In this article I will explain a 5 assorted power bank circuits using 1.5V cell and 3.7V Li-ion cell which can be built by any individual for their personal emergency cellphone charging functionality. The idea was requested by Mr. Irfan
What is a Power Bank
Power bank is a battery pack which is used to charge a cellphone outdoors during emergency situations when an AC outlet is unavailable for charging the cellphone.
Power bank modules have gained significant popularity today due to their portability and ability to charge any cell phone while traveling and during emergency requirements.
It is basically a battery bank box which is initially fully charged by the user at home, and then carried outdoors while travelling. When the user finds his cellphone or smartphone battery reaching low, he connects the power bank to his cellphone for a quick emergency topping-up of the cellphone.
How Does a Power Bank Works
I have already discussed one such emergency charger pack circuit in this blog, which used chargeable Ni-Cd cells for the intended function. Since we had 1.2V Ni-Cd cells employed in the design we could configure it to the exactly required 4.8V by incorporating 4 of these cells in series, making the design extremely compact and suitable for optimally charging all types of conventional cell phones.
However in the present request the power bank needs to be built using 3.7V Li-ion cells whose voltage parameter becomes quite unsuitable for charging a cellphone which also uses an identical battery parameter.
The problem lies in the fact that when two identical batteries or cells are connected across each other, these devices begin exchanging their power such that finally an equilibrium condition is achieved wherein both the cells or the batteries are able to attain equal amounts of charge or the power levels.
Therefore, in our case suppose if the power bank utilizing a 3.7V cell is charged fully to about 4.2V and applied to a cellphone with a drained cell level at say 3.3V, then both the counterparts would try to exchange power and reach a level equal to (3.3 + 4.2) / 2 = 3.75V.
But 3.75V cannot be considered the full charge level for the cell phone which is actually required to be charged at 4.2V for an optimal response.
Making a 3.7V Power Bank Circuit
The following image shows the basic structure of a power bank design:
Block Diagram
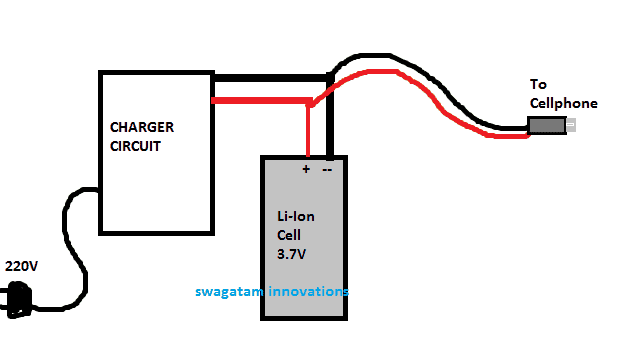
As can be seen in the above design, a charger circuit charges a 3.7V cell, once the charging is completed, the 3.7V cell box is carried by the user while traveling, and whenever the user's cellphone battery goes down, he simply connects this 3.7V cell pack with his cellphone for topping it up quickly.
As discussed in the previous paragraph, in order to enable the 3.7V power bank to be able to provide the required 4.2V at a consistent rate until the cellphone is completely charged at this level, a step up circuit becomes imperative.
1) Simple Power Bank Circuit using 18650 Li-Ion Batteries
The following figure shows the simplest and the best power bank circuit design that you can build and implement quickly.
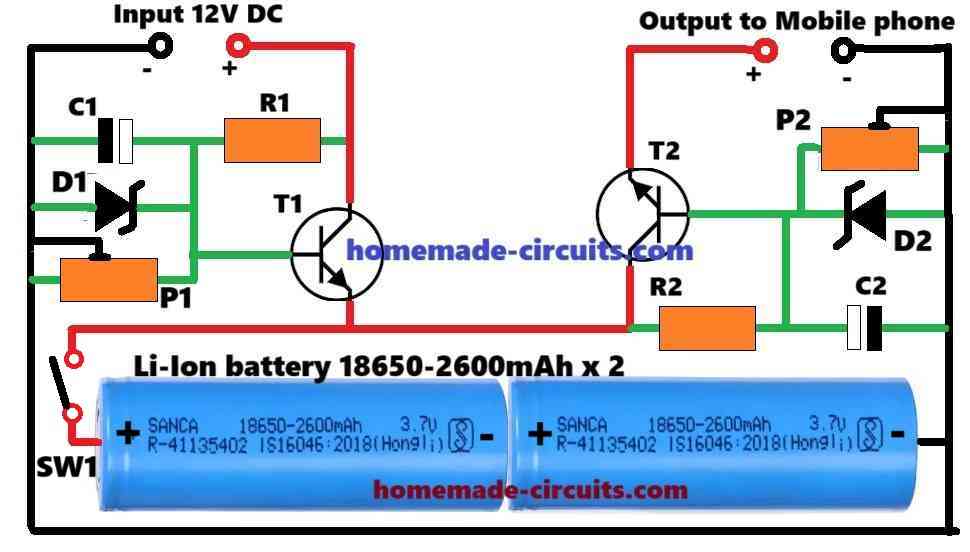
Parts List
- Resistors are 5 watt CFR
- R1, R2 = As per the calculations
- C1, C2 = 100uF/25V
- D1 = 9V zener diode 1 watt
- D2 = 6V zener diode 1 watt
- T1, T2 = 2N3055
- P1, P2 = 1k preset
- SPST ON/OFF Switch = 1
The circuit incorporates two identical emitter-follower transistor regulator stages, whose output voltages can be adjusted and fixed using presets.
One regulator stage forms the charger section of the power bank, while the second regulator stage constitutes the charging output for charging a mobile phone.
Input Stage for Charging the Internal Power Bank Battery
One regulator circuit can be seen configured around T1, R1, D1, P1, C1 which forms the input side of the power bank.
This input side is supposed to be supplied with an external 12V DC for charging or topping up the internal Li-ion Batteries of the power bank, whenever they are exhausted.
R1 supplies the base voltage and current for T1. This voltage is stabilized to around 9V by the zener diode D1.
Since T1 is configured as an emitter-follower, its emitter terminal follows its base voltage producing around 9 - 0.6 = 8.4V at the emitter end. The 0.6V is the internal drop of the transistor.
This 8.4V from the T1 emitter supplies the charging voltage for the two 18650 batteries connected in series.
The above 8.4V specifies the full charge voltage for the two batteries (4.2V + 4.2V).
However, since there's no over charge voltage cut-off in this T1 configuration, it is recommended to keep the battery full charge level a shade lower than 8.4V.
Ideally this can be reduced to around 8.2V for an optimal charging of the power bank batteries without the danger of overcharging them.
The 8.2V can be set by appropriately adjusting the preset P1.
Output Stage for Charging External Mobile Phone
The circuit configured around T2, R2, D2, P2, C2 forms the output stage of the power bank.
This stage supplies the output voltage for charging an external mobile phone.
The working of this T2 emitter follower regulator stage is exactly similar to the T1 stage explained above.
However, for this regulator the output voltage is optimized with a 5V output which becomes perfectly suitable for charging any mobile phone or smart phone.
The setting up of the 5V output is precisely done using the P2 preset and the D2 zener diode.
Power bank Resistor Calculations
The resistors R1 and R2 decide how much current can be achieved across the emitter side of the transistors.
These output currents determine how fast the internal battery of the power bank and the external mobile phone can be charged.
R1 and R2 can be calculated using the following formula.
R1 = [Input Voltage - (0.6 + Battery Voltage)] x hFE / Max Charging Current
Assuming the battery voltage to be 7.4 V (3.7 + 3.7), Max charging current to be 1 amp and hFE for 2N3055 = 70, we can solve the R1 value as shown below:
R1 = [12 - (0.6 + 7.4)] x 70 / 1 = 280 Ohms (Nearest Standard Value = 270 Ohms)
Power = 12 - (0.6 + 7.4) x 1 = 4 watts or higher.
R2 = [Input Voltage - (0.6 + Battery Voltage)] x hFE / Max Charging Current
Assuming the battery voltage for charging an external cell phone is 5V, hFE = 70 and Max charging current = 1 amp
R2 = [8.2 - (0.6 + 5)] x 70 / 1 = 182 Ohms (Nearest Standard Value = 180 Ohms)
Power = [8.2 - (0.6 + 5)] x 1 = 2.6 watt or higher.
2) IC 555 Boost Power Bank Circuit
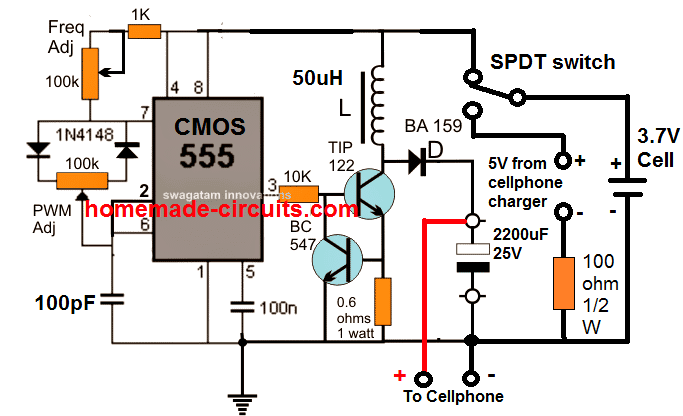
3) Using a Joule Thief Circuit
If you think that the above IC 555 based power bank charger circuit looks cumbersome and an overkill, you could probably try a Joule thief concept for achieving quite the same results, as shown below:
Using 3.7V Li-Ion Cell
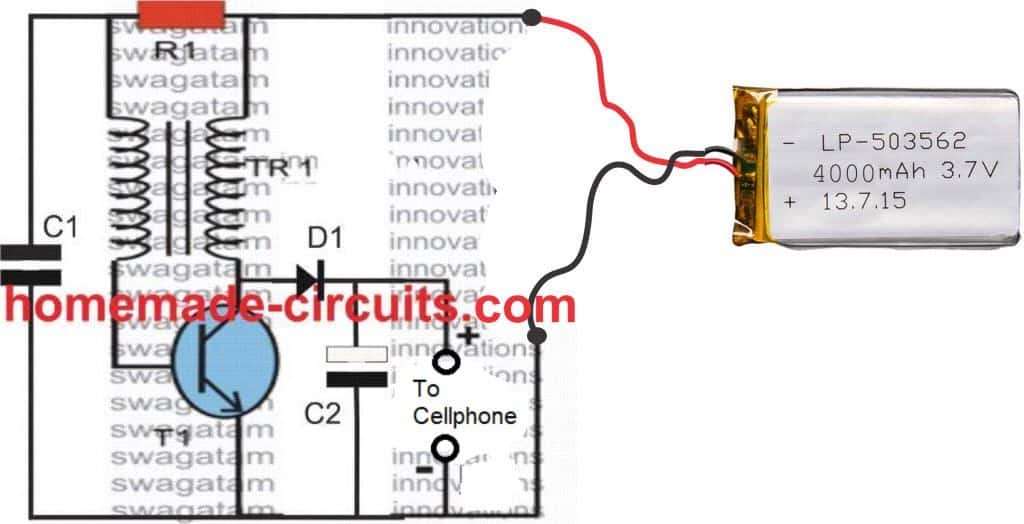
Here, you can try 470 ohm, 1 watt resistor for R1, and 2N2222 transistor for T1.
1N5408 for D1, and a 1000uF/25V for C2.
Use 0.0047uF/100V for C1
The LED is not required, the LED points could be used as the output terminal for charging your smartphone
The coil is made over a T18 Torroidal ferrite core, with 20:10 turns for the primary and secondary, using multistarnd (7/36) flexible PVC insulated wire. This may be implemented if the input is from a pack of 5nos of 1.5V AAA cells in parallel.
If you select Li-Ion cell at the input source, the ratio might need to be changed to 20:10 turns, 20 being at the base side of the coil.
The transistor might need a suitable heatsink in order to dissipate optimally.
Using 1.5V Li-Ion Cell
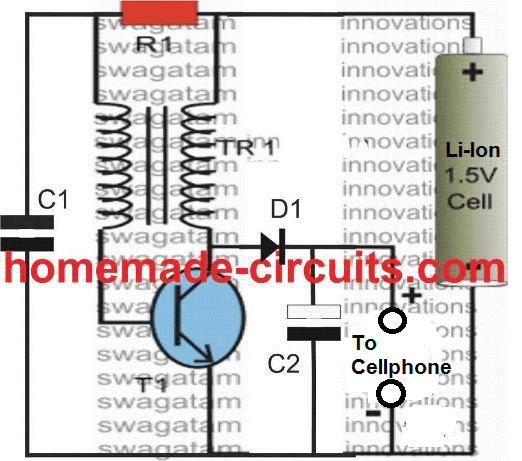
The part list will be the same as mentioned in the previous paragraph except the inductor, which will now have a 20:20 turn ratio using a 27SWG wire or any other suitable size magnet wire
4) Using TIP122 Emitter Follower
The following image shows the complete design of a smartphone power bank with charger using Joule thief circuit:
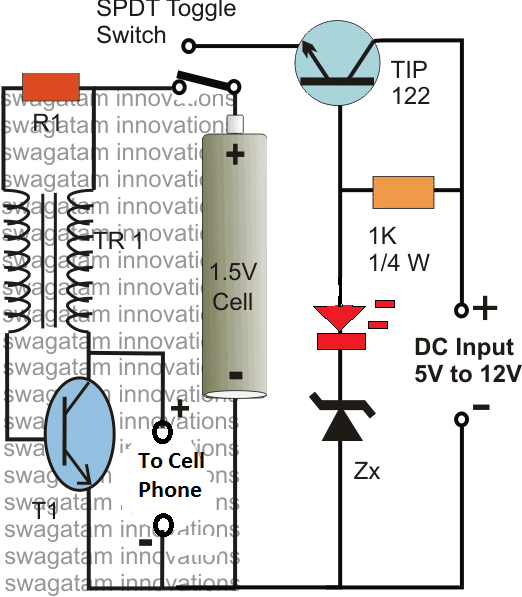
Here the TIP122 along with its base zener becomes a voltage regulator stage and is used as stabilized battery charger for the attached battery. The Zx value determines the charging voltage, and its value must be selected such that it's always a shade lower than the actual full charge value of the battery.
For example if a Li-Ion battery is used, you may select Zx as 5.8V in order prevent the battery from overcharging. From this 5.8V, the LED will drop around 1.2V, and the TIP122 will drop around 0.6V, which will ultimately allow the 3.7V cell to get around 4V, which is just around sufficient for the purpose.
For 1.5V AAA (5 in parallel), the zener could be replaced with a single 1N4007 diode with its cathode towards ground.
The LED is included for roughly indicating the full charge condition of the connected cell. When the LED lights up brightly, you may assume the cell to be fully charged.
The DC input for the above charger circuit could be acquired from your normal cellphone AC/DC charger unit.
Although the above design is efficient and recommended for an optimal response, the idea may not be easy for a newcomer to build and optimize. Therefore for users who might be OK with a slightly low tech design but much easier DIY alternative than the boost converter concept might be interested in the following configurations:
The three simple power bank circuit designs shown below utilizes minimum number of components and can be built by any new hobbyist within seconds
Although the designs look very straightforward, it demands the use of two 3.7V cells in series for the proposed power bank operations.
5) Using Two Li-Ion Cells without Complex Circuit
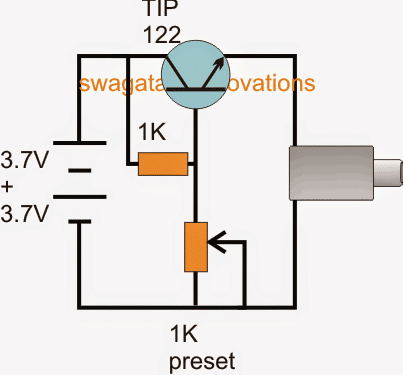
The first circuit above makes use of a common collector transistor configuration for charging the intended cellphone device, the 1K perset is initially adjusted to enable a precise 4.3V across the emitter of the transistor.
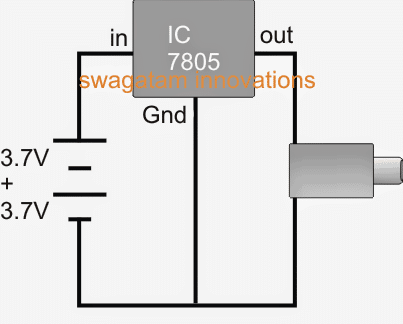
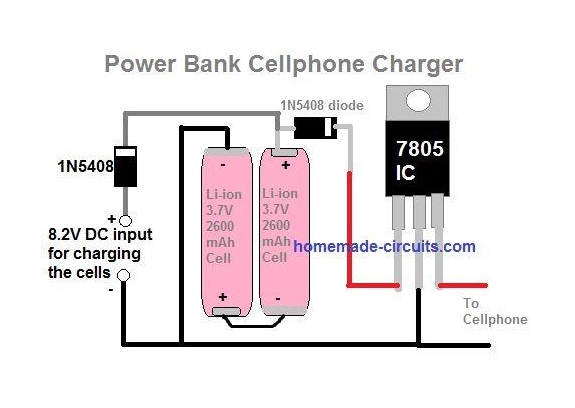
The second design above uses a 7805 voltage regulator circuit for implementing the power bank charging function
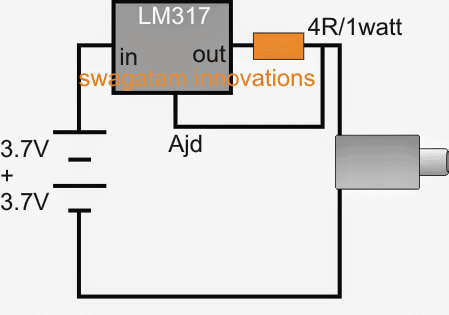
The last diagram here depicts a charger design using an LM317 current limiter. This idea looks much impressive than the above two since it takes care of the voltage control and the current control together ensuring a prefect charging of the cellphone.
In all the four above power bank cell phone charger circuits, the charging of the two 3.7V cells can be done with the same TIP122 network which is discussed for the first boost charger design. The 5V zener should be changed to a 9V zener diode and the charging input obtained from any standard 12V/1amp SMPS adapter.
There is this power Boaster been made in Nigeria and the boaster is used on generators or inverters with 1000watts output. Please would you share with me the possible design of this Boaster circuit and how it works
Power booster is possible only through a transformer for all regular loads, but if you want to power only resistive loads then you can use capacitors.
Sir in the ic 555 boosted circuit, can i put 6x 3.7v 18650?
Hi Kenji, yes you can, however first it is important to setup and optimize the circuit using a single cell…
Sir the 5v from the phone charger is for charging the battery in the ic boosted circuit?
Yes, that’s correct.
Another question sir can increase the voltage of the battery to 8.4v, it will not affect the circuit?
You can use it, but If you have 8.4V source then the boost converter might not be needed, you can use the 8.4V directly to charge a cellphone via a regulator??
Ok thanks
What is the output current, and how do i increase it, im planning to use this circuit in my project thnaks
Power is upto 3 amps, you caan increase it upto 6 amps by using TIP35 transistor.
Ne555 will work here? Srry im new with electronics and i dontwhich 555 should i buy, Thanks
Any IC 555 can be used here, all will work.
Its should be cmos version?
Yes, CMOS will be better since it will consume less current…
Can it charge 2 cellphone at same time?
Please try with a single phone first, if it works then we can easily upgrade it for 2 phones.
Sorry but I can’t find a ba159, what can i use?
Try FR107 or any fast recovery diode if your inverter frequency is higher than 500Hz, if it’s less then use 1N5402
i cant find 50uh inductor, 100uh will work?
The coil will actually need to be experimented and set by trial and error. Start with 100 turns of enameled copper wire over a ferrite rod or ferrite ring, and check the boosted voltage level and also make sure the driver transistor is not heating up. If the transistor heats up, increase the number of turns until heating stops. But if the voltage is not getting boosted that would indicate a faulty 555 configuration.
i made the circuit but the voltage continues to rise and when i put a load the voltage drop to around 3.3 volts
The 555 boost converter will need to be optimized correctly. Which load did you use, and which battery did you use (mAH rating?)
I sent the image sir .However, you may wish to give me a circuit diagram with parts list for power bank that can charge two android phone at the same time using 3.7v X 6 or more.
Momoh, I saw your images but without checking it practically it can be difficult to troubleshoot the fault. So it is better to build a the circuit yourself which is much easier.
I will design the required circuit and update it in the above post, I will let you know once it is done.
I have updated the new power bank circuit under the title 1) Simple Power Bank Circuit using 18650 Li-Ion Batteries
Thank you sir.
Question: Can be battery more than two,looking at what is the diagram?That is another 2 bat.connect in series and be in parallel with the former?
You are welcome Momoh,
Yes, you can add another 2S battery parallel to the existing pair.
But before buying more batteries please verify the charging procedure of the circuit using two batteries only.
can this charge 2 phones at a time if another out put is being tapped from ”out to phone” as shown?
You will have to test it practically to know the exact results. Please do the testing procedures step by step.
great sir
Good day sir.
i bougth a power bank circuit(module).How can i connect it to six 3.7v battery?i did connection in parallel to the B+ and B- .In the module it has usb pots(male and female) but becoming hot when connected. I would like to sent you the pic.Thanks
Hello Momoh,
You can upload the image to any free online image hosting site and send me the link here, I will try to figure it out…
Pls how can I step up current in a 12v circuit
Which circuit diagram are you referring to?
I need circuit for 9 batteries to make 50,000mah
Good day Mr swag,
PLS due to unavailability of resources,can I simply use only diodes as many as possible in combination of two 3.7volt battery ???? connected in parallel to make a power bank to charge all kinds of android phones without burning their(the android phone) charging circuit or system,and if YES,PLS show me a diagram .
Hi Franklin,
Yes you can use diodes if transistors are not available to you. However the diodes will need to be high power diodes such as 1N5402. Two fully charged 3.7V Li-ion would produce around 8.4V. to drop this to 5V, you would require around 5 diodes in series.
Alternatively, you can simply buy any 5 V, 3 Ah rechargeable battery and use it in your power bank unit to directly charge any cell phone.
January 4th. 2023
Hello Mr.Swagatam
1) IC 555 Boost Power Bank Circuit.
I built 1) and I am getting 5.1 volts out of it, bit when I plug im the phone to charge, the voltage fluctuates between 4.1 to 5.1 volts.
The phone indicates thats its charging, but what is really happening is that the phone nattwry percentage drops.
could you tell me what am I doing wrong and what I can so to rectify rhe issue.
thank you.
Mike
Hi Mike,
did you connect a 1000uF or 2200uf capacitor at the output of the 5.1V supply?
Also which value did you use for the current limiting resistors?
January 5, 2023
Hi Mr. Swagatam,
I did connect the 2200uf/25v capacitor at the output and the values of the resistors is the same as in the diagram. I didn’t have a BA159 diode at hand so I replaced it with a FR104 fast recovery diode, could that cause the fluctuation? The remaining components is the same as in the diagram.
Thank You
OK, thanks for the reply! Which value resistor did you connect for the 0.6 ohms?
This resistor is responsible for limiting the output current which can affect the charging process.
Another factor is the input supply current which must be at least 1 amp.
And the winding of the coil must be done using a 1 mm magnet wire.
Mike
January 7, 2023
Hello Mr. Swagatam,
Thanks for your reply.
I had a 1 ohm resistor instead of the 0.6 ohm resistor and the coil and the current in the circuit and get back to you.
Thank You
Mike
Mike
January 7, 2023.
I need to check the coil and see how much current the circuit is drawing.
Mike
Hello Mike, 1 ohm will limit the output current to 0.6 amps only. Try 0.6 ohm or 0.5 ohms instead.
Hello Swagatam,
Thank you for the info, I will find the 0.6 ohm or 0.5 ohm resistor and test the circuit again.
Mike
OK, no problem Mike!
Hi! Am am an aspiring electronic engeneer and hobbist. I have like your idea on making power bank. I tried (2) that and i succeeded
Thank you for trying the project. I am glad you could succeed with it.
I want it in a simple form for a junior student
HOW CAN I MAKE A BOOSTER THAT BOOST 1.5 VOLTAGE 5 VOLTAGE WITH HOME MADE MATERIAL OR SPOILT TORCH OR SPOILT DVD PLAYER OR SPOILT RADIO
You can try a joule thief concept, as explained in the following article:
3 Best Joule Thief Circuits
Please can you teach me how to make a power bank?
You can build a simple power bank circuit using the following design, there’s nothing complicated about it:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/power-bank-circuit.jpg
Good day sir. I want to construct a power bank for phone that can charge 1-4 cell phone at a time using 6 of 3.7v battery. I need a circuit diagram.
Hi Momoh, you can try the following configuration:
thank u sir.i believed that if these batteries are wholly meant to charge a cell phone at a time it will last longer in term of its capacity?can the above charge any type of cell phone?where should i place led indicator light for out put? Remain blessed.
Thanks Momoh, yes you can charge any type of cellphone using the 2 series cell concept explained in the above article, however, the mAh capacity of the cells in the power bank may be different for different phones. Unfortunately an LED cannot be placed because LED will consume extra power and deplete the power bank battery faster.
Good day sir.Kindly help me out of this: i am having a bontel product(big phone,not android anyway),the batteries are flat.i opened it discovered it is 3.7v ty pe of battery.i removed the old and put the new one when i insert it,it show enough charging from battery level indicator but it is not charging when connected.It is the same failure i got from trying to replace a new battery with old one in a lap top. All connections are carefully followed.What is the way out to achieve this sir while carrying repairing sir.
Hi Momoh, sorry, solving a phone or laptop related issue can be difficult for me since I can’t figure out how the phone is functioning internally.
sir the problem we get hete in africa is we cant get all the component needed. What is the way out? thanks you sir for contibuting
Hi Hizbullahi, You can try buying it from an online store.
hello bro good morning for our side about this your transistor power bank
1 it didn’t increase charging
2 i want to have a lesson with you bro
3 about the calculation of resistor
ok bro please reply me in time
Hello philip, for the single transistor circuit make sure to have a powerful transistor and a powerful transformer, to match the current requirement of the battery.
If you are unable to optimize the circuit, it is better to use the two battery circuit, which is failproof and will give guaranteed results.
Thank you sir for this eye opening, I’m a layman but i find the 4 example very simple to do. I mean where 1N5408 and 7805IC was used.
But I would like to integrate the TIP122 and the zener diode circuit unit in the TIP122 emitter follower circuit into it and I don’t know how to do it. Can you please give me a diagram for the integration?
Thanks in advance.
Thanks Jayman, here’s the design as per your requirement:
Thanks so much I’ve assembled the design but when tested with a multimeter, the output voltage is 4.76V it’s not up to 5v hence it’s not sufficient enough to charge my infinix Android phone.
Thanks for your time
You can remove the 7805, and use 4 or 6 1N5408 diodes in series until you have 5 to 6V at the output
Sorry for bothering you sir, the 7508 is now charging my phone and it increases the charge but it’s damn too slow, what can I do to correct that?
Try two 7805s in parallel and check the response, but make sure to put both over the same heatsink
Thank you sir, after using two 7805 in parallel the charging speed showed a positive response.
At that time the battery pack voltage was at 7V and the output voltage was 4.9V.
But when the phone was charged to about 54 percent, the battery voltage as decreased to 6.1v and the output voltage was 4.1v respectively.
At this point the phone only shows charging but didn’t increase again.
Then I noticed that both the 1N5408 and the 7805 that was generating heat before is not heating up again but was cold.
Jayman, it is the internal circuitry and connections of the phone which is causing the battery to switch at different charging rates. If it would be an open battery you wouldn’t have had such issues.
If your 7805s heats up then it may not be supplying proper current for the phone battery.
In that case you will have to replace it with a 5 amp regulator such an LM338 regulator circuit with heatsink or the one that is shown below:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/lm317-variable-switch-mode-power-supply/
How come
Sir, am repairing a 20000mah Power bank. I changed d charging port because it wasn’t charging and it was charging normally & could also charge phone but due it’s light weight, d owner complained that I should replace d bad batteries to increase d weight of d Power bank but d power bank stopped charging phone thereafter. Maybe I mistakenly remove a tiny resistor or component during soldering. Pls what should I do to make it charge phone again? -Femi
Adeniyi, Without practically seeing and examining the device it can be very difficult to judge the fault or the resistor value.
Sir, I’m confused a bit at the zener diode point. I want to connect a red LED to it as shown in the original design before this integration was done. But which terminal of the diode will I connect to the red LED and which terminal will go out to the negative point for charging the cell from the zener diode?
Novice, you can connect the LED in series with an appropriately selected zener diode, just make sure that together they produce an output voltage of 8.4V for the battery pack. The longer leg (anode) of the LEd will to transistor base
I couldn’t get LM 338 only LM 317 is available at my reach here and the maximum amp that it could give is 1.5 can I connect it in parallel just like I did for 7805?
That will give you with great difficult near 3 amps if the heatsink is really large. make sure to connect both of them over a common heatsink.
Before that, test each of the ICs separately through their standard variable voltage regulator designs, as I have explained below, if both the ICs work correctly, then you can put both of them in parallel with the resistor/pot network.
How to Use LM317 for Making a Variable Power Supply Circuit
I’ve tried the LM 317 the output current of 1 is 2 so two of it gave 4A.
But the problem is not solved yet in the sense that all these transistors works by stepping down the input current to around 5/6V depending on the input but let’s say generally by reduction of 2v from the incoming one.
So once the input voltage reach 6 or 5v the output voltage will also drop to 4v or lesser making it insufficient enough to continue charging the phone.
So I think a voltage booster is actually what’s needed to make it work continuously so that the output voltage can always be between 5 to 6v.
So I’ve some scrab power bank panels with me since it has a ready made boost converter coil, I’m thinking of a way to use the coil in my own circuit so that my output voltage can always be 6v maximum to charge the phone
You will need a buck converter version for that. You can try the following circuit in hat case:
LM317 Variable Switch Mode Power Supply (SMPS)
How can I get all d power bank spare part?
Hw can I also learn it very well?
Please reply me!
Please can you give a diagram of a 3.7 to 5v power bank
You can modify the first circuit from this article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/12v-car-laptop-charger-circuit-using/
In the second to the last diagram, can we reduce the input voltage to 5v/2A so that normal phone charger can be used to recharge the cell.
And can the batteries be more than two let’s say for example arranging 5 in parallels in 2 segments and then connect the two back in series so as to increase the mAh of the battery to up to 10,000 mAh and more while the voltage will remain at 7.4V. is that possible and does it need any additional components to achieve that?
5V cannot be used to charge two 3.7V cells in series, that is why 8.4V is shown in the second last diagram.
Yes you can connect as many cells you like, in series/parallel connections to increase the mAh capacity of the power bank as per the required specifications.
But at the end of the page you recommend 12v charger won’t it cause a damage to the circuit?
Then there’s no indicator led in the circuit how do I know when the cell is fully charged/discharged?
I have recommended 12V with a TIP122 emitter follower circuit, as shown in the 2) example from the following article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/how-to-make-simple-dc-to-dc-cell-phone/
for indication you can add the following circuit across the battery terminals:
Battery Full Charge Indicator Circuit using Two Transistors
Hi
I have a problem with my power bank since the inductor stoped connecting then I used wire to connect it and since then the power bank stopped charging instead it keeps reducing instead of charge
Please sir tell me what to do
The inductor is one of the the main components in the power bank, if you short it, it will never work
hello,i have batteries ,wire ,and a battery booster can i use the booster to create a gate way for charging the battery and charging of phone….?!
I have a battery of 7.4v and 1000mAH, is it possible to build power bank with 5v output,, If possible, can I get a circuit diagram please!
You can use a 7805 IC to get 5 V output
Nice design sir…. the output is 5v how many Ampere??
Thanks Desmond, it will depend on the input current and the coil dimensions
charging current at inputs seems the same as that of 6v/200mAH, is this the case ? if yes then charging 3.7v lithium battery with 200mah will take a very long time to charge. please explain.
yes it will take long, but will charge it safely…you can increase the current if you wish
Hi swagatam
my question is what is the principle behind switching off of the 6v/200mAH bulb as the battery get charged?
thanks a lot
Hi Abba, as the battery reaches full charge level, the TIP122 emitter also reaches a point where it is almost equal to the base voltage which stops the transistor from conducting any further and also the battery stops accepting any further current, together this stops any current from flowing into the battery and thus shuts down the bulb
hi Swagatam
I appreciate your effort for explaining the circuit and the concept behind them. my question is can you please elaborate more on how diode 1N4007 can be use to keep the transistor BC557 off during the charging phase of the battery(first circuit)?
thanks in advance
Thanks Abba, the 1N4007 from the TIP122 emitter applies a direct positive voltage on the base of BC557 which blocks the negative supply from the 10K resistor and thus shuts down the base bias for the BC557
thanks a lot, i get the concept now. my other question is how can i calculate the value of the individual resistors in a circuit especially if the circuit is a complex one.
thanks in advance.
It can a very long discussion not possible to do it through this comment box, you can perhaps join the forum and learn from the scratch…in short basically the base resistor for a transistor is selected as explained in the following article
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2012/01/how-to-make-relay-driver-stage-in.html
for an IC it is as per the datasheet of the IC.
Dear sir
I want to make a boost converter using 6v battery. Can you help me to make a boost converter circuit with an output voltage and current of 12v and 1.5A to power my 12v LED Bulb.
Thanks in advance
Noah, you can study the following article and accordingly build the design as per your requirement
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2015/10/calculating-inductor-value-in-smps.html
Thanks Swag
you are welcome!
Hi…In your first circuit ….TIP 122 beside the diode BA159 heated very much after using heat sink……how can i reduce the heat of TIP 122
Hi, the frequency will need to be optimized correctly for getting the desired results and to keep everything cool….connect a voltmeter across C, the keep tweaking the pots until you find maximum voltage across C.
this will ensure the most efficient working of the TIP122
I hope you have the current limiting transistor also installed as shown in the design.
yes………but till now i am facing another problem……output voltage is shown 4.44 volt and phone is showing charging….but charging level will not increased ……..what will be the problem……
please use an ammeter in series with the positive of the charging line, and check the current level……it should be at least 50% of the battery AH rating….if not then rewind the boost inductor using two or three parallel wires.
bro till now i am facing the same problem after increasing the inductor turn……and the current remain 0.07A after increasing…..now how can I increase the current ……
it can be difficult for me to troubleshoot your circuit without checking, if you are not able to optimize the boost circuit you can simply use a LMN317 power supply, set it at 4.1V and charge a Li-Ion cell which has an AH eating much higher than your cellphone battery, and use the set up as the power bank
Hi. My power bank circuit is complaint. Its battery is 3.7v but the output is required 5v1A. .plz help me..plz given a simple booster circuit diagram.am not a professional. .
you can use any IC 555 based boost converter circuit for this….I have already posted this in my website…you can search it using the search box at top right.
sir… is this circuit using cmos version of 555. from the sheet normal ne555 need minimal voltage 4.5 volt… or did you ever succeed with normal ne555
7(555) indicates a CMOS version, please refer to the diagram and see the number on the IC.
Sir, what's the rating for the transistor that's suitable to stop the power bank from turning of while a phone is charging (the voltage of the 5 power bank battery is 3.7v each )
Chinwike, I could not understand your question…which transistor are you referring to??
thank you
THANK YOU SO MUCH SIR
FOR YOUR USEFUL CIRCUITS AND EXPLAIN .
You are welcome
Hello Sir I'm now in 5th from ECE branch i wish to be design a Power bank. Sir… Of 10000mAh capacity Sir… Help me Sir
Hello, please provide all the technical details of the power bank, as per your specifications.
Sir there is a large power loss in case of second circuit using ic 7805. Is there any way to minimize the loss?
you can try a buck converter circuit instead
Sir, I’ve used the 1N5408 and 7805 circuit. It indicates charging but the charging is not increasing but rather decreasing and the 7805 IC generate much heat. What should I do to correct the errors?
Novice, if your mobile phone is showing “charging” then it must keep charging, it shouldn’t decrease. You can put one more 1N5408 diode at the OUT pin of the 7805 and check the response. The 7805 will heat up since it is a linear IC, you will have to use a heatsink with it to control the heating. If you want minimum heat dissipation then you may have to replace the 7805 circuit with the following one:
LM317 Variable Switch Mode Power Supply (SMPS)
Sir IAM USING LGABB41865 BATTERYS
OF 5 BATTERYS SINGLE BATTERY HAVE
2600mah TOTAL 5 BATTERYS mah of 13000 mah because please give circuit for that power bank charging and out of 1amp and 5volts please help me sir
give all the specifications correctly
Thanks a lot sir, nice design. I can't find the charging unit and battery connector on the 3rd simply diagram.
thanks Ochin, the charging of the 3.37V cells can be done through any standard adapter externally.
in the last paragraph I have mentioned the word "LM317 charger" with reference to the cellphone which is supposed to be charged using the shown emergency power packs.
the battery of the power pack needs to be charged from an external charger which could be your cell phone charger unit
Well done sir, I tried to charge my power bank with combination of three cells from laptop battery, I don't know their capacity. So my power bank leds that used to be off, now is always on blinking as if it's charging whether is not connected to a charger. Please do you know what might have happen to my charger and how-to rectify the problem?
Arhyel, what is the input specification of your power bank?…this specification will help us to know how much input is required to be fed safely to the unit…if it was more than then your PB could be damaged
Can i replace 3.7v battery to 6v lead acid? It is compatible??
yes you can do that
How much baat including in perelal and improve the nex by nex Mobil charj
you can calculate it through the link given in the article….or do it with some trial and error….please read the full article for knowing the details.
sir how i can check a 7805 ic
you can do it by actually supplying an input voltage across the specified pins and checking exactly 5V across its output pins
respected swagatam
my powerbank charging only 10 scecond then auto cut off why?
if i can make another one with its 2 battery (3.7v*2ps)–if that batteries are sutable for ur circuite used LM317 ic –is this ic will heat-
Hi AZ, check the voltage with a voltmeter while the cell is charging, it could be reaching the full charge value quickly…this may be because your charging current is high,,,,check this first
I would like to know what are the theories used in creating a power bank?
Thank you.
And also please tell me how much volt requierd for charging a 18650 cell
it's same as described above…4.2V
Sir curcuit is good but a bit complicated
And also please tell me which type of bulb used in curcuit
A tourch bulb ?
Prince, you can use a 3V torch bulb rated at 200mA or above.
Sir this powerbank is 3.7V to 5V/2A ? Right? So how about if the battery is at 4.2V What will the output .. ?
and also i want to rem0ve the bulb …and replace it with led and resistor c0nnected to supply batt. Or output ? How can i done this?
Romeo, you can adjust the PWM pot to get a precise 4.2V
the bulb is a safe and an easy option to verify the charging condition…LEd indicator will not work in that position and might require a complex circuit using an opamp
Hi Swagatham
For Ni-Cd cells, the charging current is calculated by deviding 'Battery capacity Ah/10'.
How can I calculate the safe charging current and charging timeof Li-Ion and Li-Po batteries….?
Hi Anil,
as a rule of thumb for Li-ion and Lipo batts you can use a charging current as high as their AH level…so for example if the AH of the battery is 2AH then the charging current could be 2amps, but the temperature of the batt could be crucial and will need to be monitored manually or by some automatic method
Hi sir,
Can you please help me to make a 3.7v mobile battery level indicator, I want to do this by using ATtiny85, for this I have use concept of voltage divider, so I have taken Vin as 4v, R1 as 130 ohm and R2 as 910 ohm for 3.5v Vout.
Thanks.
Hi Pawan, sorry, I do not know how to do it with a ATtiny85….
good post sir, what is the max current of the last current control circuit, can we build boost converter using attiny micro controller and a 7 segment display interface , i want to increase efficiency because i used 6*1.2v 2700mah which doesent charge my 2000mah android a single time the 7805 getting heated up and a lot of power is wasted there, i bridged 2 7805 ics together but there is no improvement the charging current is very low 150ma i connected directly 4 cells without any regulator and the phone got charged with with 1500ma current but due to voltage fluctuations the charge controller in the mobile disconnecting the power source. any help is appreciated thank you sir.
Thanks Seelamsetti,
just use 4 of the 1.2V cells in series and connect the output directly to your cellphone, no need of using a 7805 IC, as shown below:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2012/11/homemade-cell-phone-emergency-charger.html#
yes MCU can be used for making a power controller circuit
…if your cellphone is disconnecting the power due to fluctuations then you can add another pack of 4 cells in parallel or try bigger 1.2V cells
thank you sir
i have been waiting for so long for this kind of circuit
i will definately build it sooner n give updates thanks for this BOSS SWAGATAM
you are most welcome Adesina!!
Sir the circuit above is so interesting.
Is there any idea that can modefie or improve the above circuit like for example adding of a small solar panel to charge up the battery 3.7v.
Thanks Angelous, yes definitely you can use a suitably rated solar panel and use it to charge the 3.7V cells.
sir why did you used bulb? it is possible to change that into the red LED?
Bulb will pass sufficient current for charging the battery and also indicate the situation, LED will not pass sufficient current and will not serve purpose, it will remain lit forever, not allowing the battery to get charged.
LED will require an external circuit for the indications… which can make the circuit more lengthy…
Thanks sir for this circuit
What is the output amp in 1st circuit
I want 1 amp output from 1st circuit
Thank you very much
Mayank, you can calculate and change the 0.6 ohm resistor for fixing the desired current capacity of the circuit…accordingly the cell mAH will also need to be upgraded to the intended level
sir this circuit can give cAPAcity of 10000 mah ?
the formula for calculating the resistor is
R = 0.6 / max current output (amps)
Also tell where charging pin or female usb connector is attached…?
and which point is used to connect the cells…
And how much cell we connect in this circuit…
Irfan, Everything's shown in the diagram, I am sorry if you are not able to understand the diagram then it would mean that you are very new in the electronics field, and this circuit can be extremely difficult for a new comer…so I think you should rather try the other 3 circuits instead of the first….
Thanks sir.. there is some confusion for me.
1- Is it control the discharge levels of Li-ion cells..
2- is it control the over charging of Li-ion cells…
3- is it delivers the 2amp for smart phone sharge
Once again thanks for the circuit… B-)
Irfan, the cell will not discharge unless connected to a cell phone
the cell will not overcharge but when the indicator lamp shuts off you should remove the input supply…
2amp may be obtained if the cell is rated at 3000mAH