Below are a list of Transistors and diodes marked ‘TUP’ (Transistor, Universal PNP), ‘TUN’ (Transistor, Universal NPN), ‘DUG’ (Diode, Universal Germaniuml or ‘DUS’ (Diode, Universal Silicon).
This indicates that a large group of similar devices can be used, provided they meet the minimum specifications listed in tables 1a and 1b.
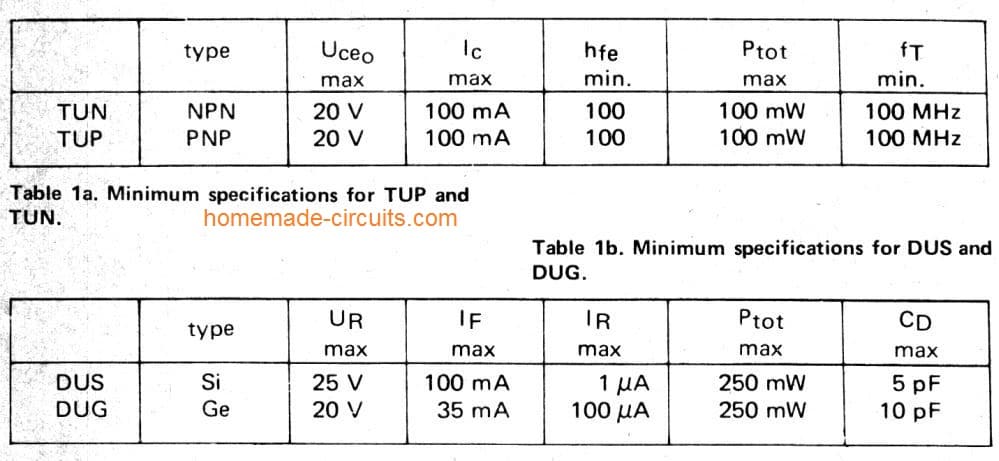
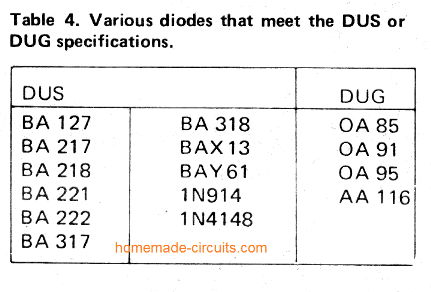
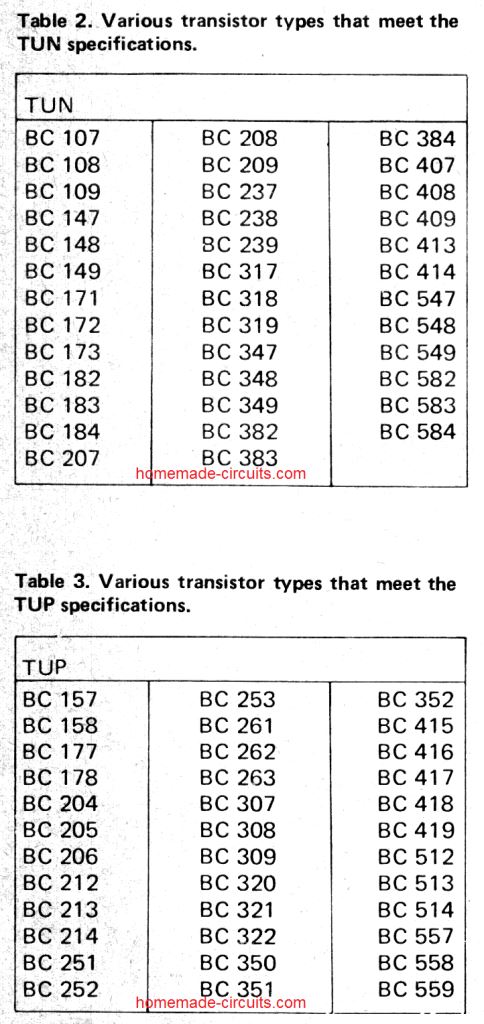
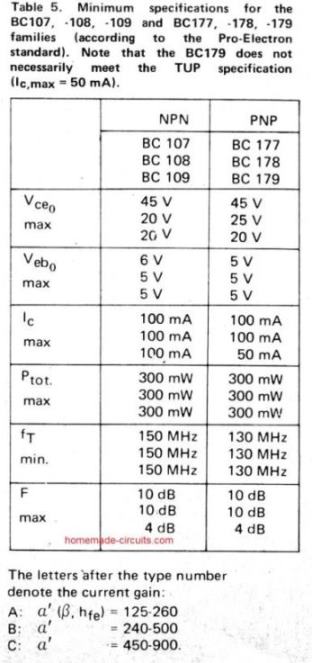
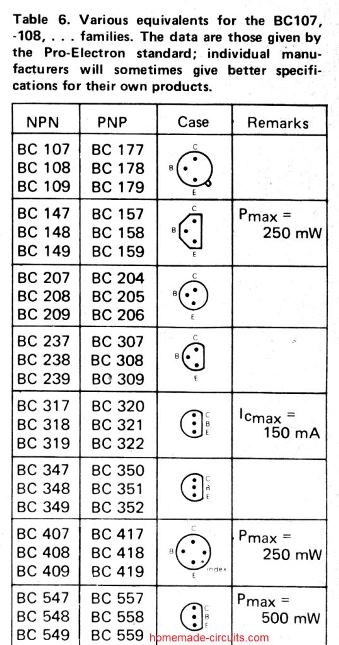
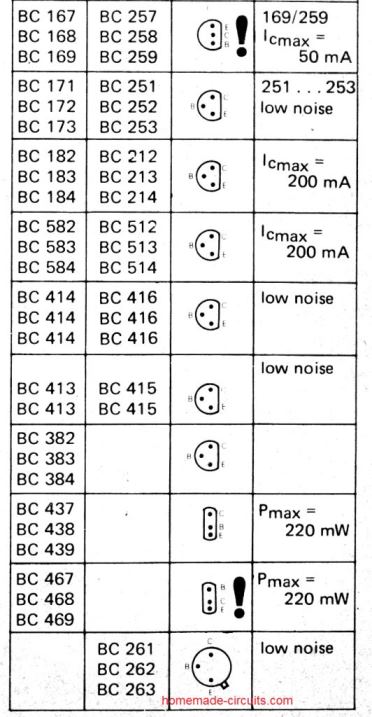
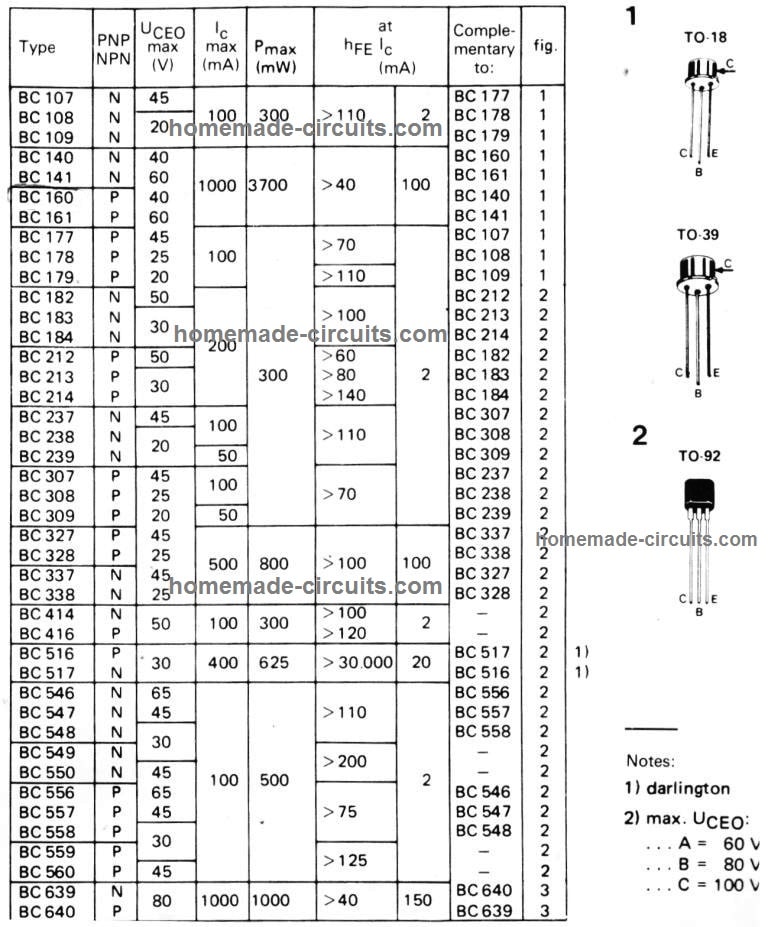
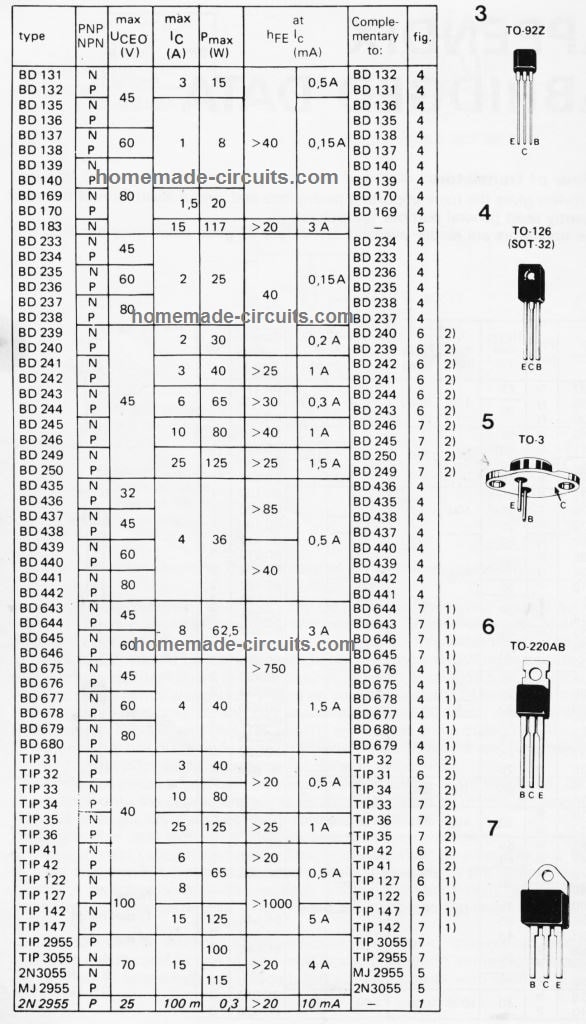
Detailed BJT Datasheet, Pinouts with Complementary Pairs
The following figure shows a vast range of bipolar transistors and their detailed specifications. You can learn about their NPN/PNP polarity, Uceo, Ic, Pmax, hFE, an also regarding equivalent numbers, or complementary pairs.
Bipolar transistors work with four distinctive areas of operation, characterized by BJT junction biases.
Forward-active (or simply active)
The base–emitter junction is forward biased and the base–collector junction is reverse biased. The majority of bipolar transistors are designed to handle the highest common-emitter current gain, βF, in forward-active mode. In such a scenario, the collector–emitter current is roughly proportionate to the base current, but most of the times greater, for small-scale base current changes.
Reverse-active (or inverse-active or inverted)
By reversing the biasing factors of the forward-active region, a bipolar transistor switches into reverse-active form. In this setting, the emitter and collector areas swap their tasks.
Due to the fact that many BJTs are built to enrich current gain in forward-active mode, the βF in opposite form appear to be many times lesser (2–3 times for the standard germanium transistor).
This transistor function is hardly ever applied, typically used just for failsafe situations plus some kinds of bipolar logic. The reverse bias breakdown voltage on the base might be an level of dimension smaller in this region.
Saturation
Having both junctions forward-biased, a BJT acquires saturation mode and makes it possible for high current conduction through the emitter to the collector (or the other route when it comes to NPN, with negatively charged carriers moving from emitter to collector). This method refers to a logical "on", or a shut-off switch.
Cut-off
In cut-off, biasing situations are reverse of saturation (both junctions reverse biased). There exists hardly any current, that compares to to a logical "off", or an open switch in this mode.
Need Help? Please Leave a Comment! We value your input—Kindly keep it relevant to the above topic!