I have explained four simple boost converter circuits in this post, which can be built and used for converting a low level DC voltage inputs to a higher level DC voltage outputs.
Video Demonstration
What is a Boost Converter
A DC boost converter circuit is designed for stepping-up or boosting a small input voltage levels to a desired higher output voltage level, hence the name "boost" converter.
Since these circuits basically step up a low voltage to a higher voltage levels, they are also know as step-up converters.
Although a boost converter circuit may involve many complex stages and calculations, here we will see how the same could be built using minimum number of components, and with effective results.
Basically a boost converter works by oscillating current though a coil or inductor, wherein the voltage induced in the inductor is transformed into a boosted voltage whose magnitude is dependent on the number of turns and PWM of the oscillation frequency.
Basic Working Principle of Boost Converter
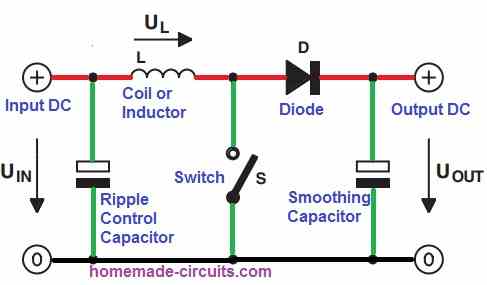
Referring to the figure above, the basic working principle of a boost converter topology can be understood from the following points:
When the switch S is switched ON, the coil voltage UL becomes equal to the input voltage and the current through the coil begins increasing linearly.
Next, if the switch S is turned OFF, the coil ensures that current through it keeps flowing independent of how much the output voltage rises. The current at this moment flows via diode D.
In this situation, the coil voltage UL is negative and the output voltage is higher than the input voltage.
As a result, the current flowing through the coil decreases linearly. During this period, the coil supplies the output with a stepped-up, boosted voltage.
After this, if the switch S is switched ON again, the process repeats. The above process repeats continuously as long as the switch S is switched ON/OFF repeatedly.
This causes the output to get a continuous supply of a stepped-up voltage. The smoothing capacitor makes sure the boosted voltage is filtered correctly and is a pure DC.
You may also like: Make this 1.5 V to 3.6 V boost converter for LED flashlights
1) Simple 5 V to 12V Boost Converter Circuit
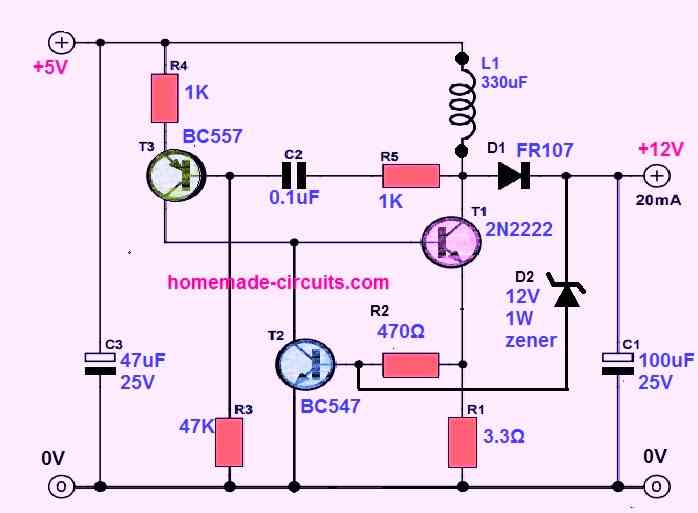
In the first concept as shown in the figure above, the input DC supply can be anywhere between 3 V and 5 V.
We can adjust the output voltage to 12 V or some other desired voltage by tweaking the zener diode D2.
So, when output voltage tends to increase excessively, T2's operating point shifts, causing T1 to switch on for a shorter duration of time (or maybe not at all).
We can expect the stepped-up output voltage to be around 12.6V at a 20 mA output current. The input current at a 5 V input voltage will be around 64 mA.
This translates to an efficiency of 77%, which is not bad at all for such a straightforward circuit.
2) How to get +5V, -5V Dual Supply from 1.2 V
If you are looking for a circuit to boost 1.2 V NiCd supply to 5 V then you can use this second circuit below.
Moreover, this circuit will allow you to get a dual +5V and -5V supply from a 1.2 V DC single supply input.
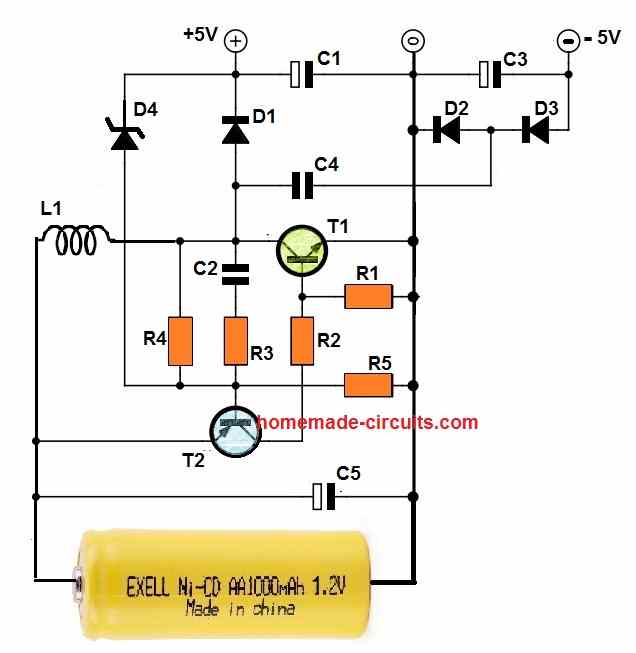
Parts List
- All resistors are 1/4 watt 5% unless specified
- R1, R5 = 1 K
- R2, R3 = 100 Ohms
- R4 = 2.2 K
- Capacitors
- C1 = 10 uF / 25 V Electrolytic
- C2 = 0.01 uF Ceramic Disc
- C3 = 1 uF / 25 V Electrolytic
- C4 = 0.1 uF Ceramic Disc
- C5 = 10 uF / 25 V Electrolytic
- Semiconductors
- D1, D2, D3 = FR107
- D4 = 5.1 V 1/2 watt zener diode
- T1 = 2N2222
- T2 = 2N2907
- Inductor
- L1 = 270 uH 500 ma
The step up converter is basically formed using T1, L1 and D1.
Zener diode D4 functions as a feedback at the base of transistor T2 and provides the required stabilization for the circuit.
The maximum current output capacity of this circuit is around 10 mA at +/- 5V.
The circuit will provide a maximum efficiency of 60% which does not looks too impressive. However with an input DC of just 1.2 V you cannot except more than this.
3) Flyback Type 1.5 V to 30 V Boost Converter using a single BJT
The third boost converter circuit shown below uses a joule thief flyback topology.
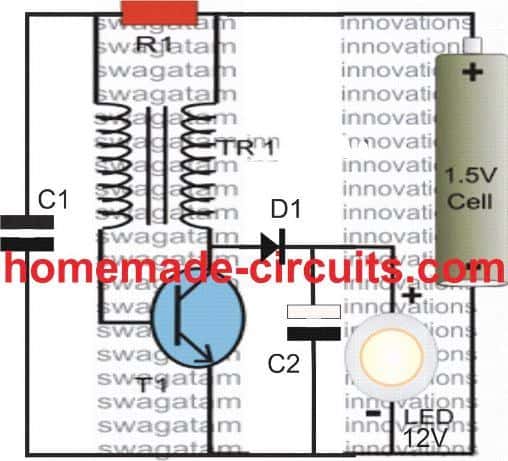
Parts List
- R1 = 1K 1/4 watt
- D1 = 1N4148 or a Schottky diode such as FR107 or BA159
- T1 = any NPN power BJT such as TIP31, 2N2222, 8050 or BC139 (on heatsink)
- C1 = 0.0047uF
- C2 = 1000uF/25V
Inductor is built using 20 turns each of super enameled copper wire on a ferrite torroid T13. Wire thickness can be as per the output current requirement.
In the above design a single BJT and an inductor is all that's needed for visualizing an incredible 1.5V to upto 30V boost.
The circuit works using a joule thief concept and utilizes an inductor in the flyback mode for generating the specified high efficiency output .
Using a flyback concepts allows the two side of the transformer isolated and ensures better efficiency, since the load is able to operate during the OFF time of the BJT, which in turn prevents the BJT from overloading.
While experimenting I found that adding C1 drastically improved the performance of the circuit, without this capacitor the output current did not look too impressive.
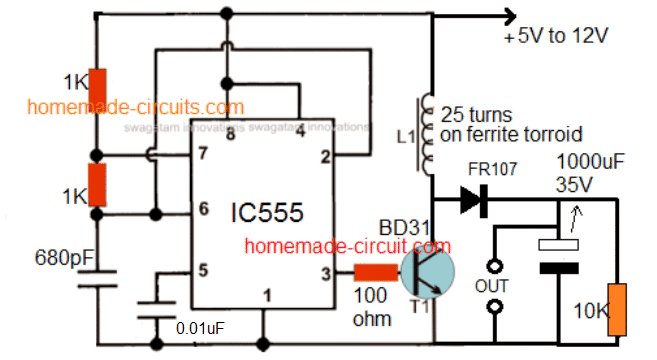
4) 3.7 V to 24 V Converter
Now let's refer to our fourth step-up converter design which will boost a 3.7 V input DC to 24 V output DC.
This simple circuit is built using an IC 555 circuit for boosting USB 5V to 24V, or any other desired level. The same design can be used for boosting a 3.7 V to 24 V from a Li-Ion cell.
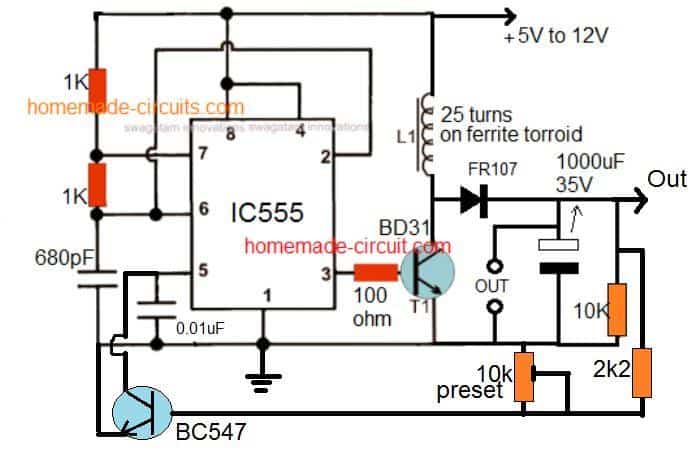
The above circuit can be regulated with a feedback as shown below:
The idea looks quite straightforward. IC 555 is configured as an astable multivibrator whose frequency is decided by the values of resistors and capacitor at pin#7 and pin#6/2.
This frequency is applied to the base of a driver transistor TIP31 (incorrectly shown as BD31).
The transistor oscillates at the same frequency and forces supply current to oscillate within the connected inductor with the same frequency.
The selected frequency saturates the coil and boosts the voltage across it to a greater amplitude which is measured to be around 24V.
This value can be tweaked to even higher levels by modifying the turns of the inductor and the frequency of the IC .
Sirji, thanx for quick reply. Just for reminder, I’m already working on the car laptop charger ckt. I asked for the ways for making this adjustable! Please suggest some ways that can vary the output voltage without modifying the turns of the inductor!
Maddy, you can modify it in the following manner to get an adjustable boosted output.
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/adjustable-boost-converter-circuit.jpg
Sirji I have a small question! Most of the commercially available booster ckts have variable output facility with them. Can we have any modifications for our booster ckt have this freedom! Say by adding a pot at any stage to vary the output. This wud make it more versatile! Thanx in advance!!
Maddy, the 555 IC boost converter is adjustable using the feedback pot.
The following designs are also adjustable:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/high-power-dc-to-dc-converter-circuit-12-v-to-30-v-variable/
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/12v-car-laptop-charger-circuit-using/
Sirji! Thnx for the advise! But I’ve used some wrong terms here! Actually I was asking for the disturbance due to the magnetic field of the inductor to the Audio content being amplified in RF range! Presently the ckt is perfectly working with 19v adapter! But I was intending to raise the supply up to 24v. Searching the net I came across various methods said before. So I asked for your expert advise!! Thanx again!
Thanks Maddy, glad to know the circuit is working for you.
Yes, in that case it is better to encapsulate the ferrite inductor inside a Mu-metal enclosure.
Let me know how it goes.
Sirji, I finally got my ferrite core at a decent price from a radio technician. Before putting everything to PCB, I’ve a final hurdle to remove! I wud be using this booster to power a small RF amplifier ckt. So the question is, should I shield above inductor inside some Mu-metal or steel type enclosure to prevent the noise from this booster from disturbing my RF amplifier ckt? Or the simplest method to do this is to keep both ckts far away from each other. Or another way is just to keep the inductor away! And if this is done, is there any effect over the output voltage? Please advise!! Thanx again!!
Maddy, Referring to the following booster converter circuit, this is suitable for high power loads, if your load is a small RF amplifier then this circuit may be an overkill:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/laptop-charger-12-V-to-19V-converter-circuit.jpg
Regarding the RF noise, it can be eliminated by using an large filter capacitor across the supply terminals of your RF amplifier, in addition to the one which is already included at the boost converter circuit output.
Let me know if you have any further doubts.
Sir just to get a ferrite core, I’ve extracted a torroidal ceramic magnet from small speaker. having 2″ external and 1″ internal dia. I could not find any other solution over the Internet for 3″ long, 1cm dia ferrite rod. The available ones were very small in size. Now I’m planning to demagnetize above torroid using AC current using shielded wires. I don’t know how long it wud take. But in the mean time, if you do know of any such cheap rod being sold online, please give me the link! Thanx again, Sirji !!
Hello Maddy,
the ferrite rod size is not critical at all, you can choose any standard ferrite rod, or even a standard ferrite ring can be used.
I don’t think a magnet can be converted into an inductive core by demagnetizing it.
All components gathered!! Except Ferrite core. I searched but ended with whooping prices!! Sir can I prepare a core using Powdered Iron as seen over the Internet!! Just using the term “DIY Ferrite core alternatives” gives you different sites that show you how one can make one using cheaper materials. What opinion do you have about this? Or the same cmt be made using Air core too?
Thanks Maddy,
Referring to the following diagram:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/laptop-charger-12-V-to-19V-converter-circuit.jpg
Ferrite core will make the inductor a lot smaller and compact, whereas the same inductor can be quite bulky if an iron core is used and also for an iron core the frequency will need to be drastically reduced.
I don’t think there’s any cheaper alternative to ferrite cores, so it is not possible find any suitable alternative.
Air core is possible which will be even bigger in size than an iron core inductor.
If you are sure you can make a proper iron powder core, you can try it, but then the winding might need to be increased 5 times more and the frequency reduced proportionately.
The frequency can be reduced by increasing the base capacitors of the BC548 transistors.
Sir thank you for your quick response! I’ve a bit of problem here! As per your advise, the circuit should have a IRF640 but can I use IRF3205 there?
Hi Maddy, no issues, you can use any appropriate MOSFET whose voltage and current ratings are higher than the input/output ratings of the circuit.
So, an IRFF3205 would be perfectly fine here.
Sir, I have a 19V, 2.1A Laptop adapter! Please suggest me any boost converter circuit that can be made using locally available cheap components to up-convert above DC supply to 24V, atleast 1A DC! For one week or so, I have become a fan of your site. The more I dive into different articles, the more curious I become about the extent of knowledge still on your site but hidden from my eyes.
Thank you so much Maddy, I am glad you found the site helpful.
I think you should try the first circuit design from the following article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/12v-car-laptop-charger-circuit-using/
You will have to experiment a little with the coil to get the perfect desired results.
Let me know if you have any problems.
I’ve been following your educative posts and used most of them on my projects successfully. I thank you for that most sincerely. Currently, my question is; I want to boost 48v from a SMPS to 54v to charge two 48v 100AH connected in parallel ie these are EMS intelligent batteries. I need a schematic diagram.preferebly and possibly if this converter out put can be variable.Thanking you in advance.
Thank you for your kind feedback, glad I could be helpful.
I think you can try the first circuit from the following article, however this circuit will need to be experimented and modified appropriately as per the 48V input and 54V output.
The output can be made variable by removing the zener diode and the 10k, and replacing them with a potentiometer instead.
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/12v-car-laptop-charger-circuit-using/
can i put a coil of copper wire instead of an inductor
Yes copper coil will do but the inductance has to be matched correctly
What will I change in the circuit if I replace the Bc557 with A1015 bjt
You can try it, no changes will be required.
Good day sir,
Please can you help me on how to build 5V 2AMP, step up converter that works on voltage from 3v to 4.2v.
Using 50, or 100khz transistor oscillator.
I have a 5,000mah li-lon battery to power it
Hi Chidonlite,
I think you should try the first circuit from the above article. You can tweak and adjust the 12V zener diode to get the desired voltage at the output. For 2 amp current, the 2N2222 can be replaced with a TIP31 and the BC557 with a 2N2907…
Hi @Swagatam. I really need your help with a boost converter circuit that I can use in my car to power up my laptop. The laptop takes in 18.5vdc at 3.5amps. thanks
Hi Breno1, You can try the following design. The inductor can be built by winding 25 or 30 turns using 1 mm super enameled copper wire over a ferrite core. The ferrite core can be a ferrite rod or a ferrite ring. The 24V zener can be replaced with a 20 V zener diode
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/switching-solar-boost-converter-circuit.jpg
Thanks a lot for the circuit @Swagatam.
1. I have two inductors each has 15 turns, will it work if I connect them in series to get 30?
2. About the capacitors. Am I to us same type i.e polarized electrolytic capacitors?
@Breno1,
1) No two series coils will not work, you must build the coil over a single ferrite core
2) The nF capacitors can be disc ceramic type, uF capacitor can be an electrolytic.
Please I need circuit diagram for 12vdc to 400vdc converter
You can try the following design:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/how-to-convert-12v-dc-to-220v-ac-using/
For the flyback circuit could I use 5v input instead of 1.5v?
You can use 5V, but then the output would be above 24V
That is what I need, thank you
You are welcome! Glad you found the post helpful.
Hi sir, thanx for wonderful circuits and your knowledge to, am my question is what if I use tip41c instead of BC 547 will the circuit function properly?
Thank you Nedi,
I don’t think TIP41C would work correctly instead of BC547, because BC547 has high gain and requires very little current to switch ON, while TIP41 might need a lot more current to switch ON. This might need modifications for the base resistors of the transistor.
Hi, what could you suggest I use to boost a dc 2.0 volt RSSI (relative signal strength indicator) voltage up to about 5 dc volts so I can run a bar graph module. This to show how much RF signal my radio is getting.
Hi, you can try the second or the third circuit from the above article, it should work for your application.
Sir, I thought the minimum supply voltage for lm555 is 4.5v, how then is it able to boost 3.7 lion battery to 24volts. Is it really possible that way.
Moses, you can use the CMOS 7555 IC which are rated to work from 3 V onward.
Yes I have recently made did experiment .by using mje 13003 transistor and 10k resistor and capacitor 35 volt 2200 uf. And the input is 3.7 while the output replect about 28 volt DC.but de battery did not last at all
sir i want to know if it is possible to connect phone batteries together either in series or parallel. If it is possible i have a plan to connect four of them in parallel each of 2500mAH. But i want you to help me with a circuit that can be able to charge it automatically
Hi Alimon,
You can connect the batteries in parallel. However making an automatic charger can be difficult for a newcomer, therefore I would suggest using a high current LM317 based power supply and adjust its output to exactly 4.1 v so that over charging of the battery can be avoided.
4 batts in parallel would mean a total Ah rating of 10 Ah which will require a charging current of 5 amp. You can use a 9V 5 amp transformer to build the voltage/current source for the LM317 circuit.
You can try the following circuit for the mentioned purpose. Use only 2nos of 2N3055 in the circuit, that will be enough:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/high-current-LM317-power-supply-circuit.jpg
These circuits look nice, and the principle is explained well.
Is there any circuits that can boost low voltages?
From as low as 30mV to 5V, other than using an LTC3108.
Or from 0.8V to 5V
Yes boosting 0.8V can be possible through a joule thief circuit. You can try the first circuit explained in the following article:
3 Best Joule Thief Circuits
Thank you, I don’t really understand why, but I’m looking through the article.
Is it possible to boost from as low as 0.1V. without using a 1:100 current transformer (cause that’s not available in my region)
Without a transformer that can be impossible. Moreover I think 0.4V is the last limit which can be boosted using a joule thief circuit….0.1 is too low for boosting
Hello there can i use a peice of ferrite rod instead of a ferrite toroide.
yes you can do that!
Cheers mate that will save me from having to wait a week for delivery of toroid core.
Sure, no problem, and wish you all the best!
Please email me via dr.blackschleger@gmail.com so i can share a circuit photo with you, and,
happy Fathers’ Day, Professor Swagatam !
Thank you Doctor B, My email is homemadecircuits @ gmail . com
hello sir,
sir, if i use the first circuit “Simple Boost Converter using a single BJT” with 3.7volt input is there any component values that need to be replaced?
is this circuit efficient for long time use?
Hello Ningrat, for 3.7V you don’t have to change any components in the first diagram, however the BJT specs actually depends on the load specs.
Yes the circuit is efficient for a long term use.
Hello good afternoon, what is the output amperage of the circuit with Lm555 ..
It is 1 amp because TIP31 is used, you can try TIP35 for higher amps
Swagatam, in your article on boost converters, specifically diagram “3.7 to 24V converter”, there is a 10K resistor on the output side. I can’t figure out what its purpose is. It appears that it would bleed energy from the output capacitor. What is its purpose?
Also, when does the diode conduct? It appears it conducts when T1 is off. When T1 is on the coil conducts, right? Please explain a little more where the “boost” comes from.
Thank you, regards, Cris
Cris, yes the 10k is the bleeder resistor, and will act like a load when no real load is connected.
When the transistor is ON, the coil keeps storing the charge until it has reached its peak voltage specification. Then when the transistor switches OFF, this stored peak voltage is fired back as a boosted voltage.
The peak voltage depends on the number of turns, higher turns will generate higher voltage, and proportionately lower current.
hello im interested in making a earth battery im asking can i use a joule thief to take the volts form 0.5 to 12 volts and how to get more amps
Hi, Either you get amps, or volts, you can never get them together for free…
for an earth battery you may have to integrate huge number of plates in series parallel to get a decent power output
Glad to find this article, Well done Swagatam.
Please I want a boost converter design in which I will use 100w/12v panel to charge 4*18ah/12v 48v system.
Thanks
Thank you Seun, I think the following design will be more suitable for your application:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/high-power-dc-to-dc-converter-circuit-12-v-to-30-v-variable/
Mr. Swagatam
I like your “simple boost circuit. I appreciate your response, the 12 v laptop charger circuit, I’ll study it. I find now that we need to get up to approx. 200 volts output from 9 volts input. I still need a bit of couching. Thanks again. Vernon
You are welcome Mr. Vernon!
For higher voltages you can using a small 9-0-9V 220V 100mA transformer, and use it in place of the inductor shown in the IC 555 circuit. This is hopefully help to accomplish the required results quickly!
Good morning
Working on a project that includes “boosting” 9v DC (battery) to 50 to 100v DC.
We’re not sure of the circuit design or components. We want it to be able to recharge for follow on use. (all going in a small package).
Have you done such a project that you could permit us to reference?
We appreciate the assistance.
Hello, you can try the first concept presented in the following article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/12v-car-laptop-charger-circuit-using/
Mr Swagatam, I was still wrong in wrapping the enameled wire on the toroid, could you give an example in the form of a picture, but not a symbol
Mr.Rudi, the winding is not critical at all. Just wind the two sides anyway you want, and after connecting it to the circuit if the circuit doesn’t work, just interchange the wire ends of any one of the winding, and your circuit will start working instantly.
Good evening sir,pls I we like to learn more on dis DC 1.5 converter to DC 12 voit
Good day sir please for the first diagram I can’t really find a 1000uf capacitor and also the 0.0045uf
So can I try using 220uf and 22uf
Ordu, 1000uF can be replaced with 220uF, but the 0.0047uF value cannot be altered, you can adjust the value through series parallel capacitors if required.
Please is there any other pwm oscillator ic I can use instead of 555 or can I equally use the popular viper22A or Rm6203 used for flyback converters, will it work.
You can use TL494 IC or similar, but VIPER can be difficult since it is configured to work with high voltage rectified AC.
Ok I’ve just made the circuit, and am continuously having this problem of magnetostriction. According to my research, I find out that it is due to low frequency switching. So please can you tell me how I increase the switching frequency, and also the factors and components value that affect the frequency of operation.
If you are referring to TL494 circuit, you can change its Rt, or Ct values to change its frequency.
No it’s the first version of the joule thief circuit.
Did you confirm the frequency with an oscilloscope? Since it’s a self oscillatory type circuit frequency is pretty much fixed. For higher frequency you can probably try the following version:
8X Overunity from Joule Thief – Proven Design
Dear sir Swag, truly you have swag! I have been looking for this information for years but thanks to you I found it! Also, can the resistor be added after the toroidal core? Like directly at the base of the transistor?
Thank you Miracletech, yes you can try that for the first diagram. For more options you can also refer to this article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/1-watt-led-driver-using-joule-thief/
Ok. Thank you so much.
can we use this circuit(555) to boost voltage from solar panel (12v to 15v)?
yes, it is possible.
Dear Swag,
I do have a 12volt @75 amp dc battery and do intend to use to power about five led corn light bulbs and rating for each is 359 milliamps and wattage for each is 26 watts. I will be using the constant current method to drive the led driver to power the lead lights. The led driver can be a buck boost converter, sepic dc dc converter or cuk dc dc converter. The problem I am having is that of stepping down the high dc current from 75 amps to manageable one like say 13 amps. If it were ac it would be easier. What I am requesting from you is a general method which I can apply.
Dear Bernard, what is the voltage spec of the LED, there’s no need of a buck boost circuit, you can directly use the supply for the LEDs after configuring the LEDs appropriately.
Good evening sir,
very difficult to leave your pages. Your information is always precious.
Transistors in Darligton mode would lift me the current in these joule thief if powered by solar cell?
If not, is there any other way to get a current gain?
If it were a buck converter would there be a way to take advantage of the current of the dissipated voltage?
Thank you very much in advance.
A lot of Swag light
Thank you Marcelo, appreciate your interest very much!
A Darlington may help to increase the current transfer response. However, using many thin wires together for the winding may also help to gain more power from the design. A joule will normally work like a boost converter so not sure how it may be turned into a buck converter…but I don’t think this concept can be used effectively used for charging bigger batteries.
Hello sir
For giving the gate pulse to the BJt can i give it through Arduino?
like pwm technique
Hi Parsiva, you can do that, just make sure that the duty cycle and the frequency are optimally adjusted.
Goodday sir I really want to appreciate you for good work thank you very much please keep up
Sir please I build a boost converter using 555 timer to drive my mosfet, and I use a mosfet in place of the transistor but each time I power it up the mosfet get really hot please what could be the cause I have checked but can find any fault in the circuit
Hello faith, keep the frequency at around 50 kHz, and test by gradually increasing the turns until the MOSFET stops heating, this is perhaps the easiest trial and error way to optimize a boost converter.
Which turns is it the number of turns i.e the inductor
There’s only one component in 555 circuit which has turns, it’s L1
Sir I have seen my mistake all this while the diode was connected wrongly but now is working very well thanks for your assistance
Glad you could solve it!
Sir I did exactly what you said it still the same I noticed that when ever I connect the power supply it like both positive and negative are connected together it al hiways spark and if I try leave it for some second the wire Wil burnt out but if i remove the inductor it will not happen, and the output power is not boost please what could be the cause. The inductor I’m using is wound on a toroid core
How many turns did you use? and what at what frequency did you set your IC 555?
Sir I’m really confused here, I even try building the boost without the 555, i.e the simple circuit were I have just inductor, diode pull button switch and capacitor, when ever I pushed the switch the inductor Wil connect it to ground i.e shorting the circuit why this happening
The switching should be in millisconds, if you hold it even for 0.25 seconds it will create a short circuit. You can read the following article for more info:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/how-boost-converters-works/
sir I made this circuit but its not working I can’t find 680pf but am using 2A682k then I cant get tip31 and am using tip41 while testing it its just sparking as if I shot the circuit of the battery then the transistor is getting hot please help me
damilare, 2A682k = 6800pf, it’s not 680pF
In your present set up increasing the number of turns to 5 times more than the shown value, and check the results. Wind it on a ferrite rod.
adofo I have 5v 500ma solar panel. can I use your booster convert to run car tape
5 x 0.5 = 2.5 watts that’s too less for a car tape, it won’t work
Hello,
Sir can i use N-channel mosfet instead of transistor? for T1 & BC547?
is there any modifications for this?
Thanks a lot..
Hello Paul, mosfets will require minimum 9V to turn ON fully, so it cannot be in these applications.
Thanks for the reply then can i use 13003 transistor for T1?
I am sorry Paul, for BC547 you can use a mosfet since the gate would be receiving a boosted 12V so no problem.. MJE13003 won’t be suitable here!
I cant find any TIP31 Its hard to find here in our place but i found TIP41 & TIP42, can it be used here in the circuit ?
Thanks…
TIP41 is fine, it will work…
Sir Can I use 100nf cap instead of 680 pf? i cant find that capacitor.. and 1n4007 diode instead of FR107.
thanks again..
Hi Paul, There’s a huge difference between 100nF and 680pF, so it won’t work. You can try the first circuit instead.
Hmm, if Paul been asking about replacing T1 BJT with 13003 it would probably work, since 1300x family is just (high-voltage) NPN BJTs, not anyhow worse than any others. They are pretty typical in CCFLs and dumbest “electronic transformers”, esp these for “halogen lamps” and even some cheap SMPS designs.
It will work but with poor efficiency, that’s the reason we have such a huge range of devices designed for different voltage or current specs, otherwise the manufactures could have designed a single all purpose 1kv transistor : )
Yes, but if one goes for joule thief or 555-driven circuit, especially with BJT as switch and FR107 as diode, they don’t have to expect superb efficiency or awesome output power in compact package, right?
This said, joule thief is funny thing to power small led or so out of 1.5 volt battery. Only few relatively exotic and expensive DC-DC ICs would start up from voltages that make “joule thief” happy.
Actually a joule thief circuit is supposed to be extremely efficient, that’s why it’s called a “joule thief”. Yes, it’s been one of the most interesting inventions so far, considering the fact that it can work even with voltages lower then 0.5 V.
Joule thief key property that makes it interesting is that it runs down to like 0.3V or so, draining 1.5V batteries way below what most of other electronics could afford. Say, most CMOS-based ICs have a problem that 0.3V is way below of threshold voltage. Even “special” boost ICs like NCP1400 would start up from like 0.8V – then it would hold down to like 0.3V as well – because they start up, and then supply self out of own boosted output. However it implies startup problems if battery got below 0.8V and “cold” start happens.
This said, joule thief is kind of “blocking oscillator” – so it got no reasons to be terribly efficient. Waveforms aren’t really perfect, BJT drops some tenths of volt on C-E junction even if current is small, etc (FETs get edge in this regard generally, but most MOSFETs got threshold over 1V, so running less than 1V is a problem, lowest I know have Vg_th=0.8V). However joule thief gets its edge over many other circuits when it comes to using 1.5V batteries, draining them way more completely compared to most other circuits. So it would start and work out of batteries most equipment considers long “dead”. That’s where it gets extra power margin – partially negating its imperfections, so overall performance looks rather good.
p.s. I’ve finally got right one of these 10-year-led-blink, without getting it working I would have felt ashamed way too much – failing such a simple thing is a LOL. Grossly simplifying one (as suggested on youtube comments – just thief, cap and resistor). I’ve used 5.6uF 1206 SMD cercap, 5.1M 0805 resistor, PMBS3904 in sot 23 and hi-eff blue led – overall I’ve got shy 10uA average current while still getting very persuading bright blue flash about once in couple of seconds. I’ve also found funny enclosure for this little cheat, making it look like part of office alarm system, haha. A perfect joke for few vandal-unsafe places, granted most expensive part is battery and enclosure. And according to my computations battery would last … for hell knows how long, at 10uA average it would rather self discharge I guess. That’s probably best use of joulr thief I’ve faced to the date XD
What is the advantage to get add on a transistor BC547 feedback circuit? Please give me reply….
it is for keeping the output voltage restricted to a specified limit, and preventing any rise beyond that limit.
Thanks for yours valuable reply.Yours support in electronic science field really dedicated…god bless
.
It is my pleasure Biju!
Please for the bjt booster , how can I reduce the voltage to 7v instead of 30v as designed to charge a smart phone
sorry, you cannot use a 1.5V AAA cell to charge a smart phone.
Thanks Swag, but can 3.7v lithium battery power the 555ic. You said +5v to 12v input.
Hi Grace, yes you are right, normal 555 ICs will not work with 3.7V but the CMOS version (7)555 can be used which is rated to work with minimum 3V
Hi Swagatam! I have tested the above circuit which uses a 555 timer and the output is 38.6 volts using a 100uH through hole fixed inductor. I tried changing the pin 6 to pin 7 resistor to 10K with no change. I have 22uH, 47uH, 68uH, 100uH, 220uH, 330uH 470uH, 1MuH inductors. I tried 47uH inductor and the output voltage was 38.9v. I tried 220uH and the output voltage was about 37.8v. I tried 3v, 6v, 9v, 12v input with almost the same results. It just takes longer to reach max voltage as the supply voltage is reduced.What should I modify to get 20-24v output? I only have 20volt 1/2 watt Zener available. I looked at other posts which use a Zener to control the output voltage but they require a 1-watt Zener. Thanks!
Hi Norman, you can adjust the voltage either by changing the number of turns of the inductor or simply by adjusting the 1K value between the pin#6 and 7.
Thank you sir for replying
Hello sir Swagatam,
Thanks a lot for this post.
I would like to use the IC555 version to boost 3.7V Li ion battery to 12V. What modifications do I need to make to achieve this?
Will the output be suitable for powering circuits that have ICs in them?
Thanks Godson, you can use the same design as shown in the above article
Good afternone sir!
I would like to use this boost converter (the first picture) to lit the LED at night and
as a charger (at day) of 4.5 v cell (3×1.5 cell) .The LEd position will be also the position of cells .And on the position of the cell (on the above picture) will come a small solar panel.can you show me how to do a current limiting that can be used for both task (maybe by useing poti?).
Thankyou in advance!
Hello Shigida, I think for this low current application you could probably limit the current with a resistor in series with the battery positive or negative terminal. The resistor value could be calculated using Ohms law:
R = V/I
where V will be output voltage minus battery voltage and I will be the safe charging current of the battery. Make sure the max output is slightly lower than the battery’s full charge level.
hello, how can i make the Simple Boost Converter using a single BJT circuit work with a solar panel to charge the battery?
Hi, please see the diagram at the bottom of this article, it might be just what you are looking for
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/simplest-automatic-led-solar-light/
thanks for the reply.
however i would like to use 1 battery instead of 3 to keep the circuit as small as possible.
All the circuits referred here use a single battery. So perhaps you can try the first design from the above article
Good day Swag
I am looking for a diagram to build that can do the following. Dc booster
I got solar panels that is 53 volt and an element rated 48v resistance 7 ohm. If i connect directly it pull the panels down to 3volt.i dont want to buy a geyserwise mppt just for this.
Hi Corne, a boost converter will not solve your problem, neither is it required.
A 48V 7 ohm element would require a current of 48/7 = 6 amps. So is your 53V panel rated to provide this much current? You can check this by momentarily connecting an ammeter across the solar panel during peak sunlight.
Your element is rated at 48 x 6 = 288 watts, so you will need a 300 watt panel to ensure that the voltage does not drop too much.