The circuits I have explained here are 10 best small timer circuits using the versatile chip IC 555, which generates predetermined time intervals in response to momentary input triggers.
The time intervals can be used for keeping a relay controlled load ON or activated for the desired amount of time and an automatic switch OFF once the delay period has elapsed. The time interval can be set by selecting appropriate values for an external resistor, capacitor network.
IC 555 Internal Circuitry
The image shown below represents the internal schematic of a standard IC 555. We can see that it us made up of 21 transistors, 4 diodes, and 15 resistors.
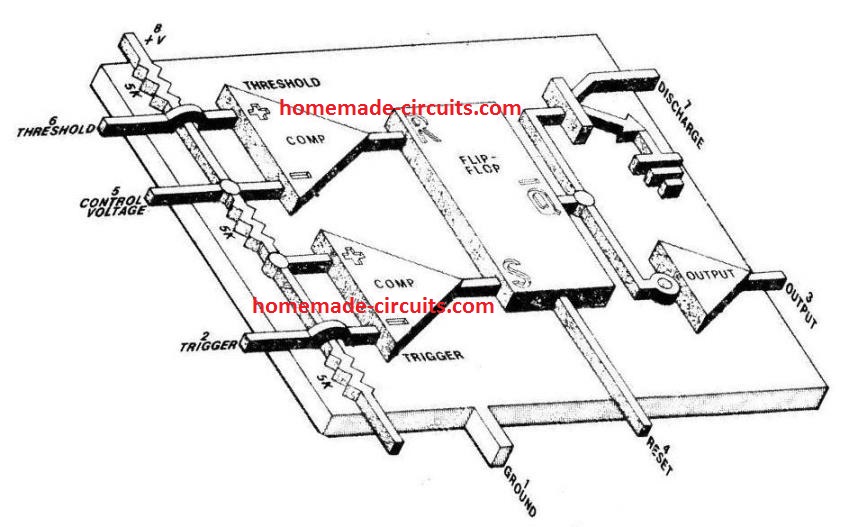
The stage involving the three 5 kohm resistors work like a voltage divider stage which produces 1/3rd voltage level at the non-inverting input of the trigger comparator op amp and a 2/3 voltage division on the inverting input of the threshold comparator op amp.
With these trigger inputs the two op amps control the R/S (reset/set) flip flop stage, which further control the ON/OFF conditions of the complementary output stage and the driver transistor Q6
The output state of the flip flop can be also set by triggering the reset pin 4 of the IC.
How IC 555 Timers Work
When IC 555 is configured in the monostable timer mode, the TRIGGER pin 2 is held at the supply level potential through an external resistor RT.
In this situation, Q6 remains saturated, which keeps the external timing capacitor CD shorted to ground, causing the OUTPUT pin 3 is to be at a low logic or 0 V level.
The standard Timer action of the IC 555 is initiated by introducing a 0 V trigger pulse at pin 2. This 0V pulse being below the 1/3rd level of the DC supply voltage or the Vcc, forces the output of the trigger comparator to change state.
Due to this, the R/S flip-flop also changes its output state, turning off Q6 and driving OUTPUT pin 3 high. With Q6 switching OFF disconnects the short across CD.
This allows the capacitor CD to charge via the timing resistor RD until the voltage across CD reaches 2/3rd supply level or Vcc.
As soon as this happens the R/S flip flop reverts to its previous state, switching ON Q6 and causing a quick discharge of CD. At this instant the output pin 3 returns back to its earlier low state yet again.
And this is how the IC 555 completes a timing cycle.
As per one of the characteristics the IC, once triggered it stops responding to any subsequent triggers, until the timing cycle is completed.
But if one wants to terminate the timing cycle, this can be done at any moment by applying a negative pulse or 0 V to the rest pin 4.
The timing pulse generated at the IC output is mostly in the form of a rectangular wave whose time interval is defined by the magnitudes of R and C.
The formula for calculating this is: tD (time delay) = 1.1 (value of R x value of C) In other words the timing interval produced by IC 555 is directly proportional to the product of R and C.
The following graph shows the plotting of time delay vs. resistance, and capacitance using the above the time delay formula. Here tD is in milliseconds, R is in kilo Ω , and C in μfarads.
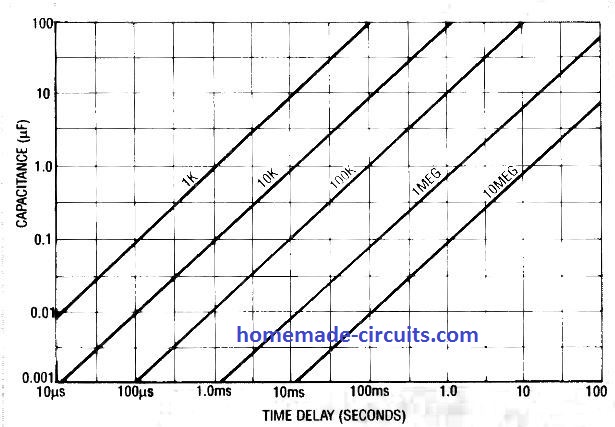
It shows a range of time delay curves and the linearly changing values with respect to the corresponding values of RT and C.
It is possible to set delays ranging from 10 µseconds to 100 µseconds by selecting appropriate values of capacitors from 0.001 µF to 100 µF and resistors from 1 k Ω to 10 meg Ω .
Simple IC 555 Timer Circuits
The first figure below shows how to make a IC 555 timer having a fixed period output. Here it is set to 50 seconds.
It is basically an IC 555 monostable design.
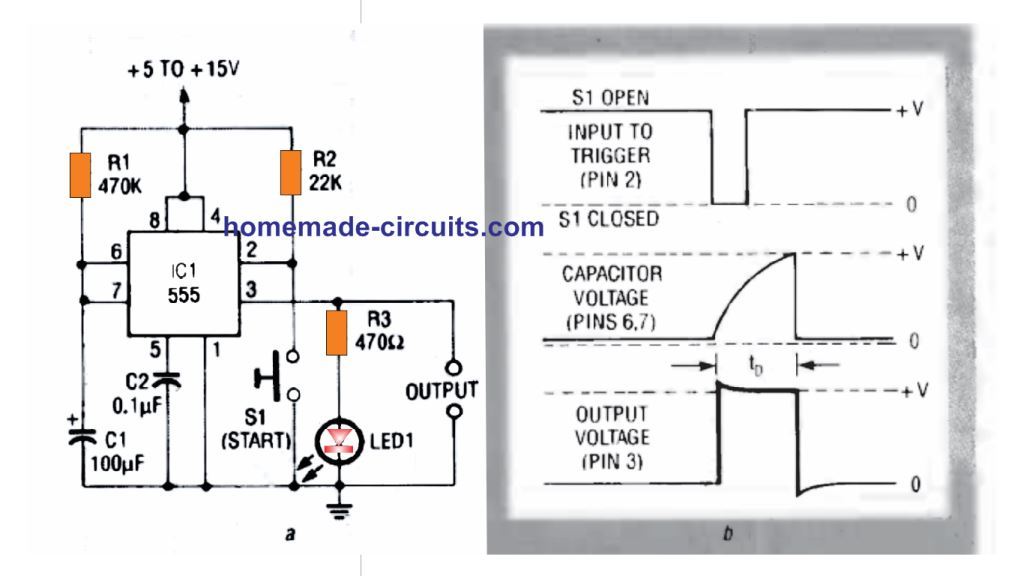
The adjoining figure shows the waveforms obtained across the indicated pinouts of the IC during the switching process.
The actions as described in the waveform image initiates as soon as the TRIGGER pin 2 is grounded with the pressing of momentary START Switch S1.
This instantly causes a rectangular pulse to appear at pin 3 and simultaneously generates an exponential sawtooth at DISCHARGE pin 7.
The time period for which this rectangular pulse remains active is determined by the values of R1, and C1. If R1 is replaced with a variable resistor, this output timing could be set as per user preference.
The LED illumination indicates the ON and OFF switching of the output pin 3 of the IC
The variable resistor can be in the form of a potentiometer as shown in the following figure 2.
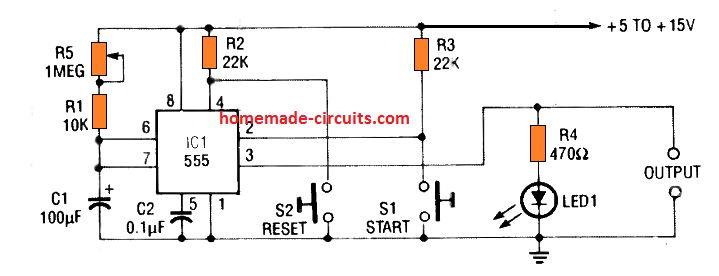
In this design the output can set to produce time periods from 1.1 seconds to 120 seconds through different adjustments of the pot R1.
Notice the series 10K resistor which is very important since it safeguards the IC from burning in case the pot is turned to its lowest value.
The 10 K series resistor also ensures the minimum resistance value required for the correct working of the circuit at the minimum pot setting.
Pressing the switch S1 momentarily enables the IC to start the timing sequence (pin 3 going high and LED turning ON), while pressing S2 reset button allows instant termination or resetting of the timing sequence so that the output pin 3 reverts to its original 0 V situation (LED turning OFF permanently)
The IC 555 allows the use of loads with maximum current specifications of up to 200 mA.
Although these loads are normally non-inductive types, an inductive load like a relay can be also effectively used directly across pin 3 and ground as shown in the following diagrams.
The 3rd figure below we can see that the relay can be wired across pin 3 and ground, and, pin 3 and positive.
Notice the freewheeling diode connected across the relay coil, it is highly recommended for neutralizing the dangerous back emfs from the relay coil during switch OFF instants.
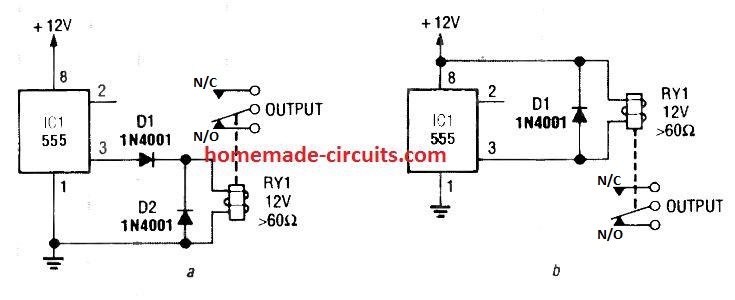
The relay contacts can be wired with an intended load for switching them ON/OFF in response to the set time intervals.
The 4rth circuit diagram shows the standard IC 555 adjustable timer circuit having two sets of timing ranges and an output relay for toggling the desired load.
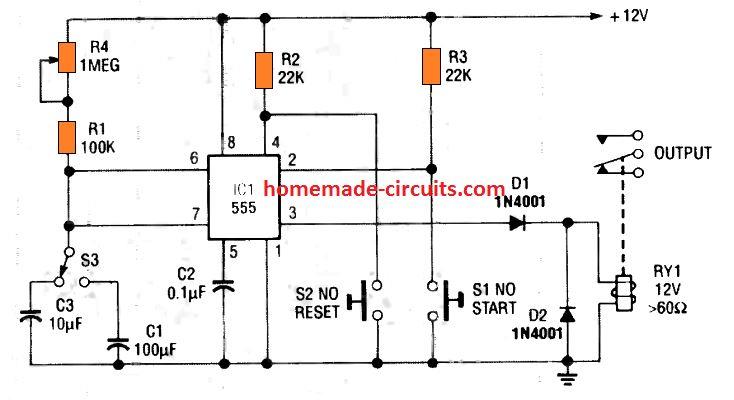
Although the schematic looks correct, this basic circuit may actually have a few negative aspects.
- First, this design will drain some current continuously, even while the output of the circuit is in the off state.
- Second, since the two capacitors C1, and C3 have a wide tolerance specs, the pot neds to be calibrated with two individual set up scales.
The above discussed flaws can be actually overcome, by configuring the circuit in the following manner. Here we use a DPDT relay for the procedures.
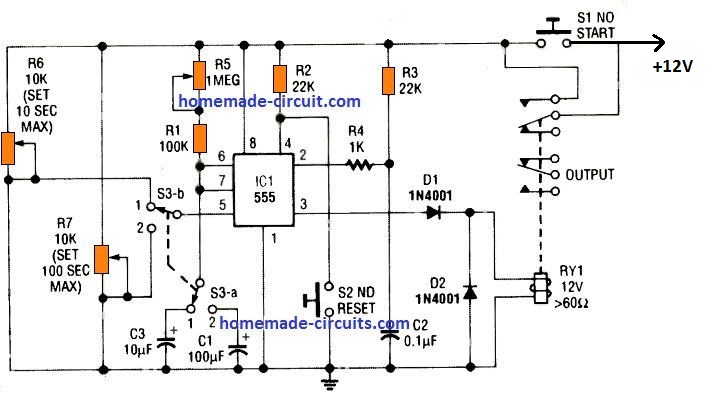
In this 5th IC 555 timer diagram we can see that the relay contacts are joined in parallel with the START switch S1, which are both in the "normally-open" mode, and ensures there's no current drain while the circuit is OFF.
To initiate the timing cycle, S1 is pressed momentarily.
This instantly powers the IC 555. At the onset, C2 can be expected to be fully discharged. Due to this, a negative switch ON trigger is created at pin 2 of the IC, which initiates the timing cycle, and the relay RY1 switches ON.
The relay contacts which are connected in parallel with S1 enables the IC 555 to remain powered even after S2 is released.
When the set time period elapses, the relay is deactivated and its contacts revert to the N/C position disconnecting power from the entire circuit.
The timing delay output of the circuit is basically determined by R1 and potentiometer R5 values, along with the values of either C1 or C2, and depending on the position of the selector switch S3 a.
Having said this, we must also note that the timing is additionally affected by how the potentiometers R6 and R7 are adjusted.
They are switched through the switch S3 b and integrated with the CONTROL voltage pin 5 of the IC.
These potentiometers are introduced to effectively shunt the internal voltage of the IC 555, which might otherwise disturb the output timing of the system.
Due to this enhancement the circuit is now able to function with utmost accuracy even with capacitors having inconsistent tolerance levels.
Furthermore, the feature also allows the circuit to work with a solitary timing scale calibrated to read two individual timing ranges as per the positioning of the selector switch.
For setting up the above accurate IC 555 timer circuit, R5 must be initially adjusted to it maximum range. After this, S3 may be selected to position 1.
Next, adjust R6 to get a 10 second ON timing output scale with some trial and error. Follow the same procedures for the position 2 selection, through the pot R7 for getting an accurate scale of 100 seconds
Timers for car lights
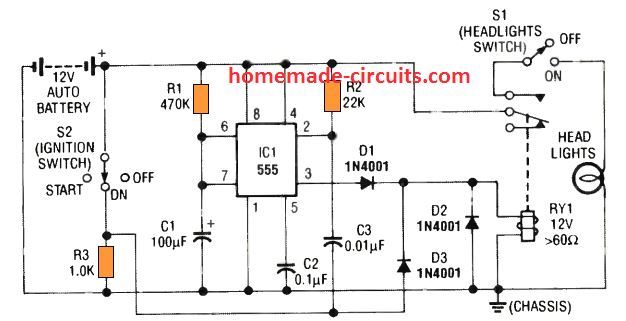
This 6th simple car headlight IC 555 based timer prevents the car headlights from shutting off as soon as the ignition is turned OFF.
Instead, the headlights are allowed to remain illuminated for some preset delay, once the driver locks the car ignition and walks off towards his destination which may be his home or office.
This allows the owner to see the path and enter the destination comfortably with visible illumination from the headlights.
Subsequently, when the delay period elapses the IC 555 circuit switches off the headlights.
How it Works
When the ignition switch S2 is turned ON, the relay RY1 energizes via D3. The relay enables the headlight operations via the upper relay contacts and the switch S1, so that the headlights works normally through S1.
At this point the capacitor C3 associated with pin 2 of the IC remains completely discharged because both its leads are at the positive potential.
However, when the ignition switch S2 is turned OFF, the C3 capacitor is subjected to a ground potential via the relay coil, which suddenly causes a negative trigger to appear at pin 2.
This triggers ON the IC 555 output pin 3, and allows the relay to remain energized even though the ignition is switched OFF.
Depending on the values of the timing components R1 and C1, the relay stays energized keeping the headlights ON (for 50 seconds), until finally the time period elapses and pin 3 of the IC turns OFF de-energizing the relay and the lights.
The circuit does not create any interference with the usual functioning of the headlights while the car is running.
The next 7th timer circuit shown below is also a car headlight timer which is controlled manually instead of the ignition switch.
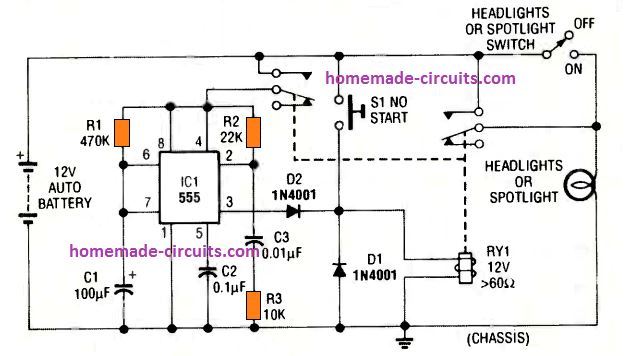
The circuit utilizes a DPDT relay having two sets of contacts. The IC 555 monostable action is initiated by pressing S1 momentarily. This energizes the relay, and both the contacts move upward and connect with the positive supply.
The right side pair of contacts activates the headlights, while the left side contacts power the IC 555 circuit.
The C3 causes a momentary negative pulse to appear at pin 2 which triggers the counting mode of the IC, and pin 3 becomes high latching ON the relay.
The headlights are now switched ON. Depending on the values of R1 and C1 the pin 3 output keeps the relay and the headlights energized (for 50 seconds in this case), until the C1 charges up to the 2/3rd Vcc, turning pin 3 low, and turning Off the relay and the headlights.
1 Minute Porch Light Timer
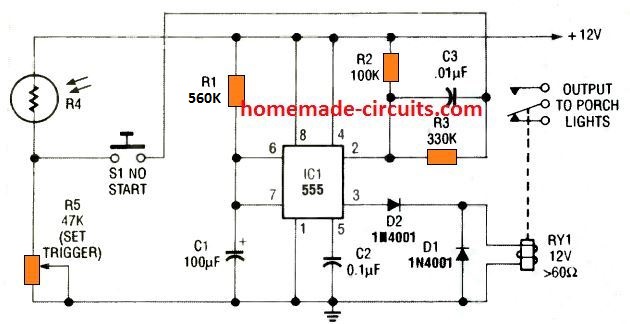
This 8th circuit shows simple porch light timer circuit that can be activated for a minute only during night time. During day time the LDR resistance becomes low which keeps its junction with R5 high.
Due to this, pressing S1 has no effect on pin 2 of the IC. However, when darkness falls, LDR resistance goes infinite, developing an nearly 0 V at the junction of R4 and R5.
In this condition when the switch S1 is pressed, causes a negative trigger at pin 2 of the IC 555, which activates pin 3 to high and also turns ON the relay. The porch light attached with the relay contacts illuminates.
The circuit stays triggered for around 1 minute, until C1 charges to the 2/3rd Vcc. The IC now resets to the turn pin 3 low and de-energizing the relay and switching OFF the porch light.
The switch S1 may be in the form of a small hidden switch near the door handle/hinge, or under the mat which activates when the owner steps on the mat.
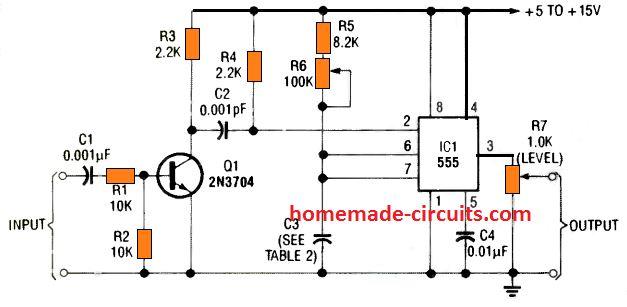
Tachometer Application
A monostable timer circuit using IC 555 can be also effectively implemented for making a tachometer circuit which will provide the user with accurate information regarding the frequency and engine timing.
The incoming frequency from the engine are first converted to well dimensioned square wave through an RC differentiator network and then fed to pin#2 of the monostable.
The differentiator network transforms the leading or trailing edges of the square wave signal into appropriate trigger pulses.
A 9 th practical circuit below shows how an RC network and a transistor converts any input signal with any amplitude into well formed square waves for generating ideal triggering pulses, switching between the full IC Vcc level and ground.
Mains AC Delay Timer
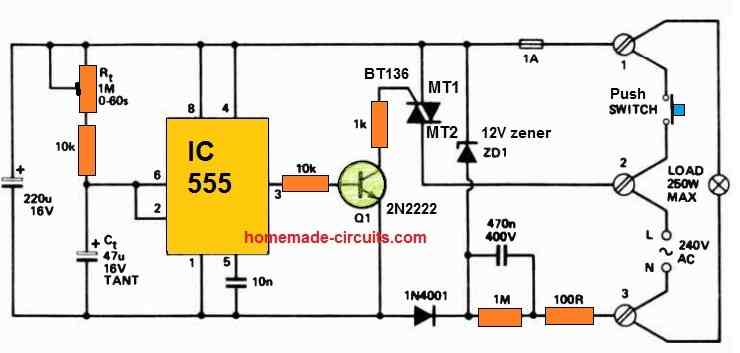
Perfect for an automatic corridor lighting timer, this IC 555 delay timer setup utilizes a momentary action push-button switch with mains rating.
When the switch is pressed, the timer initiates its operation, lasting for a duration precisely equal to 1.1 times the product of R1 and C1.
Once this time elapses, both the load and the entire circuit disconnect simultaneously from mains power.
Conclusion
In all of the circuits presented so far, the 555 functions as a monostable (one-shot) timing period generator. The required trigger signals are fed to TRIGGER pin 2 and a timed pulse at the output pin 3 is delivered.
In all the designs the signal applied at TRIGGER pin 2 are appropriately dimensioned to form a negative edged pulse.
It ensures that the trigger amplitude switches from an "off' level higher than 2/3rd of the supply voltage to an "on" value lower than 1/3rd of the supply level.
Triggering of the IC one shot monostable actually happens when the potential at pin 2 is pulled down to 1/3rd of the supply voltage level.
This requires the trigger pulse width at pin 2 to be higher than 100 nanoseconds but lower than the pulse which is intended to appear at the output pin 3.
This ascertains the elimination of the trigger pulse by the time the set monostable period elapses.
Thank you very much for your quick response, I will simulate it in the pcb wizard
OK, no problem…
By the way, it must be between 5 to 10 minutes. Something simple like the first circuit..
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/simple-delay-timer-circuits-explained/
OK, then my previously suggested design will be alright for you.
Hello good afternoon, my name is Carlos and I am a faithful follower of the website. I’m looking for a simple timer circuit that starts when powered… Without a pushbutton… Thank you very much.
Thank you Carlos, you can try the following circuit, please ignore the red wire, it is not relevant for your application:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/burglar-alarm-with-delay.png
However this is not a long duration timer….it’s maximum delay could be around 30 minutes depending upon the values of R2 and C2
In the 2nd circuit the start and reset have the same outcome. reset also start the timer and not stop timing.
When S1 is pressed and the timing initiates, pressing S2 will stop the timing in the middle and reset the circuit back to it original standby condition.
Please can I have circuit diagram of 1minute on 30minutes off timer using 556 timer ICe
I don’t have it at this time, if possible I will try to design it…
Good afternoon Swagatam
I am really enjoying your web site, and yet again I would be extremely grateful if you could
help me with your expertise, the above circuit you helped me with, works just fine, but for one problem, after the 555 times out the next cycle starts before the comparator has time to clear, so is there a way of introducing a small delay
(a few hundred milli seconds) prior to your start pulse transistor to allow comparator to
clear, or are we into cascading timers?
Many thanks in advance
Regards
Thank you Derek, Glad I could help!
Do you want the Q1 BC547 to start with a slight delay? You can do it by replacing R2 (10K) with a 100uF capacitor
Hi Swagatam
Thank you very much for your fast response, I have implemented your suggestion and everything is now working as designed, the only thing I have changed is the value of the cap from 100uF to 22uF as I only require a few milliseconds
Once again many thanks
Regards
That’s great Derek, Glad it is solved now.
Hi
With regards to your 9th practical timer circuit (transistor), is the value of C2 (0.001pF) correct? as I cannot source one. and one other question what is the purpose of the 8.2K resister prior to the pot
Many thanks in advance
Hi, that’s seems to be a printing mistake. It is supposed to be 0.001uF, however you can use a 0.1uF also. The 8.2k ensures that the IC 555 does not get damaged if accidentally the pot is rotated fully towards the the positive supply side. You can use any resistor between 4k7 and 10K instead of 8.2K
Hi, thank you for your fast response,
I am not sure if this is right design for my needs, maybe you could possibly help me if tell you my requirements,
The input to the TLC555 is feed from the output of a MCP6542 comparator (which is positive and active until the 555 times out) The time I require is variable between 1 and 15 seconds, also the output of 555 needs to be positive, is this something you help me with
Many thanks in advance
By the way this is a fantastic web site
I can help you but I could not understand the requirement correctly. You mean to say the comparator output switches ON the 555 input so that the output of the 555 remains ON for the set amount of time then it switches OFF. As soon as the 555 output switches OFF it also switches OFF the comparator? But how does initially the comparator switch ON, because initially the 555 output will be switched OFF so the comparator will be also remains switched Off, so how the comparator is supposed to switch ON initially for feeding the 555 circuit?
Hi sorry for the confusion I have not given you the complete picture, the timer is just a one part of the system,
when the timer times out it initiates the next part of the sequence so the comparator resets and carries on until the detection, this is repetitive system
hope I have clarify d this for you
No problem, can you please tell in a step wise manner what stages you require in the design and how the stages need to function?
Hi,
I will give a little bit more info about the system, the main part is a linear actuator moved by a stepper motor with a Bourns AMM20B position sensor mounted on the shaft giving 0-5vdc feedback of position
The comparator is configured as window comparator with high and low inputs set via two slide pots
so in essence they form 2 electronically moving limit switches, on the threshold at each end the actuator reverses
The output from the comparator is cmos push pull +5vdc, but opto couplers can be fitted if this helps your design.
a) so when either threshold are meet the comparator goes high +5vdc this is when we use this to start the timer the output from the comparator goes to the input of the 555
b) when the timer starts, the output from the 555 goes high (this is used to stop actuator moving ) and because it is not moving the input to the 555 will still be high
c)on timing completion the output of the 555 goes low this will start the actuator and clear the input to the 555
My only concern is although the system is very fast, starting the actuator at the end of timing may not clear the input unless some thing could be put around it
d) the above procedure happens at each end of the stoke and the timings may be different so we will to have two sets of timers
e) Timing range variable 1-15 seconds
I hope this makes some sort of sense
If there is any more information you require please get in touch
Best regards
OK, I have understood the basic functions of the required design. I think the following monostable should do the job for you. Let me know if you have any further questions
Thank you for your speedy response,
I could could not find your alternative design “alt=”555 monostable with relay ON/OFF timing” />'” I get an “ERROR 404” If you could point me to that
I am going build this circuit and try it out, I am assuming by your diagram that the output of the 555 is positive, because of the speed of the system I will not be using a relay as they can be too slow and subject to bounce, instead I am going to try using a CD4066 to interface with the controller.
This looks to be a good design, many thanks
Regards
You are most welcome!
Here’s the diagram link which I had referred to you:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/555-monostable-with-relay.jpg
You can remove the relay and use a 4066 IC. Yes the IC 555 output will be positive in response to the positive trigger input from the op amp.
Hi, thanks for your answers
I have a further query, regarding the value of C2 in the latest drawing you supplied me it states 1uF is this correct? as in a previous communication you said it could be either 0.001uF or 0.1uF, or is that value specific to my needs.
sorry to be a pain
Regards
Yes, I have changed it to 1uF, because in my experiments I have seen that a slightly larger value capacitor at pin#2 of the IC enables faster and reliable switching of the IC, which sometimes does not happen with smaller value capacitors such as 0.1uF or 0.001uF.
I’ve studied the above 555 timer circuits (have even built the 10 led tacho circuit with 555 timer you published) and I’m now trying to work out how to adjust the npn magnetic sensor input of a cheap Aliexpress tacho display so that it will show speed (kmph) on the display (it’s small and will fit nicely on my self built monster) instead of rpm.
Can you please push me in the right direction?
I tried to investigate the issue you are facing, but unfortunately I failed to figure out a proper solution.
I have an existing momentary switch circuit that I am attempting to automate:
Start with a 12VDC power source, which currently passes through a momentary switch to toggle a function on/off for an appliance. I would like to install an automated activation circuit “in parallel” with the momentary switch which toggles this feature at power-on without my pushing the momentary switch (but still allow the existing switch to function if I do push it). This circuit would delay ~15 seconds after power is applied to the appliance, pass the supplied 12v for ~0.25 seconds (mimic the momentary switch) and then go dormant, only resetting when power is cycled. Preferably without relays being involved since I’m being picky.
Any guidance is much appreciated.
Sorry, I am unable to understand the functioning of the circuit. I will need a schematic to understand this.
Swagatam, thank you for the prompt response. I have found a commercially available alternative after much searching and will go that route. Thank you for such great content!
Jose
You are welcome jose, Glad the problem is solved.
Hello Swagatam,
I am an artist in the need of an LED dimmer that very slowly (14.75 days) and smoothly brightens then dims slowly (14.75 days) then repeats this cycle ad infinitum. I need the circuit to support a very bright LED strip light at 12VDC. Can you direct me an existing circuit design that can do this?
Thank you.
~Paul
Hello Paul, 15 days is a long, and I do not have any analogue circuit designed to accomplish this job.
I think this can be probably done through an Arduino, but since I am not good at coding Arduino, would be difficult for me to do this.
I hope I can find an appropriate solution soon, and then I can update it for you…
Dear Sir,
I am trying to have a repeating on / off from two double a batteries to a polarized glass
The on/off should be equal at around 50 milleseconds and continuous as long as activated. Would a 555 be appropriate?
Driving Voltage: 28-49 VAC
Power consumption: 3 to 5w / M^2
I know little about this area.
Thank you for sharing your expertise.
Hello Dan, IC 555 astable can be used but a precise 50% duty cycle may not be possible with this IC.
Instead you could go for any CMOS based astable circuit, or a 4060 based circuit.
You can also accomplish this using a transistorized astable multivibrtaor.
Dear Sirs
I need some assistance with a project, and I am so! glad I saw you site.
I need a 5 volt DC delay timer that when supplied with voltage starts timer which activates a momentary contact
I currently am using a 555 delay time however when supplied with power starts timer then activates the contact which is (continuous) I need momentary !
Please help
Hello Jackie, for a momentary action add a capacitor in series with the base of the NPN transistor that is driving the momentary switch. Also make sure to add a 10k resistor across base/emitter of the NPN transistor
Hi. Thanks for providing previous information about the proximity detector.
Is it possible to get a 555 timer to give an output to flash a small LED once every 45 seconds while ever power from a 9v dry cell is applied to the circuit? (Like a smoke detector does) I am after this to indicate if a small life support system alarm, that is only used at night, is operating to detect a power failure. I understand that the R/C combination controls this but am at a complete loss trying to fathom out where to start using the appropriate formulas. I am in my 80’s, can usually follow circuits & construct small projects if component values are shown but unfortunately these calculations are beyond me these days. Thanks for any help or assistance you can provide. Regards, Les.
Thanks for your question.
What is the ON time for which the LED is supposed to flash?
Probably 1/2 to 1 second or thereabouts not really fussy, whatever is easiest. Sorry for the delay in replying, I don’t get to a computer that often. Thanks
You can try the following design:
for inserting the flasher circuit across positive and pin3 of the IC 555, you can try the following design:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/12/OneTransistorLEDFlasherCircuitDiagram2CImage-1.jpg
I would like to implement timers on some battery operated Christmas ornament. Push the button and it’s on for 8 hours and off for 16, and just leave it for the whole of December. Is it doable without a microcontroller?
You can probably try the second circuit from the following article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/how-to-make-simple-programmable-timer/
or this one with a microcontroller
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/arduino-2-step-programmable-timer-circuit/
Hello sir,
I’ve gone through some of your posts and was encouraged. Please, I need circuit that will indicate an incoming power of 220v and it will initiate an alarm that will last for about 2-5 seconds and then goes off.
Hello Jerry, please provide the specifications of the alarm??
Dear Swagatam,
Have been a avid follower of your website and YouTube channel.
I need a light activated switch which will keep relay (12v) activated for 10 to 30 seconds.
Thanks in advance
Thank you dear Chandan, you can try the “porch light timer circuit” explained in the above article. You can keep S1 permanently ON, and switch the relay by focusing a flashlight on the LDR.
In your application the LDR and the R5 pot must be swapped with the each other
Thanks dear
Will assemble one and let you know.
No problem!
hi
i need to be able to push a button and keep a relay energised for between 5 and 60 seconds.
will be going into the engine bay for a car so will operate on 12v dc.
would like to try and build it my self but if such a thing can be bought for reasonable price i would also be interested.
Hi, the first circuit from the above article is exactly what you may be looking for.
Hello Swagatam,
I wonder if you can help me out. I’m a beginner and I want to build a circuit for a certain purpose.
A circuit based on the 555 timer with two push buttons. One button is to turn on a LED and the other button to turn the LED off. But the LED, when it is turned on, must be blinking.
I build a cicuit where the LED is turned on but not blinking. It is not difficult to build such a circuit, but having a blinking LED, that’s a problem for me.
Cab you help me out?
Thank you.
Hello Pedro, I think you can replace the LED with the following circuit module, which will provide you with the desired blinking LED output
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/how-to-make-single-transistor-led/
“1. First, this design will drain some current continuously, even while the output of the circuit is in the off state.”
Is all the current drain through the relay or are there other places through the 555 or S3 that current is draining?
Any IC based will require some current to remain operative, for IC 555 this may be around 5 mA drain. Alternatively you can try the second circuit from this article, which will not drain any current once the relay is OFF
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/simple-delay-timer-circuits-explained/
Thank you. My application requires I power my circuit from a battery, so I want to prevent drains wherever possible.
In that case you can try the transistorized one shot circuit.
Sir,
How can I send a single output pulse of 3 or 5 seconds when the input trigger (without switch) is constant ON? Which of the above circuit will be suitable for my application?
Application: Submersible pump starter starting capacitor auto-bypass after starting***
Please HELP!
Abhirup, you can make the first circuit with the following modifications:
Replace S1 with a 0.22uF capacitor. Connect a 100K parallel to this 0.22uF.
Replace 22k with 10K.
Adjust the 470K to get 3 second ON.
In this condition whenever you switch ON power to this circuit, the output will be ON for 3 seconds and then switch OFF
Hello swagatam
i designed an electronic car and i want to control it with remote,how do i make the wirless remote control?
Hello Charles, you can probably apply this concept:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/make-remote-controlled-toy-car-circuit/
Hi, thanks for the quick response. What I need is a timer up to 8 minutes. But very stable … Regarding this circuit what would be the value of the crystal?
Hi, you can make the design and test the delay at pin3, and also adjust the capacitor value for the adjusting the delay. I think pin3 will provide more than 8 minute range.
Hello good afternoon, I am a faithful follower of the website. This time I want to know if you have a precision timer circuit … Maybe with quartz crystal for more precision. Up to 10 minutes From already thank you very much.
Thank you Carlos, you can try the last option presented in the following article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/how-to-understand-ic-4060-pin-outs/
Hi Swagatam
Thanks for this, but I’m using PIC micro controller and not Arduino dev board.
The programmer I’m using to transfer my hex file to the chip is top2008 universal progamer.
Please Kindly help me.
Thanks
Hi Goddey,
My knowledge of microntroller is not good, however I think Arduino also uses a PIC microcontroller, that’s why I thought may be the same code could be used in your IC also.
Hello
I’m using pic16f887 for an led blinking project but the circuit is not working.
The programmer I’m using is top2008 universal progamer
Pls can someone help with what could be wrong?
The following article might help you to solve the coding:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/learning-basic-arduino-programming-tutorial-for-the-newcomers/