In this article I have explained a very simple method of acquiring 220V DC from a 12V DC source. The idea utilizes inductor/oscillator based boost topology with the help of the IC 555.
Circuit Operation
Referring to the circuit diagram below, we see that the entire idea is based upon the versatile, evergreen IC 555.
Here it's configured in its standard astable multivibrator mode for generating the required pulses at a frequency determined by the resistors 4k7, 1k and the capacitor 680pF.
The duty cycle may be appropriately adjusted by experimenting the 1K resistor.
The output is received at pin#3 of the IC, which is fed to the gate of an N-channel mosfet.
When power is switched ON, the positive pulses emanating from pin#3 switch ON the mosfet into full conduction.
During the above periods the 12V high current potential is pulled to ground via the coil by the mosfet.
As we all know inductors always try to oppose instant changes in current polarity through it, therefore during the negative pulses when the mosfet remains switched OFF, forces the coil to dump the stored potential in it in the form of high voltage EMF pulse into the output.
This voltage may be equal to 220V DC and gives rise to the required potential at the shown outlet of the circuit.
The above straightforward operation is repeated continuously at the given frequency providing a sustained 220V DC at the output.
The BC547 and its base network is introduced for limiting the output voltage to the required degree.
For example if the required output is 220V, the 47K preset may be adjusted such that the220V mark never exceeds, irrespective of the coil back emf rate or the input voltage fluctuations.
The mosfet can be any 30V, 50 amp type, for example a NTD4302 may be used.
The coil wire should be thick enough to hold up to 30 or more amps.
Circuit Diagram

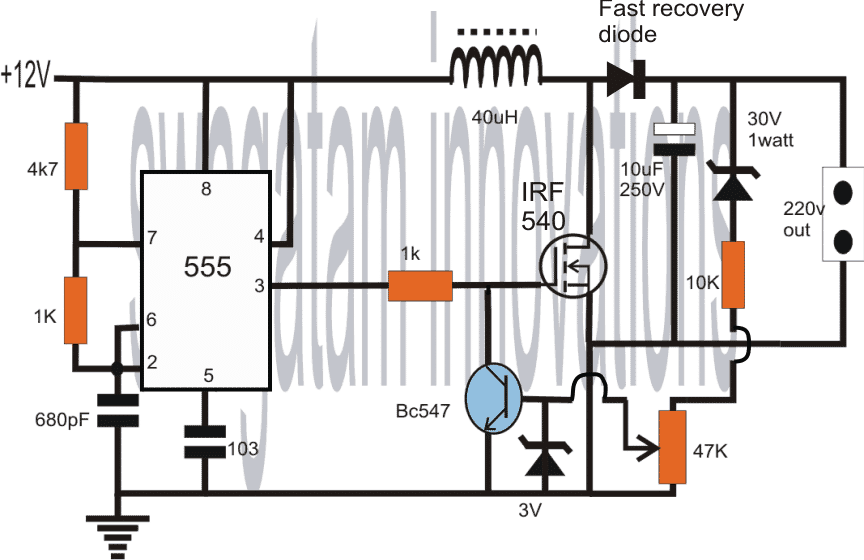
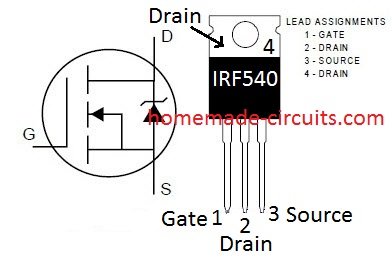
NOTE: THE MOSFET IS MISTAKENLY SHOWN AS IRF540, WHICH IS NOT APPROPRIATE FOR THIS APPLICATION, SO PLEASE REPLACE IT WITH AN IRF840 MOSFET.
WARNING: THIS CIRCUIT INVOLVES HIGH VOLTAGE, EXTREME CAUTION IS ADVISED WHILE HANDLING THIS CIRCUIT.
IC 555 Pinout Details
Mosfet IRF 540 Pinout Details

I can’t see the AC side of this circuit… looks like a boost converter can you explain how the ac signal is generated and captured? I’m really interested in what I’m missing here. Boost yes. Using the mosfet to switch short the inductor and capture the EMF. The BC547 regulates as described but maybe I’m misunderstanding something. Can you explain in detail? Thanks a lot Andrew
Sorry about the confusion, you are correct!
It is actually a 12V DC to 220V DC boost converter circuit.
I have now changed the article content and the title accordingly.
Hi
In order to work the mosfet have to be rated for Vdrain = Vout+Vf(diode). So IRF540 doesn’t fit for this application because his Vd max is 100V
You are absolutely right, please upgrade the MOSFET to IRF840.
Agree
How is the above inductor wounded and using which wire
You can wind a 1mm thick super enameled copper wire over a ferrire rod. Create number of turns which produces 40 uH value
Excellent…
thank you
i want to use a 12v dc motor mechanically coupled at the shaft to another motor shaft of a 220v ac motor– the idea is to get 220v from the driving force of the 12vdc motor. am currently doing this with a hydro generator. again the idea is to have the 12v motor make the 220v ac motor supply power to feed itself with the proper invertors in line . can this work.
That is definitely possible, however the output power of the 220V motor will be just 70 or 80% of the 12V motor power.
How much time can I use from DC 12v 45 AH to AC 220v 65W?
Hi, I need to build a transformer to be used as a inverter. 12vdc input to 220vac output at 50 hertz.
The total load the transformer must be able to take is 4 KW. I would very much like to know the wire size in mm for the 220vac side, the thickness of the wire and the number of turns.
The same applies to the 12vdc side having a center tap.
If you have a schematic, using normal components for the low voltage side to create the 50 hertz, using Mosfets. I would need a pure sine wave and not a square wave.
I would really appreciate your help.
Hi, I do not have the details of the wire size for the transformer, it will need to be selected from a chart or a table maybe.
You can probably refer to the following article for any details:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/how-to-make-transformers/
For the sine wave inveretr you can try the following concept:
Arduino Pure Sine Wave Inverter Circuit with Full Program Code
Thank you very much for your helpful circuits
fish shocker circui
Can you explain more.
Coil about 40 mikrohenry-how many turns on what(Ferrite ring,ferrite EE trafo or)Which diameter off wire?How many ampers in outside,outside power?
Can I run a1or 2 hp water pump ? Thank you very much.
No, you cannot run 2 hp load with this circuit
Then what I’ll do if I want to do this?I mean Is there any circuit or electonic devices you know to run 1hp load with DC? Thanks a lot….
you will need a 24V to 220V inverter 1 kva
Hello Swagatam!
Can this circuit be used to power the “Cell Phone Battery Charger Station in Villages “(www.www.homemade-circuits.com/installing-solar-universal-cell-phone/)
Hi Shigida, yes it can be used after proper adjustments
Swagatam,Thanks a lot.
would you mind telling me which part and how to adjust the ckt in order to get posibilly more watt out of it?
Shigida, you will have to manually experiment with trial and error, and find out which frequency produces the maximum voltage output, once this is fixed then you can replace the coil with a thicker wire coil for upgrading the current capacity of the coil.
If I convert a 12 or 15 or 50v to 230v can I connect this to home appliances if it is possible means please explain it in detail and if not means give the solution to implement the home appliances to it.
you can connect appliances which are SMPS based for exmple TV sets, LED lamps, amplifiers but not that require AC sinewave inputs like refrigerators, mixers, fans etc.
I can fool around with the RC timing parts of the ic to get the frequency but can you assist me with the coil, how man turns do you think I would need to get such high voltage.
you can try 100 turns initially, for more info you can refer to the following article
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2015/10/calculating-inductor-value-in-smps.html
Can I adjust this to get about 40 to 60khz at about 400v ac?
If so do you have any idea how much turns I would need on the inductor.
yes that's possible by appropriately setting the coil dimension and the RC timing parts of the Ic
Sir, please, give me a..idea about dc to dc converter from 12volt to 36volt for my 30watt 36volt led chip.because,i have to drive this led light from 12volt battery…
Swapan, you can try the concept which is explained in the above article.
I need a circuit of 500 watt 12 volt DC to 15 volt DC converter
You make a mistake; put a high speed diode after switching.
If you work with SMPS, high speed diode always needed!
thanks, I have corrected it now!
Thank you Manjumdar for sharing your ideas regarding this circuit built. It has been really helpful.
you are welcome Miracle.
I am trying to tell you that if 150 watt voltage booster inverter is connected to 150 watt battery,without any load or minimum wattage of load on inverter.Then,battery backup depends on inverter rating or load rating????
it will obviously depend on the load, without a load the inverter will consume negligible amount of current.
Sir, if I connect 15 watt cfl bulb to 150 watt inverter with 200 watt battery.Then, how much hours it will keep bright.
Sudip, please calculate it here:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/p/battery-calculator.html
sir how to get 24v in the circuit? and what is the frequency???
andrie, you will need to reduce the inductance of the inductor by some trial and error to get 24V at the output….for 24V you can remove the BJT and the zener diode stages which are shown at the output section of the circuit.
hello sir, please i want to make a transformerless inverter (no ferrite core transformer) with 12vdc input and 220vac as output, the wattage should be between 200watts and 500watts. is it possible?
sorry that's impossible….
Sir which ic I used for Dc 12v to 220v Ac up to 20amp current
I didn't understand what you are saying?
yes it should be also rated at above 300V…you can replace it with a IRF840
In the schematic, the output 220 volts is connected across the drain – source terminals of the 30 v mosfet ??
hello sir
can i use this circuit for charging of a dc input fan?
wat is the case when the input given 12v battery is discharged?
can i giv a input to this circuit by 12v rechargeble battery?
which mosfet i hav to use to this circuit (say the mosfet number)?
Sir you have mentioned that we can use TIP122 instead of NTD4302, then what should be the pin configuration of TIP122? I mean how should I connect the transistor into the circuit?
Dipto, yes it's possible, join its base to pin3 of the IC via a 10K resistor, emitter to ground and collector to coil
Thank you sir for your reply I will be using TIP122 instead of NTD4302 since I couldn't find them in the shop.
can i use IRFZ44N mosfet
Sir
I want to make a power inverter for 48v dc to 220v ac. Plz guide me…
Krishna, you can try the following:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2014/11/48-v-inverter-circuit.html
Hi Swagatam !
May I ask if this circuit can be used to power a laptop charger ?
Thanks
Hi Roney, yes you can used it for charging a laptop from your car battery, the inductor will need to be dimensioned and tweaked appropriately until the required 19v is achieved…
You can get high voltage at high frequency (not 50Hz) but the current would be around 100mA. How much is your load?
ok I tried building this circuit on electronic work bench but only got 8v out,
keep the BC547 disconnected initially and then check…
Which coil would i use to get 110v at 50hz
you'll have to find it by experimenting with different number of turns.
hi iam doing a project in which i need to convert 6v DC to 230v AC . after converting can i use any electrical appliances from the output of 230v AC
search for any IC 4047 inverter circuit and you can use it for your application
hi swagatam majumdar,
is possible with this circuit to fed an solenoid water valve (7w) as valve of washing machine or an little motor (4w) as flat of wave oven?
maybe is better to think an inverter circuit more complex as that you have posted in other pages?
thank you so much
regards
andrea
Hi Andrea, for a DC application, the above circuit could be used, but for AC devices an inverter would be more preferable.
220v ac 2amp load
you will need a 400 watt inveter for that, the above circuit will not work
plz reply i m waiting
hello nitin,
please tell me all the technical details of your project, only then i would be able to suggest regarding the above circuit integration.
hello sir nice work…i m planing electrick go kart powerd by sewing machine motor can i use this circuit??
i have 30ah battery ..sorry for bad english…reply fast..thank u sir….u r genius,
Hi Swagatam
I am working to use this circuit (excluding the transistor network) as a simple laptop charger from car battery.
1) One option needs a mosfet with following properties:
25V, 5A and RDS(on) 3.5 Ohms
I am not sure if such mosfet is available because such RDS(on) value is for small current mosfets.
2) The second option is to reduce the input voltage to 6V but, that needs high current regulator.
Which of these two options is more practical?
Hi Abu-Hafss,
The first option looks fine, you can use a higher rated mosfet such as IRF540 etc. it would also work as good and fulfill the results.
But that is 44mOhms whereas I need 3.5Ohms!
it's 44 milliohms which is a lot better than 3.5ohms, meaning the ON resistance of the drain to source will be just 44 milliohms.
Hi Swagatam
Can this circuit be used to power a 30-40W soldering iron?
If yes, would 12V-5A input be enough?
Hi Abu-Hafss,
yes it can be used, 12v/5amp would be just enough for that.
Hi Swagatam
I am considering to use this transformerless circuit to provide high voltage in CDI. Any comments/modifications?
Hi Abu-Hafss,
Yes, it's worth trying.
Hi Swagatam
As per my usual practice, I have simulated this circuit and got following findings;
The frequency is 510Hz. If it is decreased to 50-100Hz, the output becomes more than 1kV.
The inductor is 250µH. The capacitor is 10µF.
Following is the wave pattern:
https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/u/20969135/230V%20output.gif
There is one issue i.e. how do we convert it to 230VDC? The CDI capacitor needs HV DC for charging which is provided thru a diode (half wave rectification) but, this output cannot be rectified, neither thru half wave rectification nor full wave.
If the capacitor value is increased, the output decreases.
Hi Abu-Hafss,
You can experiment with the number of turns of the inductor for getting different voltage levels at the output, because that's the only component that is directly related with voltage boosting.
Hi Swagatam
The out put is sort triangular waves of AC 230V (fluctuating between 0-230V not between 230 and -230 at 510Hz. How do we convert it to DC??? Single rectifier or bridge rectifier is not working, the output remains the same.
Maybe, the simulator is experiencing some difficulties in performing the rectification. Based on your experience, if you simulate in your mind, do you think the rectifier/capacitor should work to give a smooth DC output?
Hi Abu-Hafss,
Just connect a couple of 10uF250V(in parallel) across the output, no diodes are needed.
sir can i use the polyester fluorescent ballast for inductor…
It will depend on the output voltage requirement, if the inductor is able to produce it then it would be fine.
Thank you sir for your reply, I'll try it.
Rashid
Hello Sir,
How can i modify this circuit to run a 150 or 100W fan.
Thank you in advance.
Rashid
Hello Rashid,
you will have to modify the coil by experimenting a little with the no of turns and wire gauge until it satisfies the conditions.
Obaid just take out 220V AC, add a step down transformer that makes it 24V and then add a bridge rectifier and two filter capacitors electrolytic 10uF 25V and a 7812 IC, u'll get 12V
okay sure i will try that and see what is the result, Thanks again sir.
Thank you sir, I had tried joule before but the problem is the current supply is not high enough.I need at least 100mA. Can I know how to increase the current or is there any way to do it?
Use parallel wire winding, meaning use two or three wires together and then wind them as per the data, this will increase the current of the transformer,also you will have to use more number of cells in parallel for supplying the required amount of current.
Hi Sir, sorry to ask this question here as I could not find a dc to dc step up circuit in your forum. I am thinking is it possible to modify this circuit to step up 2vdc to 12vdc? Thank you.
Hi Unknown,
the above circuit will require a minimum of 4V to operate correctly, I think you should try the following circuit, might just work:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2012/10/1-watt-led-driver-using-joule-thief.html
Dear sir ,
I have a battery 12v 32ah sf sonic jet , how can i charge by home made circuit ,I would like to use it as 200 Watt CFL inverter, kindly help me to making a 3 amp constant current battery charger,
thanking you,
Jayanta Roy
Bonjour Monsieur.
Pour le transistor mosfet il faut celui qui peut supporter une tension de 220V ?
Dear Jayanta,
You can try the second circuit shown in this link, but I am not sure about the transformer details you may have experiment with its size and wire gauge:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/high-current-10-to-20-amp-automatic/
you can use the square wave symbol range for checking the frequency operation of the circuit…..
if it's not working with a mosfet you can try a transistor instead, try a TIP122.
Your DMM should have a frequency measuring option, normally indicated with "kHz" symbol, otherwise it won't help.
In response to the 555 frequency triggering, when the mosfet is in the ON state, the inductor stores the specified amount of electrical energy in it and during the mosfet OFF state reverts it to the output. This back emf from the coil constitutes the 220V at the ouput…
It would be dangerous to use the above type of configuration for your requirement, you may try the following design:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2013/06/0-300v-variable-voltage-current.html
Please refer to this post, it has all the details:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2013/05/55v-110a-n-channel-mosfet-irf3205.html
Yes you can use a DMM which has a frequency feature in it.
hello again,
i need to make a just opposite project converting 220v AC to 12v/24v DC help me please or please give me link of the same 🙂
It will be difficult for me to identify exactly how you fixed the mosfet, I hope you've put it correctly.
What kind of inductor did you use and is your IC generating the required high frequency?? these two factors determine the correct operating conditions for the circuit.
Qual seria a função do DIODO ZENER , no circuito ?
If the output voltage exceeds the zener value, the zener conducts and switches ON the BC547, which in turn switches OFF the mosfet ensuring that the output never exceeds the value of the zener voltage
I would like Mr. Swagatam engineer
to teach me how to put a feedback circuit
with photo coupler in an inverter output equal to 127vac
the feedback circuit will monitor this voltage of 127vac
and make sure that it never drops or changes in any way always form
127vac and never change. Mr. could be showing here
through an article
– CI USED = SG3525
– PHOTO USED = PC817
Endel, you can refer to the following post!
The first 3 circuits, all have a feedback control, but without an opto coupler. Opto coupler can be difficult to set, so no opto couplers are used.
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/sg3525-pure-sinewave-inverter-circuit/