers, I understood that using a battery lower than 12V will not make the circuit work. Can you please explain why? Also, how to solve this problem if I’m using a 7V 5.4 A battery?
Hi Nik,
It will work at 7V also but not as efficiently as it would do at 12V. You can see the graph in the following image which shows the drain current response to gate voltage.
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/mosfet-gate-voltage-1.png
thanks a lot is just that i looking for
It’s my pleasure!!
Hello sir, is it possible to build this circuit without the use of a transformer? and if so, how? Thank you in advance
Sorry Nik, this circuit cannot be built without a transformer. For transformerless design you can probably try one of the concepts from this article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/5kva-transformerless-inverter-circuit/
Thank you for the quick reply!
Hello Sir, i have tried troubleshooting my design but one mosfet over heats. I would like to ask if i use 3 similar BJTs and one different can it have an effect on the output?
Hello Cracker, Please specify which BJTs have you used, I’ll let you know whether they are suitable or not.
You can try the mosfets with other form of inverters like with IC 4047 or with transistors, and check whether still the mosfets heat up or not. This will confirm if the problem is with the mosfet or something else. Alternatively you can change the particular mosfet to verify the same!
Am using three 2N 5551 and one BR N551
They look OK to me. If you want to avoid transistors you can use a single IC 4093 or IC 4049 and connect the mosfets directly with their output configurations.
Thank you sir, i have the following questions….
1. what is the maximum power in watts can i achieve using a 12v Battery?
2. Which transfomer setup is the best for this inverter, iron core or the ferrite core transformers
3. Is there a way to increase efficiency of this setup?
Hi Cracker,
1) The maximum power will depend on the Ah rating of the battery, multiply 50% of the Ah value with the battery voltage
2) If size is not a concern then an iron core concept is reasonably good and easy to set up, otherwise it’s ferrite core
3) maximum efficiency with a full bridge topology can be achieved only with a specialized driver IC such as this:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/simplest-full-bridge-inverter-circuit/
Thank you sir for giving perfect info about this model.
1. In reference to https://www.homemade-circuits.com/simplest-full-bridge-inverter-circuit/ can we incorporate arduino for Pure sine wave? and if yes how do i do it?
2. Why are commercial UPS rated 650Va/325W yet they only have 4 Mosfets and a 12V/7Ah battery is it logical?
3. Personally i have a 12V/18Ah Battery and i was looking at generating atleast 500W from it with several mosfets in parallel.
Hi Cracker,
The Ah rating provides us the maximum breakdown tolerable discharge/charge rate of the battery. it depends how much you care about your battery. Operating the battery at the full Ah level will very soon kill the battery. The commercial UPSs probably shows the maximum power of the inverter but it may not be recommended to use 7Ah battery for getting the mentioned power output. The recommended charge/discharge rate for a lead acid battery is 1/10th of its Ah rating. The higher the rate the quicker the battery will deteriorate and vice versa.
Thank you sir for the detailed info you offered, after i am done designing how do i tell the exact wattage my circuit outputs?
– is it wrong to mix different Mosfets in parrallel
– the output at the mosfet drain is around 6V is there a way to raise it to 12V so that I can use a 12-0-12 transformer?
Thanks Cracker,
Your transformer wattage rating will be the maximum wattage capacity of your inverter. You will have to use a battery that will complement this wattage level.
It is OK to use different mosfets as long as their ratings and specifications are well within the required range.
The 6V is probably the average voltage due to its frequency. The peak should be 12V only. You can use an oscilloscope to confirm this.
Hello sir,
I started the project and now looking at upgrading it to a more powerful one. I have ordered 20 HY4008W MOSFETS hope they are good for a 1.5KW power inverter. My problem is the transformer, my current demo inputs between 5.5V & 6.0V to the transformer and am wondering which is the best transformer to use between 6V-0-6V & 9V-0-9V.
with arduino we can virtually incorporate any inverter features with a wide range of sensor available but my Question is What are the best features can i add
Hello Cracker, the best features of an inverter are probably a sinewave output and an over voltage control, both are presently included. Among other features can be to have an automatic overcharge/low battery cut off and overload shut down. However adding all the features from a single Arduino can be difficult?
Thanks Sir,
Since am good at arduino manipulation i will use two of them with serial communication.
Kindly advice on the transformer to use as i had requested previously. 6-0-6 or 9-0-9
You can use 9-0-9V transformer for the present code
hello guys noticed an issue I built the design but the MOSFETs are heating up even on no load I don’t know if any one has a solution to that
Hello, please allow the Arduino to boot first and then connect the transformer center tap with the battery. Please see the second last diagram for the warning message and please do accordingly.
Hello Swagatam,
I want to experiment with your design but I cand find 7404 in Farnell database.
Is it the same with SN7404N ?
Thanks!
Hi Adez, the CMOS stage is actually not needed, you can effectively use the second design with 4 BJTs and 2 mosfets.
But please take care of the booting issue in Arduino by including the delay timer stage in the mentioned design
Good day my precious Boss, kudos to you on the good work on electronics. I want to ask some questions related to the circuit you recommended sir.
1. I want to use 6 mosfets will i use six 1K or that two will take care of it.
2. i want to add LCD to it using thesame arduino, hope it wont affect the PWM signal. or i should use different arduino for that.
Apex, for increasing capacity you can increase the number of mosfets, no need of adding extra resistors, you can connect all the gates together and join them with the collector of the transistor.
You can use an LCD if you have the code, I am not sure how it would impact the inverter PWM, most probably it shouldn’t
Sir, I have simulated the Circuit in Proteus 8.1 got PWM output exactly as u shown in ur website,also tested the mosfets switching state by connecting the leds across two channels working fine. When i connected 12v bulb at the output it is not glowing constantly fraction of secs it is glowing high & again dim just like blinking,to fix that i also used 0.22uf capacitance at the transformer output. I m trying to build pure sine wave inverter 12v dc (from batteries )to 120vAc . Can u help me out to get pure sinewave ? Also can u tell me software for simulation other than proteus?
Hello Sandhya, which design did you build?
I recommend the second design, please build the second design exactly as shown and check the output.
And please make sure to use the first code presented in the following article.
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/arduino-spwm-generator-circuit/
Sorry, I do not use simulators so I cannot recommend any, I always make sure to build circuits practically and check the response in an oscilloscope.
Is there low battery cut and overload function? plz make me understand
Thanks dear
Mehedi, there’s no battery charging or cut off included in this design, you will have to add it separately.
i Think this is most easiest inverter to build. its possible to connect solar charger Battery terminal to this circuit to charge the battery?
Thanks Paaker, yes definitely you can integrate a solar charger with the battery…
can it be used for 60Hz 230V transformer? can it be used for high power applications?
yes it can be customized for any transformer, and any desired power output
Thank you for your topic
I would like to ask a question is it possible control the phase angle and the voltage amplitude from the code.
Phase angle can be precisely adjusted by suitably altering the pulse widths and the number of pulses in each block. However this will need to be also complimented by suitably adjusting the capacitor value at the output of the transformer.
hello sir, can 7404 be replaced with 7414?
Hello Aditya, yes that’s possible, 7414 is Schmidt NOT gate IC which will work better than 7404 in most cases
How to improve the rate of defect of automotive PCB
Hi sir.. can I know, how many watt of bulb you using?. Thank you
Hi Uthaya, it is a 10 watt bulb because the transformer is 1 amp rated. A 1 amp transformer with a 12V battery will produce 12 watts only, and with a PWM this may be reduced to 6 watts
Could you please tell me what code should i use? because i used both arduino codes on SPWM and didnt work as expected.
use the code which is shown in this page: https://www.homemade-circuits.com/arduino-spwm-generator-circuit/
I checked by compiling it just now and it gave me no errors.
hi sir,
i followed exact circuit below your video but still cant get 240V. im get 170v and not producing sinewave after transformer. i havent build the hardware, im doing in protues 8.1
simulation software.
Hi Uthaya,
I would recommend you to build the set up practically using a small 1 amp transformer, and a 12V 7 Ah battery, and then measure the waveform using an oscilloscope to confirm the actual results
now i can produce 220V but not sine wave.. any idea about sine wave?
attach a 0.22uF/400V or higher value capacitor at the transformer output
Hi Mr Swagatam
I have finally constructed the circuit and test it on various transformers , and under different load , eg , 675 Watt Drill together with some Let Light, The Circuit is working 100 % , and I thank you a lot for that , I have designed a an Eagle PCB Layout for it , and also made few changes as integrating a Solar Charger to it , Will mail the Layout for others to try out ,Thanks a million, keep up with this good work
That’s wonderful vhafuwi, I am glad it is serving your purpose.
However there are a few modifications that needs to be done in the circuit, you will be able find the updated designs soon which might help you and other viewers to further improve the outcome of the inverter
What is the specification of the transformer?
I am using 6-0-6/230V , 50Hz transformer.
But we are generating higher frequency SPWM which cant be fed to 50 Hz transformer.
So what should be the rating of the transformer?
And where to connect filter (at the primary / secondary side)?
Thanks
transformer rating is OK, just make sure the transistors are oscillating and delivering the current to the transformer winding. You can initially replace the transformer winding with 6V bulbs, and check whether they are illuminating dimly or not? If not then the transistors may not be conducting due to some issue
Thanks a lot for the circuit.
I am getting SPWM signals at the two MOSFETS.
But when I connect 12-0-12 / 230 V transformer to it, I am not getting 230V ac sine wave , instead I am getting very distorted sine wave in mV.
I want a low power(i.e very low current) and a pure 230 V AC sine wave output.
Do I have to connect resistor between MOSFET and transformer?
Is there anything which I made wrong on the circuit?
Thanks
The functioning is very straightforward and it should start working immediately, actually for low current application, mosfets are not required.
You can make the first circuit, and replace the mosfets with TIP122 transistors, and connect then directly wit the transformer, it should immediately start working with an output of around 250V
What is the filter circuit to be used at the output of the transformer for pure AC sine wave?
My application is for low current and 230V
you may have to use capacitor an LC type filter to produce a pure sinewave, as shown in the following example article
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/modified-sine-wave-inverter-circuit-2/
Where to connect the GND of arduino in the circuit ? And do we have to connect any load to test the citcuit? (Like LED etc)
I rigged up the circuit and changed HIGH to LOW in SPWM code , but I’m not getting output.
Once I got a sine wave but RMS voltage is in millivolts.
I used 12 0 12 to 230V transformer.
I gave 9v to arduino from different source (not from 12V battery)
Thanks
Ground is already connected via the 7812 IC to the battery negative, if you are using an external source for Arduino make sure to connect the negative with the inverter battery negative otherwise you will get no output.
by the way a 9V battery will not work, you must use at least a 12V 7 Ah battery and a 6-0-6V or 9-0-9V 2 amp transformer.
Thanks a lot for the answer sir.
I am using Regulated DC power supply instead of a 12 V lead acid battery.
Why we have to use 6-0-6 or 9-0-9 , 2A transformer instead of 12-0-12 transformer ?
I don’t need very less current at the output , but I need a pure 230V sine wave control signal.
And is it the positive terminal which should be connected to the center tap of the transformer?
Please suggest me if have to add anything to the circuit .
Thank you so much
You are welcome.
You don’t have to connect anything else in the circuit, just make sure the negative of the external supply to the arduino is connected with the battery negative.
The center tap of the trafo will go to the battery positive
the output will be SPWM which will need some filtration to look like a pure sine.
Hello Swagatam , I have replicated the design and it is working very nice, Just a small question , what changes do i have to make to use PC817 Optocoupler to isolate the circuit
vhafuwi, you can use the first example from this article
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/how-to-drive-relay-through-opto-coupler/
but instead of BC557 use another BC547 here, emitter will go to ground and collector to positive via a K resistor….the mosfet gate then can be connected with the collector of this BC547.
Hi
Thanks again for such a wonderful circuit , what is the best way to test if gates are switching properly without oscilloscope
Regards
glad you liked it….connect LEDs across the two channels with respect to ground and with 1K resistors with individual LEDs, increase the delay at seconds in Arduino code
Thanks for the prompt response, just a bit of clarity, I must connect LED accros the two channel , eg The Cathode of the LED go to the ground , 1k resistor to channel and the to Anode ,
From Channell I Connect 1k Resistor then connect it to LED Anode then connect LED Cathode to the Ground , Am I right
you are right!, the 1K can be on the cathode or anode side, it won’t matter.
Thanks sir, your work is amazing here, I will be expecting sir.
you are welcome!
HI I wanna build an inverter of 1.5kva using arduino programming of atmeg328, so what I really need from you now is full function programming code of this ic which include all necessary activity of inverter function, that’s all I need from you sir. Here is my email olayinka06@live.com
I’ll try to update the info when I have time…
Dear Swagatam
can the breadboard version ( https://www.homemade-circuits.com/make-arduino-breadboard/ )be used to generate the pulse to drive the BJT and MOSFET after the code has been correctly uploaded
Yes surely it can be done, it can be used just as like any other normal Arduino board
Thanks, I appreciate you.
I will keep you updated when I start, my challenge is getting an oscilloscope to monitor waveforms.
Thanks Swixx, for the scope you can try the following concept
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/single-channel-oscilloscope-using/
thanks once again
you are really great
you are most welcome!
Hi Swag! Did you tested this circuit with inductive loads? I want to use it on a grundfos water pump.
Thank you for sharing this project!
Hi elektroman, I did not test it but it was verified by others readers, moreover the concept is a standard concept which is implemented in all conventional inverters
the given circuit is not correct i have made it in proteus but it does not give the proper result.
forget proteus, build it practically and you will find it works flawlessly…all sinewave inverters circuits work with the same principle…
Or if you know a valid reason why it won’t work, you may point it out…. otherwise your statement does not make sense…
good day sir
can the Bjt be used to drive multipe mosfets in parrallel, or is it better to drive more BJTs first before the mosfets
Hi swixx, yes that’s possible, you can add more mosfets in parallel with a single BJT, more BJTs won’t be required…
ok thanks for the speedy reply
is there possibility of one of the mosfet drawing more current due to disparity in same manufacture-model, leading to thermal runaway and gradually affecting other mosfets, if this is possible how can it be prevented.
i want to use build a 1kva inverter but with pulse width from an arduino, purposely for powering a fridge which run power is 70watts but starting watt unknown.
my fear is if there will be current loss if not running at full amperage
mosfets are actually less vulnerable to thermal runaway than BJTs due to their positive temperature coefficient property, still to be on the safer side you can use common heatsinks for the mosfets on each channel, this will ensure equal heat distribution among the mosfets and therefore more efficient conduction.
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/transistor-facts/
Good day, I trust you are doing great.
will it be a good idea, to use voltage doubler circuits to incrementally get to 48 volts then use a 48/240 volts step up transformer.(what value mosfets do you advice on)
This is to reduce current going through the primary winding of the transformer.
my challenge being, getting a voltage doubler that can handler a 1000 watts. ,as well as getting a centre tap 48 volts transformer.
finally do you think using this method we can increase to 120 volts , before using a 2:1 ratio transformer to step up as this transformers are generally more reliable
using a boost converter will cause unnecessary wastage of power and increase inefficiency of the system, so I won’t recommend that, instead it would be a good idea to use batteries in series to get the required a 48V input.
In case you totally want to avoid the center tap trafo, that may be possible using a ferrite trafo based inverter, first boost the battery voltage to the required mains level, turn it to DC and then again switch it back to a low frequency mains AC
the university professor ask for simulation. then suggest me on what software it should be implemented?
thanks for reply
I highly recomend use opto couplers to isolate arduino from high power.
Regards.
thanks, yes since Arduino is a fairly expensive unit it must be safeguarded by all means
how do you implement the optocoupler into the circuit.
thanks
Sir
Ineed a ckt for half bridge ivertor to convert 300v dc to 150v ac. So ineed to handlel high voltage on input side. I cant find any stepdown invertor ckt for handle 300v dc in input side in online. So pls suggest a ckt
Naseef,
you can try the following IC
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/half-bridge-mosfet-driver-ic-irs21531d/
I have designed the circuit stated as above.But when i connect 5 watt CFL load voltage drops down to 170 volts and CFL doesnot glows.And when i connect 9 watt LED, it starts blinking.No load voltage was 250 volts.how to keep voltage constant.please help.
what is the rating of the transformer and battery that you have used??
What the watt can I load on this circuit?
And how can I calculate the watt of my laptop charger it’s input 100-240v 1.6a and output 19.5v 3.33a
inverter power will depend on the battery ah and the trafo ampere rating….multiply 19 with 3 to get the charger’s max wattage spec
Sir how can i make inverter using bipolar technique
by bipolar do you mean using bipolar transistors?
I mean by using Bipolar PWM technique
why do you intend to have a bipolar pwm instead of a unipolar inverter?
Give me circuit of grid tie inverter using aurdino with complete details and code plz for 100 watt
presently I do not have an Arduino GTI circuit, if i find one will try to update it…
Inverter with pwm bipolar technique
Why we give 12v dc to transformer??
so that the 12V can pass and oscilate through the trafo winding and switch ON the induction process
Actually i did simulation with bipolar pwm technique which is east that’s why i ask about it
If you can tell me your exact requirement, I will guide you to the perfect design from this website
How can i synchronize two dc voltages? Plz give me details!!
Please give me the circuit diagram of 100watt inverter and complete details of components used in circuit .
Secondly guide me how can i tie that inverter with grid
You can build the design which is explained above, this will easily give you a 100 watt output provided your trafo and the battery are rated at minimum 100 watt and 10 Ah respectively
Where’s uni polar circuit diagram sir
I wanted to know why you preferred bipolar pwm instead of unipolar pwm, please clarify so that I can know the objective of your requirement.
Why we give 12v dc to transformer??
Kindly tell me exact value of transformer and battery to get 100watt.
I’m doing synchronization of inverter with grid please guide me how can i do it…
Give me complete details please sir
synchronizing a GTI is not so easy, without knowing all the details it won’t make sense to try such a difficult project.
you can refer to the following post for gaining some relevant knowledge and then probably try the concept:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/homemade-100va-to-1000va-grid-tie/
Hi swagatam, please can i use an attiny45 or any other arduino and if yes must it be a pwm pin or any other pin?
Thank for your time.
Hi Miebaka, you can use any Arduino as long as it accepts and generates the indicated PWM and waveform…PWM pins are not required because here basically we are using the Arduino as an oscillator.
Sir
I nees 150v dc to 110v ac output invertor . No need to step down . So can i use the above ckt as iam mention after any change inthe ckt . If its not possible Pls reccoment any other idea
Thanks
Naseef, you will need a full bridge concept for achieving your requirement as shown below:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/?s=full+bridge
or a half bridge network can be also tried, but the output will be 50% less than the input
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2015/03/220v-dc-inverter-ups-circuit.html
Thanks a lot sir for your valuable rply.
Sir need to ask u one more question that is , to adjust the spwm signal from Arduino can I use low pass filter just after pin 8 and pin 9 of Arduino from where we r getting output spwm signals .
And I have chose 4.7 uf capacitor value with 1k potentiometer to adjust the frequency , is this right value
Manish, what is the purpose of this low pass filter? and what frequency are you trying to adjust, the Arduino frequency can be adjusted by altering the delays within the code, nothing can be done through external means.
Sir could u please tell the rating of Transformer and amperage that u mentioned in latest diagram ..
Manish, With a 12V battery, the transformer voltage rating can be anywhere from 6-0-6V to 9-0-9V, the PWM from the Arduino will need to be adjusted accordingly depending on this voltage rating of the transformer.
the transformer current specification will depend on the output wattage requirement, same for the batt AH rating.
This indeed is another nice project since am familiar with Arduino I think doing this will really go in my favour, thanks a lot Swagatam Innovation. But before I try this project, I have two question.
1. Will this inverter be able to power a fan without issues?
2. Is there any kind of analog MOSFET that can create pulse instead of just turning on and off?
Cos this can help create a better PWM without harmonics.
Thank again for you contribution to science.
Thanks Miebaka,
According to me if a proper filter is added which can be simply a high value capacitor at the output of the inverter, then inductive loads can be expected to work without noise.
You can achieve a harmonic less pure sine output by using an emitter follower BJT/IGBT, or a source follower mosfet topology, just as we find in power amplifiers.
To be precise you can use a power amplifier and modify it into an inverter efficiently.
However avoiding PWM and harmonics would mean inviting heat and lots of heat on the mosfets:)
you can refer to this article to know more:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2012/02/making-sine-wave-inverter-from-audio.html
It has to be sorted out by you…the concept is crystal clear in front of you, and there’s nothing mysterious about it….the Arduino output would be generating 5V peaks for the PWMs….5V is enough to trigger any BJT…but may be not enough for the mosfets, still it should work.
you can confirm the output with LEDs by increasing the delay time to may be 1/2 second…..the code even has a small dead time to ensure that the mosfets never turn ON together.
but again if the fets are ON without the gates connected then it has nothing to do with the Arduino, the problem could be somewhere else.
hello sir , can u help me.. i will control single phase motor , i need arduino uno code for VFD 220v , 1hz – 50hz..
please help .. thanks
I am sorry raki, I don’t have this code at the moment!
sir,
I want to design 12VDC to 230VDC ,100W(MAX) ,pure sine wave inverter for solar system.
I don’t want to use any Micro controller .
can you post any relevant circuit for my requirement .
Manish, you can perhaps try the second design from this article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2013/10/pure-sine-wave-inverter-circuit-using.html
Sir ,
Thanks for your reply.
Can I used step down transformer with secondary side connected to circuit and primary to output or only step up transformers are used ?
Manishu, yes you can use any standard step down trafo in the opposite mode…..
please i need a complete arduino inverter ciruit with working feedback pure sine wave with protections.
first build the inverter stage successfully, then you can proceed by adding the remaining stages one by one.
Sir can i use above circuit as a fish stunner/shocker ..i have 12volt and 85Ah battery …
Muhib, you can try an ordinary high voltage generator circuit, the above sophisticated Arduino based design is not required
i require a driver circuit for
mosfet which enhance the 5V output of arduino to 12V to feed mosfet,
* suggest me a driver circuit.
* i am making circiuit for 240V , 350 watts output,
* which mosfet i should use ? irf3205???
*can i use more mosfets parallel to overcome heat issue of mosfets,
* what transformer should i use,,,,,, i am using 7ah 12V battery,
required output 230V, 350watt, guide me rating of transformer?
you can use a 4093 IC and use its gates like NOT gates by shorting its inputs and then it would effectively raise the 5V input to 12V.
IRF3205 will do
you can try as many mosfets as you want, in parallel
12V 7ah battery will be too small, and not produce more than 60 watts, you will require a 100AH, 12V for getting anything near 300 watts
thanks fred! appreciate it!
Ainsworth, yes a resistor should be across gate to source to drain electrons from the metal oxide semiconductor gate to the source. 100K to 1 Meg ohm. An unconnected insulated gate voltage can float to a positive voltage and turn on the N channel mosfet make a short connection from drain to source. Ie proper operation of n channel mosfet. 2nd verify electrical ground connection from arduino circuits to your smps power circuit mosfets. If not connected. Then circuits Can float with low output 0.7V from arduino can be 4.3V measure on mosfet gate to source. Effectively turning on n channel mosfet. Battery ground, arduino ground, n channel mosfet ground all tied together. Good luck on debugging circuits. Thanks for arduino sine wave code and circut. Bless you and thanks for Sharing. Fred WB7ODY
that clearly indicates your FETs are not good, because connecting the gate with source should keep the fets completely shut off, if still it is conducting then surely the fets have some fault
You can try using BJTs like TIP122 or TIP142 instead of the mosfet and check the response.
If u have some parts I would want you to test the circuit with a transformer, I think it may require a optocopler.
you have already tested the waveform which simply needs to applied to the gates of the mosfets, there's nothing complex in the design at all, since you have already started with the project it would be easier from your side to finish it,
you should change the doubtful fets and replace them with BJTs, and confirm the results.
I think it is just a matter a minutes to identify the exact location of the fault, by doing some basic tests as already suggested by me in the previous comments.
Fuses cannot be a crucial thing in any circuit while testing, unless the circuit involves dangerous parameters and unpredictable results, here the inverter is supposed to work without any fuse…if you are forced to use a fuse that means your inverter has a serious fault which cannot be solved by replacing fuses rather it should be done by checking and rectifying the fault
As I mentioned before you should check the response of the FEts without connecting the gate supply, and by keeping the gates grounded..if still the FETs conduct would indicate faulty fets.
puling high current without load is a fault and as good as a short circuit.
By the way there's no point in working with faulty, doubtful, devices…if you have slightest doubt regrading the parts either you must replace them or quit the project until correct parts are bought.
…you can also try a small good readymade trafo (1 amp) and test the response, that will give you clear idea regarding the proceedings.
you are saying your trafo is good, your fets are good, there's no chance of any short circuit, and yet your fuses are blowing, how can that be possible?
from here I can say your FETs are bad for sure or may be there's something that's causing a a short circuit which you must diagnose and rectify. without a short circuit or overload a fuse can never even a new hobbyist will know that!
if I would be in your place I would have first tried BJTs instead of mosfet for testing purpose, because BJTs are more manageable thn mosfets
mosfets gate resistor should always be low, in fact higher resistance might cause heating up of a mosfet and damage.
alternatively you can remove the Arduino and check with a 4047 IC, to see the difference, there are actually many methods through which you can check the fault.
another method is to connect car bulbs in series with the mosfet drains, and remove the gate supply, if the bulbs keep glowing even without gate supply would quickly indicate a faulty fet.
where is the arduino code swagatam
Hi Ravi, please click on the link which is highlighted in the second paragraph of the article
fro where i can find the arduino code
Q1.is there any way to start single phase 3hp induction motor on home 5kva inverter ? because starting current is very high may be more than 30 amp but running at full load max current is 15 amp . Q2. is running above mentioned motor, possible on pwm based pure sine wave inverters?
It may be possible and tackled comfortably by adding an external battery bank with the existing battery. once the motor is initiated, the external battery bank can be removed, or disconnected with a help of a switch.
i have question. inverter is only 5kva ratings.
than how adding a battery to it increases its output power ?
it should be able to produce the extra power for a few seconds.
but if you are concerned about it, then the best option would be to change the inverter with a 1 kva rating
sir thanqew for ur valuable reply.
can you please suggest components for above systematic to bulid 6kva inverter and approx prize estimation for it?
You are welcome,
for making a 6kva inverter you can use the same Arduino board and its code.
for increasing mosfet power you can add more of them them in parallel, each mosfet should have it's own gate resistor and diode.
the transformer will also need to be rated as per the mentioned specification.
the battery voltage should be selected as high as possible, may be at 84V would be great and this will allow the transformer to be relatively smaller and the associated wiring to be manageable.
I can't say about the prize, you will need to find it out from the market.
for rating of mosfet …
if i have two mosfet each one rating 50watt and one for possitive cycle and another for negetive cycle .does it means i have inverter of 100watt or only 50watt??
Gurmel, both the mosfets will need to be of the same polarity as shown in the diagram that N-channel.
the mosfets do not decide the power output, it's the battery AH rating and the trafo wattage rating which determines the output delivery, the mosfets simply needs to be rated adequately so that it is able to handle the power pushed by these elements.
the power power will depend on the trafo Voltage x current value and only if the battery has the capacity to deliver the amount of current which trafo is rated at
Sounds Good. Can you please post the link here as I am unable to use search box in my android. may be some css issue.
The search box is right at the top of the article.
anyway here are the links:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2014/07/5kva-ferrite-core-inverter-circuit.html
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2014/05/twin-or-split-battery-charger-circuit.html
Great Swagatam. You're my hero. Will contact you again if needed. thank you so much for your quick response and help. May God bless you.
you are most welcome Saqib!!
adding to my previous question. do you have any kind of pure sine wave inverter schematic that can power on a 1 to 1.5 ton Air Conditioner. Actually I bought a land for fish farming and wanting to power up things in my sitting area there with inverter because of lack of electricity there.
Saqib, you can try the following design
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2016/04/solar-inverter-circuit-for-15-ton-ac.html
Great. one more thing Can this be used with batteries? because I wanted to run this in night as well. Also solar panel isn't possible for me due to low space around sitting area and placing panels to any other area isn't affordable for me. what is the idea behind is that I will use two sets of battery banks one online and one offline on charging stat. inverter should be smart enough to detect low battery and switch input to secondary battery bank and start charging the first one while should run at least 1 ton Air Conditioner thats why I was thinking of 5kva inverter. if there any possibility then please write an article on this as soon as you can. I can buy this from market but you better know what we ask, we don't get. better to make it ourselves as per our requirements and have fun of electronics.
Solar panel is actually not compulsory, you can use any suitable DC source with the suggested circuits, just make sure the voltage and the current specifications are correctly matched with the inverter and the load.
most of the ideas are already published in this website, you just have to search it using the search box.
I have a 5KVA inverter circuit included in this website, I also have an automatic twin battery charger circuit which you can use for automatically detecting, and selecting the charged battery when one of them gets discharged.
However all these circuits are strictly for the experts who know all the basics of electronics and have the required practical experience in the field, it's not for the newcomers, so please make sure you have an expert with you while you try the proposed designs.
Hi Swagatam,
I need to build 48vDC to 220vAC 5000KVA Pure Sine wave Inverter. Can you please share schematic and number of power transistors or mosfets and transformer specifications. I also need to know battaries specifications. thanks
Hi Saqib,
you can first try building the following design successfully, then I'll tell you how to proceed and make the sine wave integration
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2014/11/48-v-inverter-circuit.html
Hello sir , can one achieve a pure sine wave if it he uses pins 8 and 9 of the arduino but this time with an l293d IC instead of MOSFET, 12-0-12 transformer, 12v battery?
Hello obenobe, yes you can use the L293 with the above Arduino for controlling a motor, but I am not sure about a trafo operation….I think that may be possible too.
Thanks
Hello sir niceone… Can one use an l293d motor driver IC instead of the MOSFETs, with a 12-0-12 transformer and a 12v battery?
thanks…yes that's possible, you can use it..
But it will be less weight. what is your opinion if we used dc booster in Pure sine wave inverter. we will be thank full if you have any Diagram.
Secondly in pure sine wave 3K Inverter which one will be very effective to give us pure sine wave Arduino or IC 4047 with 555.
Can we used dc booster to step up voltage to avoid transformer
a booster will also involve a transformer…
Thanks, swagatam,
Can we use F3415s Mosfet in this ckt.
thanks, the mosfet rating will depend on your power requirement, and it must be N channel type…
This is the waveform coming from public 8 and 9.
https://goo.gl/photos/8HG4xR4dtD5dZTxe7
that looks perfect, and quite similar should appear at the trafo output, which should get transformed into a perfect sinusoidal waveform with the addition of a capacitor (0.33uF/400V) and possibly an inductor, as shown in this example circuit
4.bp.blogspot.com/-khKat0UA8Jw/UITpCnNd7yI/AAAAAAAAA_A/8x-KAD2aHLE/s1600/simplest60+Hz+Inverter+circuit+diagram.jpg
What do you think would be causing me to get high frequency?
it's the 6 pillars on each cycle which might be confusing the scope…you can add a capacitor at the trafo output and see the difference…
Hi sir i am planing to make an inverter of 48v to 240v pure sine wave. I try to search here and i didnt find a pure sine wave 48 v circuit.. My inv transformer is 48v – 0v 12amps & secondary is 240v.. Sir please help me.. My mail id is vineethhari@ymail.com
Hi Vineeth,
you can convert any of my 12V sine wave inverter cirucits into 48V, simply by applying 48V to the center tap of the transformer, and then step down the 48V to 12V for the DC circuit stages, because the involved DC circuits cannot work with 48V…..you can drop the 48V into 12V by using the principle as shown the following design. see the BC546 section
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2014/11/48-v-inverter-circuit.html
Felicitaciones que gran trabajo….Una pregunta estoy usando batería de 24V y el transformador es de 220VAC, debo hacer algún cambio al código de Arduino o no es necesario? y que capacitor debo usar a la salida del transformador para obtener la onda seno pura?..Gracias por tus aportes.
Me complace que le haya gustado el artículo, no tendrá que cambiar nada para la batería de 24V, solo asegúrese de usar un 7812 IC para el Arduino. El condensador de salida debe probarse aleatoriamente. Inicialmente puede probar con 0.22uF / 400V y luego verificar gradualmente la respuesta aumentando este valor.
Mil gracias por su pronta respuesta, olvide comentar que en mi país trabajamos con 60hz, todo sigue igual o debo hacer modificaciones en Arduino o en alguna etapa del circuito?,otra consulta,deseo implementar el temporizador de retardo para evitar problemas en el encendido pero a 24V y en tu diagrama está a 12V,debo hacer cambios? GRACIAS POR TU VALIOSO APORTE A NUESTRA HERMOSA PROFESIÓN…
You are most welcome Mekatronik, yes for getting 60Hz the code will need to be changed a bit.
As you can see the total delayMicroseconds on each channel of the code adds up to 10000 that’s 10 mS…you will have to adjust and reduce the values proportionately so that the total adds up to 8333 microseconds or 8.33 mS
hola el cambio que me sugieres de 8.33mS para 60hz lo debo hacer a estos valores?
const int sPWMArray[] = {500,500,750,500,1250,500,2000,500,1250,500,750,500,500};
O en esta sección del código?
estoy un poco confundido,gracias por tus aportes.
// Loop for pin 1
for(int i(0); i != sPWMArrayValues; i++)
{
if(sPWMpin1Status)
{
digitalWrite(sPWMpin1, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(sPWMArray[i]);
sPWMpin1Status = false;
}
else
{
digitalWrite(sPWMpin1, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(sPWMArray[i]);
sPWMpin1Status = true;
}
}
Hi, you will have to adjust the delays proportionately such that the total for each channel is 833.33
I asked that question time after time but never actually got a reply. So let me get it straight just this once.
If my battery source on an inverter is 12v that means the transformer should be 6-0-6v and if it's a 24v battery source then the transformer will have to be 12-0-12v ect.
And that's the case for all your inverters? If any exception could you send me the link to the exception and im not refering to something like your cascade design.
Please show me where you have asked this question, and did not get the reply?
when you use PWM it cuts off a portion of the actual waveform and this results in a reduced average voltage or the RMS value of the waveform, to compensate this the transformer needs to be lower with its primary V specs, so that the reduced PWM waveform matches the reduced value of the trafo.
for example if the PWM waveform average value is 7V for a 12V peak, then the trafo should be 6V/220V which will yield approximately 230V.
instead if we applied 7V PWM waveform to a 12V trafo that would proportionately reduce the output to:
7/12 = x/220
12x = 7 x 220
x = 128V at the output
it applicable only for PWM chopped sinewave inverters, NOT for all inverters….
In this case it's a spwm so it's applicable here. So my battery is 12v so I need to use a 6-0-6v transformer then
yes that's correct
I checked the video which you sent, I am afraid the results are not correct.
the code of the Arduino cannot be wrong because it contains simple delays in the form of ON/OFF periods…and these ON/OFF periods must produce PWM kind of waveform in the oscilloscope, your scope waveform looks weird.
secondly, if you add all the delay periods in the code, it comes to 10000 microseconds that's equal to 10ms…so 10ms on each cycle gives 20ms on the two channels…dividing 1 second with 20ms, gives 50 Hz, and that should eb the frequency…how can it be 600Hz??
Also how could I stop diodes from getting damaged?
which diodes are you referring to??
Sorry I should have said Fet instead of Diodes.
But since my transformation is a 12v transformer then that explains why I was getting 57v.
I tried a 12v transformer, I was getting 57v, I used irfz44n and they burnt up 2 times, while running they weren't hot, I think they burnt up because of of constantly adjust alegator clips on battery terminals to get a better connection.
But since the voltage was that low and the frequency is so high I was wondering if you tested this circuit.
mosfets can burn due to many reasons, and definitely not due to frequency issues because mosfets are designed to handle very high frequencies.
it's a Pwm circuit and the transformer cannot be 12V for a 12V supply, it has to be 6-0-6V or some other value as pert the calculations, I think this issue has been discussed countless number of times in this website…
the above design is a an obvious circuit and will work without fail.
I have tested it with LEDs with a slow delay effect and it behaved perfectly as per my brain simulation.
once this was confirmed, I simply reduced the delays so that the sequence corresponded a 50 Hz frequency across the two channels with 7 varying SPWM pillars for each cycle,
anybody can easily interpret this.
you can verify the pattern on an oscilloscope if you have doubts.
Using a 12v battery I can use a 12v transformer for this circuit?
you are wonderful Mr. Swagatam Majumdar, please how many can i make 500Watt inverter of arduino
thanks alex, you can achieve that by using 600 watt mosfets and a 600watt trafo….and a 24V 150AH battery
Gud work sir
Thanks Hassan…
Gud work sir
Hi Swagatam,
I want to make an inverter to drive some gauges that require approximately 2 amps at 115v AC @400Hz, using a 28v DC imput. The Arduino seems like the right tool. Would you be kind enough to make up a circuit diagram?
Regards,
Mark
Hi Mark,
you can try the same design which is published in the above article….just assemble it, and start using it for your specific need.
the transformer will need to be a 24-0-24V 10amps/120V for your mentioned application
Hi Swagatam,
I have tried PWM charge controller using arduino and it is successful. Iam using it in my home generating 80 watts of power from 200 watts panel. I know its very poor.
BTW, I admire your works and I keep looking at your blogs very often.
I came across this very interesting circuit and I want to try this inverter.
Just to be sure, I have few 4905 PNP mosfets lying around from previous project, Can i use the same in your circuit? Source of mosfet connecting to Battery -ve and Drain of mosfet to transformer?
2. Transformer rating: secondary 12v-0-12v/15A, primary 220V. What will be my output power? is it 12×15=180 Watts? So if i increase the transformer rating to 30A can i get 360 watts of power? ofcourse with some 10-15% losses…
Hi Sham, if you are using an Arduino based controller and getting 80 watts from 200watts, then it's not worth using…or may be you haven't built it correctly, a linear IC circuit would give much better results than this.
as for the above Arduino sinewave inverter, yes it's indeed an interesting and handy little inverter which will give you pure sinewave just by hooking up a couple of fets and a trafo.
Pchannel mosftes might not work correctly here since the design is meant for N channel mosfets, so you will have to replace your p channels with N channels and then test the results.
your watt calculation is quite correct, but for a 12V battery you may have to employ a 9-0-9V trafo
Sham, I checked the link you sent, but I could not go through the diagrams since it everything quite elaborate….
one thing i can say, if PWM is used without a buck or boost converter then it's meaningless…it will simply block the excess power from the panel and indirectly waste power. In that case its' better to use a LM338 based circuit, or simply use a panel having a nearby specs to that of battery.
When you are using Arduino based design the outcome should be highly advanced and efficient, otherwise it's pointless.
if you need an MPPT circuit you can check out the first two articles from this website
you can regulate the output 220 volt from the code of the ordino.
without a feedback that’s not possible.
Hi Swagatam, Appreciate your quick response. I am using Arduino for doing multiple tasks, like auto change over to AC/Battery, solar energy monitoring etc… as u said it looks like something is wrong.. My 100w x2 panels are generating appx 7-9 amps peak. But inside ckt it's getting down to 6.8 amps max. ��. I need your help in solving this. After reading ur article, am thinking of some issue in calculating the duty cycle fed to P channel MOSFET. Let me check that and update you.
I will purchase 9-0-9v trafo, N channel MOSFET and try the ckt. Here I need to control the amount of power used and alert me when solar power generated is less than power consumed. I hope I will succeed in this.
Hi Sham, what kind of circuit are you using for the controller, is it a buck converter? also specify the V and I of the panel.
duty cycle for the above circuit is 50% for the positive negative halves, and the individual phases are SPWMs with varying duty cycle.
Wow Swagatam.. xlent link. Thank you. I will to go through them one by one.
Yes.. now I am realizing the necessity of Buck converter. In one of your article you had mentioned about both Buck and boost.. I had not understood at that time.. I will go thru again.
Btw, to my understanding, I should use Buck converter with 10 amps rating for my work right? Bcos panel amp rating is 10 amps.
You are welcome Sham,
if you wish to use a buck converter with a 10amp pnel, then it should be rated higher than 10amps, because when the panel voltage is reduced by the buck converter it is supposed to convert the unused voltage into current…therefore current would go above 10 amps.
you can find it dividing the solar panel wattage by the battery voltage.
Sir, what of feedback, isn't that and essential part in inverter operation?
Oluwole, feedback is not an essential part for an inverter, it's just an added feature.
If you have your transformer correctly matched with the battery then feedback won't be necessary
Arduino Uno ups code fix out put 220v
Then how would you regulate voltage at different load??
Do you have a voltage regulator with your home AC mains input?? how does it regulate different loads
Hello sir,I am looking to build the above spwm inverter using arduino.am using 24vdc input so should I regulate it to 12v for the driver circuit stage and if so,what of the power mosfets can they work with 24v supply as well.my transformer is 24v 0 24v 5A.i will add one more battery(12v) to make 36v DC supply as per my trafo rating.please help.
Hello Yusuf, yes you must regulate it through a 7812 for supplying the BJT collector arms and the Arduino.
Thanks sir.so concerning the average spwm voltage from Arduino .should it produce 24v rms from the transistor stage according to rating of trafo.(24v 0 24v)then what would be my peak to peak voltage is it regulated12v supply (through collector arm)or the main 36vdc supply from battery. I am a mere beginner in power electronics.please help.
Yusuf, All the collector resistors and the Arduino must connect with 12V.
only the transformer center tap must connect with 36V Dc.
All the grounds (-) must be connected in common.
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/how-to-connect-bjt-and-mosfet-with/
Thank you for the link it helped.in my case am having PNP BC557 as the level shifter instead of BC547.how will I connect it to the Arduino if the polarity is reverse.i think it is collector to negative line(-12v) ,base to ground of Arduino and emitter to positive line(+12v).is it right.mosfets are N channel.then what about the rms value relative to the transformer(24v 0 24v) .what should be the average voltage produced at the output of Arduino BJTs.
Glad it helped Yusuf! You will have to set the average value of the Arduino output whose ratio x/5V corresponds to the 24/36 transformer/battery ratio. Meaning x/5 should be equal to 24/36 or 0.66….. or the value of x must be 66% of 5V
x is the average output voltage from the Arduino
Thanks alot.what about the pNP transistors that I have.are they applicable in this circuit.i ought to connect them in reverse of npn.i.e, base terminal to ground of Arduino,collector to ground of supply line and emitter to positive of supply line.
PNP with N-channel MOSFETs will give opposite results, and PWM duty cycles will get inverted, so it won’t work!
Hello Sir.i got the BC 547 transistors with the respective resistors.you asked me to realize a value (x) which would be average voltage from arduino.x/5 should correspond 24/36.so x should be around 3.3v.my question is from what points at the output should I measure the required 3.3v.then what about at the collectors and emitters of each BC547.as I saw above,,what value does this measurement represent.thank .
Hi Yusuf, you can measure it directly across the Arduino output and the negative supply terminal
Thanks,I will measure the voltage using multimeter.so regarding the code ,to produce roughly(3.3v average output from Arduino)should I increase or decrease the delay microseconds proportionally or what can I do to the code to achieve that.please help
Yusuf, please see the conversation between Serd and me…actually the code is optimized for 3.2V RMS, or at 70% duty cycle. You can use the code directly for your application without changing anything
Can i use a 6v transformer for this inverter? Can i power it from 12v battery?
I tried your first code and second code, but there is a problem in your second code. The bulb is blinking in the second code.
Please use the first code which is the tested one. With the first code, you can use 6 – 0 – 6V transformer with a 12V battery.
I made it. It consumes lot of current and mosfets are getting hot. I used irfz44n mosfets. Can i fix it by adding more two mosfets parrerel?
I made the circuit using attiny13a microcontroler. Can i use it?
The mosfets should not become hot without a load on the transformer output. For example in my experiment I had attached a load of 100 watt at the output and I found the mosfets getting hot a bit.
So in your case if the mosfest are heating up without a load then something may be wrong with your code or the circuit.
Adding more number of mosfets will not help if the mosfets are heating up without a load.
You can measure the voltage across the base/emitter of the right side BC547. This will be give you the voltage that must be used for the primary side of the transformer.
If the transformer (6-0-6V) is lower than this value then also the mosfets can heat up.
IRFZ44 is fine, but I am not sure if attiny13a can be used instead of an Arduino.
Olá como passar o código hex do inversor senoidal para 60 hz..com pic..