As the name suggests a preamplifier circuit pre-amplifies a very small signal to some specified level that can be further amplified by an attached power amplifier circuit. It basically acts like a buffer stage between the input small signal source and a power amplifier. A preamplifier is used in applications where the input signal is too small and a power amplifier is unable to detect this small signal without a preamplifier stage.
In this post I have explained 5 preamplifier circuits which can be quickly made using a couple of transistors (BJTs) and a few resistors. The first idea is based on the request presented by Mr. Raveesh.
Circuit Objectives and Requirements
- Electronics is my hobby since so many years. Often I will be browsing your website and found many useful projects. I require a favor from you.
- I have a FM transmitter module which works on 5 volts DC with provision to connect from Computer through USB or from audio out from any other device through 3.5 mm audio jack.
- The module works great in computer USB mode with great signal strength, quality and coverage. But when I connect the same through audio input jack from DTH set top box the signal strength becomes weak even with full volume in both set top box and FM module. I think the audio signal level from set top box is not sufficient for the FM module.
- Please suggest me a good quality stereo audio small signal preamplifier circuit which can work from 5 or 6 volts single supply, that would not load the set top box, preferably using good low noise op-amp with detailed circuit and parts label.
1) Preamplifier using two Transistors
A simple pre-amplifier circuit can be very easily built by assembling a couple of transistors and some resistors as shown in the following figure:
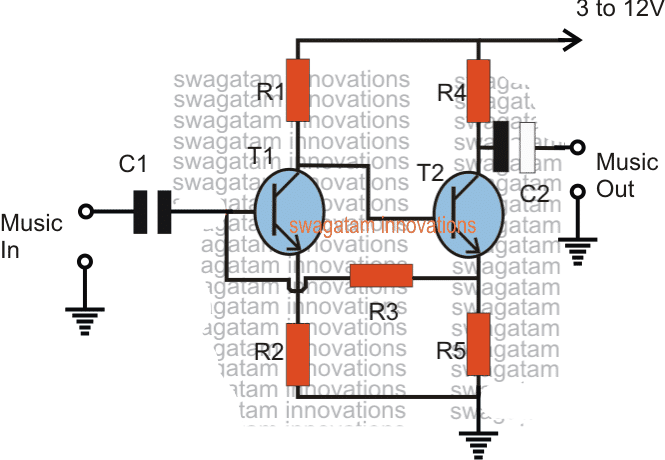
The circuit is a simple two transistor pre-amplifier using a feedback loop for enhancing the amplification.
Any music as we know is in the form of a consistently varying frequency, therefore when such a varying input is applied across the indicated C1 end terminals, the same is delivered across the base T1 and ground.
The higher amplitudes are processed normally and is reproduced with a potential that's approximately equal to the supply voltage, however for the lower misc amplitudes T2 is allowed to conduct at the higher ratio which is allowed to pass to its emitter.
At this time when the actual enhancement of the music is implemented by transferring this accumulated higher potential back to the base of T1 which correspondingly saturates at a much optimal rate.
This push pull action ultimately results in an overall amplification of an insignificantly small music or data input into a significantly larger output.
This simple circuit enables boosting extremely small or minimal frequencies to an appreciably bigger outputs which can be then used for feeding lager amplifiers.
The discussed circuit was actually popularly used in old cassette type playback recorders in their preamp stages for boosting the minute signals from the tape head so that the output from this small amplifier became compatible for the attached high power amplifier.
Parts List
- R1 = 22K
- R2 = 220 ohms
- R3 =100k
- R4 = 4K7
- R5 = 1K
- C1 = 1uF/25V
- C2 = 10uF/25V
- T1/T2 = BC547
Adjustable Preamplifier Circuit
This useful preamplifier circuit is an enhanced version of the above design. It has a voltage gain which can be set at any level between five and one hundred times by using a feedback resistor of the appropriate value.
The input impedance is high, being typically about 800K and a low output impedance of around 120 ohms is obtained.
The noise and distortion produced by the circuit are both very low.
A maximum output signal level of about 6 volts peak to peak can be handled before clipping occurs.
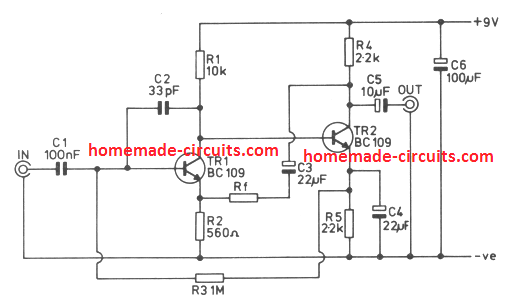
The figure shows the circuit of the unit, and this is a straight Forward two transistor, direct coupled arrangement, with both transistors being used in the common emitter mode. R2 provides local negative feedback over Tr1, and provides a convenient point tn which overall negative feedback can be applied to the circuit.
This feedback is obtained from the collector of Tr2 via D.C. blocking capacitor C3 . and the value of RF determines the amount of feedback that is applied to the amplifier. The lower the value of this component the more feedback that is applied, and the lower the closed loop voltage gain of the unit.
The required value of Rf is found by multiplying the required voltage gain by 560. Thus, a voltage gain of ten limes, for example, requires Rf to have a value of 5.6k.
It is recommended that the voltage gain should be kept within the limits stated earlier. C2 rolls of the high frequency response of the amplifier, and is necessary as instability might otherwise occur.
The upper -3dB response of the unit is still at about 200kHz even if the amplifier is used at a voltage gain of hundred times. When used as lower gains the upper -3dB point is pushed proportionately higher. The lower -3dB point is at approximately 20 Hertz incidentally.
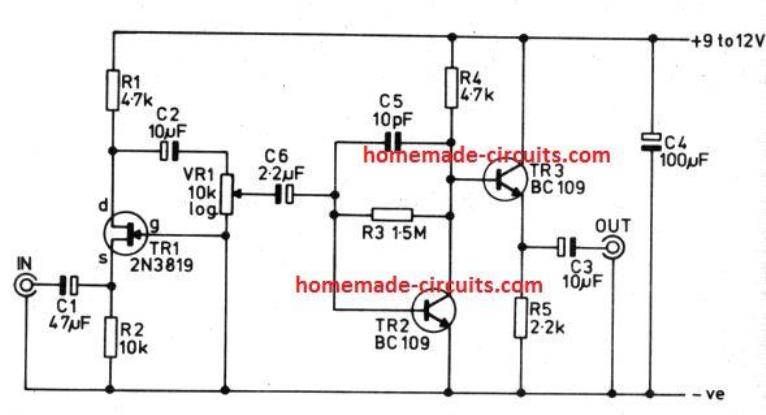
Another Transistorized Preamp design
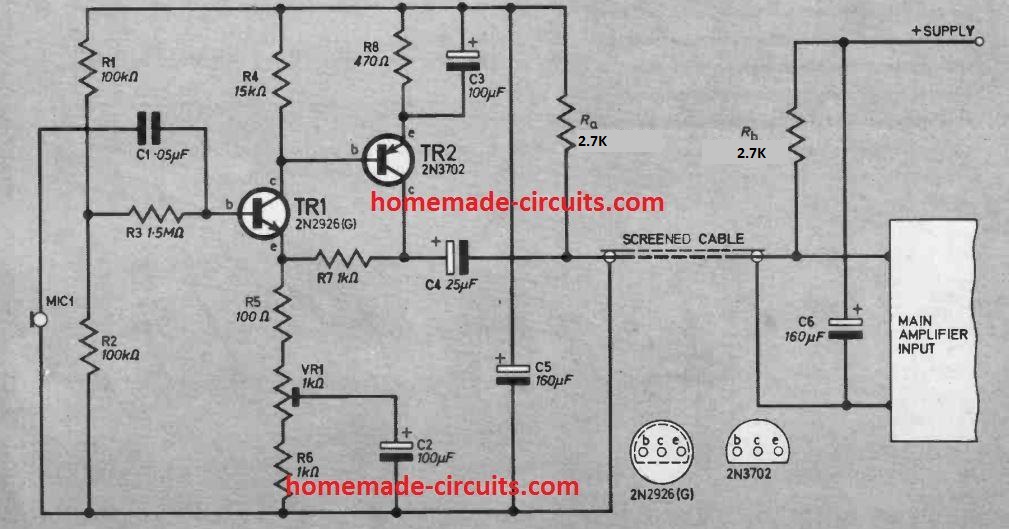
This is a high impedance input 2 stage preamplifier that features an adjustable voltage gain, from 1.5 to 10. This gain can be varied by setting up VRI and becomes handy where the MIC sensitivity required to be varied often.
As shown above, the circuit is actually designed for crystal microphones or ceramic cartridges.
Parts List

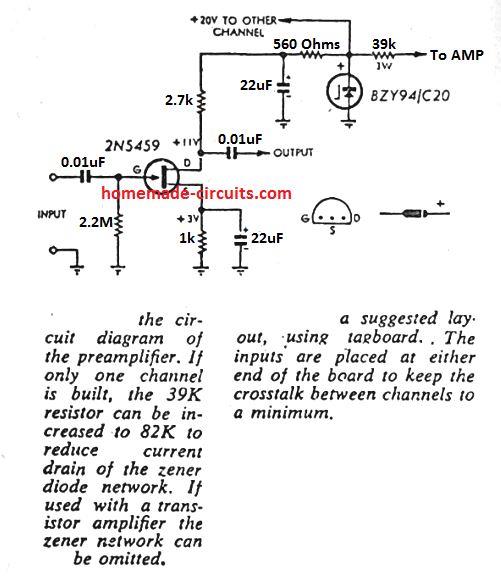
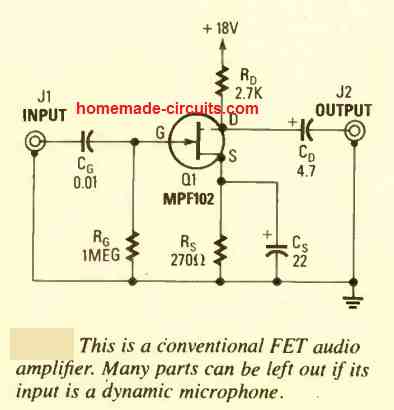
2) Using an FET
The second preamplifier design looks even simpler as it works using a single low cost JFET. The circuit diagram can be seen below.
The circuit is self explanatory, and can be integrated with any standard power amp for further amplification.
Guitar Preamplifier
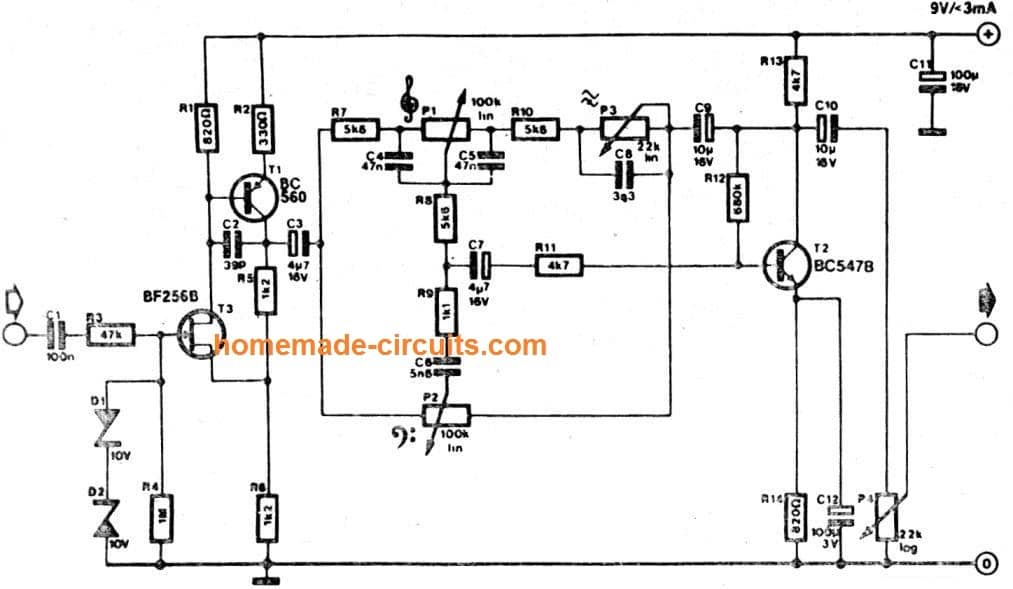
It usually becomes necessary to hook up an electric guitar with a mixing panel, a audio deck or a portable studio.
As much as wiring is concerned, that may be not an issue, however matching the high impedance of the guitar component with the low impedance of the line input of the mixing panel does becomes an issue.
Even the unsuspecting high impedance inputs of those units aren't well suited for the guitar output. As soon as the guitar is plugged into this kind of input, you hardly see a signal feasible for the panel or deck to process.
It might be likely to attach the guitar to the (high-impedance) mic input, however that is commonly way too sensitive for the function, which leads to clipping of the guitar signal too easily.
The matching amplifier introduced in this article answers these difficulties: it features a high- impedance (1M) input that will stand up to voltages of over 200 V. The output impedance is fairly small. Amplication is X2 (6 dB).
Dual tone control, presence control and volume control are offered. The circuit is designed for input levels of up to 3 V. Over this level distortion rises, but that may be, naturally, a decent outcome having guitar music.
True clipping of the input signal is not going to take place until eventually significantly bigger levels above the minimum guitar specs are utilized. The circuit is powered by a 9-V (PP3) battery through which the circuit pulls a current just around 3 mA.
3) Stereo Preamplifier Using IC LM382
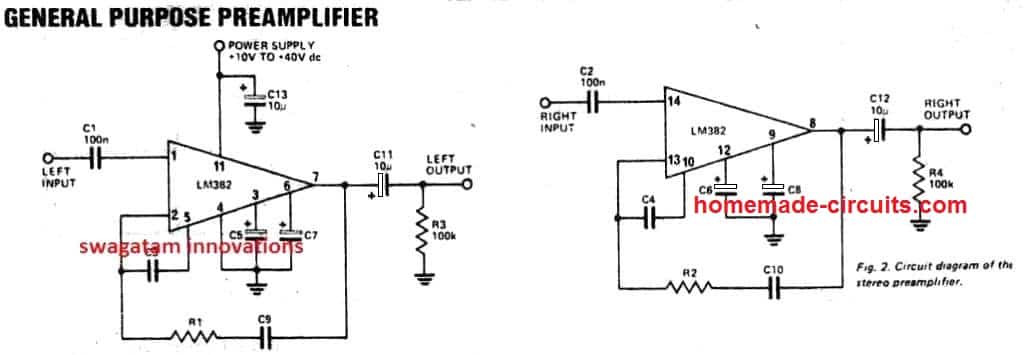
Here;s another nice little preamp circuit using a dual opamp IC LM382. Since the IC provides a dual opamp package two preamps could be created for stereo application. The output from this preamp can be expected to be very good.
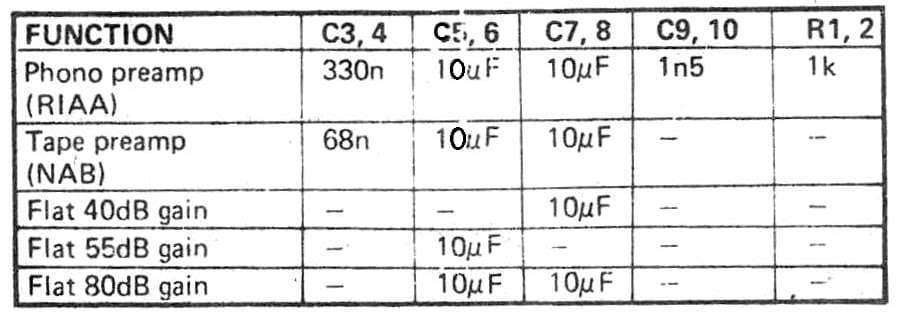
Parts List
R1, R2 = see the below given table.
R3, R4 = 100K 1/2 watt 5%
C1, C2 =100nF polyester
C3 to C10 = see table
C11 to C13 = 10uF/25V
IC1 = LM382
4) Balanced Preamp
If you are looking for something more sophisticated, you may want to try this balanced preamplifier design. The circuit is elaborately explained in this article which you can refer for your reading pleasure.
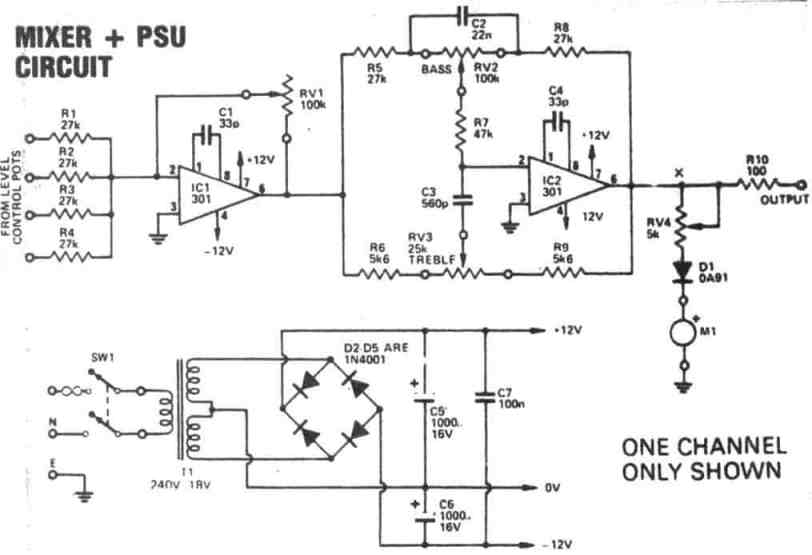
5) Preamplifier with Tone Control
A tone control normally includes bass and treble features for tweaking the dynamic quality of the music.
However, since a tone control also has the ability to amplify the incoming it can be effectively used like an outstanding Hi-Fi preamplfier circuit stage.
This we have a system which works two ways, foe enhancing the tone quality of the music and also preamplifying the music for the subsequent power amplifier stage.
The complete circuit of this fifth preamplifier can be seen below:
UPDATE
Here are a couple of more preamplifier circuits that may interest you.
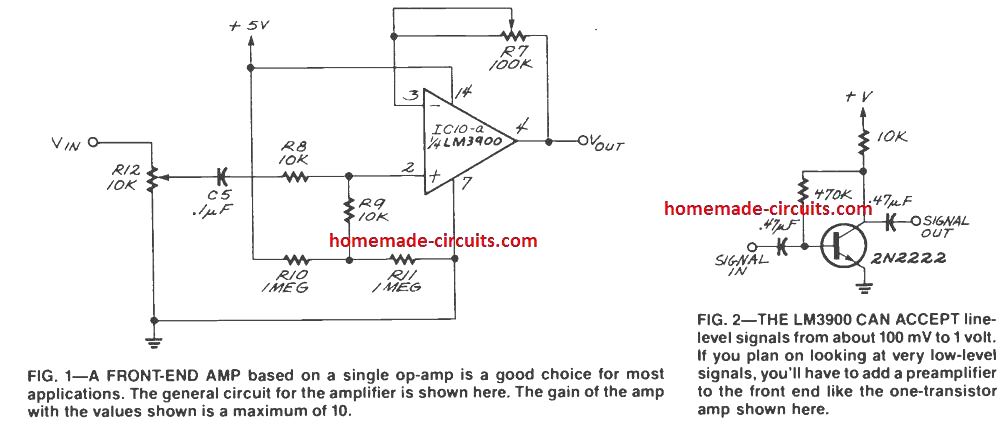
6) Low Z (impedance) MIC Preamplifier Circuit
The circuit described so far, are of course, only suitable for use with high impedance microphones, and provides insufficient gain for use with low impedance types.
These usually provide an output signal level of about 0.2mV. R.M.S., which is about one tenth of that generated by a high impedance microphone.
The circuit diagram is for a preamplifier that can be employed with low impedance microphones, and should give an output signal of around 500mV. R.M.S.
The prototype was found to work well with both 200 ohm and 600 ohm impedance dynamic microphones, but it should also work well with electret types which have a built-in FET buffer amplifier, but no step-up transformer.
The unweighted noise performance of this circuit is not quite as good as that of the previous circuit, but is still about -60dB referred to 500mV R.M.S.
This circuit is really an adaptation of the second design. The FET input stage uses the common gate mode rather than the common source one.
The common gate configuration gives reasonably good voltage gain together with a low input impedance (a few hundred ohms) which matches the microphone reasonably well.
The only other change in the circuit is that the emitter of Tr2 connects direct to the negative supply rail and there is no feedback resistor here.
This is done to boost the gain of the circuit, which as explained earlier, needs to be about ten times higher for a low impedance microphone.
Zero Noise Preamplifier Circuit
In numerous applications (audio, computing devices, aerospace amplifiers, communications, etc.) an exceptionally low-noise preamplifier stage becomes necessary, and just about any model strategy that could minimize noise by even 1 dB is welcomed with passion by everybody involved.
The circuit demonstrated below provides a fundamental design concept, although not quite ideal, the final results to date are encouraging.
Applying even the highly sensitive measuring devices at our fingertips we still could not determine virtually any output noise signal whatsoever!
Having said that, currently there seems to be still one leftover issue: the gain of the circuit is zero.
Automatic Gain Control Preamplifier Circuit
This microphone preamplifier features automatic gain control, which maintains the output quality relatively consistent within a broad selection of input ranges.
The circuit is particularly well suited for driving the radio transmitter modulator and enables a large typical modulation index to be accomplished.
This can possibly be applied in power amp systems and intercoms to deliver better intelligibility and make up for varied speakers specifications.
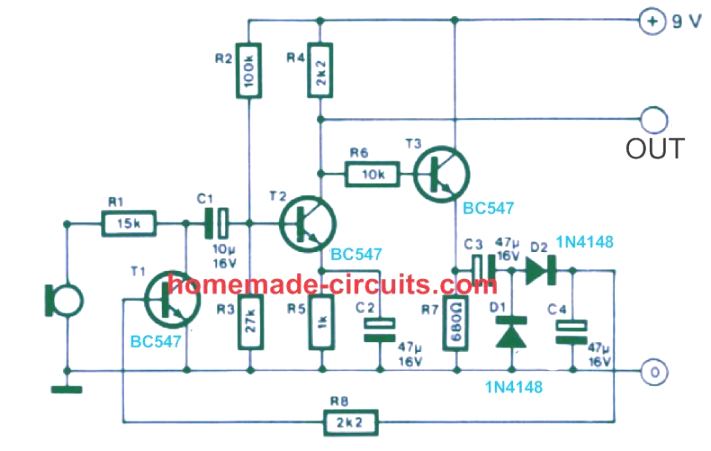
The specific signal amplifier stage is T2, which works in common emitter mode, the output signal being extracted from its collector.
A part of the output signal is supplied by means of emitter follower T3 towards a peak rectifier containing D1/D2 and C4. The voltage across C4 is employed to regulate the T1 base current, that constitutes section of the input attenuator.
At reduced signal concentrations the voltage on C4 is minimal, and T1 pulls very little current.
When the input signal level rises, the voltage on C4 goes up and T1 switches on harder, causing higher suppression of the input signal.
The overall effect is that as the input signal heightens it has to go through an increased degree of attenuation and the output signal thus continues to be reasonably constant across a wide range of input signals.
The circuit is appropriate for inputs having a peak input level up to 1 volt. The microphone could be substituted by a tiny loudspeaker for converting the circuit into an intercom.
1.5 V Preamplifier circuit
While most amplifiers come without adequate input sensitivity and hardly any room within their enclosure, independent low power pre-amplifiers which could be integrated externally may be very useful.
These need to have a bare minimum number of parts and likely be powered with just one dry cell.
The independent 1.5 V preamplifier circuit I have explained below is made up of individual amplifying transistor preceding an emitter follower. DC negative feedback keeps the operating level stable.
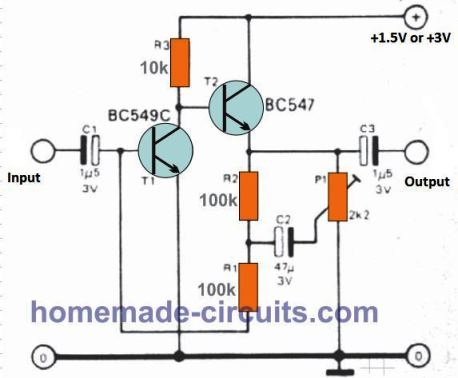
The gain is roughly x 10 to x 20. If the signal source provides impedance of more than 100 k ohms, some amount of gain control is possible through P1.
A reasonably long-term battery back up could be acquired through the use of a couple of 1.5 volt dry cells (in series) rather than one.
If the power falls under 1 volt the amplifier may stop functioning.
Typical dry cells frequently deplete quickly to 1 volt and have to subsequently be thrown away, although it may take longer for each one of two cells to drop to 0.5 volt. Current draw at 3 volt supply will probably be around 450 microamps.
Miscellaneous Preamp Circuits
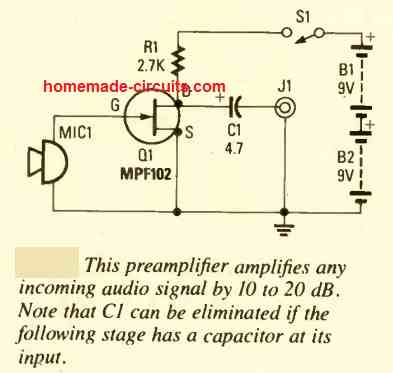
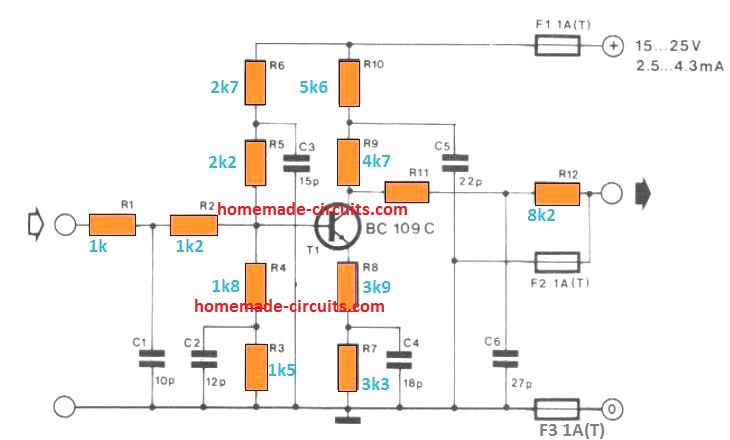
Micro-volt Preamplifier
This preamplifier design can amplify extremely small input signals in the range of microvolts
As a result, the preamplifier must give a significant amount of voltage gain in order to match the output to a hi-fi amplifier, which requires a signal level 1,000 times greater.
Because the input signal may climb at a rate of 6dB per octave, the preamplifier must also offer equalization.
At increasing audio frequencies, nevertheless, low microvolt frequencies are inefficient and require considerably lower roll-off. Q1 and Q2 are utilized in a typical two-stage, direct coupled, common emitter amplifier, with frequency-selective negative feedback provided by C3 and R4.
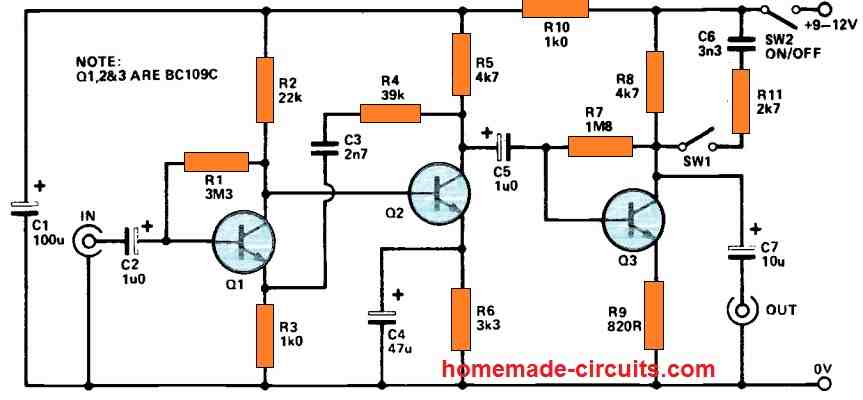
In addition, the midband voltage gain of the input stage is adjusted at around 46dB. With that kind of a low input level, it is apparent that low noise transistors (such as the BC109C) are required to get excellent performance.
It additionally helps to operate Q1 with a low collector current, approximately 200uA. Q3 serves as a low gain common emitter stage, providing extra amplification. R9 adds negative feedback to adjust the voltage gain of Q3, and the given value yields a gain of around 14dB.
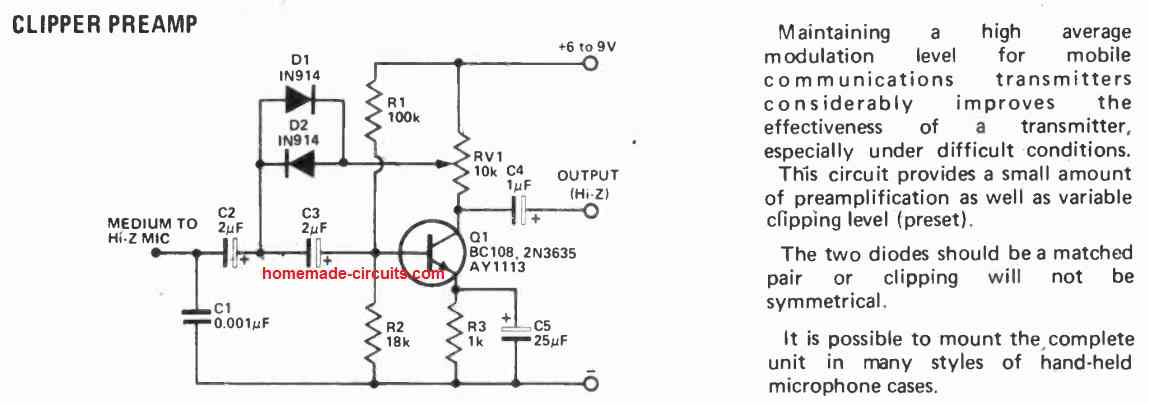
Enhanced MIC Preamplifier Circuit for tailored Output Response
In the realm of speech communication, customizing the response of the preamplifier that follows the microphone enhances speech clarity and minimizes unwanted background noise interference affecting the signal.
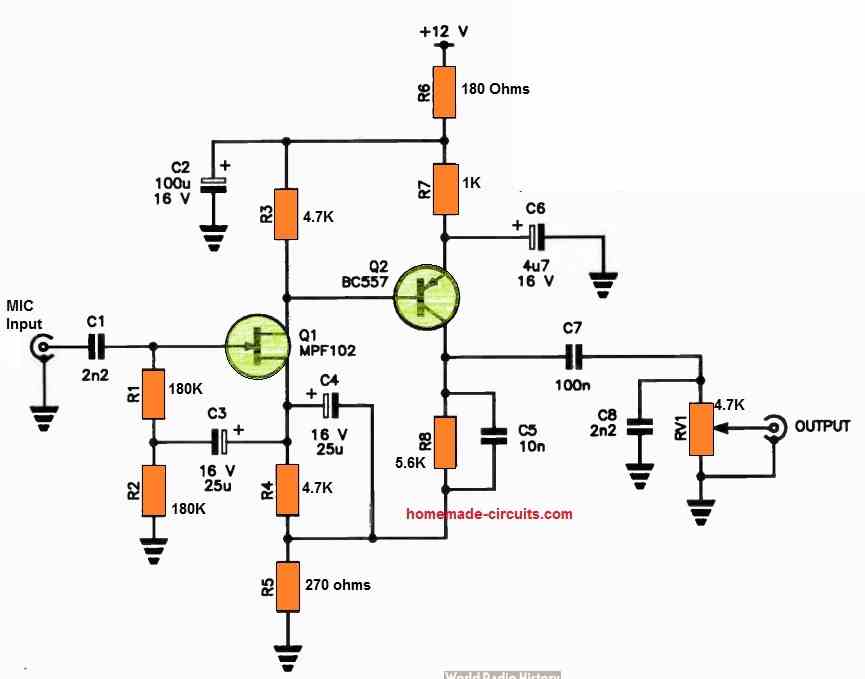
This circuit is engineered to achieve the necessary roll-off slopes below 300 Hz and above 2 kHz. Notably, the higher frequencies experience a considerably swifter attenuation compared to the lower frequencies.
The input stage utilizes a JFET to establish a high-impedance input, which is then directly linked to Q2, a common-emitter stage with bootstrapped feedback to Q1.
The circuit operates with a 12 V power supply and can accommodate both low and high-impedance dynamic microphones.
In instances where a low-impedance microphone is employed, it may necessitate the addition of an appropriate load resistor across the input connector. RV1 is responsible for regulating the output level.


Comments
Thank you so very much for sharing your knowledge and expertise with us on this forum. I am wondering, if in one of the above two transistor type preamps if I may use a ge npn transistor first to gain some sort of color for the signal. Also, if I were to use a higher gain transistor like an A14 first, and then used the low gain ge npn transistor, would I get an overdriven signal? Or would it be a saturated signal? I am not green, but I am far from an expert. Thanks so much.
Thank you for sharing these great circuits. Would it be possible to use one of these preamp circuits to override the preamp in my Philips N4307 open reel tape recorder that will not record but plays back ok ?
Thank you for your feedback, the above circuits are general purpose preamplifier circuits and should work with any standard power amplifier circuit.
Great website. Appreciate your hard work.
I built the simple 2 transistor bootstrap amp this morning.
I tested it. Very NICE!
It’s an excellent audio driver for the LM386 line of amplifiers.
If you can build the 386 on a ground plane and drive it sufficiently,
you can operate it at about half volume with no distortion. More efficient and power to spare.
This little bootstrap amp is clean with good frequency response.
Very nice for hobby radio work. I hope to build many more for future projects.
Big thumbs up to you !
Thank you for the encouraging feedback, appreciate it very much, and glad you found the circuit useful. I hope the other readers will find this review interesting.
Thanks for the quick reply about the 1.5v preamp. I can see where C1 connects to the base of T1 , my question was does C1 connect to the emitter of T1 then connect to R1 or does the leg bypass T1 and connect direct to R1. Please excuse my ignorance
No, C1 is not connected to the T1 emitter, it is directly connected to R1. T1 emitter is connected to the ground line only.
In the 1.5v preamp circuit, is the reverse polarity of C1 correct and does it bypass T1 and go direct to R1.
It doesn’t actually matter since the audio is an oscillating AC….no it does not bypass the transistor T1
In the circuit diagram under “Another Transistorized Preamp design” (high impedance two stage), can you explain the purpose of C3 that is between the power source and emitter of TR2? And, can it’s capacitance be increased without ill-effect? I would like to use some spare parts ofva different spec that I have on hand. Thank you.
It is for ensuring optimal current transfer to the emitter/collector of TR2. Higher values can damage the TR2.
Both can be used for reproducing good HiFi audio. I do not have a subwoofer amp at this moment, will try to find and update it soon….
I only need a subwoofer preamp with a filter. Maybe 12 db. filter. Maybe only 1 Fet in the signalway.
Presently I do not have it, if i get it, will update it for you!
Which one do you recommend for a headphone amplifier? the idea is monitoring an acoustic electric guitar.
I recommend the first one!
However for guitar, I would rather prefer the op amp circuit described in the following article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/100-watt-guitar-amplifier-circuit/
Which one do you recommend for a headphone amplifier?
for headphone, you can try one of these:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/mini-audio-amplifier-circuits/
I am a STEM teacher at a public school. I am interested in developing a unit on radio frequency engineering and basic electronics. I plan on having students build a simple AM radio (tuning coil, diode, ear piece, antenna and ground). I would like for the students to build a transistor-based amplifier. What would be your suggestions? I also feel like this would need a pre-amp because of the low power. Is this correct? If so, what would you suggest for a pre-amp?
Thanks.
Creighton
Mostly a radio circuit will be already equipped with a transistorized preamplifier so an external pramp will not be required. Instead you can use the output from the receiver circuit and integrate it directly with a small amplifier, such as this one:
Mini Audio Amplifier Circuits
or the following LM386 based amplifier can also be used:
LM386 Amplifier Circuit – Working Specifications Explained
For simple radio circuits you can refer to the following post:
Simplest AM Radio Circuit
Hi sir,
I have an audio amplifier at home. It was very old and so I recently modified it. I put a usb board and added one tone control circuit from Aliexpress. The power amplifier is STK 4141. When I turned on the amplifier, it is working, but the volume is very low. After checking the circuits, I found that the tone control circuit has no gain at all and so a preamplifier is required. Which pre-amplifier is best for this circuit. Thanks in advance for your reply.
Hi Sabu, you can try the first design, it should work for your requirement
HI
first of all thank you for sharing your knowledge .
there is a problem in one of the pictures in site .
In a picture that indicates a guitar preamp circuit , the quality is not appropriate and there are some unreadable information .
I’ll be really thankful if you send me a higher quality one.
yours faithfully Esmaeil Rezaee
Hi, the original print in the magazine itself is blurred. I tried to scan it again but this is the maximum I could get:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/preamplifier-for-guitar.png
However, the parts numbers are recognizable when visualized carefully.
Thank you for your consideration!
Since I’m a beginner it’s almost impossible to even guess what are they .
I’ll be thankful if you send me a list of the pieces of that specific guitar preamp although if you don’t it’s completely understandable .
No problem, however,If you are a beginner, then you must first learn the parameters thoroughly otherwise building and testing this project can become very difficulty ultimately.
Thank you
Hi,
I’m looking at the 1.5 V Preamplifier circuit and I could use some help with understanding a couple of the parts, as the picture isn’t super clear (and I am not too familiar with schematics):
C1: it looks like the diagram says 1u5 – is the “u5” the same as microfarad (uF)? Is it a 3V 1uF capacitor?
C2: I can’t tell if the diagram says 47u or 4.7u. Is this microfarad (uF)?
C3: (same question as C1)
P1: it looks like this says “2k 2” – is this a 2k variable resistor?
Any help appreciated.
Hi,
C1 = 1.5 microfarad
C2 = 47 microfarad, for 4.7uF you might have seen it as 4u7
P1 = 2.2 kilo ohms
Thank you for clearing that up. I have one more question, about the transistors. When I search for BC547 and BC549C on sites like digikey.com and mouser.com, I am getting a ton of variations. Are these are all equivalent or will only certain ones work?
For BC547, I see part numbers like:
BC547A A1
BC547A A1G
BC547ATA
BC547B
BC547B A1
BC547B A1G
BC547B TIN/LEAD
BC547BBU
BC547BTA
BC547BTF
BC547C A1
BC547C A1G
BC547C B1G
BC547C-AP
BC547CBU
BC547CTA
BC547CTFR
BC547-ND
BC548BTA
2156-BC547-ON-ND
For BC549C, I see part numbers like:
BC549C A1
BC549C A1G
BC549C B1G
BC549C,112
BC549C_J35Z
BC549CBU
BC549CG
BC549CTA
BC549CTF
BC549CTFR
Any help appreciated.
You can ignore all those variations choose any one of them if your supply voltage to circuit is below 24 V, and the current load for the transistor is below 60 mA.
BC547 is the one which will be suitable even up to 50 V, the attached subscript is not critical.
Thank you for clearing that up.
If I am plugging in a passive electric guitar, I assume the current load would be below 60 mA?
Yes, much below 60 mA
Hello,
Based on your response to my question, I replaced R3 with a 500K trimmer pot and was able to make the preamp much more useful to drive my audio amp. With the 500K trimmer pot installed, I was able to reduce the resistance between the first transistor base and the second transistor emitter to around 30K which eliminated some unwanted squealing in my audio amp. I also found that if you reduce the resistance too much, the sound from the audio amp has too much treble. I’m sure that a 100K pot would also work just as well.
Just wanted to let you know.
Thanks again.
Sounds interesting! Thanks very much for this useful information!
Thank you sir very much!
No problem Sir!
Thank you sir for that quick response.
Can you tell me what the gain would be for the first circuit as it is shown above assuming 12V power?
Thank you!
As per the available information from a relevant source, it should be 26 dB or a voltage gain of 20
Hello,
Can you advise me of the gain for the Preamp circuit above that is labeled 1) Preamplifier using two Transistors?
Also, I would like to be able to vary the gain of this circuit. Can you tell me the best place to insert a gain control? I assume it would just be a pot?
Thank you very much.
Hi, I think it can be done by adding a variable resistor in series with R3
Thank you for sharing with us these awesome circuits, ‘appreciated…especially the 1st preamp circuit. It really works for me, used for my project/s. Simple yet very efficient and effective. Very useful too! Again, thank you sir!
hi again sir, just dropping by to ask one more thing… from the 1st schematic diagram circuit, the C1 is what type of capacitor (ceramic, mylar, electrolytic)? thanks in advance sir!
thank you so much for the reply, sir. appreciated!
hi and good day sir! ok great! yeah, i tried a ceramic type and it works too. so if it’s an electrolytic type, the negative side of the electrolytic cap should go to the mic? or should be the + side? thanks for your prompt reply sir.
thanks so much once again, sir! appreciated the quick reply. ok sir, this is noted. now, i have peace of mind, haha! ty sir! have a nice day!
likewise sir!
No problem, have a nice day!
Actually both polar and non-polar should work when used across an amplifier input output stages. The negative side should be towards the music input side or MiC side.
Hi Harold, it can be any non polar capacitor, a disc ceramic will also work…
Great, glad it helped you, thanks for the feedback…
Dear Sir!Can we use this Circuit instead of a Transformer of Loudspeaker?
No that's not possible…
Sir excuse my ignorance but, what is the function of R3?. Your website is amazing!!!
Tranks you.
TUERESUECO, it is for providing a feedback loop which enhances the amplification many folds, without R3 the amplifier will be unable to amplify the input efficiently
But sir what should I do if I am not able to get a 10 amp transformer in market. And I am using 7.6Ah battery. I'm using IRF 540 MOSFETs and 2.2uf capacitor in its astable multivibrator.
Abhishek, get rid of the mosfets and build it using 2N3055 BJTs which will give you confirmed results.
Make it exactly as shown in the following article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2012/07/simplest-and-best-100-watt-inverter.html
Sir, it's an astable multivibrator oscillator using 2n2222a and 2.2uf capacitor, and there are MOSFETs IRF 540 on each side, now I have checked the components using multimeter and the value of two transistors just different by 2 or 4 number and MOSFET are good but could you tell me what could be the fault and factors on which I should focus? And can replacing MOSFETs IRF540 with IRFZ44N give me good results.
If the problem is regarding the flickering of a CFL then increasing the trafo amp will not help, it could be due to a faulty oscillator circuit or some other fault….because any CFL under 100 watt will easily light up brightly with your existing trafo and battery.
What is the ampere of Transformer with turn ratio 19:1 12v centre tapped? How to do all that calculations. And other thing I Want to ask that by adding a 8A OR 10A transformer, will the CFL stop that minor blinking problem?, because all other things I have checked correct.
then there's no other way of achieving the mentioned results, you can do it only by upgrading the trafo and the battery specs.
7.6AH is quite less and will not provide more than 100 watt at the output
Dear sir I want a circuit to amplify an ac signal of 220-240v ac output from my inverter to amplify current. Its a square wave Inverter I have made it by astable multivibrator and two MOSFET and a 5 amp 12-0-12 transformer. The output Is fluctuating. Please suggest a circuit which do not contain any IC, to stabilize the output or amplify it, I have transistors 2n2222a,2n3904,2n3906,bc547,bc 557,and MOSFET IRF 540 and 630.and 68ohms, 510ohms, 10k ohms resistance as unused component so suggest me to utilise them all in that circuit
Dear Abhishek, no need of any external circuit, to amplify you just have to upgrade the trafo from 5 amp to 10 amp or as desired.
and thee battery AH must be also upgraded appropriately.
The trafo voltage rating should be preferably 9-0-9V for a 12V battery
Hi sir,
I tried to run a DC motor (found in trimmer) using a power supply circuit from LM317 , 12v transformer. The diodes & IC's were over heating, please provide me a driver simple circuit.
Thank You
Hi Karthik, the IC and the diodes will heat up if the load current is above the 50% of their maximum handling capacity…..so if the motor is rated at around 500mA then those parts will heat up….for the diodes you can try 1N5408 and for the LM317 use a large hetasink to control the dissipation.
Pls sir what power can this amplifier produce and can i use this circuit as a preamp in my homemade lm3886 amplifier in the sense that i want to use the input of this amp as my music input and the output as the lm3886 amplifier input so the amp will sound much louder at it's final output(speaker) is that a good idea?
victory, yes you can use this circuit for your application, it's exactly meant for such applications.
however if the source music is already loud enough for the LM3886 input then in that case the above circuit could be useless and an overkill….
Dear sir good day to you
I have used 12v motor It is made to put the pcb hole but it often reaches temperatures. How can I avoid it? Please Provide appropriate protection circuit
Motor specification:
25000 RPM no load speed at 12V
No Load Current – 1A, Stall Current – 10A
0.36 Kgcm torque
Thank you
Dear Rajkumar…power the motor through an LM338 circuit….the LM338 has an internal high temperature protection….you can attach this IC with the motor body, so if the motor heats up, the IC will also heat up, and its internal circuitry will shut off the current preventing any possible damage to both the devices, whenever the heat crosses sat around 90 C.
Dear sir
I can not believe it !!! It is very pleasant, how to set volume control
you can connect a pot across the C2 for implementing the volume control feature.
Sir can I use lm386 as amplifier for this? tnx Sir
yes you can…