In this post I will explain a simple car laptop charger circuit for charging laptops from a 12V car battery using a IC 555 based boost converter. The idea was requested by one of the avid readers of this blog.
Making a 12V to 19V Converter
May I request you for a circuit diagram for a transformerless small 100w inverter which can be used with a car 12V battery to power a laptop? I've found one circuit online but as I am a very new comer to electronics, I didn't understand that. Your help will be highly appreciated. Thanks
You may also like: 12 V to 19 V Converter Circuit
The Transistor Astable Design
A classic boost converter which will perfectly suit the proposed 12 V to 24 V car laptop charger application can be quickly built using a fully transistorized design as shown below:
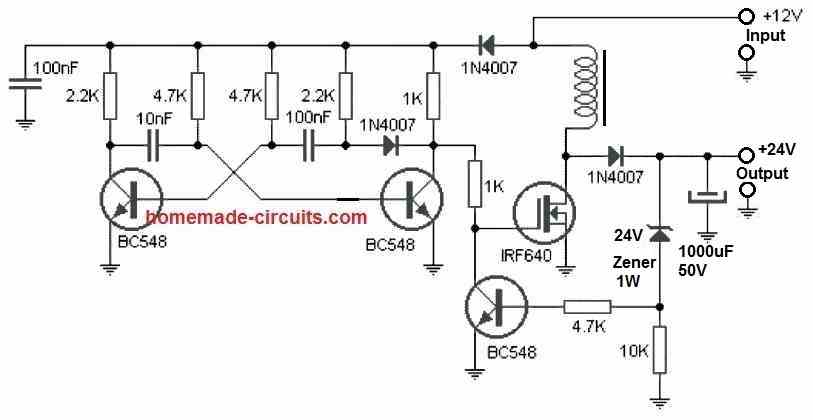
All the shown parts are standard, or could be replaced with other suitable equivalents.
The inductor which is one of main parts of the circuit is built over a ferrite rod 1 cm in diameter, by winding 100 turns of super enameled copper wire having 1 mm thickness.
Actually, the inductor is dependent on the frequency of the transistor astable. For higher frequencies the number of turns will proportionately go down, and is a matter of some experimentation. The turn number will also depend on the ferrite core shape, and may significantly decrease if a ring type ferrite core is used.
The IC 555 Design
The proposed car laptop charger circuit is actually a simply boost converter unit designed for generating the required laptop charging voltage.
A simple boost converter can be made using the IC 555, I probably have discussed it through many other posts in this blog.
As may be witnessed in the following figure, a simple yet very efficient boost converter circuit can be constructed for using with laptops from any high current source having a lower voltage than the laptop charging level.
Circuit Diagram for the Boost Converter
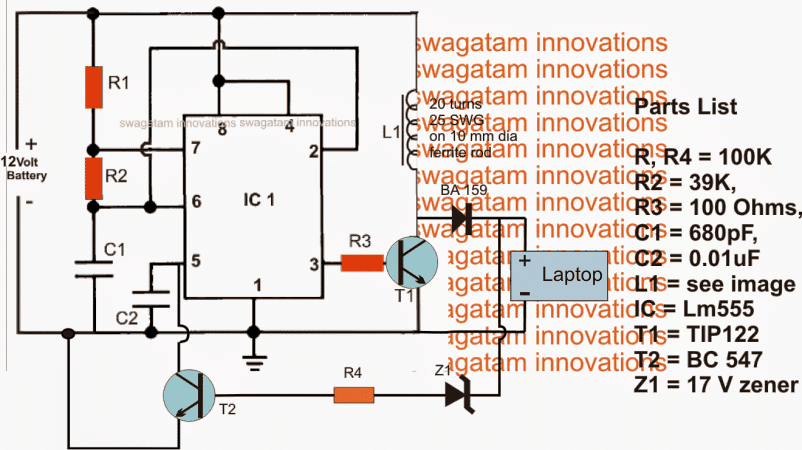
The various stages included in the above 12 V laptop boost charger circuit may be understood as follows:
IC1 which is a 555 IC is configured as a standard astable for generating a stable predetermined frequency at the rate of 12 kHz which is acquired at pin3 of the IC.
The above high frequency output is fed to the base of a driver BJT T1 for inducing the above frequency with high current in L1.
Due to the inherent property of the inductor L1, during every OFF time of T1, an equivalent amount of boosted voltage is kicked back from the inductor L1 and supplied to the load connected at the output via the fast recovery diode BA159.
The load here is the laptop which accepts the boosted voltage for charging its internal battery.
Since the laptop may require a precise 19 to 20V for the operations, the output from L1 must be regulated and stabilized in order to make things safe for the connected laptop battery.
The above criterion is taken care of by introducing T2 and the associated R4 and Z1 components.
Z1 is selected to be exactly equal to the laptop charging voltage that is at 20 V (17V is wrongly shown in the diagram).
Whenever the output tends to drift away from this value, Z1 gets forward biased triggering T2, which in turn grounds pin5 of the IC.
The above situation immediately reduces the IC 555 pin3 voltage to minimal levels for that instant until Z1 stops conducting and the situation is restored to the safe zone....the switching is sustained at a rapid speed maintaining a constant voltage for the laptop.
This car laptop charger circuit can be used for charging a laptop in any car which uses a 12V battery.
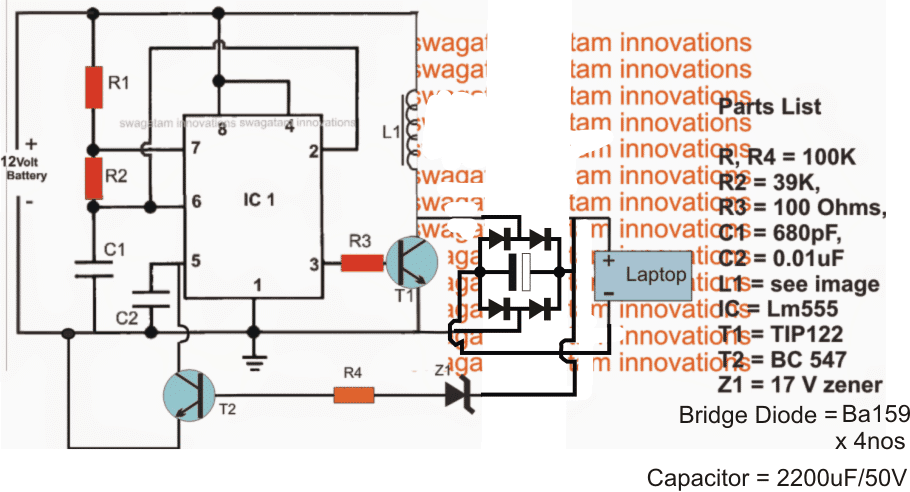
Adding a Bridge Rectifier at the Output
The above design can be much improved by employing a bridge rectifier at the output instead of a single diode, as illustrated in the following diagram:
Using MOSFET Voltage Doubler Circuit
In this post I will explain a simple circuit which may be incorporated for charging a laptop while driving in car or some other vehicle. The circuit runs without incorporating an inverter or inductors in its configuration Let's learn more.
Using Voltage Doubler without Inductor
The good thing about this circuit is that it does not rely on an inductor topology for the required actions, making the design simpler, and yet effective.
As we all know a laptop runs using a DC potential from an in built Li-Ion battery just as our cell phones do.
Normally we utilize a AC DC adapter for charging a laptop battery in homes and offices, these adapters are actually SMPS power supplies rated with the required and matching specs of the laptop battery.
However the above power supply units work only with AC supplies, and in places where an AC outlet may be available. These units will not work in places where an AC source is not present such as in cars and other similar vehicles.
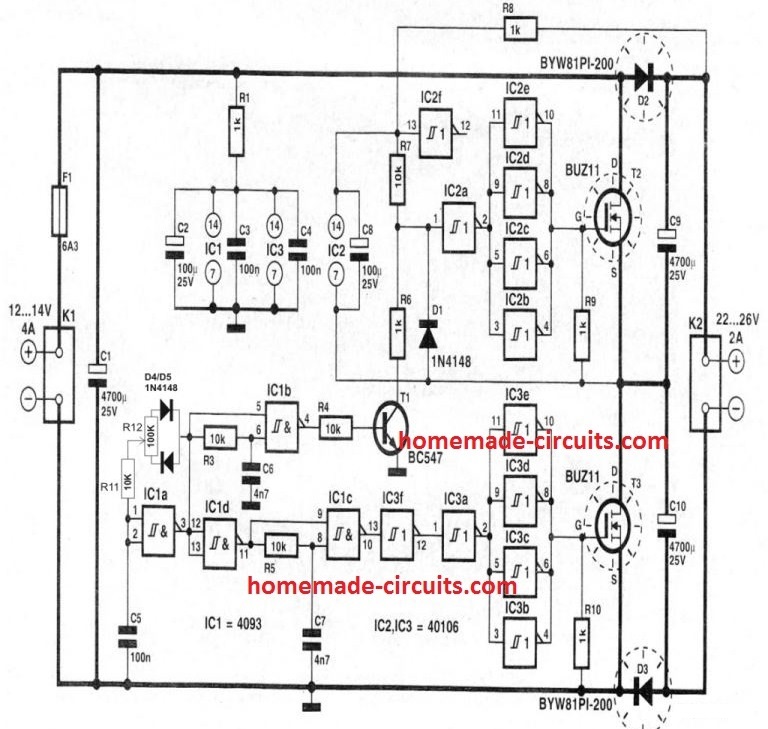
A novel little circuit presented here will allow a laptop battery to be charged even from a DC source such as a car or truck batteries (12V). It's a very simple, cheap, versatile and universal circuit which may be dimensioned for charging all types of laptops by adjusting the relevant components provided in the circuit. It's a simple plug and play charger circuit.
Normally most of the laptop adapters are rated at 19V/3.5Amps, however some may be rated at higher currents for facilitating fast charging.
PWM Charging Control
The discussed circuit has a voltage adjustment features (via PWM) which may be suitably adjusted as per the required specs.
The current may be suitably safeguarded by adding a 3 ohm 5 watt resistor at the output positive terminal.
As can be seen in the circuit diagram, the design is basically a powerful DC to DC voltage doubler circuit which utilizes a push pull mosfet stage for the required boosting of the voltage.
The circuit requires an oscillator stage for initiating the proposed operations which is configured around IC1a.
The components R11, R12, C5 along with the two diodes becomes a neat little PWM controller which sets the duty cycle of the entire circuit and can be used for adjusting the output voltage of the circuit.
Typically the circuit would generate around 22V from a 12V source, by adjusting R12 the output may be tailored to an exact 19V, which is the required laptop charging voltage.
I didn’t find lm555 can I use ne555 instead?
Yes, any 555 ic will work…
And again I can’t find ferrite rod what should I do please ????
Any type of ferrite will work the one which are used in radio receivers are the best.
Or you can use a ferrite ring core also, select a bigger one so that it can accommodate at least 100 turns using 0.5mm thick magnet wire
can i use any of this circuit to increse the out put to 240v with a input of say 120v
It may be possible but for that you will have to upgrade all the transistors to 400V and calculated the resistors using an astable calculator.
Please how many amp is the output
Will depend on the coil and the transistor power
Hello Sir, my name is Precious Victoria from Nigeria. I really love what you are doing here. I wish I could be on your team.
Thank you Precious, I appreciate your thoughts very much!
Greetings Sir,
So sorry correction of the first comment
You are doing a great job. Please sir I need your help with a circuit that will help me switch automatically between two batteries connected to my inverter so I will not use a panel to charge the batteries. They work interchangeably
Hi Donald, you can try the last circuit from this article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/automatic-dual-battery-charger-with/
Hi Swagatam,
First I thank for your help. I made some projects. I want to supply power from 12V battery to My old laptop when there isn’t main power. My laptop(LG Xnote LW25) hasn’t battery and charger adapter is 18.5V/ 3.5A. Which one should I change. Can I use UF4007 instead of BA159? And any other alternatives for 17V Zener and TIP122.
Thank You.
Thank you PLAA, I think you can try the first circuit which looks more robust and reliable. The 555 circuit is also good but you may have to experiment with the coil a bit to find exactly what number of turns provides the best results. 1N4007 can be tried but BA159 will be better, you can also try FR107. Instead of 17V zener you can use two 9V zener in series. You can use TIP3055 instead of TIP122
Thanks. I’ll try to do it.
Hi Swagatam,
I have bought a cheap 12VDC source to 19VDC(selectable) power adaptor for my laptop that generates a lot of heat (almost too hot to touch) and so wastes a lot of my valuable off-grid amp-hours. It smells like something’s burning/melting too. If there are several circuit types that cater for this requirement then which of these, in your mind, is likely to be the least wasteful and the most efficient? I have skimmed over some of the comments here regarding heating and possible tuning so is my observed problem down to the fact that the circuit I have bought is an approximation of the ideal design to cater for the selectability rather than being optimised for the fixed output voltage that I need? Thank you.
Hi Tim, if the adapter is heating up without a load then it is a faulty design, if it is heating up with load then probably the parts are not appropriately rated. Even with the selectivity feature a switched power supply should not heat up.
The first design from the above article can be optimized for a fixed output or even a selectable output without much heating up, provided the coil is correctly wired
Is there any chance you or anyone has created digital version of these circuits on an application like EveryCircuit?
Hi Swagatam, I’m testing the circuit (IC555 with rectifier bridge – L1 20 turns) with a regulated power supply (12V 2amps). I’m getting 27V of output (testing with a 1k resistor connected). The TIP122 is quite hot. Should I reduce turns from the coil, and add a bigger heatsink? I’m using a 35mm * 25mm *15mm aluminum heatsink.
Hi Juan, I think you can try increasing the number of turns, and use a thinner wire, may be a 30 SWG. Heatsink may be also required, and you can also experiment with the PWM adjustment.
Hi Swagatam
What if I have the input of 30v DC and the desired output is 19v -3amp
Then what are the changes I need to make???
Thanks
Hi Shuvam, you will need a buck converter for that, not a boost converter
hi, what shall be max current for this circuit?
Hi, it is around 1 amp
hi dear sir i would require an circuit that convert input 220v to 5 v withe transformerless and fully to be protected from hi voltag withe output 5 volt to doing input voltag for chip atmega
Hi dear sedigh,
you can try the first circuit from the following article, you can adjust the pot to set the required 5 V:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/how-to-make-led-bulb-circuit/
sir , i am doing a project on electric vehicle charger so i need some information regarding , AC-DC converter circuit for single phase 230v , can you help me with circuit design for an output to charge the electric car battery
Hi Varun, I will try to help, please provide the full specification of the battery.
Hi Swag,
I remember posting a while back about making a high speed shutter using a 35v solenoid on a 5-6v circuit. The issue was charging a capacitor to deliver that jolt to the solenoid on command. I already have an ATTINY85 to control the signal to activate the shutter.
I think the last post I made on the question vanished as I cannot find it anymore.
So which circuit would I use to do this? I think from memory it was a 555 circuit.
Thanks as always!
Hi Nathan, do you remember under which post it was posted? because I don’t remember deleting any comment so far.
As for the mentioned question, you could use an IC 555 based monostable for powering the solenoid for a fraction of a second in response to the shutter triggering. You can implement the concept shown in the following article
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/intruder-position-indicator-security/
remove the piezo connection and replace it with the trigger from the MCU. Use a higher value for C1, may be around 4.7uF for an optimal response. The output ON time can be adjusted by tweaking the R3, R4 C2 values.
I remember you said a few posts were lost in anti spam plugins. I searched for the original and couldn’t find it.
I have the sketch for triggering and sending the signal to the shutter for the desired amount of time already on the ATTINY85, so simply charging the capacitor and releasing the charge into the solenoid is the part of the circuit I need to do. Thanks, I’ll check the link.
Can you please post the question in the forum section, I will try to figure out the design and post the schematic there.
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/community/electronic-circuit-forum/
i have query about my laptop charger project.
Using a step-down transformer (220V to 12V) with the polaroid capacitor (35V 1000microF), diode(N4007) and resistor(1K)….the voltage we are obtaining is 18 V instead of 12V.
how is this possible? kindly point out this issue and will be really thankful for that.
The 12V from the transformer is the RMS values of the AC. If you connect a rectifier and a filter capacitor, the output turns into DC having the peak value of the AC. The peak value can be calculated by multiplying the RMS voltage with 1.414.
12 x 1.414 = 16.96
Hi,
Hey I’m looking at the picture you posted, is it really this circuit that is shown? ‘caus the components don’t match as far as I can tell(unless the BC547 and some other comps are hidden somewhere)…
I’m wondering about how this circuit is optimized for a laptop requiring 19.5V/4.74A(90w), and how much current it would consume on the 12V input side…
I wonder if there is any way to have the inductance(ex. 150mH or 330µH or other value, if relevant) equivalent for the inductor, If possible… I have access to NI Multisim, a circuit simulation software and I’d like to run some tests before purchasing the parts(In case I need bigger/smaller caps or resistors or a TIP142 instead of the TIP122)…
It would be for a sailboat(the less current we use, longer battery autonomy we have)…
’till now we’re using a 12->120V(AC) 200W power invertor, I don’t remember the power consumtion it pulls as we haven’t used it since september ’17…
I understand the basics of your circuit, but sadly I don’t yet have enough knowledge to determine if this circuit would allow any power saving, if anybody has any info on this matter, I’d be very grateful.
Best regards.
Hi, the picture and the diagram are different. The picture was referred by the requester, while the diagram was designed by me.
You can study the last expression presented in the following article, for evaluating the output voltage from the buck converter
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/calculate-current-voltage-buck-inductor/
However if you are using a 12V to 120V inverter then the above circuit won’t be necessary, you can simply purchase a ready made laptop charger and use it with your 120V output from the inverter
Ok so If I understand correctly, you’re saying that on the power/current consumtion and efficiency side, it’s better to keep using a 12V to 120V with the OEM(120V->19.5V 4.74A) laptop charger?
Thanks for the fast answer!
Yes that’s right, otherwise it would be an overkill, converting battery 12V to 120V, then back to 12V from 120V, and yet again from 12V to 19V.
Just to be sure you understood my first post correctly, I am considering this circuit to connect the laptop directly on 12V batteries by converting 12V->19.5V/5A, thus bypassing the 120V AC inverter and the AC OEM laptop charger.
I tried simulating your circuit, bus as I can’t get an exactly matching inductor value, I can’t get a relevant simulation…
In that case the above circuit can be used.
I do not have the exact data for the coil and the frequency, it will need to be identified with some trial and error, by building and experimenting the circuit practically.
If possible I may solve it myself with a video within a couple of days.
Hi again Swag,
That would be great.
In the meantime, I’ve found an interesting alternative circuit that seems to be simpler, based on the LM2587-ADJ and requires fewer components. It’s also providing an higher frequency, at 100KHz.
I’ll evaluate both options once I’ll have all the components specs.
Hi Mpil23,
The mentioned IC seems to be a buck converter IC, not a boost converter. It is designed to reduce input voltage, your requirement is the opposite
Sorry, but you seem to be misstaken about the LM2587-ADJ….
It’s more expensive, but appears to have good performances.
There’s even already-made circuits, which aren’T set for the voltage/intensity I’m looking for, as 12->24V/1A or 5V->12V/1.2A…
OK yes, I seem to have read the datasheet in a hurry and interpreted the diagram wrongly. in that case you surely can give it a try.
Hi Swag,
I must really apologize for wasting you time, but I was like a kid in a toy shop with all the circuits. I should have read the description properly. This is a clever and very elegant solution. The trick lies in the Zener to protect the battery. Goes right to the heart of the problem.
I assume this will work for a 20V, 3.25A input. I cannot see any protection circuit for when the battery is full, so maybe I should look for another circuit. But that’s fine, I will build this one in any case for practice. See what it does.
The queries from project builders are very useful, so I should read them as well for problem solving.
Great!
Go well,
Christo.
Hi Christo, that’s the correct way to proceed! Reading the whole content will allow you to get clearer idea regarding the concept, and experimenting practically will help you to verify your learning…and never be afraid of failures, it is the part of the course.
The input will be 12V for the circuit which will be boosted to 20V for the laptop battery
Hi,
Thank you , this is a blessing. I can use your circuits with confidence because you explain component characteristics very well. I found two circuits, this one and the MPPT charge controller that I may use for my project.
I want to build a charger for a 12V battery as main back up power to my Lenovo G580 laptop when I am out of the car. I want to make this unit as compact as possible and preferably add a solar panel as first power source.
The input leads to the back up battery from the panel are connected in parallel to the output leads to the laptop. How do I isolate the laptop from the solar panel or grid power in case I forget to throw the DPDT switch to isolate the charging power?
I can also later power my Huawei B315 router from this with another small circuit. Could you possibly give me some search terms to find circuits like that here?
Thank you Christo,
If you have understood the stages well then surely you will be able to make them successfully, I wish you all the best!
If you have any further doubts please feel free express them here.
Is this circuit’s output current arround 5 ampere Sir? If i want to use it to supply 100watts/ 24volts dc stereo car amplifier do i need to change the tip122 to a higher one?
Azzam, for 5 amp you may have to upgrade the design by using thicker wire for the coil, and a 2N3055 BJT in place of TIP122
Thx v much sir..
hi bro, i am planning to build a phone battery charger (5v/500mA) ,from a 4v/2Ah rechargable battery. but i am having a problem to boost 4v to 5v. iv tried a joule thief circuit with zener stabilzation at 5.1v but its not working also i could not find a ready made ic
so plz can you tell me how to modify the joule thief circuit or is there any other method to charge mobile battery from 4v rechgble btry.
Hi Kiran, a Joule is the right circuit for such applications, just make sure that you dimension the secondary side winding optimally by using reasonably correct number of turns and by using bifilar winding technique, that is by using many thin copper wires together forming a bunch, and then winding it on the core….preferably use a torroial core, and try to adjust the winding such that it gives around 5.5V without a zener assistance.
PLEASE SIR AFTER DESIGNING THE BOOST CONVERTER MY MOSFET WAS HEATING VERY FAST. AND THE OUTPUT WAS 51VOLT BUT WHEN LOAD IS APPLIED IT GOES DOWN TO 11VOLT.
MOSFET USED IRF3205,IRF2805
BATTERY VOLTAGE 12VOLT 7AMPS
what is your load voltage and current specs?
to solve heating issue adjust the frequency by adjusting R1 value.
How do I use the ammeter,? I can use the voltmeter
connect ammeter probes directly across the output wires for a 1 or 2 seconds and check the reading quickly….make sure the ammeter’s range is appropriately set.
Good day Sir,I have been for a while ………………pls sir, how do I get the power rating of my inverter i.e ,The output ,using my voltsmeter,……thanks sir
Hi AG, you can do it using voltmeter and ammeter, check the output using both these meters and multiply the result
Many thanks sir.
Sorry to disturd again.
1. Can I also use panel of 100watt 5.1A 19v directly to the this circuit in a daytime.if not,suggest me any way to modifier the circuit? I will use the battry to at night.
2.your Automatic solar light circuit using relay changeover could use the above panel to charge the 14.5v.470wh battry alone ?if not possible suggests me other way.
Best of luck!
Abubakar,
the above circuit is for 12V input, not for 19V, what is your actual requirement by the way??
which automatic solar light with relay are you referring to??
Thanks sir ,But i do not know how to measure the output of my inverter.
measuring is not required, you can tell by refering to the specification of your inverter, I am sure it will be either 220V or 120V,
By the way you should be already knowing this??
sir now am geting exactly 25v and thats fine. thanks so much
am left now with handling the heating transistor only
That’s great OLupot, remember the frequency must match the inductance otherwise the transistor can get hot, therefore you can try tweaking the frequency also to control the heat…this might again result in the reduction in the output voltage and you may have to add a few more turns on the coil until you get just the right balance.
hello sir am now geting a doubled voltage of up to 40v from 12v but i want 24. i had made 23turns . but also it has blown up my tranistor. stil working on it
Good, that means your circuit is now working, connect a 1K resistor at the output and recheck the voltage, if still the voltage remains at 40V then you can reduce a few turns from the coil and check the response….use a 100V rated BJT uch as TIP31C etc
may be am not putting it right.All I needed is to use the battery for longer hours while watching TV. I have a smaller TV before.It uses an adaptor connected to a step down transformer.I also want something like that for this big TV 38” .how best can I go about it .Which circuit diagram ,do I build for it or how best can I do it sir.I need your expertise advice
you just have to tell me your TV input specs and inverter output specs…
if these two match then you can do nothing about it because everything is perfect in that case.
if your adapter is converting the inverter 220V to TV DC level then still it is perfect as long as the adapter is not malfunctioning or the TV is not malfunctioning
The battery is okay,blc I use it and its serves without the TV.What I need is the circuit diagram that will tap little from the inverter and boost it for the requirement of the Tv,which ic 220v,1.8A.Thanks
what is the output from the inverter? is it not 220V?
Hello Sir swaggatam .I really appreciate your contribution in simplifying electronics for the lovers of it .I am, AG, I love electronics.please I need a help,my flat screen TV drain my battery quickly when I use it on my inverter.
I need a circuit that supplies that will take little from my inverter and supplies (220v ,1.8A) that is required by the TV ,in other to make my battery last longer when am watching TV on my inverter. thanks
Thanks AG, your TV is probably consuming what it requires for operating correctly from the inverter…so it’s not the fault of your TV.
Your battery may be draining quickly either because it is not appropriately rated as per the TV wattage specs or it is old and has lost its efficiency.
ya its giving out a clear sound and 6.7v.
keep increasing the frequency until the sound just vanishes…after this you can try it with the boost converter stage, it should work, I hope you have wound the coil over a ferrite core.
hello sir i get 6.5v at pin#6 and 12.7v at the output input 12.9v . i stil have a problem with the inductor but atleast its promising i keep looking out for where the fault is but also need ur help thanks
is your IC 555 oscillating? first you must verify this using a frequency meter or a small loudspeaker connected across pin#3
Salil, the current simply depends on the specs of the transistor and the coil provided the input is also sufficiently high in current…you can upgrade the transistor rating accordingly and use a thicker wire for the coil to acquire 6 amps at the output…
Sir…how much max current can it supply?
Can I use the same circuit for 19v, 6amp specs?
Hi, swagatam
i find your site useful alot and i visit it always, thumbs up to you and your good work
please, i want to ask can use a 12 volt @7AH lead acid battery for this project?
Thank you Koby, yes definitely you can use a 12V 7AH battery for the discussed purposed
hello, the circuit looks really promising on the photo so i tried to simulate it but didnt get any voltage or rather 93 nV which is basically nothing and i did try changing the inductor but that didnt make any difference either.
I really like you post which are very helpful for a newbie like me. It helps me to learn alot.
Thank you.
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B4EByIot_JMncEV1SVdYc3pZVjQ/view?usp=docslist_api
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B4EByIot_JMnQlNrLVh0c0wxbWs/view?usp=docslist_api
Hi, The circuit is a standard IC 555 boost converter design so there's no doubt about the configuration, it has to work. I would suggest you to build it practically and check it…I am sure you would be able to get the results instantly, because I could get an instant boost conversion when I tried it. I could boost a 12V source to 80V.
Alternatively you can try removing the BC547 feedback link and see if that helps the situation in your simulator.
very good post..
i should try..
swagatam ji can i salvage one of output filter choke (toroid core) of 450w coputer smps to use as a inductor for the boost charger?
regards
chinmaya
bhubaneswar
thank you chinmaya kumar, yes you can do it, but you may have to manually adjust the number of turns of the inductor with respect to the frequency and duty cycle for getting the most favorable results
can you send for me printed circuit of project ? Thank you
Hello sir
Tip 122 transistor heats up for the circuit that I followed as mentioned. And after sometimes it gets damaged. Any solution for it.
did you use a heatink for TIP122?….or you can also try a 2n3055 instead which is more powerful than TIP122
Try connecting a 1k series resistor on the input of the PWM,it helps on reducing the heat of the switch(transistor or mosfet). And heatsink too. I based this on your other circuit that uses PWM.
Sir why the voltage drop down from 19.5 to 14 or 15 volts when laptop is connected?
It's due to lack of adequate current….use more parallel wires with the existing coil turns to increase current…or may be the input itself is lacking the required current
So R2 will be a pot, do I need to increase the no of turns of the inductor to achieve a higher voltage at only 30 volt max?
yes higher coil turns will enable proportionately higher level of voltage
hello sir,
is it possible to acquire an adjustable voltage by replacing Z1 into a 30 volts zener and R4 into a potentiometer?
the output voltage would be 12-30 volts adjustable.
and if T2 will also be change what could be the replacement.
hello jerico, using a pot for R4 will not help to achieve this…a better approach would be to use a pot for R2, and use it as a PWM control and for varying the output voltage
I have connected 1k across 2200 uf
Are there any replacement of tip 122 with high current and voltage ratting?
TIP142 is one transistor that's rated higher than TIP122
you can also try 2N3055
Hi I have successfully adjusted this circuit for 19.5 v output now I m going to connect the charger pin. But the pin have three wires red and black for +ve and -ve and third one I think for sensing its color is white. Where to connect that wire or leave without connecting?
according to me the white wire could be left open and only the red and the black wire considered…..It's better to consult a laptop technician to be entirely sure.
I soldered this circuit it givese 18.5 V at the output but after a few seconds it heat up the tip122 any solution? I also coconnected 2200uf/25 v dielectric capacitor but still it heating up!
TIP122 may show some heating that's normal, however you can try changing the frequency and see the response.
Replace R1 with a 1M pot and experiment with its adjustment and check the results.
make sure to connect a 10k resistor in series with this pot otherwise your 555 may be at a risk of blowing-off while adjusting the pot.
also make sure to connect a resistor across your 2200uF cap…a 4k7 will do
Zafar can i please have a diagram of your final circuit?
The wire gauge is used is 25
gauge is not important, the diameter of the ferrite core and the number of turns are only critical
Respected sir I connectted 2200uf /25v and 1k across the output I also connected the bc547 and 1 ohm resistor with tip122 as u mansion in the other diagram. Now the output of the ckt is around 11.5 V . I changed the no of turns from 15 to 20 but the output is not increasing.
Zafar, it's simple boost circuit and should work as stated, it will be difficult to troubleshoot your assembly because I can't check it practically.
You can Google "IC 555 boost converter circuit" and see the other online versions, and correct the design accordingly.
read only those circuits which has a coil (inductor), other versions could be useless
Hello Majumdar happy to see this circuit.. as i was making a mini project "solar powered laptop charging" for my school competition..
im using a ups battery for the source which is powered by solar panel..
i need to know that this circuit can be used to charge the laptop from 12v 7.2ah ups battery..
Hello Sanjay, yes this circuit can be used with a 12V 7.2 ah source also….but the coil is crucial and should be experimented correctly to get the most favorable outcome.
the diameter of the ferrite rod that I used will be around 15 mm so can I reduce the no of turrens?
initially try with 30 turns and then you can experiment by reducing the turns and simultaneously checking the voltage.
if possible add a current control stage with the TIP as indicated in the following article in order to make the circuit failproof:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2015/11/make-this-power-bank-circuit-using-37v.html
I soldered this ckt but I did not find ba157 in market so I connected general diode 4001. when I connected the ckt to 12 v battery it burrent the tip 122. sir can u tell me the cause of burning of tip122
connect a 1K resistor and a 2200uF/25V across 1N4001 output and ground…if still it burns then the coil could be the one which will need to be examined, and wound again
Sir.can I use this circuit to charge a nickel cadmium battery of 9v.I am getting output from the solar panel in a range of 6v.300ma can I able to change this voltage into 9v for charging my nickel cadnium battery.I have one more doubt that how to choose a charging current to charge the nickel casnium type batterybattery.please reply sir
Vijay, yes you can use this circuit for your application, for controlling current you can employ a LM317 circuit and use it in between the solar panel and the above explained boost circuit.
You can use the first design shown in the following article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2013/06/universal-high-watt-led-current-limiter.html
The circuit from the first picture was sold to me as a LED 12V 100W power booster supply. But the LED had a max of 38VCC and the circuit was burning out at 32V.
So now i am study your underwater LED light controller to see if i could get more light out of the LED with that one.
what was exactly burning in the circuit? if it was the capacitors you can change them to 50V specs, anyway thanks for updating the info.
sir if we charge our battery by too much high frequency,will not the battery damage???????
A pulsating voltage can actually induce healthy effects on a connected battery….but if you are not sure, you can add a 100uF/25V capacitor after the BA159 diode, which will convert the output to a pure DC
which email are you referring to? please click on the diagram and check the out parts list on the right, everything is given there….all the resistors are 1/4 watt rated
I have updated the bridge rectifier circuit at the bottom of the article
No, Inductances do not have substitutes
sorry I do not have any simulation details because I have not yet simulated it. I have only tested it practically with perfect results
simulation is not actually necessary for such a simple design, you can simply make it and start using it
this is one of the simplest and the most reliable one that you can get, anything simpler than this looks difficult
can anybody tell me from where should i get the inductor mentioned above please its urgent
just wind 20 to 30 turns using a 20SWG magnet wire over a ferrite rod, that's all your inductor will eb ready…
sorry no idea about it, you can try the above circuit instead.
A dc dc boost converter uses IC LT1370HVCT7 from linear technologies, i could not find this in markets , any possible substitutes for this? if so please help….
thank you…