The lead acid battery charger circuits I have explained in this article can be used for charging all types of lead acid batteries at a specified rate.
This article explains a few lead acid battery charger circuits with automatic over charge, and low discharge cut off. All these designs are thoroughly tested and can be used to charge all automotive and SMF batteries up to 100 Ah, and even 500 Ah.
Introduction
Lead acid batteries are normally used for heavy duty operations involving many 100s of amps. To charge these batteries we specifically need chargers rated to handle high ampere charging levels for long periods of time.
Lead acid battery charger are specifically designed for charging heavy duty batteries through specialized control circuits.
The 5 useful and high power lead acid battery charger circuits presented below can be used for charging large high current lead acid batteries in the order of 100 to 500 Ah, the design is perfectly automatic and switches of the power to the battery and also itself, once the battery gets fully charged.
UPDATE: You may also want to build these simple Charger circuits for 12 V 7 Ah Batteries, check them out.
What does Ah Signify
The unit Ah or Ampere-hour in any battery signifies the ideal rate at which the battery would be fully discharged, or fully charged within a span of 1 hour.
For example, if a 100 Ah battery was charged at 100 ampere rate, it would take 1 hour for the battery to get fully charged. Likewise, if the battery was discharged at 100 ampere rate, the backup time would last not more an hour.
But wait, never try this, as charging/discharging at the full Ah rate can be disastrous for your lead acid battery.
The unit Ah is there only to provide us with a benchmark value which can be used for knowing the approximate charge/discharge time of the battery at a stipulated current rate.
For example when the above discussed battery is charged at 10 ampere rate, using the Ah value we can find the full charge time through the following formula:
Since charging rate is inversely proportional to the time, we have:
Time = Ah Value / Charging Rate
T = 100 / 10
where 100 is the Ah level of the battery, 10 is the charging current, T is the time at the 10 amp rate
T = 10 Hours.
The formula suggests it would ideally require around 10 hours for the battery to get optimally charged at 10 amp rate, but for a real battery this may be around 14 hours for the charging, and 7 hours for the discharging.
Because in real world even a new battery won't work with ideal conditions, and as it ages the situation may get even worse.
Important Parameters to be Considered
Lead acid batteries are expensive, and you will want to ensure that it lasts as long as possible. So please do not use cheap and untested charger concepts, which may look easy but may harm your battery slowly.
The big question is, is ideal method of charging a battery essential? The simple answer is NO. Because when we apply ideal charging method as discussed in "Wikipedia" or "Battery University" websites, we try to charge the battery at its maximum possible capacity.
For example, at the ideal 14.4 V level your battery may be fully charged, but it can be risky to do this using ordinary methods.
To achieve this without risks you may have to employ an advanced charger step charger circuit, which can be difficult to build, and might require too many calculations.
If you want to avoid this, you can still charge your battery optimally (@ around 65%) by ensuring that the battery is cut-off at a little lower level.
This will allow the battery to be always under less stressful condition. The same goes for the discharge level and rate.
Basically it must have the following parameters for a safe charging which does not require special step chargers:
- Fixed Current or Constant Current (1/10th of Battery Ah Rating)
- Fixed Voltage or Constant Voltage (17% higher than Battery Printed Voltage)
- Over Charge Protection (Cut-OFF when Battery gets charged to the above level)
- Float Charge (Optional, not compulsory at all)
If you do not have these minimum parameters in your system, then it may slowly degrade the performance and damage your battery, reducing its back up time drastically.
- For example, if your battery is rated at 12 V, 100 Ah, then the fixed input voltage should be 17% higher than the printed value, that's equal to around 14.1 V ( not 14.40 V, unless you are using a step charger).
- Current (ampere) ideally should be 1/10th of the Ah level printed on the battery, so in our case this can be 10 amperes. A slightly higher Amp input can be fine since our full charge level is already lower.
- Charging auto cut off is recommended at the above mentioned 14.1 V, but it's not compulsory since we already have the full charge level slightly lower.
- Float Charge is a process of reducing the current to negligible limits after the battery has reached full charge. This prevents the battery from self discharging and holds it at the full level continuously until it's removed by the user for usage. It is completely optional. It may be necessary only if you are not using your battery for long periods of time. In such cases too it's better to remove the battery from the charger and top it up occasionally once every 7 days.
The easiest way to get fixed voltage and current is by using voltage regulator ICs, as I have explained below.
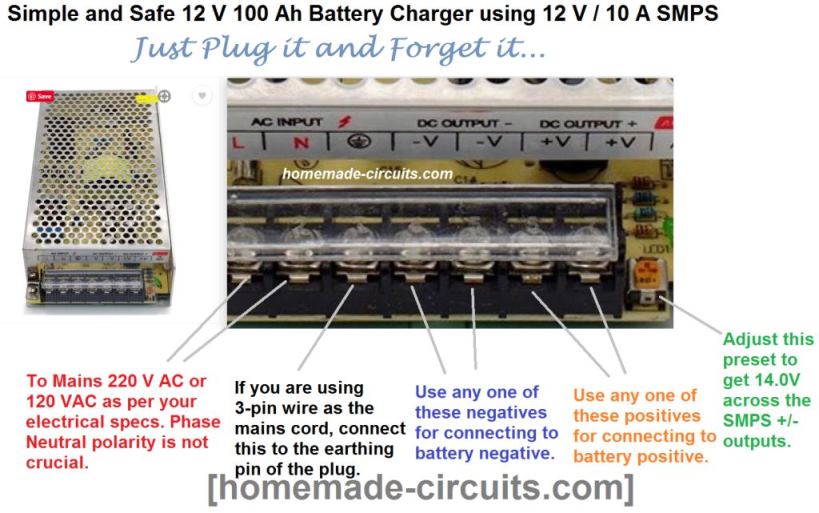
Another easy way is to use a ready made 12 V SMPS 10 Amp unit as the input source, with an adjustable preset. The SMPS will have a small preset at the corner which can be tweaked to 14.0 V.
Remember you will have to keep the battery connected for at least 10 to 14 hours, or until your battery terminal voltage reaches 14.2 V.
Although this level may look slightly undercharged than the standard 14.4 V full level, this ensures your battery can never get over charged and guarantees a long life for the battery.
All the details are presented in this infographic below:
However, if you are an electronic hobbyist and interested to build a full fledged circuit with all the ideal options, in that case you can go for the following comprehensive circuit designs.
[New Update] Current Dependent Battery Auto Cut OFF
Normally, a voltage detected or voltage dependent automatic cut off is used in all conventional battery charger circuits.
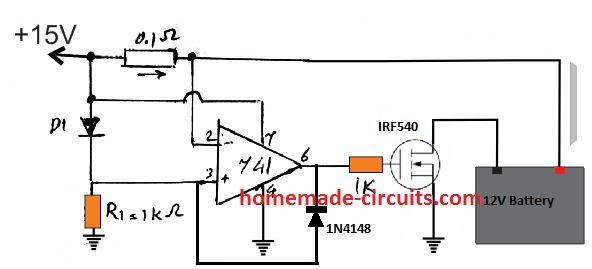
However, a current detection feature can be also employed for initiating an auto cut off when the battery reaches its most optimal full charge level. The complete circuit diagram for the current detected auto cut off is shown below:
How it Works
The 0.1 Ohm resistor acts like a current sensor by developing an equivalent potential difference across itself .
The value of the resistor must be such that the minimum potential deference across it is at least 0.3V higher than the diode drop at pin 3 of the IC, until the battery has reached the desired full charge level.
When the full charge is reached this potential should come down below the diode drop level.
Initially , while the battery is charging, the current draw develops a negative potential difference of say -1V across the input pins of the IC.
Which means that the pin 2 voltage now becomes lower than the pin3 voltage by at least 0.3V. Due to this pin 6 of the IC goes high allowing the MOSFET to conduct and connect the battery with the supply source.
As the battery charges to its optimal level, the voltage across the current sensing resistor drops to a sufficiently lower level causing the potential difference across the resistor to become almost zero.
When this happens, pin 2 potential rises higher than pin3 potential, causing pin 6 of the IC to go low, and switching OFF the MOSFET.
The battery thus gets disconnected from the supply disabling the charging process. The diode connected across pin 3 and pin 6 locks or latches the circuit in this position until power is switched OFF and ON again for a fresh cycle.
The above current dependent charging circuit can be also expressed as given below:
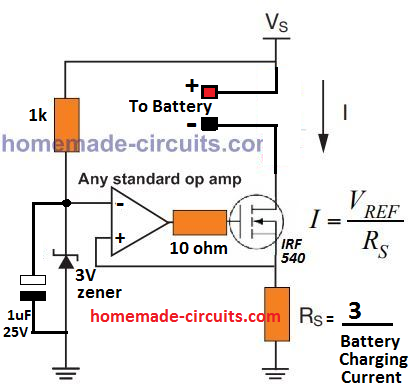
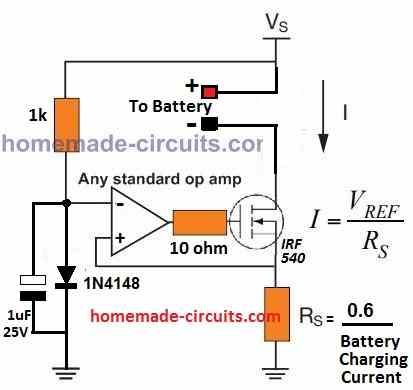
When power is switched ON, the 1 uF capacitor grounds the inverting pin of the op amp causing a momentary high at the op amp output, which switches ON the MOSFET. This initial action connects the battery with the supply via the MOSFET and the sense resistor RS.
The current drawn by the battery causes an appropriate potential to develop across RS which raises the non-invering input of the op amp above the reference inverting input (3V).
The op amp output now latches ON and charges the battery, until the battery is almost fully charged. This situation reduces the current through RS such that the potential across it drops below 3 V reference and the op amp output turns low, switching OFF the MOSFET and the charging process for the battery.
The above current dependent battery charging system design can be understood more elaborately in the below comprehensively drawn diagram, which can be used for charging very high capacity batteries in the order of 200 Ah to 500 Ah very safely:
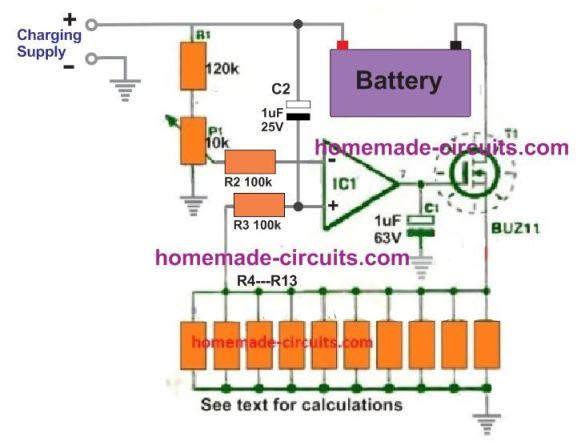
Adjust the 10 k preset so that just around 0.3 V or 0.4 V is available at the (-) input of the op amp, and set the R4---R13 resistor bank such that their net resistance is:
R = 1 / Max charging current.
Suppose the battery is 100 Ah, then the max charging current will be 10 amps, therefore,
R = 1 / 10 = 0.1 Ohms
Calculating the Parameters Accurately to Improve the above Design
The gate resistor affects the charging and discharging of the MOSFETs gate capacitance, which determines the switching speed. The formulas and explanation for improving the circuit are given as shown below:
Sense Resistor (Rs): We can calculate the charging current through the sense resistor:
I = Vref / Rs
Where:
I is the battery charging current.
Vref is the reference voltage applied to the op-amp's non-inverting input.
Rs is the sense resistor value.
To calculate Rs we can use the following formula:
Rs = Vref / I
For example if Vref = 0.6 V and the target charging current is 1 A:
Rs = 0.6 / 1 = 0.6 ohms
The power dissipation across Rs is given by: PRs = I2 * Rs
For a 1 A charging current:
PRs = 12 * 0.6 = 0.6 W
Please Choose a resistor with a power rating of at least 1 W for safety margin.
Reference Voltage (Vref): You must adjust the Vref to be stable and can be generated using a precision voltage reference IC or a resistor-divider network with a Zener diode. If you want the charging current needs to be adjustable then a potentiometer can be used to vary Vref.
Capacitor (1 µF): This capacitor stabilizes the op-amp input. It s value can be estimated using the time constant:
Tau = R * C, Where the Tau is the time constant, the R is the equivalent resistance seen by the capacitor and C is the capacitance value.
Make sure to Use a low ESR ceramic capacitor to ensure proper filtering.
MOSFET (IRF540): The IRF540 has a threshold voltage (Vgs(th)) of ~4 V. You must ensure that the op-amp can supply sufficient gate voltage for full enhancement. If the op-amp supply voltage is low (e.g., 5 V) then you must replace the IRF540 with a logic-level MOSFET like IRLZ44N.
Diode (1N4148): This diode ensures the proper operations but for better efficiency it can be replaced with a Schottky diode which has a lower forward voltage drop.
Op-Amp Selection: You must choose an op-amp with rail-to-rail output if the gate drive voltage of the MOSFET is close to the supply voltage. The Examples include LM358 (basic design) or TLV2372 (for better performance).
Example Calculation:
Let us Assume that a 12 V battery with a desired charging current of 1 A:
Vref = 0.6 V Rs = 0.6 / 1 = 0.6 ohms (use a 1 W resistor or higher)
Power dissipated in Rs:
PRs = 12 * 0.6 = 0.6 W
Then you must Choose the IRLZ44N as the MOSFET (logic level). Use a 1 µF ceramic capacitor for stabilization.
1) Using a Single Op amp
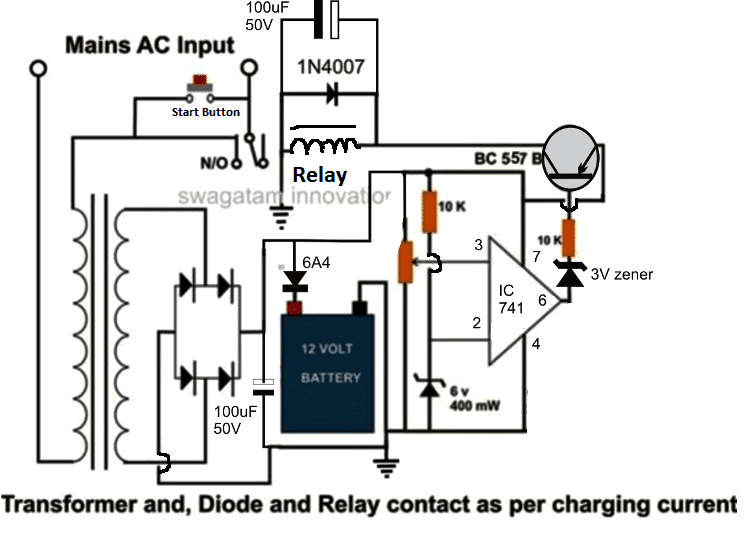
Looking at the first high current circuit for charging large batteries, we can understand the circuit idea through the following simple points:
There are basically three stages in the shown configuration viz: the power supply stage consisting of a transformer and a bridge rectifier network.
A filter capacitor after the bridge network has been ignored for the sake of simplicity, however for better DC output to the battery one can add a 1000uF/25V capacitor across the bridge positive and negative.
The output from the power supply is directly applied to the battery which requires to be charged.
The next stage consists of an opamp 741 IC voltage comparator, which is configured to sense the battery voltage while it is being charged and switch its output at pin #6 with the relevant response.
Pin #3 of the IC is rigged with the battery or the supply positive of the circuit via a 10K preset.
The preset is adjusted such that the IC reverts its output at pin #6 when the battery becomes fully charged and reaches about 14 volts which happens to be the transformer voltage at normal conditions.
Pin #2 of the IC is clamped with a fixed reference via a voltage divider network consisting of a 10K resistor and a 6 volt zener diode.
The output from the IC is fed to a relay driver stage where the transistor BC557 forms the main controlling component.
Initially, power to the circuit is initiated by pressing the "start" switch. On doing this, the switch bypasses the contacts of the relay and powers the circuit momentarily.
The IC senses the battery voltage and since it will be low during that stage, the output of the IC responds with a logic low output.
This switches ON the transistor and the relay, the relay instantly latches the power via its relevant contacts such that now even if the "start" switch is released, the circuit remains switched ON and begins charging the connected battery.
Now as the battery charge reaches about 14 volts, the IC senses this and instantly reverts its output to a high logic level.
The transistor BC557 responds to this high pulse and switches OFF the relay which in turn switches of the power to the circuit, breaking the latch.
The circuit gets completely switched OFF until the start button is pressed once again and the connected battery has a charge that's under the set 14 volt mark.
How to set up.
It's very easy.
Do not connect any battery to the circuit.
Switch ON power by pressing the start button and keep it depressed manually, simultaneously adjust the preset such that the relay just trips or switches OFF at the given rated transformer voltage which should be around 14 volts.
The setting is complete, now connect a semi discharged battery to the shown points in the circuit and press the "start" switch.
Due to the discharged battery, now the voltage to the circuit will drop under 14 volts and the circuit will instantly latch, initiating the procedure as explained in the above section.
Circuit Diagram for the proposed battery charger with high ampere capacity is shown below
2) 12V, 24V / 20 amp Charger Using two opamps:
The second alternative way of achieving battery charging for a lead acid battery with high amperage can be observed in the following diagram, using a couple of op amps:
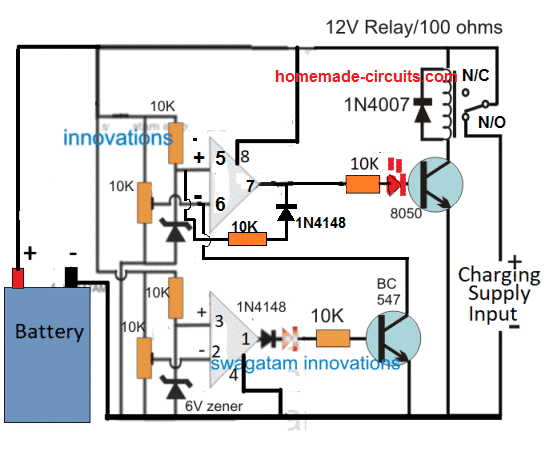
The working of the circuit can be understood through the following points:
When the circuit is powered without a battery connected, the circuit does not respond to the situation since the initial N/C position of the relay keeps the circuit disconnected from the charging supply.
Now suppose a discharged battery is connected across the battery points. Let's assume the battery voltage to be at some intermediate level, which may be between the full charge level and the low charge level.
The circuit gets powered through this intermediate battery voltage. As per the setting of the pin 6 preset, this pin detects a low potential than the pin 5 reference level. which prompts its output pin 7 to go high.
This in turn causes the relay to activate and connect the charging supply to the circuit and the battery via the N/O contacts.
As soon as this happens, the charging level also drops to the battery level and the two voltages merge at the battery voltage level. The battery now begins charging, and its terminal voltage begins increasing slowly.
When the battery reaches it full charge level, the pin 6 of the upper opamp becomes high than its pin 5 causing its output pin 7 to go low, and this switches off the relay, and the charging is cut off.
At this point another thing happens. The pin 5 is connected to the negative potential at pin 7 via the 10k/1N4148 diode, which further lowers the pin 5 potential compared to pin 6.
This is called hysteresis, which ensure that even if the battery now drops to some lower level that won't trigger the op amp back to charging mode, instead the battery level now has to drop significantly down until the lower op amp is activated.
Now, suppose the battery level keeps dropping due to some connected load, and its potential level reaches the lowest discharge level.
This is detected by pin 2 of the lower op amp whose potential now goes below its pin 3, which prompts its output pin 1 to become high and activate the BC547 transistor.
The BC547 grounds the pin 6 of the upper op amp competely. This causes the hysteresis latch to break due to pin 6 potential dropping below pin 5.
This instantly causes the output pin 7 to go high and activate the relay, which yet again initializes the charging of the battery, and the cycle repeats the procedure as long as the battery remains connected with the charger.
LM358 Pinout
For more auto cut-off charger ideas, you can read this article regarding opamp automatic battery charger circuits.
Video Clip:
The set up of the above circuit can be visualized in the following video which shows the cut off responses of the circuit to the upper and the lower voltage thresholds, as fixed by the relevant presets of the opamps
3) Using IC 7815
The third circuit explanation below details how a battery may be charged effectively without using any IC or relay, rather simply by using BJTs, I have explained the procedures:
The idea was suggested by Mr. Raja Gilse.
Charging a Battery with a Voltage Regulator IC
I have a 2N6292 . My friend suggest me to make the simple fixed voltage high current DC power supply to charge an SMF battery.
He had given the attached rough diagram. I don't know anything about the above transistor. Is it so ?
My input is 18 volt 5 Amp transformer. He told me to add 2200 uF 50 Volt capacitor after rectification. Is it works ?
If so , is there any heat sink necessary for transistor or/and IC 7815 ? Is it stops automatically after battery reaches 14.5 volt ?
Or any other alteration needed ? Please guide me sir
Charging with an Emitter Follower Configuration
Yes it will work and will stop charging the battery when around 14 V is reached across the battery terminals.
However I am not sure about the 1 ohm base resistor value...it needs to be calculated correctly.
The transistor and the IC both may be mounted on a common heatsink using mica separator kit.
This will exploit the thermal protection feature of the IC and will help safeguard both the devices from overheating.
Circuit Diagram
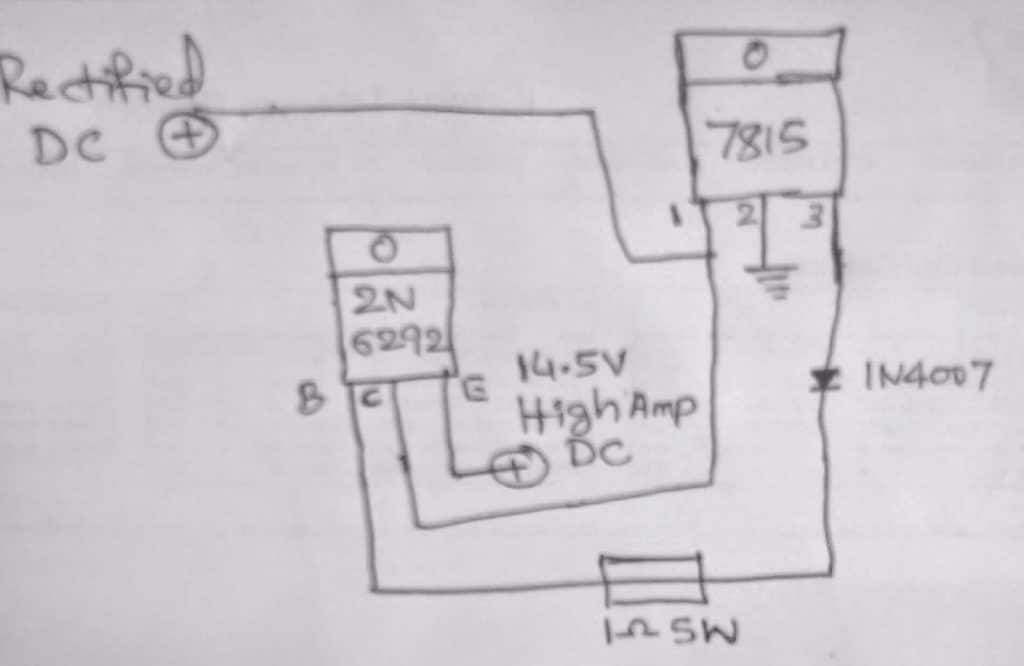
Circuit description
The shown high current battery charger circuit is a smart way of charging a battery and also achieving an auto shut off when the battery attains a full charge level.
The circuit is actually a simple common collector transistor stage using the shown 2N6292 power device.
The configuration is also referred as an emitter follower and as the name suggests the emitter follows the base voltage and allows the transistor to conduct only as long as the emitter potential is 0.7V lower that the applied base potential.
In the shown high current battery charger circuit using a voltage regulator, the base of the transistor is fed with a regulated 15 V from the IC 7815, which ensures a potential difference of about 15 - 0.7 = 14.3 V across the emitter/ground of the transistor.
The diode is not required and must be removed from the base of the transistor in order to prevent an unnecessary drop of an extra 0.7 V.
The above voltage also becomes the charging voltage for the connected battery across these terminals.
While the battery charges and its terminal voltage continues to be below the 14.3 V mark, the transistor base voltage keeps conducting and supplying the required charging voltage to the battery.
However as soon as the battery begins attaining the full and above 14.3 V charge, the base is inhibited from a 0.7 V drop across its emitter which forces the transistor to stop conducting and the charging voltage is cut off to the battery for the time being. As soon as the battery level begins going below the 14.3 V mark, the transistor is switched ON again...the cycle keeps repeating ensuring a safe charging fr the connected battery.
Base resistor = Hfe x battery internal resistance
Here's a more appropriate design which will help to achieve optimal charging using IC 7815 IC

As you can see, a 2N6284 is used here in the emitter follower mode. This is because 2N6284 is a Darlington transistor with high gain, and will enable optimal charging of the battery at the intended 10 amp rate.
This can be further simplified by using a single 2N6284, and a potentiometer as shown below:
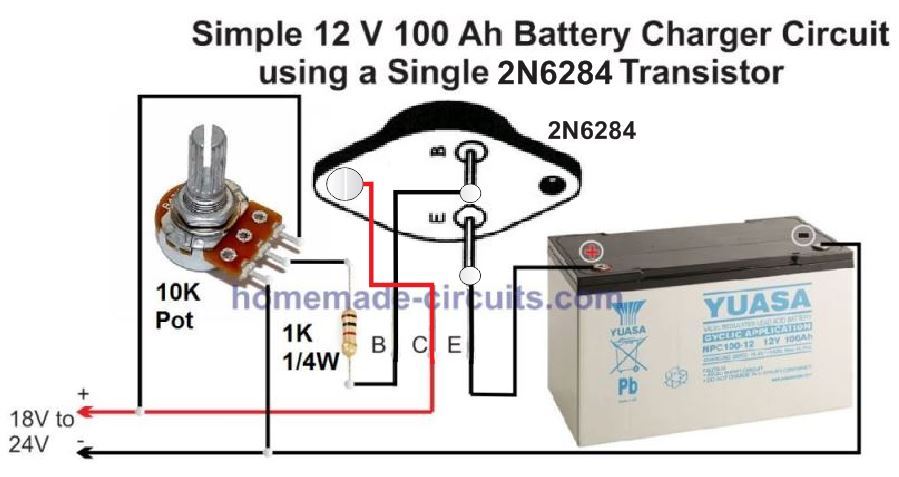
Make sure that you adjust the pot to get a precise 14.2 V at the emitter of the battery.
All the devices must be mounted on large heatsinks.
4) 12V 100 Ah Lead Acid Battery Charger Circuit
The proposed 12V 100 ah battery charger circuit was designed by one of the dedicated members of this blog Mr. Ranjan, I have explained more regarding the circuit functioning of the charger and how it could be used as a trickle charger circuit also.
The Circuit Idea
My self Ranjan from Jamshedpur, Jharkhand. Recently while googling I came to know about your blog, and become a regular reader of your blog. I learned a lot of things from your blog. For my personal use I would like to make a battery charger.
I have a 80 AH tubular batery and a 10 Amps 9-0-9 volts transformer. So I can get 10 amps 18-0 volts if I use the two 9volts leads of transformer.(Transfomer is actually obtained from an old 800VA UPS).
I have constructed a circuit diagram based on your blog. Please have a look on it and suggest me. Please note that,.
1) I am belonging to very rural area hence there is a huge power fluctuation it varies from 50V ~ 250V. Also note that I will draw very less amount of current from the battery( Generally using LED lights during power cuts) approx 15 - 20 Watt.
2) 10amps transformer i think safely charges 80AH Tubular Battery
3) All diodes used for the circuit are 6A4 dides.
4) Two 78h12a used as parallel to get 5+5 = 10 amps output. Although I think Battery must not draw full 10 amps. as it will be in charged condition in day to day use so internal resistance of battery will be high and will draw lesser current.
5) A switch S1 is used thinking that for normal charge it will be kept in off state. and after fully charging the battery it switched to on state to maintain a trickle charge with lower voltage. NOW question is that is this safe for the battery to kept in charge unattended for long time.
Please reply me with your valuable suggestions.
100 Ah battery charger circuit diagram designed by Mr. Ranjan
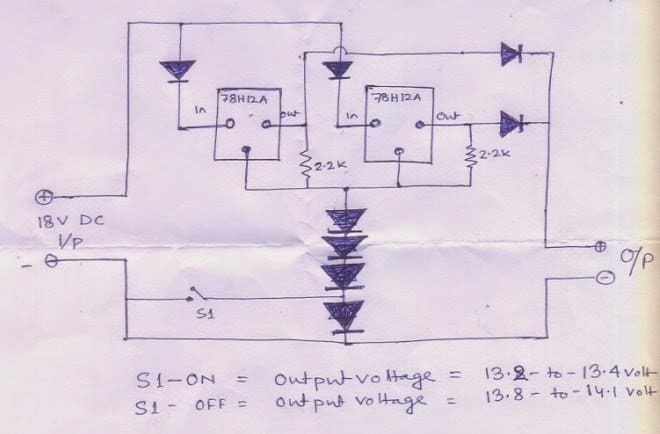
Solving the Circuit Request
Dear Ranjan,
To me your high current VRLA battery charger circuit using IC 78H12A looks perfect and should work as expected. Still for guaranteed confirmation it would be advisable to check the voltage and current practically before connecting it with the battery.
Yes, the shown switch can be used in the trickle charge mode and in this mode the battery can be kept permanently connected without attending, however this should be done only after the battery has been fully charged upto around 14.3V.
Please note that the four series diodes attached with the GND terminals of the ICs could be 1N4007 diodes, while the remaining diodes should be rated well over 10amps, this could be implemented by connecting two 6A4 diodes in parallel at each of the shown positions.
Also, it is strongly recommended to put both the ICs over a single large common heatsink for better and uniform thermal sharing and dissipation.
Caution: The shown circuit does not include a full charge cut-off circuit, therefore the maximum charging voltage should be preferably restricted between 13.8 to 14V. This will ensure that the battery is never able to reach the extreme full charge threshold, and thus remain safe from over charge conditions.
However this would also mean that the lead acid battery would be able to attain only around 75% charge level, nevertheless keeping the battery undercharged will ensure longer life for the battery and allow more charge/discharge cycles.
Using 2N3055 to Charge a 100 Ah Battery
The following circuit presents a simple and safe alternative way of charging a 100 Ah battery using 2N3055 transistor. It also has a constant current arrangement so the battrey can e charged with the correct amount of current.
Being an emitter follower, at the full charge level the 2N3055 will be almost OFF, ensuring the battery is never over charged.
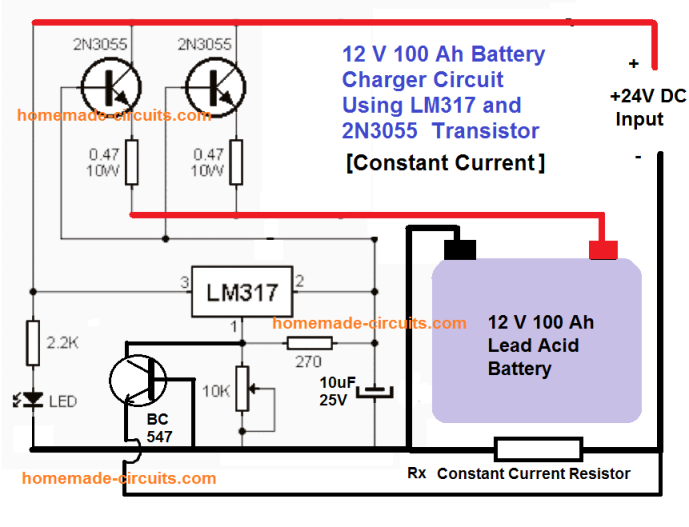
The current limit can be calculated using the following formula:
R(x) = 0.7 / 10 = 0.07 Ohms
Wattage will be = 10 watts
How to Simply Add a Float Charge
Remember other sites may present unnecessarily complex explanation regarding float charge making it complex for you to understand the concept.
Float charge it simply a small adjusted current level which prevents self discharge of the battery.
Now you may ask what's self discharge of the battery.
It's the declining level of charge in battery as soon as the charging current is removed. You can prevent this by adding a high value resistor such as a 1 K 1 watt across the input 15 V SOURCE and the battery positive.
This will not allow the battery to self discharge and will hold the 14 V level as long as the battery is attached to the supply source.
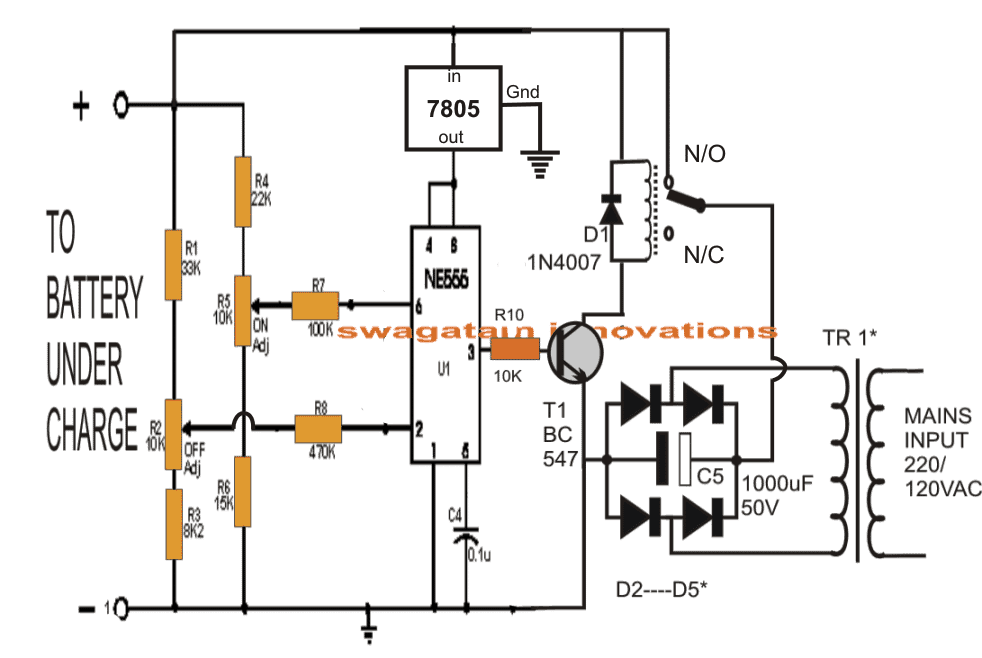
5) IC 555 Lead Acid Battery Charger Circuit
The fifth concept below explains a simple, versatile automatic battery charger circuit. The circuit will allow you to charge all types of lead acid battery right from a 1 Ah to a 1000 Ah battery.
Using IC 555 as the Controller IC
The IC 555 is so versatile, it can be considered the single chip solution for all circuit application needs. No doubt it's been utilized here too for yet another useful application.
A single IC 555, a handful of passive component is all that's needed for making this outstanding, fully automatic battery charger circuit.
The proposed design will automatically sense and keep the attached battery up to date.
The battery which is required to be charged may be kept connected to the circuit permanently, the circuit will continuously monitor the charge level.
If the charge level exceeds the upper threshold, the circuit will cut off the charging voltage to it, and in case the charge falls below the lower set threshold, the circuit will connect, and initiate the charging process.
How it Works
The circuit may be understood with the following points:
Here the IC 555 is configured as a comparator for comparing the battery low and high voltage conditions at pin#2 and pin#6 respectively.
As per the internal circuit arrangement, a 555 IC will make its output pin#3 high when the potential at pin#2 goes below 1/3 of supply voltage.
The above position sustains even if the voltage at pin#2 tends to drift a little higher. This happens due to the internal set hysteresis level of the IC.
However if the voltage continues to drift higher, pin#6 gets hold of the situation and the moment it senses a potential difference higher than 2/3rd of supply voltage, it instantly reverts the output from high to low at pin#3.
In the proposed circuit design, it simply means that, the presets R2 and R5 should be set such that the relay just deactivates when the battery voltage goes 20% lower than printed value and activates when the battery voltage reaches 20% above printed value.
Nothing can be as simple as this.
The power supply section is an ordinary bridge/capacitor network.
The diode rating will depend on the charging current rate of the battery. As a rule of thumb the diode current rating should be twice that of the battery charging rate, while the battery charging rate should be 1/10th of the battery Ah rating.
It implies that TR1 should be around 1/10th of the connected battery Ah rating.
The relay contact rating should be also selected as per the ampere rating of TR1.
How to set the battery cut off threshold
Initially keep the power to the circuit switched OFF.
Connect a variable power supply source across the battery points of the circuit.
Apply a voltage that may be exactly equal to the desired low voltage threshold level of the battery, then adjust R2, such that the relay just deactivates.
Next, slowly increase the voltage up to the desired higher voltage threshold of the battery, adjust R5 such that the relay just activates back.
The setting up of the circuit is now done.
Remove the external variable source, replace it with any battery which needs to be charged, connect the input of TR1 to mains, and switch ON.
Rest will be automatically taken care of, that is now the battery will start charging and will cut off when its fully charged, and also will get connected to power automatically in case its voltage falls below the set lower voltage threshold.
IC 555 Pinouts
IC 7805 Pinout
How to Set Up the Circuit.
The setting up of the voltage thresholds for the above circuit may be done as I have explained below:
Initially keep the transformer power supply section at the right hand side of the circuit completely disconnected from the circuit.
Connect an external variable voltage source at the (+)/(-) battery points.
Adjust the voltage to 11.4V, and adjust the preset at pin#2 such that the relay just activates.
The above procedure sets the lower threshold operation of the battery. Seal the preset with some glue.
Now increase the voltage to about 14.4V and adjust the preset at pin#6 to just deactivate the relay from its previous state.
This will set up the higher cut off threshold of the circuit.
The charger is now all set.
You may now remove the adjustable power supply from the battery points and use the charger as explained in the above article.
Do the above procedures with lot of patience and thinking
Feedback from one of the dedicated readers of this blog:
Hi, you have made a mistake on preset R2 and R5, they should not be 10k but 100k, I just made one and it was a success, thank you.
As per the above suggestion, the previous diagram may be modified as shown below:
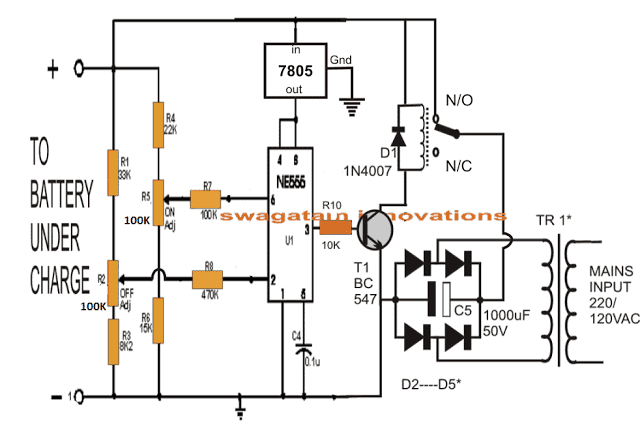
Design Steps for Automatic Lead-Acid Battery Charger using IC 555
Specifications:
- Upper cutoff voltage (V_cutoff): 14.4V (fully charged battery).
- Lower restart voltage (V_restart): 11.8V (recharge threshold).
- IC 555 supply voltage (V_CC): 12V.
Step 1: Voltage Divider for Battery Voltage
The battery voltage must be scaled to match the internal reference levels of IC 555:
- Lower reference: V_CC/3.
- Upper reference: 2 × V_CC/3.
The voltage divider is designed using resistors R1 and R2. The scaled voltage V555V_555V555 is calculated as:
V_555 = V_battery × (R2 / (R1 + R2))For proper operation:
- At V_cutoff (14.4V), V_555 = 2 × V_CC / 3.
- At V_restart (11.8V), V_555 = V_CC / 3.
Use these conditions to calculate R1 and R2
Step 2: Calculations for R1 and R2
For Upper Cutoff (14.4V):
At V_battery = 14.4V, the scaled voltage is:
V_555 = 2 × V_CC / 3
V_555 = 2 × 12 / 3 = 8V Using the voltage divider formula:
8 = 14.4 × (R2 / (R1 + R2))
R2 / (R1 + R2) = 8 / 14.4 = 0.555 Choose R1 + R2 = 100kΩ (standard value for simplicity):
R2 = 100kΩ × 0.555 = 55.5kΩ
R1 = 100kΩ - 55.5kΩ = 44.5kΩ For Lower Restart (11.8V):
At V_battery = 11.8V, the scaled voltage is:
V_555 = V_CC / 3
V_555 = 12 / 3 = 4V
Using the voltage divider formula:4 = 11.8 × (R2 / (R1 + R2))
R2 / (R1 + R2) = 4 / 11.8 = 0.338 Choose R1 + R2 = 100kΩ:
R2 = 100kΩ × 0.338 = 33.8kΩ
R1 = 100kΩ - 33.8kΩ = 66.2kΩ Step 3: IC 555 Connections
- Pin 2 (Trigger): Connected to the voltage divider to monitor the lower threshold.
- Pin 6 (Threshold): Connected to the voltage divider to monitor the upper threshold.
- Pin 4 (Reset): Tied to V_CC (12V) to avoid accidental resets.
- Pin 3 (Output): Drives a relay or NPN transistor to control charging.
Step 4: Output Control
- Use the output of Pin 3 to drive a relay or an NPN transistor (e.g., BD139).
- Add a flyback diode (e.g., 1N4007) across the relay coil to protect against voltage spikes.
Final Component Values
Voltage Divider Resistors:
- R1 = 44.5kΩ (for cutoff), 66.2kΩ (for restart).
- R2 = 55.5kΩ (for cutoff), 33.8kΩ (for restart).
Relay: Rated for the charging current (e.g., 5A for a 12V 7Ah battery).
Flyback Diode: 1N4007.
Power Supply: Stable 12V for IC 555 (use a voltage regulator if needed)
IC 555 Current Dependent Battery Charging
The IC 555 lead acid battery charger circuit could be also built using a current sensor at its pin#2.
The complete circuit diagram is shown below:
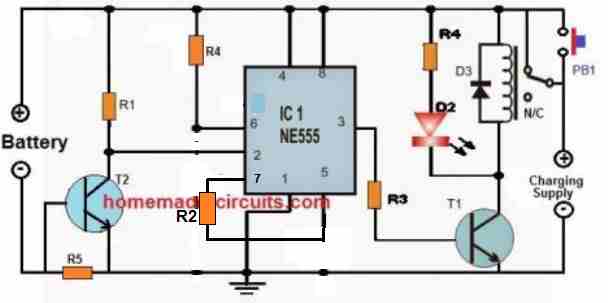
- R1, R3 = 10k
- R2 = 100k
- LED resistor can be 1k
- Pin#6 resistor R4 can be shorted with jumper link
- R5 = 1 / max charging current
- Relay = 12V relay for 12V battery.
- Relay diode = 1N4007
- T1, T2 = BC547
How it Works
The circuit is actually configured as a set/reset latch circuit.
The R4 can be replaced with a wire short.
At the start when power is applied, the relay contact being at the N/C, the circuit does not respond.
Pressing the PB1 push button, initializes the circuit by momentarily supplying the current throgh the PB1 to the battery.
The battery acts as the load, and creates a voltage drop across R5, which triggers ON the T2.
With T2 conducting pin#2 of the IC is held low, which prompts the output pin#3 to become high, and switch ON the relay.
The relay contacts now changes to N/O point and the circuit gets latched. The PB1 pressing is thus only required momentarily, and then it can be released.
As the battery gets charged, the voltage across R5 keeps getting lower, until the point when the battery is almost fully charged, when the R5 voltage drop is unable to hold the T2 ON any longer.
T2 switches OFF, causing pin#2 to go high again, and this in turn causes the pin#3 to go low, and turn OFF the relay and turn OFF the charging supply to the circuit and the battery.
Wrapping it up
In the above article I have explained 5 great techniques which could be applied for making lead acid battery chargers, right from 7 Ah to 100 Ah, or even 200 Ah to 500 Ah, simply by upgrading the relevant devices or the relays.
If you have specific questions regarding this concepts, please feel free to ask them through the comment box below.



Comments
Sir, I have a few questions on IC 555 example 1, voltage regulated.
Do I have to limit charging current somehow for smaller capacity units or does setting a diode rating only limits a maximum unit capacity that can be charged? For example I have 50Ah battery unit but I would like to use it for 100Ah in the future.
What voltage needs to be supplied for a 12V battery unit? I have access to 24V supply and a regulated step-down voltage converter.
Should I consider anything specific other than current rating when selecting a relay, for example coil resistance?
Thank you and good day, Sir.
Hi Radoslaw,
With reference to the following circuit that you are referring to:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/5552Bbattery2Bcharger2Bcircuit.png
Yes, your transformer must be rated with a current which must be 1/10th of the battery Ah rating, considering it is a lead acid battery.
For example, for a 100 Ah battery, the transformer must be rated at 10 amp or a maximum of 15 amps.
For a 12 V battery the maximum full-charge cut-off limit can be set at 14.3 V.
The relay coil resistance mostly depends on its contact current rating, for high current contacts, the relay coil resistance will be lower and vice versa. You only have to consider the relay coil voltage which must be 12V for a 12V battery and the contact current rating must twice that of the charging current value, so for a 100 Ah battery, 10 amp charging current, the relay contacts must be rated at 20 amps or higher.
Thank you, however let me ask one of questions in another way:
What operating voltage needs to be supplied to the circuit from bridge/capacitor network for charging a 12V battery unit? Can I use a SMPS instead? If yes what voltage it should provide? I have access to 24V supply and I would need a 15-20A buck converter circuit if it needs to be lowered.
Thank you, Sir.
Radoslaw, For a 12V battery the SMPS should be rated at around 15V, and must have a current rating that is 1/10th of the battery Ah.
Yes, if you use a 24V SMPS then you must use a buck converter that can convert it into a 15V DC output with a current as mentioned above.
Sir, I followed your setup procedure however I cannot get the relay working properly.
I have successfully set R2 to activate relay at 11.5V on battery pins however as I try to tune R5 at 14.4V the relay never deactivates – I went through entire range on R5.
Any suggestions what am I possibly doing wrong here?
Hi Radoslaw,
When you adjust R2 preset at 11.5V, the relay will activate only when the pin#2 of the IC has reached below 1/3rd of Vcc 5V.
When you adjust R5 preset at 14.4V, the relay will deactivate only when the pin#6 of the IC has reached above 2/3rd of the Vcc 5V.
2/3rd of 5V is around 3.33V, so please check whether the pin#6 goes over 3.33V or not while adjusting the R5 preset.
If not, then try reducing the R4 value to 10k and check again….
Thank you Sir, for making it clear. I did manage to set the circuit by measuring voltage on pin #2 and #6.
I confirm this works as expected with R4@100k.
That’s great Radoslaw, thanks so much for updating the information….
Hi stumbled upon your site after looking into building a charger for a camper van. I had already bought a 12v 50A switching PSU, that i was going to modify for about 14.2v and just leave it connected all the time, but after reading this I realise that this would not be a good idea. So using your information on the simple safe 12v 100 amp charger, i had an idea that, what if the Voltage was set to 14.4v to fast charge, then when the battery becomes fully charged, drop the voltage to 14 volts to maintain, this could be done by altering the feedback voltage (resistance of the V adj pot).
I have in the past converted these SMPS to give different voltages, by altering the resistor divider network associated with the feedback pot (within reason to avoid letting all the smoke out!) Something as simple as a transistor or relay that just switches in a little more resistance.
Any thoughts ???
You are right, if you charge a 12V lead acid battery upto 14.3V, then you must cut off the supply immediately once reaches the 14.3V level.
I would rather recommend not to reach the 14.3V mark at all, instead keep the input fixed at 14V, or maybe at 13.9V, to enhance the battery life further.
If you want to fast charge the battery, you can keep the initial charging current at maybe 30% to 40% of the battery value, and then reduce the current to 10% of the battery Ah once the battery voltage has reached at around 13.5V.
Here’s a simple circuit which can be used to toggle the supply current from high current to low current for implementing the fast charging safely:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/simplest-fast-charger-circuit.jpg
Hi,
Your circuit diagrams and explanations are excellent and I really appreciate you putting up this page.
My question is how do I modify the “Using IC 555 as the Controller IC” charging circuit to provide 30 amps of charging current to the battery?
You said to upgrade the relay and the components but I’m not sure exactly what I would need to do.
I thank you very much in advance for any guidance you can give me.
Ted
Hi, Thanks very much, and glad you found the post useful!
The relay contacts are responsible for handling the battery current so the relay must be upgraded to have a contact rating of at least 35 amps to handle 30 amp current. So for 30 amp current you would a relay whose contacts are rated at 35 amps, 40 amps or maybe 50 amps.
However, there are much easier ways to charge a battery using transistors and ICs only, without involving relays. I would recommend these instead.
Let me know if you need any further assistance.
Good day sir. For the 555 timer based 12v charger, can I replace the resistors at pin#6 and pin#2 with a series 1k resistor 5.1v zener and 4.7 v zener respectively? Will it work and is there any disadvantage?
Hello Emmanuel,
I am not sure about it, you will have to test it through a practical experimentation.
Ok sir
Thanks for your reply sir. But my second doubt still not cleared by you sir. I wanted to know whether this 555 circuit i refered to can be used for cutting of the charging process alone without making it to auto charge the battery? I want it for an emergency lamp circuit without automatic charging, but only employing auto cutoff only..and what changes need to be done for that.. pls help me sir
Binoj, If you do not want an automatic low battery detection and charging, then you can remove the pin#2 preset entirely and instead connect a push button across pin#2 and ground. Make sure to have a 10K resistor connected between pin#2 and the positive line.
But please note that I have not tested the 555 circuit yet. If you want a tested alternative you can try an op amp version which will only do automatic cut off but no automatic recharging.
Simple 3.7 V Li-Ion Battery Charger Circuit
Hlo sr, regarding the ic 555 battery charger circuit, i cant figure out how the voltage regulator actually gets the power if the output from bridge is fed through the NO contact of relay. Or is there any mistake in the diagram? Can u pls clarify the relay contacts connection. And another thing is that shall this circuit be used only for auto cutoff function and not for auto charging. If so what changes are to be made??
Hello Binoj. there’s no mistake in the diagram, it is correct.
When the battery is low. pin#2 is below 1/3rd Vcc which causes pin#3 to go high and it switches ON the relay. The relay contacts shift to N/O and start supplying power to the regulator and the battery.
Initially, at the start, when the relay contacts are at N/C, the regulator and the IC get the power from the battery.
The circuit can be used for auto cut off and also for auto charging.
Hello Sir, I have a DC supply which is 26v,52amps but I just need 24v, 17 amps to charge my 24v ,170AH battery . Can you please help me with a charger I can regulate the current and voltage?
Hello sir thanks for your assistance and correction but I also have a Delta rectifier module which is 100-240v input and 54vdc-53.7A Output. Can you please assist with a charger circuit I can use with this to charge my 24v battery?
Hi Chris,
First you will need a buck converter to drop the 54V to 28V Dc, only after this you will be able to charge your battery. I don’t have this circuit with me at this moment.
Thanks for your support
Hello Chris, for charging a 24V lead acid battery fully you will require a minimum of 28 V. So even 26V is insufficient.
hi swagatam can I implement the current sensor from the second IC555 to the first IC555 circuit?
Hi Sam, both current and voltage cut off is not recommended, you can use either of them for the cut off. Using both will not make sense!
Hello Swagatam I was talking about the first circuit in this article. Can it be ok for the 200ah 12v battery and can I use 6.2v zenar instead of 6v zena? Secondly, I was asking to know if high current Mosfet’s of about 150amp are better and makes the inverter more efficient than low current Mosfet’s?
Hello Morris, I guess you are referring to the following circuit:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/12/high2Bcurrent2Bbattery2Bcharegr2Bcircuit.png
Yes 6.2V zener will also work instead of 6V zener.
Yes, higher the current the better will be the performance of the mosfet
Hello Swagatam, I have original 24v automatic charger which has two led indicators ie one for float charge and the other for quick charge. Now I bought two 100ah battery which I connected in series. Whn I connected them to that charger the red led for quick charge indicates then upon full charge or whn nearing full charge it shifts to float charge indicator. My question is that is that how the charger should be working? Can that cause any harm to the batteries? Thanks!
Hi Morris, from your description it looks like your charger controller is working correctly.
So I should not worry any harm to the bad? Now whn it shifts to float charge what happens at that time to the battery and should I just leave it to stay unplugged? Thanks sir.
Float charge is like trickle charging, using very low current, just to ensure that the battery does not self discharge. It is perfectly safe, you can keep it plugged.
Hello sir can u get me the procedure of setting the second circuit in this article to function as expected.
Hae Swagatam I built the first circuit and charged the battery. I used also an digital battery indicator to show me if around 14.4v it will trip the relay. The two voltages merged and started indicating 11.7 upto 14.6v without tripping the relay. Whn I disconnected the battery now reads 13.3v. Does it reads upto around 15v up for the real voltage itself to reach 14.4 to trip? Advise
Hi Morris,
14.6V is too high, you must not use more than 14.3V. Actually 14.1 V is the recommended level. If you adjust the preset correctly to trip at 14.3V or 14.1 V then the circuit surely trip at that point. Remember at the full charge level, the pin#3 voltage of the IC should become slightly higher than pin#2, this is when the op amp output will become high and the BC557 will shut off, switching OFF the relay. You can replace the 3V zener with an LED for the indication. Cathode will go to pin#6 of the IC and anode towards the resistor.
When you remove the battery after the full charge, the battery voltage will slowly drop to 12.8V and this is perfectly normal, do not expect it to stay at 14V permanently, because in the idle state the a fully charged 12V battery will show a voltage level of around 12.8v.
Hello Swagatam,pliz check the first circuit in this article if it is really that way. Thi is how i set it: I first tweaked my supply to around 14.0v. Then loaded it to the circuit before connecting a battery…..tweaked again the 10k preset until the relay comes to N/O because whn it comes to N/C u will find that u just continue holding the start button for it to come on. So whn it’s tweaked to activate u just find is coming on whn u press the button once but u will wait for the relay to cut off until u see he’ll my friend???????? pliz try circuit the way it is and see then tell me. I just unplug it and find the battery is full but not cutting off
Hello Morris,
I will explain you the right process for adjusting the preset.
1) Replace the 3V zener with an LED. Cathode will go to pin#6
2) Keep the 10k preset slider to ground level.
3) Keep the push button shorted.
4) Supply around 14.1V DC across the positive and the negative lines of the 741 circuit.
5) You will find the LED switching ON, and the relay clicking to the N/O side contacts.
6) Now, slowly adjust the 10K preset until the LED just shuts off and the relay switches off to N/C contacts.
Your circuit is all set now. You can now remove the push button shorting and test the set up with an actual battery.
And what will happen if I remove also the diode to the battery terminal (6A4)? I used the circuit without it coz the 6a4 I had exploded????????.
6A4 can handle only upto 5 amps so it won’t work. You can remove it. But after full charge remove the battery from the charger otherwise it might self discharge through the op amp 10K resistor
Ok sir. But does MOSFETs with high current consume more power from the battery faster? Secondly in an inverter circuit is it the oscillator stage design that makes inverter consume voltage Faster or the MOSFETs used in the amp stage. Thanks in advance my teacher.
The current rating of the mosfet suggests its maximum capacity to handle the current, its breakdown limit. The consumption of the mosfet depends on the wattage of the load connected across its drain, which is a transformer for an inverter. Yes the oscillator duty cycle determine how much average current the mosfet will consume.
Ok sir thanks for the response. Do u hv inverter charger circuit design that uses is mosfet as diode to charge battery whn battery gets low without bridge diode. I tried a separate transformer with bridge diodes to charge the 200ah battery but the four metal bridge diodes gets too hot???? pliz guide me
Hi Morris, yes I have one related post on how to use mosfet body diode for charging battery, you can read it here:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/using-mosfet-body-diodes-to-charge-battery-in-inverters/
Dear Swagatam
I am very thankful to you for the reply, and I suggest removing the old circuit and build a simple one without attaching the other accessories only working on AC &DC is it possible to get such a circuit .
I would like to thank u for the second part also.
You are welcome Nabeel, it is not possible to know or judge what circuit was used in your fan, because different fans have different circuits, there’s no standard circuit available in the market
Dear Sir,
I am from Iraq, I need your help with many things in the electronic field first is a circuit for the fan that can work on mains (ac) and a battery, that means when the AC is available it works normally but when AC goes off it will switch to the battery, in fact, the fan has a circuit and due to fluctuation of
electricity the Ic in charge burnt up In the power section and I don’t know the number or any think on it so I had to go for changing the circuit I could replace the bridge
and the Optocoupler but I can not read any number on it
second – I would like to learn how to design a PCB with easy aid
Hello Nabeel, If the fan has a circuit then it can be difficult to troubleshoot the issue without checking it practically.
To learn how to design PCB you can refer to the following article:
How to Make PCB at Home
Thanks for the detail and various different designs. I am trying to mimic what we commonly get off the shelf these days (smart charging, float, trickle, reverse connection protection, etc.) with the exception that i need it to have a continuous running capacity of 70A or more at 14.2 (up to 14.4V) . Is it possible to mod one of these? I am a electronics enthusiast with no formal training and have completed several small projects following plans. Thanks for your help.
Hi, the only advantage of a smart charger is that it allows a fast charging of the battery compared to the ordinary chargers. However, if the charging at normal speed is acceptable then smart charger is absolutely not required, moreover charging any battery at a standard slow rate is the most recommended since it promises longer life to the battery.
A Smart charger basically comprises of fast charging through 3 step charging, float charging or trickle charging, and temperature compensation.
In contrast, a normal good charger will have a constant current constant voltage charging, with float charging and trickle charging, which is extremely easy to implement yet is very safe.
If possible I will design a smart charger circuit soon and post in my blog, with all the above mentioned features.
No problem, you can ask your questions, I will try to answer them.