This LED light bar with dimmable feature will allow the user to adjust the brightness of the lamp in 4 steps, with100%, 50%, 10% and 0% illumination control at each subsequent steps.

The idea was requested by one of the avid readers of this blog. Here's the required working concept.
Hi Swag !
I stumbled across your web page whilst searching for a solution to make an effective touch led lamp.
Actually the one my dad uses at night has gone kaput. So I thought why not make him one - being an engineer in the past.
NTE’s touch dimmable led light bar. I love how it’s built and I’d like to use this as a ref to make a night lamp for my dad whose old and needs it at night….
I intend to may be use a dimmable Led bulb or a led strip to make the lamp.
If you can help me with the circuit and maybe a tutorial sort as I’ve been out of this for a long time, it would really mean a lot.
Monish
The Design
The basic design of the proposed touch dimmable LED light bar circuit can be seen in the block diagram below:
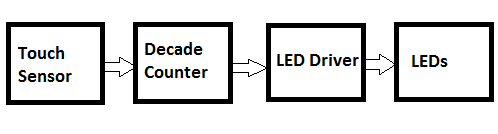
The touch sensor converts the tiny finger touch signal into amplified electrical pulses. The next decade counter stage converts these pulses into shifting logic levels across its outputs.
These shifting logic pulses are fed to the corresponding LED drivers which convert these signals into a sequentially varying voltages for the LED stage.
The varying voltages from the transistor stage which are set at specified levels cause the LEDs to illuminate with different light levels or brightness., accomplishing the dimmable effect on the LEDs.
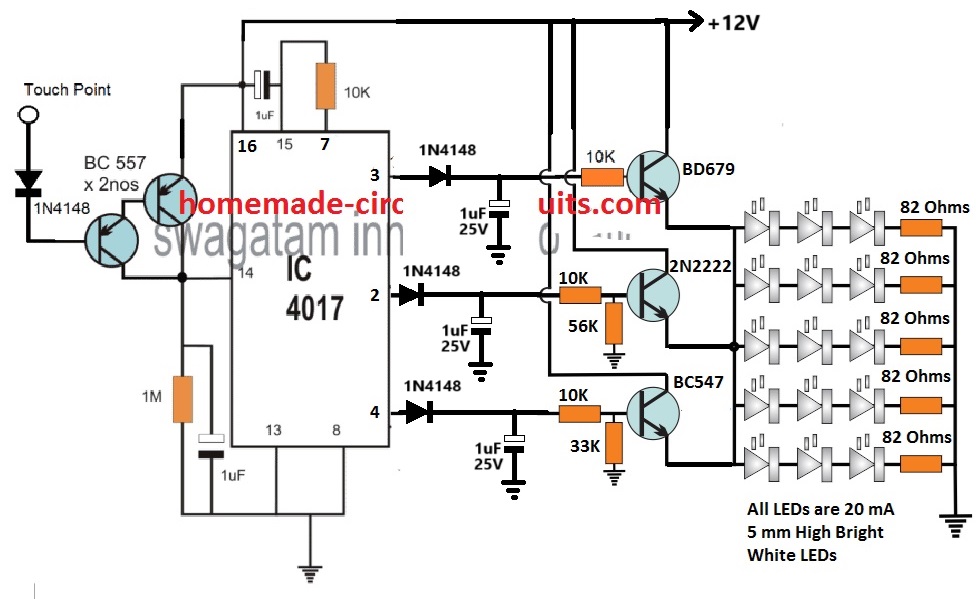
How the Circuit Works
Referring to the circuit diagram above, the basic circuit functioning could be understood with the help of the following points:
The two BC557 transistors at the left side of the diagram form the touch sensor stage.
Tiny electrical pulses from the finger are amplified to the supply level and applied to the clock input of the IC 4017.
The IC 4017 is a 10 stage divide by 10 Johnson decade counter, which responds to these input signals and converts them into a shifting HIGH logic across its output pins from 3 to 4.
Initially when the circuit is powered, the 1uF at pin15 of the IC resets the IC so that the HIGH logic is set at its first pin out #3.
Due to this the corresponding BD670 transistor stage conducts and illuminates the LED array brightly. The BD670 being a Darlington device illuminates the LEDs with high brightness.
At this stage the brightness of the LEDs is maximum also because the BD670 has no potential divider at its base configuration.
This allows it to deliver an optimum 11 V from the 12 V supply to the LEDs at full current, illuminating the array with full brightness.
When the touch sensor is touched, the decade counter responds and causes its output logic to shift from pin#3 to pin#2.
This shuts off the BD670 stage and powers the pin2 transistor stage which is also wired like an emitter follower.
Therefore, now the 2N2222 transistor becomes responsible for illuminating the LED array.
However, since the base of the 2N2222 emitter follower is rigged with a potential divider that creates around 10 V at its base, causes the emitter of the 2N2222 to have a decreased emitter voltage, at around 10 V.
The 1 V reduction of the supply to the LEDs, decreases the illumination and dims the LED brightness to 50% less than the original level.
Next, when the touch sensor is touched again, shifts the HIGH logic from pin#2 to pin#4 of the IC. Likewise, now the BC547 driver stage activates and takes over the job of illuminating the LEDs.
But again, due to a potential divider at its base set to generate approximately 9 V output at the emitter, causes the LEDs to further dim at the lowest 10% of its original full level.
After this when the touch pad is touched, the clock signal at pin#14 of the IC shifts the HIGH logic from pin#4 to the next subsequent pin which is the pin#7.
However, since the pin#7 is attached with the reset pin#15, cause the IC output reset back to pin#3. This enables the LEDs to illuminate again with full brightness.
Thus means the dimmable tube light bar does not have a switch OFF step across the touch sensitive range.
If you wish to have the switch OFF function at the last stage, after the pin#4 step, you can achieve this simply by replacing the pin#7 with pin#10.
Meaning, pin#15 now connects with pin#10 via the 10K resistor. This will allow the 3rd touch action to switch OFF the entire LED bar, and the next subsequent touch will yet again restore the LEDs to its full brightness level.
Using Current Control for Dimming
In the above concept, the LED driver section dependent on a voltage controlled dimming on the LEDs.
In this concept the transistors are configured as emitter followers and their base voltages are controlled using potential dividers.
This allows their emitters to follow the base voltage and produce an equivalent controlled voltage for the LEDs.
This controlled voltage is appropriately calculated to generate the sequential dimming effect on the LEDs.
However, calculating and adjusting the base potential divider networks can be time consuming.
Therefore to make things easier we can simply convert the above voltage controlled dimming effect into a current controlled dimming effect, as depicted in the following diagram.
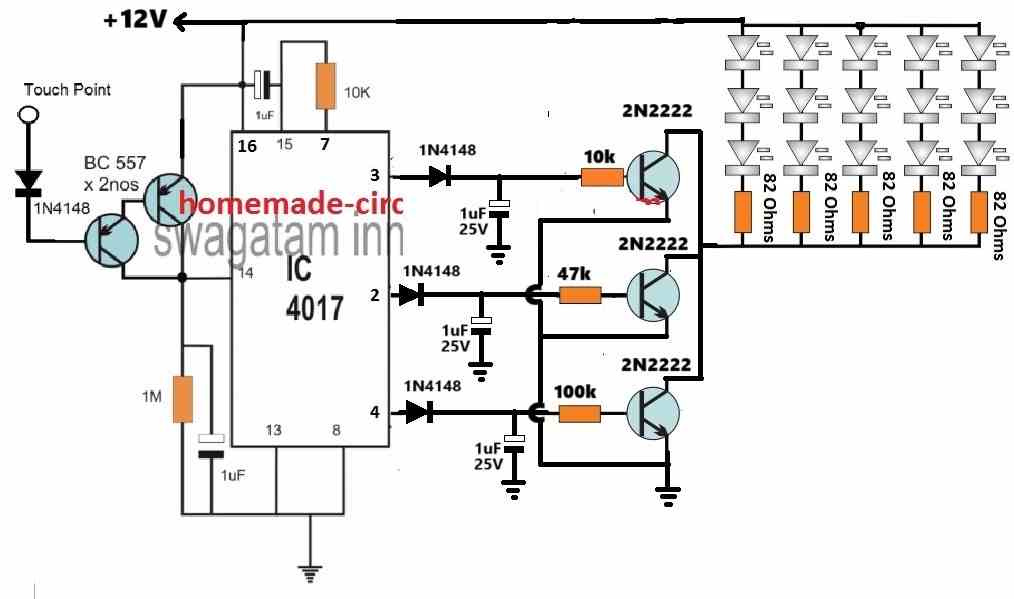
In the above configuration, the LEDs are shifted on the collector side of the transistors, and the base resistors are replaced with single resistors.
Here, the base resistors govern the collector current to the LEDs, which can be appropriately calculated for generating the desired sequential brightness control on the LEDs.
The following formula can be used for manipulating the base current for each of the transistors to illuminate the LEDs with a varied sequential brightness.
R = (Supply Voltage - Base/Emitter drop) x hFE / LED Current
Practical Example
In the above formula, the "R" represents the base resistors of the transistors.
Let the supply voltage be = 12V.
The base/emitter drop for a BJT is normally around 0.7V
The hFE of 2N2222 can be taken as 100.
Let's consider each LED to be rated at 20 ma, so each LED string with 3 series LEDs will also consume 20 ma. Since 5 LED strings are used, the LED current for generating maximum brightness on the LEDs will be 20 mA x 5 = 100 mA.
Therefore substituting the above values in our formula we get:
R = (Supply Voltage - Base/Emitter drop) x hFE / LED Current
= (12 - 0.7) x 100 / 0.1 = 11300 ohms
Thus a 11.3k resistor will cause all the LEDs to illuminate with maximum brightness.
Now, suppose we want the LEDs to illuminate with 50% less brightness on the second step. For this we have to reduce the LED current to 100/2 = 50 ma.
R = (Supply Voltage - Base/Emitter drop) x hFE / LED Current
= (12 - 0.7) x 100 / 0.05
= 22600
Therefore to illuminate the LEDs with 50% less brightness we have to select the base resistor of the second transistor as 22.6k
And so on, in this way we can generate the desired sequentially varying brightness on the LEDs, simply by changing the base resistor values of the transistors.
Good day Swagatam! I just want to ask, I’ve been able to produce a pcb out of this circuit, I tested and everything is fine but when I put in in the enclosure (which is a plastic enclosure), the sensitivity of the of the touch sensor is too weak to penetrate to the other side of the enclosure which has a thickness of 1mm. How should I modify the circuit to make it more sensitive? Does it do something about the resistance value on the touch sensor? Please give me an advice, Thank you!
Good Day Ryuchi,
The touch sensor requires physical touching with your finger, in order to toggle the IC and its outputs. If you do not touch the touch sensor pad directly with your finger then it will fail to detect the touch. In other words, there should not be a gap or a barrier between the touch plate and the sensor.
Please let me know if you have any further questions or doubts.
So I will not be able to trigger the sensor if i put it on the inside and touch it from the outside of the enclosure? Is there no way for me to adjust some values on the circuit which make the sensor detect a touch from the outside of the enclosure?
You can try increasing the touch plate area to around 1 sq inch and see if that solves the problem or not. Increasing the sensitivity too high can make the device prone to false RF triggering.
Alternatively, you can remove the IC 555 monostable section in your design and replace it with the following touch sensor module:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/ttp223-capacitive-touch-module-explained/
Thank you!?
Good day Swagatam!
Just want to ask, for designing the pcb for this project, should i place the components the same as how i can see it on the schematic? Or is there a technique that i could use to arrange the components neatly with respect to the wirings. It’s my first time designing one and im not sure where and how to start. I’ve already get all the footprints but for the footprint for the LED Strips am not sure what to put. Hope to hear from you, thank you!
Good day Ryuchi,
For the above project there are no critical aspects that needs to be followed for designing the pcb layout, just make sure all the track connections are made correctly as per the diagram. You can terminate the transistor collectors through respective pads for implementing the external LED strip connections.
Thank you very much!
You are welcome.
Hi Swagatam!
I’ve already built the circuit for the 555 timer and integrate it to the IC 4017. But it doesn’t seem to fix the switching (i still used the open wire as the touch point), i looked at the diagram again and i saw that from the “touch point” on the original circuit, it became “touch plate”. May i ask what does it mean by the touch plate? And what material should i use for it and how is it different from the open wire used before? Thank you!
Hi Ryuchi,
Did you check the 555 monostable separately? Did the LED light up for 1/2 a second and switch OFF?
If it did and still not working with your 4017 circuit then 100% your 4017 is faulty or maybe it should be built by soldering.
The touch plate does not need to be a plate, it can be any small 1 inch open wire end.
Yes, on the 555 monostable circuit, the LED lights up when Im touching it and holding it, and turns off when i remove my hand from the contact. But after i integrate it with the IC 4017, it still jumps inconsistently and when i hold the touch point it constantly counts and not producing only one output. Should the 555 timer also eliminate the constant switching of light (when connected to the IC 4017)when i hold the touch point? If that’s how it supposed to work i think i really need to solder all the parts including the timer right? Thanks for answering my questions.
Sorry, that’s not the right way to check. The touching should be momentary, you touch for a fraction of a second and remove the touch, and the LED stays illuminated for 1 second and then automatically shuts off….this is the right procedure. This must happen on every subsequent momentary touches.
Please confirm the 555 operation as suggested above. You can increase C1 to 10uF or the 100k resistor to 1M to ensure the LED stays ON for at least one second before switching OFF automatically.
I see, so i need to expect a delay for the touch part. May i know what to expect too when the 555 timer is now integrated to the decade counter in terms of switching?
You can reduce the delay to 0.5 seconds by adjusting the C1 value. After integration, as you touch the touch point momentarily the output of the 4017 must sequence from one pin to the next without any fluctuations. Please let the LED/resistor remain connected so you can see the LED illuminate and turn off on each subsequent touch.
Good day Swagatam!
I have been troubleshooting the circuit for days on the breadboard. I tried increasing the capacitance on pin 14, removing the diode on the touch sensor, and such but the switching is still inconsistent and the led strips are flickering every after touch. It produces different sequence of outputs like after output 1 is output 3, in any random sequence. I know it’s not guaranteed to work properly on breadboard but is there a way to somehow make it work with the same schematic on breadboard? Cause i even checked for the voltage input of touch sensor with and without touch, it’s working properly. Even the voltages going through the ic are fine. Any advice you can give please? Thank you!
Hi Ryuchi,
To completely eliminate the switching bounce we may have to insert a 555 ic monostable between the pin14 of 4017 and the touch switch stage. I will draw the circuit and update it soon for you.
Thank you so much! Really appreciate it!
Ryuchi, Please build the following monostable circuit separately and check the response. You can reduce the C1 value to reduce the output ON time. I am sure the output of this circuit will correctly switch ON/OFF in response to the touches. Next, you can integrate the pin3 of this circuit with pin14 of IC4017
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/monostable-touch-switch.jpg
Thank you very much! Really appreciate it!
Hello again! I am now trying to build the circuit, i saw that the power supply of this circuit is 6V, should i use a LM317P voltage regulator to integrate it to pin 14? And the number 3 pin of the 555 timer should be connected to the pin 14 right? without the LED and resistor? If i put the voltage regulator, how should i connect it between the 555 timer and the IC 4017? Also, just curious of the capacitor values, what the difference of using the 10nf and 10uf on the circuit? Just wanna know how it works, Thank you!
Sure, you can try it, but please confirm the working of the 555 monostable circuit separately first. On each touch the LED should light up for a second and then shut off.
6V is not required, no 317 IC is required. You can use a common 12V for both the circuits, 4017 and the 555 both can work with 12V.
Yes pin#3 of IC 555 can be directly connected to pin#14 of IC 4017.
You can keep the LED also connected with pin#3 of 555 which will indicate the working each time the touch plate is touched.
The 10nF ensures the 555 is not affected by spurious stray RF disturbances. 10uF decides for how long the output (LED) stays ON when the touch plate is touched. The output ON delay can be adjusted by adjusting the C1, R2 values of the IC 555 circuit
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/monostable-touch-switch.jpg
Just want to clarify, this ic 555 will eliminate the circuit of the two bc557 transistors right? If so, will a part of a circuit from the ic 555 be also connected to the vcc(just like the emitter of the bc557 from the original circuit) of the ic 4017, or just the pin14? And what should i expect for the indicator to happen because now i tried the 555 timer circuit with just a wrong capacitor since i only have 1uF here, and after i connect the supply, and touch once, it just keeps “On” (I used led strips as the indicator). Should i expect the indicator to turn off through some seconds or touch? Or it will keep turning on until the supply is removed? Sorry for lots of questions if I’m bothering you and also thank you for still answering my questions 🙂
Yes, the BC557 stage can be removed and replaced by the 555 circuit. The 555 circuit will share the same 12V supply which is used for the 4017 circuit.
The LED should turn ON momentarily and then turn OFF. If it stays ON that means something is wrong with your circuit for the IC.
Thanks! The 555 monostable circuit is working even though i used 1uF capacitors as a tester for the circuit but it gradually smells burning(capacitor) ahahah. Last question, should i still use the same value capacitors in the 555 circuit diagram even though the supply changes from 6V to 12V? Really thank you for your response!
In the following diagram, C1 value decides how long the LED stays ON before switching OFF. Please adjust the value so that the LED stays ON for half a second and then switches OFF, until again the touch switch is touched.
For 12V supply make sure the capacitor voltage ratings are minimum 25V and the LED resistor is 1K.
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/monostable-touch-switch.jpg
Thanks! So it will be the same capacitor values right? Which is better to use for this circuit, ceramic or electrolytic capacitor?
C1 is electrolytic, you will have to experiment with the C1 value, as explained in my previous comment.
C2 can be ceramic.
Hi Swagatam! I already made the circuit work! Thanks a lot! Just kind of curious what is the purpose of capacitor connected from pin 15 to pin 16 and the capacitor connected in parallel with the 1M resistor? Thank you!
That’s great Ryuchi, Glad it is working now.
The capacitor across the positive and pin#15 ensures that whenever power is switched ON, the voltage momentarily enters through the capacitor and resets the IC through pin#15. This ensures that the output always starts from pin#3 and not from any other random output pin.
The capacitor at pin#14 ensures the pin#14 is not activated any spurious signal, rather only through a genuine positive signal. It also filters the pulsating signal generated by the touch sensor.
Hi again Swagatam!
Just wanna ask about which is a good conducting wire to use as a touch sensor for the lamp because the switching of light output in every touch is inconsistent. Sometimes it switches and sometimes not. Mostly, the counter counts so fast especially when u lean your finger on the touch sensor. How can i make it consistently switching through every touch without leaning the press of my finger just to switch its output?
Also, as i checked the output of every brightness i noticed that the brightest has 10.4V something as an output then the next ones only has 7V something as an output which doesn’t produce much light as to compared to the theory. Should i replace some resistors connected to the output so I can adjust its output? Thanks!
Hi Ryuchi,
I have tested this touch sensor circuit and for me it working perfectly, and the output relay switched ON/OFF with every touch.
So inconsistent switching must not happen.
I hope you have connected all the parts exactly as shown in the last diagram correctly, and you are using a regulated 12V DC as the supply.
The sensor can be any 1 inch copper wire with an open conductive end where the touch is made.
You can try increasing the pin#14 capacitor to 2.2uF or 4.7uF and check the response.
If you wish to have an extremely accurate response without any bounce then you may have to include a monostable 555 circuit at pin#14 of the 4017 IC.
As far as the brightness of the LEDs is concerned it will solely depend on the base resistor of the transistors. You can adjust the values of the transistor base resistors and adjust the LED brightness accordingly.
May i ask what size of the wire(AWG) would you recommend? Because now im using breadboard not a pcb, should the wire fits perfectly through the hole of the breadboard? Cause that’s where i get the inconsistency of the touch. Thank you for answering again my questions. Really appreciate it!
I think on a breadboard the circuit might not work correctly, you must build the circuit on a strip board by soldering, only then expect it to work correctly, because each and every connection should be 100% perfect which cannot be guaranteed on a breadboard.
I tried to replace the maximum brightness output into 390ohm resistor and it’s producing at 11.30V something. Then i replaced the second output with a 390ohm also it now outputs 9V then the third one i didnt replace anything. Am i on the right track? Thanks!
You have to adjust only the base resistors of the 2N2222 transistors.
Yes ive adjusted the base resistors ?
Good day Sir!
I already build the circuit but i can’t make the switching of brightness work. I’ve tried to use the diode and an open wire as a sensor but it doesn’t work no matter how many times i repeat it. I also tried some simple sensor circuits online to replace the touch sensor but it still didn’t work. Im not sure if the sensor circuit is the problem or the logic of the ic. Please help me to troubleshoot the problem. if in case the problem is the ic, how should i troubleshoot it to function its switching. Thank you.
Hi Ryuchi,
Are the outputs of the 4017 switching sequentially from pin3 to pin4? Please connect LED with 1k series resistor parallel to the 1uF capacitors (after the 1N4148 diodes) to check whether the outputs are sequencing or not.
Let me know about this.
I used 12V LED strips for the outputs so I don’t need to use resistors. Do i need to modify something on the circuit if i use led strips?
Yes, in that case no need of using series resistors. I hope you are using the last circuit.
Yes im using the last circuit not the current controlled. Im using 3 2n2222 transistors as the transistors for the output also
The outputs are not switching, it stays on default
remove the BC557 transistors and connect the pin#14 intermittently to positive via a push button switch or manually, and check whether the outputs are sequencing or not.
Should i connect the positive side of the switch to the 12V?
Take a push button, connect its one terminal with pin14, and the other terminal with the positive of the. circuit. Pressing this switch alternately should cause the outputs to sequence from one to the next..
I tried it but it also didn’t work. Still the same circuit right?
That means your basic IC 4017 circuit is not working, which could be due to a faulty IC or some other connection fault.
The basic 4017 touch switch is a tested design you can find the article in the below given link. You will have to investigate the connections or try it with a new IC. Yes, all the 4017 touch switch circuits are based on the same principle.
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/simple-touch-sensor-switch-circuit/
Good day! Just wanna ask and curious, if i use 2n2222 as the transistor for all the outputs, what would be the difference? Can i still make the brightness given on this article? And what resistor value can i use for both the led and transistor base if incase i only use this transistor? Thanks!
Yes you can use 2N2222 for all the transistors and implement the brightness control.
For the base resistor, you can use the formua which I suggested previously:
R = [Collector V – (LED total forward V + 0.6)] x hFE / LED Current. hFe can be taken as 100
Once you get this, you can assume this resistor as R1, and assume the ground side resistor as R2, and then find the R2 value using any online “resistive divider software”.
If you don’t want the above resistve divider hassle, then you can replace the the ground side resistors with calculated zener diodes. This zener diode values will determine the output voltages, which can be reduced or increased for adjusting the brightness or dimming on the LEDs.
So for the LED voltage and LED current I should base it on the datasheet right? So if i use the same formula for all of the transistors, how would i know the difference between the resistors for every output brightness knowing that i use the same hfe and collector voltage? And also, one thing that i notice on the original circuit, why does the maximum brightness has the largest resistance value compared to the dimmable ones, the current output on the emitter will dictate the brightness right? Please correct me if im wrong. Thanks
Yes, thee LED specification will be as per your preference which can be referred from its datasheets.
The resistors that are connected from base to ground determine and fix the base voltage for the transistors, which is then replicated or followed at the emitters of the transistors and the across the LEDs.
You can adjust the values of these ground resistors to vary the emitter voltage and in turn the brightness of the LEDs.
Alternatively you can replace these resistors with zener diodes of different values to adjust the base voltage and the emitter voltage to change the LED brightness accordingly.
All the base resistors have same values in the above circuit, they are all 10K.
The ground resistors are the ones which cause the voltage to change for the LEDs. Lower value ground resistors cause lower voltage across the LEDs and vice versa.
Here we vary the voltage to the LEDs to change their brightness, not the current.
Thanks for the response! So R2 will be paralleled to R1 right? How would i know based on the results that my brightness is dimming? The current should decrease every solution right? But if i use the normal formulas of getting the current of the transistors what happen is that the brightest one got the lowest current and the dimmest has the largest current. May you please tell me the right formula to use for checking the current if each transistor for brightness? Thank you!
R2 is not parallel to R1, R2 is between the base of the transistors and ground. Please refer o the above diagram, the 10K resistors are R1, and the 56k and 33k are the R2 resistors.
If you want to dim the LEDs using current control, you can use the following diagram:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/dimmable-LED-lamp-circuit.jpg
You can adjust the brightness of the LEDs simply by increasing or decreasing the base resistor values.
The formula for calculating and adjusting the LED current is:
R = (Supply Voltage – 0.7)hFE / LED Current
Really thanks for giving me the response! I really appreciate it, sorry if i have lots of question. I just really want to grasp the concept of designing this circuit 🙂 Thanks!
You are most welcome Ryuchi, glad I could help.
You can also find some more information in the article, I updated it recently.
Good day again! Just curious, what type of capacitive sensor can i use aside from an open wire as a sensor which i can install without modifying the circuit. Thanks!
It is not a capacitive sensor, it is a touch sensor. You can use any metallic thing at the sensor point. It can be a stripped wire, a plate, a pad, anything conductive.
Thanks! Another question, is that sensor point installed in the PCB? Or just connected at the end of the 1n4148 diode? The metallic thing or stranded wire is just an extension for the touch point right? Cause i bought a lamp and in the PCB there is an indicated touch point and the touch point is just extended by means of a wire. Please correct me if im wrong.
Then for the individual LED, are those connected in parallel or series? Cause i assume since every row has 82 ohm resistor at the end, every row are connected in series and all of them are in parallel. So does it mean that they all have same voltage but different current? Also, Will they all turn on in every output of the transistor? Or some will stay on and some will turn off? Sorry for lots of question, just really confused cause they asked me for calculations. Thanks in advance!
The sensor point is terminated at the free end of the 1N4148. This free end of the 1n4148 can be soldered on an empty pad on the PCB so that it is connected securely on the PCB. The extended wire from the 1n4148 end must not be too long, not more than a few inches.
The LEDs are connected in series and parallel as shown in the diagram.
All the LED strings have identical current and voltage specifications and will illuminate together when each of the transistors are activated.
Yes they will run from every output of the transistors.
Each transistor is configured to generate a slightly lower or higher voltage sequentially, causing the LED to brighten up or become dimmer accordingly.
Thank you very much! Really appreciate it!
You are welcome Ryuchi!
Hi again Swagatam! Just wondering, How do you compute the current going from the collector to the emitter (Icq) for each transistor? And the voltage output (Vce) of each transistor? Cause when I try to solve it, it looks like all the Vce are the same since Vbe is 0.7? Are the base resistor really affect the voltage and current output of the transistor to the LED? Please enlighten me thank you! And if i get any answers, how would i know that im on the right track based on the datasheet?
Hi Ryuchi,
The base resistor is basically employed to control the collector/emitter current. However, once connected the base will always show 0.7V due to its internal base/emitter drop.
According to me the following formula can be used for calculating the base resistor for an emitter follower configuration.
R = [Collector Voltage – (emitter voltage + 0.7)] x hFE / Load current
For a collector load, you can refer to the following example article, which explains how to calculate the base resistor depending on the collector load:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/how-to-make-relay-driver-stage-in/
Thank you for your response, really appreciate it! If incase I still have questions, I will reach you out.
No problem Ryuchi, please feel free to ask as many questions as you want to.
Hi again! For the collector and emitter voltage, will those be the same voltage? Because there is no resistance in either collector or the emitter within the transistor except that emitter is connected to the led. Also with computing the current (collector) im kind of confused because of no resistor on the collector. And uhm, is building and relay driver a requirement for this circuit? Sorry for the multiple questions, just kinda used this concept as a beginner project for electronics that’s why i have lots of questions if you don’t mind. am really a beginner at electronics. Thank u in advance for the response.
The collector voltage will be the direct supply DC input, for example a 12V DC as shown in the above article. The emitter voltage will be the voltage that’s intended for the emitter load.
For example let’s say you want a single LED on the emitter side and require the emitter voltage to be 3.3V, then this becomes your required emitter voltage.
This emitter voltage can be set by setting the base voltage to an identical amount or maybe 0.6V higher than the recurred emitter voltage to compensate for the 0.6V base/emitter internal drop.
No worries, you can ask more questions, I will try to solve them.
So for the base to emitter voltage of the transistor, it can exceed more than 0.7V voltage to compensate for the voltage coming from the collector right? I already saw the datasheets between the transistors you used, for the current from collector to the emitter, how can i solve it without exceeding the values on the datasheet? Cause if i solve it without considering the datasheet, the base resistor on the 2n2222 is larger than the bc547, so the output on 2n2222 is much lesser. Please correct me if im wrong. Thanks
At the moment we are talking about an emitter-follower configuration, in which a load is used between emitter and the ground. In this situation the base voltage must be 0.6V higher than voltage required for the emitter load. For example if the emitter load requires 9V, then the voltage across base and ground must be set to 9.6V, this will enable a 9V to appear across the emitter load.
In this situation if you measure the emitter/ground voltage it will show 9.6V.
However if the load is on the collector side of the transistor and the emitter is directly connected to ground then the base/emitter will always show 0.6 or 0.7V no matter how much voltage is applied to the base (through a resistor).
This is because the base/emitter internal drop will always force the base voltage to get restricted to 0.7V.
If you use the formulas correctly which I suggested you in the previous comment, then your transistor will be safe and will never exceed the recommended current rating.
Hi again swagatam! I still can’t solve the proper current and voltage output for every transistor, I tried to go with every tutorial and they all have resistor on the collector to limit the current and lessen the voltage output of the transistor. I also tried to use every maximum rating of each component from the data sheet to ensure that the components are still safe for a sudden large increase of input but i still find the results not satisfactory. I still cant get the 11V, 10V, and 9V that are expected for the circuit. For this schematic, what will happen to the output voltage and current if i put a resistor on each collector of the transistor? Sorry for the troublesome questions, im still struggling. Thanks in advance for the answer!
Hi Ryuchi,
As I explained earlier the transistors in the above circuit are configured as emitter-follower voltage regulators, which are supposed to supply a regulated voltage to an emitter load.
In such configuration we want the full collector current to reach the emitter load. Connecting a collector resistor will completely defeat the purpose of an emitter follower regulator circuit.
If you connect a collector resistor your LEDs will not illuminate brightly.
Good day! I would like to ask about the LEDs used in the circuit, are those individual LEDs connected in series per row? Incase, instead of using individual LEDs, is it possible to use LED strips like 1 foot long which is about 12 LEDs? Would the resistor vary incase i use LED strips? Thanks
Hi, the shown LEDs are individual LEDs connected in series and parallel.
You can definitely replace those LEDs with a single LED strip which must be rated at 12V.
For strip LEDs the 82 ohms won’t be required, and the strip can be connected directly across the emitter of the transistors and ground.
The transistor base resistors may vary depending upon the current rating of the strips and the amount of dimming required between the steps.
Thanks for the response! but how do i choose a transistor to use in case i switched it into a normal 12V 1A LED Strips? I don’t know how to choose proper component since i am a beginner at electronics.
Every transistor will have a maximum tolerable current handling capacity. It is represented by the symbol IC which indicates the maximum collector current of the transistor. Here we are talking of BJT transistors (Bipolar Junction Transistor) as indicated in the diagram above. In the transistor datasheet if you look for “Collector Current − Continuous” that will give you a clear idea regarding the max current handling capacity of the transistor. Similarly, the parameter VCEO (Collector − Emitter Voltage) provides the max voltage handling capacity of the transistor.
For 1 amp current you can use TIP31 transistor which has a max collector current of 3 amp.
So in estimate, the circuit can only produce like 1A of current due to how small the current is passing through the components right? then for the transistors, is it the same computation even for pnp and npn transistors? Really thanks for providing informative answer!
The IC will produce only around 10 ma for the transistors but the transistor can amplify the current to any feasible extent. The degree of amplification simply depends on the gain of the transistors.
Whether NPN or PNP both are capable of amplifying the voltage and current to any level depending on their gain.
Yes, the formula is the same for both types of transistors.
Why is it negligible, is it because of how small the current is going through the Ic? By any chance how can I compute the current of the base resistors if the transistors? Thanks!
It is negligible compared to the LED current. The IC will consume around 10 mA.
The base resistor can be calculated using the following formula:
R = [Collector voltage – (0.6 + Total LED Forward Voltage)] x transistor hFE / LED current
The base/ground resistor will need to be calculated using resistive divider formula depending on how much max voltage the LED require.
Good day! I would like to ask what is the current of the whole circuit? And for the current passing through each component, how are those being calculated? Just needed in research thanks!
Hi, the current is mainly consumed by the LEDs, the current consumed by the 4017 IC is negligible. The base resistors of the transistors and the LED series resistors determine how much current the LEDs can consume.
Good day! Just wanna ask if this circuit is battery powered or outlet powered? If outlet powered, what additional component can be used in order to convert AC voltage to DC Voltage
Hi, it can be both, battery powered or outlet powered.
For outlet power, you can use any ordinary 12V, 1 amp smps adapter.
If incase i want it to be usb powered like usb to laptop or usb to a charger head cause usually usb connector has a maximum voltage of 5V, is it possible to step down the voltage of the circuit without affecting its real functionality as a 12V circuit?
The circuit can work with 5 v also, however with a 5 v only one LED can be used on each LED string. To increase the brightness you can use 1 watt LEDs, meaning total 3nos of 1 watt LEDs across the 3 transistor emitters.
Also you will need to replace the 82 ohms resistors with 10 ohm 1 watt resistors.
For the transistors you will need to use TIP122 transistors.
Alright thanks a lot! Appreciate it have a good day!
Hello again Sir! Just wanna ask how does this circuit convert ac voltage from the outlet into dc since LED is applicable for DC voltages? And for the touch sensor, is the sensor only a piece of copper wiring connected to the diode and transistor? is it possible to install a touch pad sensor on it? if so, what touch pad controllers are applicable? thank you!
Hello Ryuchi, the above circuit will not convert AC to DC from the outlet, rather you will have to use an AC to DC 12v adapter to provide the required 12V DC power to the circuit…Any metal piece can work as the touch sensor…even a small piece of open wire will also do.
Also boss “swag” I can I use the input stageof this circuit given..as the input of led dimmer circuit using same CD4017 ic but having a transistor at the output??without issues.thanks hoping to get a reply from you much love????
Yes you can use the circuit as it is shown in the diagram.
hi swag..I need a circuit touch dimmable circuit just like this above.but can Run. on 5v DC supply.I want to power a 1 watt 5v led lamp with it.thanks
Hi Joseph, you can use the same circuit which is shown above with a 5V supply and 5V LED lamps, it will still work.
So there won’t be modification and will it still be dimmable??
Also can i use a piezo sensor as the touch pad?
Yes it will still dimmable.
Piezo sensor will not work, since the touch needs to be direct finger touch
How Can i modify it to work with piezo??
Thanks
You can connect the piezo between base and ground, and a 1K resistor across base and positive of the BC557 transistor.
Hello boss ,over here..i couldn’t get bd679 or any equivalent transistor..
Can u suggest any other transistor i can use in place of it??
Hello Joseph,
The transistor numbers are not critical at all, you can try any other equivalents. You can try BD139 or TIP122 instead of the BD679….
alright boss thanks for your help I really appreciate.if I encounter any difficulty or issues,I’ll reach out to you.
No problem Joseph, you are always most welcome.
Hello boss i made the circuit.but i used a 13003 transistor in place of bd679.
When powered..the out put was low that is.the led wasn’t bright..what could be the problem and please suggest a solution
Hello Joseph, 13003 is not recommended, use 2N2222 instead you will get higher brightness.
Hi Swagatam,
I am working on a circuit that uses two 4017 which work together. The first one is driven by a 555 and rotates through the sequence and then the second 4017 gets its clock from pin 12 of the first 4017. The second 4017 drives npn transistors tocfd grounds columns of LEDs that are driven by the first 4017. The problem is the 4017 can’t drive several LEDs due to current overload. Therefor I want to drive npn transistors with the first 4017 to power a string of LEDs similar to your circuit above. With my lack of knowledge, I have never quite Understood how to power circuits with npn transistors. I know I can use a transistor pair( npn grounding pnp to supply a circuit but that uses more components and takes up extra space on the PCB. If you could please comment and elaborate to enlighten me with the proper way to drive a LED circuit with npn transistors on the high side, I would much appreciate it
Hi Norman,
For an NPN transistor, its base receives the switching signal through a resistor. The LEDs are supposed to be connected across the positive supply and the collector through a calculated resistor. The emitter is supposed to be connected directly to the ground supply. This is the basic set up that you need you implement for an NPN transistor.
You can check out the following examples:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/rotating-led-chakra-circuit-for-god-idols/
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/single-push-10-step-selector-switch/
What’s the max amount of LEDs per row?
As shown in the diagram.
15? What if need more than 15? Changing the serial resisters to LEDs is enough?
Thanks!
You can add more LEDs in parallel with individual series resistor. But if the there are too many of them then the transistor and their base resistor will also need to be modified.
Very smart and updating electronic devices and circuits. Thanks alot
Sir ,thanks a lot for this circuit , I made it and it worked well with 12v battery but when I use 12 v adapter it loses touch l.e touch does not work at all.Kindly guide me.
Bharat, try this: Connect a diode at each of the outputs of the 4017 IC such that their anode is connected to the IC output pin and the cathode is connected to the transistor base resistor.
After this, connect a 1uF between the cathode and ground of each diode.
Also try replacing the 1uF at pin14 with a 10uF.
Additionally make sure that your adapter has a high value filter capacitor in the order of 2200uF
Hi, one more question.
I have added a p-mosfet before the circuit, between the v= of the battery, and the Vcc main power line of the circuit. So that the battery stays disconnected and doesn’t drain until I am ready to use it.
The gate is connected to the source of the mosfet with a 470k resistor. I would expect the Vgs to be 0v until I pull it down with an extra transistor and an ‘on’ signal. However, without doing anything, the Vgs seems to settle at -0.3v
https://ibb.co/0ts16qs
here is the circuit. any idea what is causing the leakage? or is it a high frequency on/off oscillation? And how do I fix it?
much appreciated!
Hi, the image shows an N channel MOSFET?
But the N channel looks correct, so the diagram has no problems….I think you can try changing the MOSFET or try a BJT instead.
the n channel mosfet is the one that pulls down the gate of the p-channel mosfet (i incorrectly wrote that a transistor pulls down the gate)
so the top chip, with 8 pins, is the p-channel mosfet (dmp2022)that is giving me the problems…
Hi, never mind – I finally fixed it. The really confusing part was that I was still getting the Vgs voltage drop even when everything else was removed. i.e. leaving just the input voltage Vbatt, the resistor across G-S, and the p mosfet…
I don’t know if I fully understand why, but I think when the resistor across G-S gets very large, the own internal capacitance of the mosfet can cause a small current pulse into the resistor and cause a voltage that turns on the mosfet. I assume with 470k it was oscillating to a steady state Vgs of -.3, and with 100k to a Vgs of -0.05v. with 24k I couldn’t measure a Vgs, but the output still had .02 and was passing an initial peak that latched Vcc With 1k everything works perfect! I will try 5 or 10k tomorrow, just to reduce power loss a bit when on. But otherwise, I will live with the 1k.
Yes that was the exact problem, glad it is solved now…
you can replace 470k with 10k and check the results.
for the N channel also, you can replace the 470k with 10k, and R98 with 100 ohms
Hi can we use IR remote sensor instead of touch sensor
for IR remote you will have to modify the IC 4017 in the following manner:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/how-to-make-simple-infra-red-remote/
Hi, one further question: in my case, I put the lowest power LED level on pin3. Now I want to use a comparator so that in a particular situation, the comparator (an lm358, since I am using those already) would reset the counter & keep it in reset mode. Effectively, from then on, resetting any other power modes, and only allowing the low power light mode.
Can I run the output from the lm358 directly to the pin 15? Or would this cause problems with the reset function of pin 7? I can imagine since the output of the lm358 is either active on, or active grounded, the active grounded condition would keep the pin 7 from resetting the counter. Would a simple diode on the output of the lm358 be sufficient to prevent the grounding?
Hi, yes that will work.
You can use a diode at the op amp output and connect its cathode to pin#15 of IC 4017, for the intended results!
Hi, I am looking for a touch sensor that will work underwater. (to add in front of a dimming circuit such as this one.) So far, the most promising seems to be am infrared touch sensor, though a small window. when you cover the small window with a finger, it pulses the dimming circuit above. do you have any advice on particular infrared emitters or detectors to use? or a filtering circuit to eliminate stray reflected light from the lens or small particles in the water? or is there a better touch sensor method you can think of?
Thanks, & compliments on a great website!
Hi, you can try the following arrangement, hopefully this should fulfill your requirement:
Thanks for the quick response on a Sunday! And thanks for the circuit suggestion.
So do you think an infrared sensor is the best way to go here, or is there another technology better suited?
For the filtering of the IR sensor, I had thought to use a basic lm358 circuit, using a potentiometer to set the comparison voltage high enough such that anything below 40% or 50% relative collector current gets filtered out. And feeding the output of the lm358 directly into the pin 14 of the 4017. Is the circuit with the double 557 transistors more stable? Would I replace the 10k resistor with a potentiometer to change the sensitivity?
With the LM358, I had also thought to add a capacitor in parallel with the sensor resistor, so that the greater than 50% collector current needs to flow for at least half a second before it would switch the count up. (in order to filter out something else floating by briefly, or a brief brush against the arm or leg.) where would I place the capacitor with the double 557 circuit?
You are welcome!
Since it is an underwater application, infrared will suit better.
Sensitivity of the circuit suggested cannot be changed, since it is configured as a digital output
If you want to control the sensitivity of your optocoupler output then your op amp idea will be more appropriate.
More information regarding optocoupler interfacing can be learned from the following article:
Optocouplers – Working, Characteristics, Interfacing, Application Circuits
The capacitor could be placed at the input LED side. Two resistors could be connected in series with the LED positive line, and a suitably rated capacitor connected between the junction the resistors, and the negative line or the LED cathode line.
Hi, I think this circuit is close to what I am looking for.
I need to cycle between three states as the touch point is activated – Off – Red, Warm White, Bright White – Off. Using three separate Single Color LED strips
Do you have any suggestions for this modification, or an alternative using a single RGB strip?
Hi, you can use the same circuit, with a few modifications:
remove the 56k, 33k resistors.
remove the LEDs from the emitter side, and connect the strings in series with the collectors of the transistors.
Connect the emitters with the ground line directly.
Really nice article and very informative, thank you for the time and effort for explaining everything!