In this post I will explain how to design and build a simple power supply circuit right from the basic design to the reasonably sophisticated power supply having extended features.
Power Supply is Indispensable
Whether it's an electronic noob or an expert engineer, all require this indispensable piece of equipment called the power supply unit.
This is because no electronics can run without power, to be precise a low voltage DC power, and a power supply unit is a device which is specifically meant for fulfilling this purpose.
If this equipment is so important, it becomes imperative for all in the field to learn all the nitty-gritties of this important member of the electronic family.
Let's begin and learn how to design a power supply circuit, a simplest one first , probably for the noobs who would find this information extremely useful.
A basic power supply circuit will fundamentally require three main components for providing the intended results.
A transformer, a diode and a capacitor.The transformer is the device which has two sets of windings, one primary and the other one is the secondary.
Mains 220v or 120v is fed to the primary winding which is transferred to the secondary winding to produce a lower induced voltage there.
The low stepped down voltage available at the secondary of the transformer is used for the intended application in electronic circuits, however before this secondary voltage can be used, it needs to be first rectified, meaning the voltage needs to be made into a DC first.
For example if the transfornmer secondary is rated at 12 volts then the acquired 12 volts from the transformer secondary will be a 12 volt AC acros the relevant wires.
Electronic circuit can never work with ACs and therefore this voltage should be transformed into a DC.
A diode is one device which effectively converts an AC to DC, there are three configurations through which basic power supply designs may be configured.
You may also want to learn how to design a bench power supply
Using a single diode:
The most basic and crude form of power supply design is the one which uses a single diode and a capacitor.
Since a single diode will rectify only one half cycle of the AC signal, this type of configuration requires a large output filter capacitor for compensating the above limitation.
A filter capacitor makes sure that after rectification, at the falling or decreasing sections of the resultant DC pattern, where the voltage tends to dip, these sections are filled and topped by the stored energy inside the capacitor.
The above compensation act done by the capacitors stored energy helps to maintain a clean and ripple free DC output which wouldn't be possible just by the diodes alone.
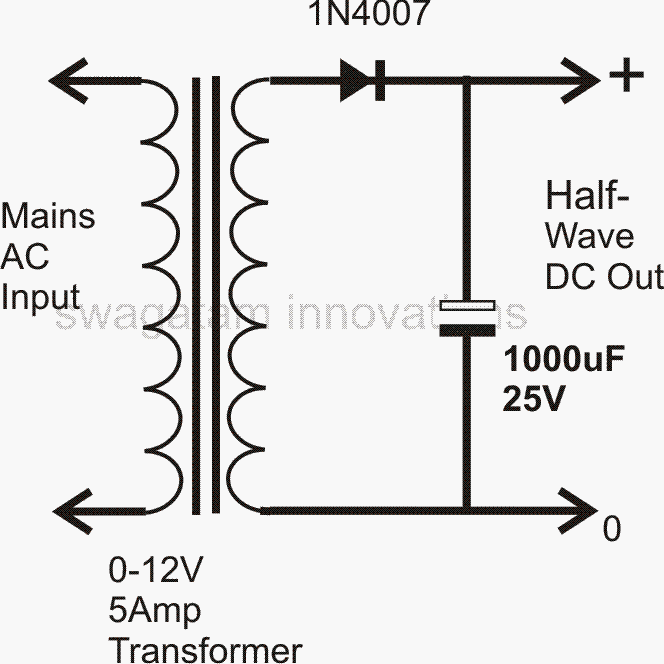
For a single diode power supply design, the transformer's secondary winding just needs to have a single winding with two ends.
However the above configuration cannot be considered an efficient power supply design due to its crude half wave rectification and limited output conditioning capabilities.
Using Two Diodes:
Using a couple of diodes for making a power supply requires a transformer having a center tapped secondary winding. The diagram shows how the diodes are connected to the transformer.
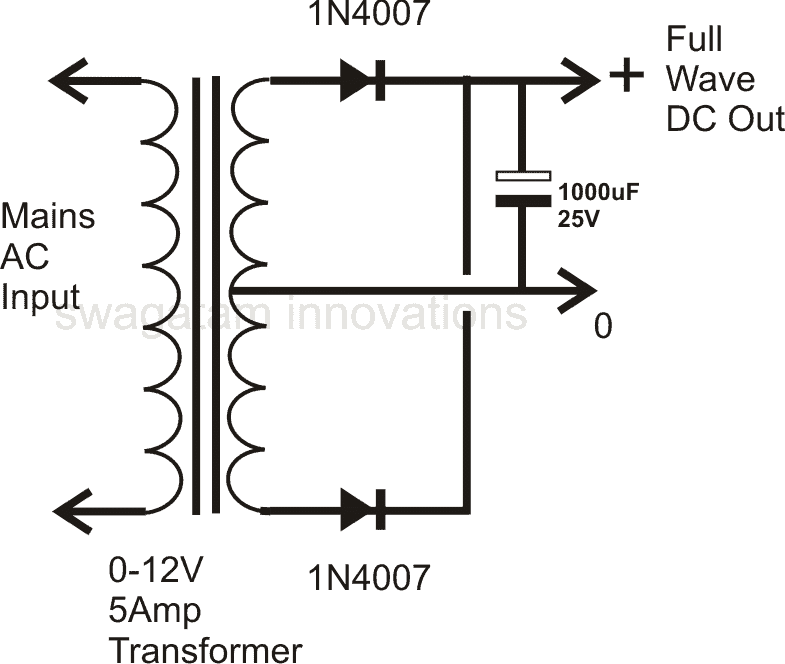
Though, the two diodes work in tandem and tackle both the halves of the AC signal and produce a full wave rectification, the employed method is not efficient, because at any instant only one half winding of the transformer is utilized.
This results in poor core saturation and unnecessary heating of the transformer, making this type of power supply configuration less efficient and an ordinary design.
Using Four Diodes:
It's the best and universally accepted form of power supply configuration as far as the rectification process is concerned.
The clever use of four diodes makes things very simple, only a single secondary winding is all that is required, the core saturation is perfectly optimized resulting in an efficient AC to DC conversion.
The figure shows how a full wave rectified power supply is made using four diodes and a relatively low value filter capacitor.
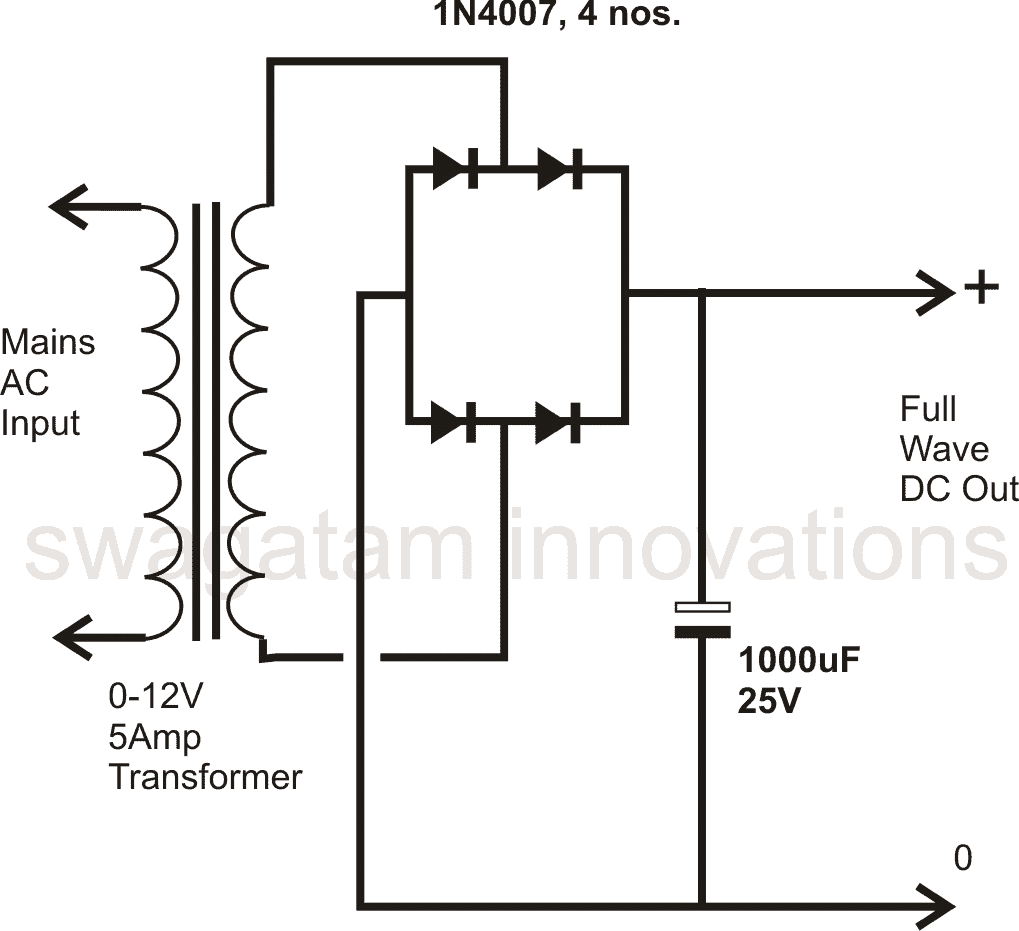
This type of diode configuration is popularly know as the bridge network, you may want to know how to construct a bridge rectifier.
All the above power supply designs provide outputs with ordinary regulation and therefore cannot be considered perfect, these fail to provide ideal DC outputs, and therefore are not desirable for many sophisticated electronic circuits.
Moreover these configurations does not include a variable voltage and current control features.
However the above features may be simply integrated to the above designs, rather with the last full wave power supply configuration through the introduction of a single IC and a few other passive components.
Full Bridge Unregulated Power Supply with Formulas
The diagram below depicts a single rail power supply. The fuse is installed in the live wire path to the transformer for safety.
The live wire is also attached to the transformer's 240V terminal; this section of the primary winding is quite far away from the secondary, increasing the unit's safety.
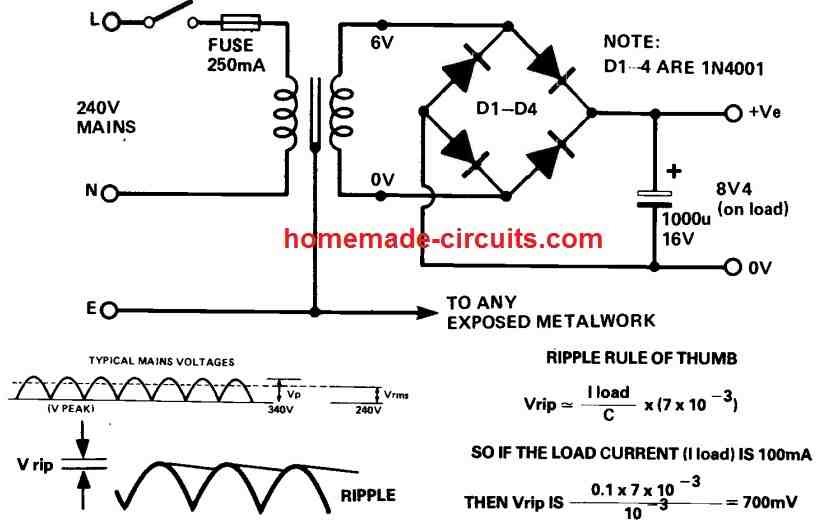
The earth should be linked to any uncovered metal and, if applicable, to the transformer shielding. The voltages mentioned are in volts rms and are AC voltages.
On load, the transformer's output is 6V rms. When the transformer is not in use, the voltage might rise by up to 25%.
The output ripple can be calculated using the following formula:
Vrip ≅ Iload / C [ 7 x 10-3 ]
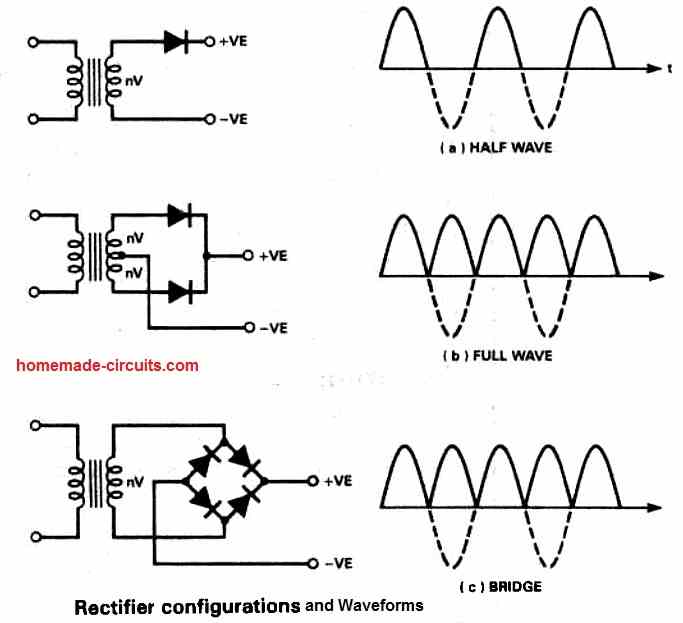
Waveform Images
The output waveform images for the various rectifiers and transformer configurations discussed above, can be seen in the figure below:
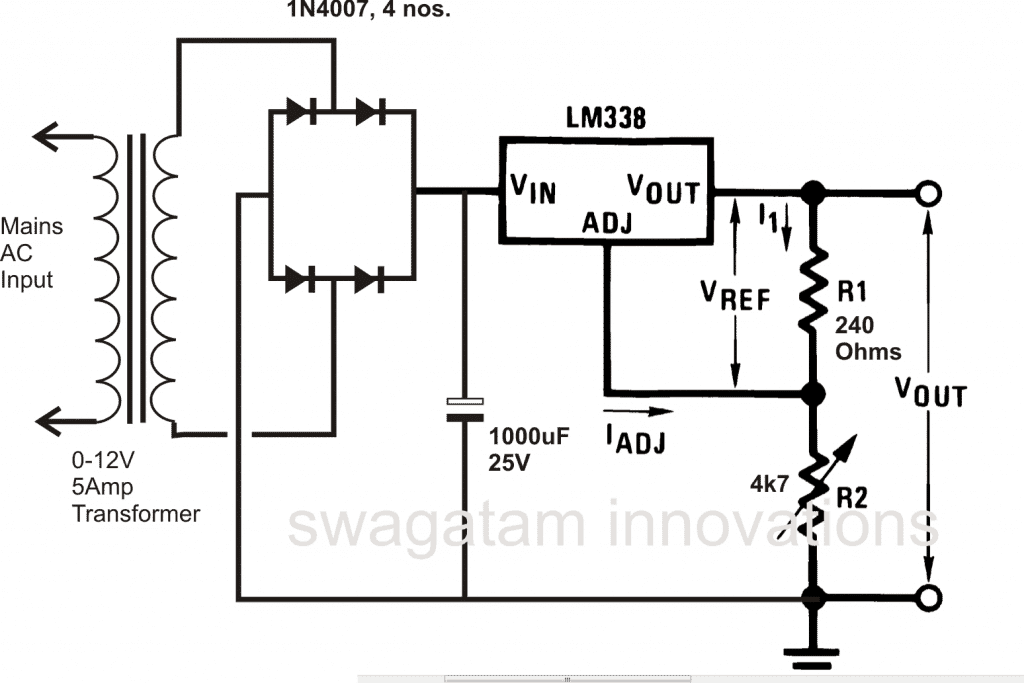
Using the IC LM317 or LM338:
The IC LM 317 is a highly versatile device which is normally incorporated with power supplies for obtaining well regulated and variable voltage/current outputs. A few power supply example circuits using this IC
Since the above IC can only support a maximum of 1.5 amps, for greater current outputs another similar device but with higher ratings may be used. The IC LM 338 works exactly like the LM 317 but is capable of handling up to 5 amps of current. A simple design is shown below.
For obtaining fixed voltage levels, 78XX series ICs may be employed with the above explained power supply circuits. The 78XX ICs are comprehensively explained for your refernce
Nowadays transformerless SMPS power supplies are becoming the favorites among the users, due to their high efficiency, high power delivering features at amazingly compact sizes.
Though building an SMPS power supply circuit at home is surely not for the novices in the field, engineers and enthusiasts with comprehensive knowledge about the subject can go about building such circuits at home.
You can also learn about a neat little switch mode power supply design.
There are a few other forms of power supplies which can be rather built by even the new electronic hobbyists and does not require transformers.
Though very cheap and easy to build, these types of power supply circuits cannot support heavy current and are normally limited to 200 mA or so.
Transformerless Power Supply Design
Two concepts of the above transformer less type of power supply circuits are discussed in the following couple of posts:
By Using High Voltage Capacitors,
Feedback from One of the Dedicated Readers of this Blog
Dear Swagatam Majumdar,
I wish to make a psu for a micro-controller and its dependent components...
I want to get a stable +5V out and +3.3V out from the psu, I'm not sure of the amp-age but I think a 5A total should be enough, there will also be 5V Mouse and 5V Keyboard and 3 x SN74HC595 IC's too and 2 x 512Kb SRAM ... So I really dont know the amp-age to aim for....
I guess 5Amp is enough?.... My MAIN question is which TRANSFORMER to use and which DIODES to use? I have chosen The transformer after reading somewhere online that the bridge rectifier cause a VOLT DROP of 1.4V in general and in your blog above you state the bridge recitfier will cause the voltage to go up?...
SO I am unsure (I am unsure anyway being new to electronics) ..... The FIRST transformer I chose was this one. Please advise me which one is BEST for my needs and which DIODES to use too.... I would like to use the PSU for a board very similar to this....
Please help and guide me the best way to make a suitable MAINS 220/240V PSU which gives me STABLE 5V and 3.3V for use with my design. Thank You In Advance.
How to Get Constant 5V, and 3V from Power Supply Circuit
Hello, you can achieve that simply through a 7805 IC for getting the 5V and by adding a couple 1N4007 diodes to this 5V for getting approximately 3.3V.
5 amp looks too high and I don't think you would require this much high current unless you are also using this supply with an external driver stage carrying higher loads such as a high watt LED or a motor etc.
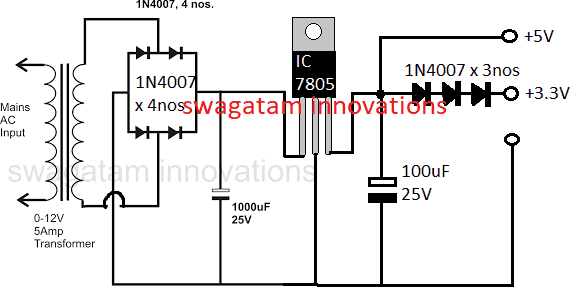
So I am sure that your requirement can be easily fulfilled through the above mentioned procedures.
for powering MCU through the above procedure you can use a 0-9V or a 0-12V trafo with 1amp current, diodes could be 1N4007 x 4nos
The diodes will drop 1.4V when the input is a DC but when it's an AC like from a trafo then the output will be raised by a factor of 1.21.
make sure to use a 2200uF / 25V cap after the bridge for the filtration
I hope the info will enlighten you and answer your queries.
The image above shows how to get 5V and 3.3V constant from a given power supply circuit.
How to Get 9 V Variable Voltage from IC 7805
Normally, the IC 7805 is considered as a fixed 5 V voltage regulator device. However, with a basic workaround, the IC could be turned into a 5 V to 9 V variable regulator circuit, as shown above.
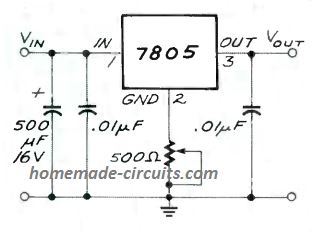
Here, we can see that a 500 ohm preset is added with the central ground pin of the IC, which allows the IC to produce a lifted output value up to 9 V, with a current of 850 mA. The preset could be adjusted o get outputs in the range of 5 V to 9 V.
For getting an increased voltage output from a 7812 IC, you can refer to this post!
Making a Fixed 12V Regulator Circuit
In the above diagram we can see how an ordinary 7805 regulator IC could be used for creating a fixed 5V regulated output.
In case you wanted to achieve a fixed 12V regulated power supply, the same configuration could be applied for getting the required results, as shown below:
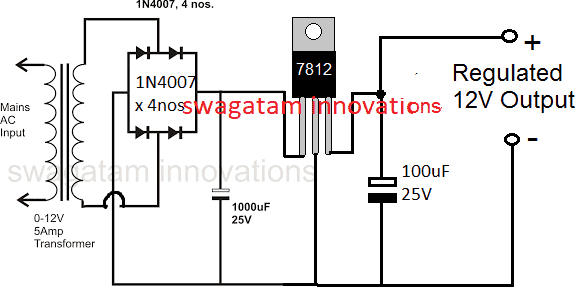
12V, 5V Regulated Power supply
Now suppose you had circuit applications which needed a dual supply in the range of 12V fixed and also 5V fixed regulated supplies.
For such applications the above discussed design could be simply modified by using a 7812 IC and then subsequently a 7805 IC for getting the required 12V and 5V regulated power supply output together, as indicated below:
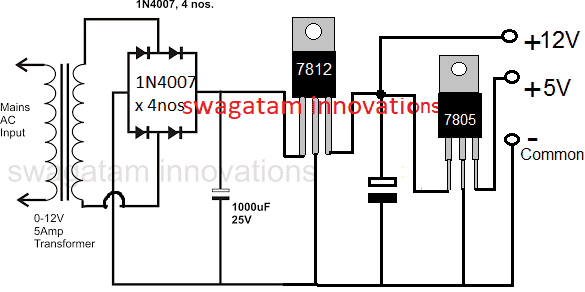
Designing a Simple Dual Power Supply
In many of the circuit applications, especially the ones using op amps, a dual power supply becomes mandatory for enabling the +/- and ground supplies to the circuit.
Designing a simple dual power supply actually involves a just a center tap power supply and a bridge rectifier along with a couple of high value filter capacitors as shown below:
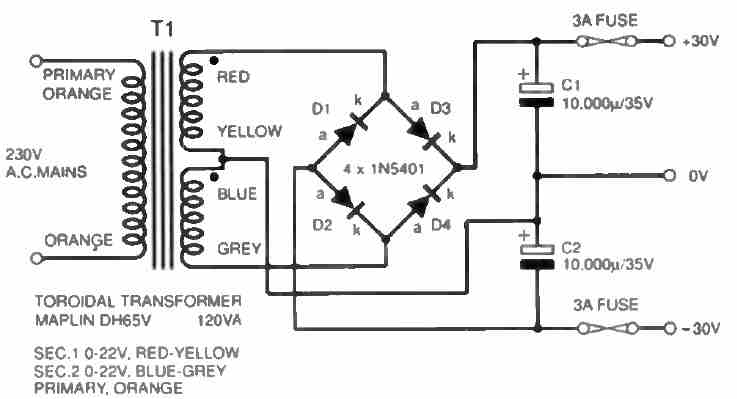
However, for achieving a regulated dual power supply with the desired level of dual voltage at the output is something which normally requires a complex design using costly ICs.
The following design shows how simply and discretely a dual power supply could be configured using a few BJTs, and a few resistors.
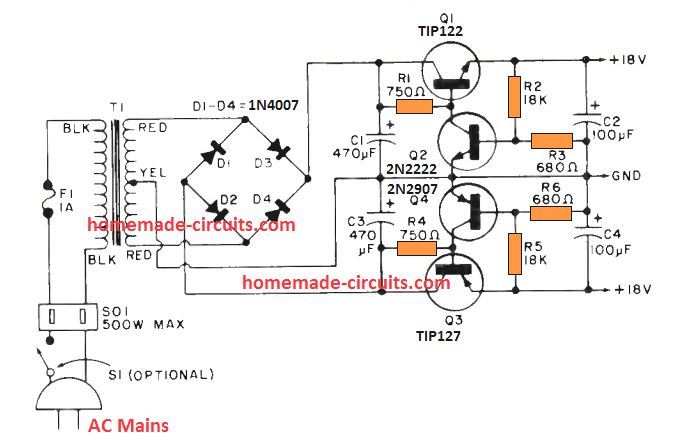
Here Q1 and Q3 are rigged as emitter follower pass transistors, which decide the amount of current that is allowed to pass across the respective +/- outputs. Here, it is around 2 amps
The output voltage across the relevant dual supply rails is determined by the transistors Q2 and Q4 along with their base resistive divider network.
The output voltage levels could be appropriately adjusted and tweaked by adjusting the values of the potential dividers formed by the resistors R2, R3 and R5, R6.
Dual Supply with a Single Opamp
If you an extra opamp left in your circuit that demands a dual supply from a single supply, then perhaps the following simple dual power supply from a single opamp configuration can be tried.
The resistors R1 and R2 work like a high impedance, and consequently economical voltage divider network. The opamp ensures that the artificial ground potential is always identical to the potential bteween the junction of R1 and R2.
The connection between R1 and R2 establishes the relationship between the a couple of output voltages; if R1 and R2 possess the identical value, exactly the same will be ensured for both the output voltages which would be perfectly symmetrical.
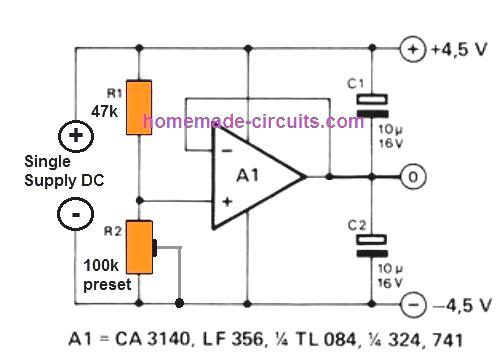
This allows us to get the most desirable feature of the circuit, it is that the R1/R2 partnership doesn't rely on the battery voltage!
An additional benefit of this active potential divider is that (as opposed to a basic resistor divider chain) it adjusts itself nicely to varying load currents moving to and from the earth supply line, especially with regards to unsymmetrical load current situations.
You can probably think of using different variants of opamps for this circuit.
The 3140 and 324 tend to be fantastic choices, despite having a battery voltage as low as 4.5 V.
Keep in mind that the highest voltage that can be tolerated by these ICs is not more than 30 V, and the maximum load current that can be tolerated by the opamp will also depend on the type of the opamp.
Designing an LM317 Power Supply with Fixed Resistors
An extremely straightforward LM317T-based voltage/ current supply, that could be employed for charging Nickel-Cadmium cells or any time a practical power supply is necessary, is demonstrated below.
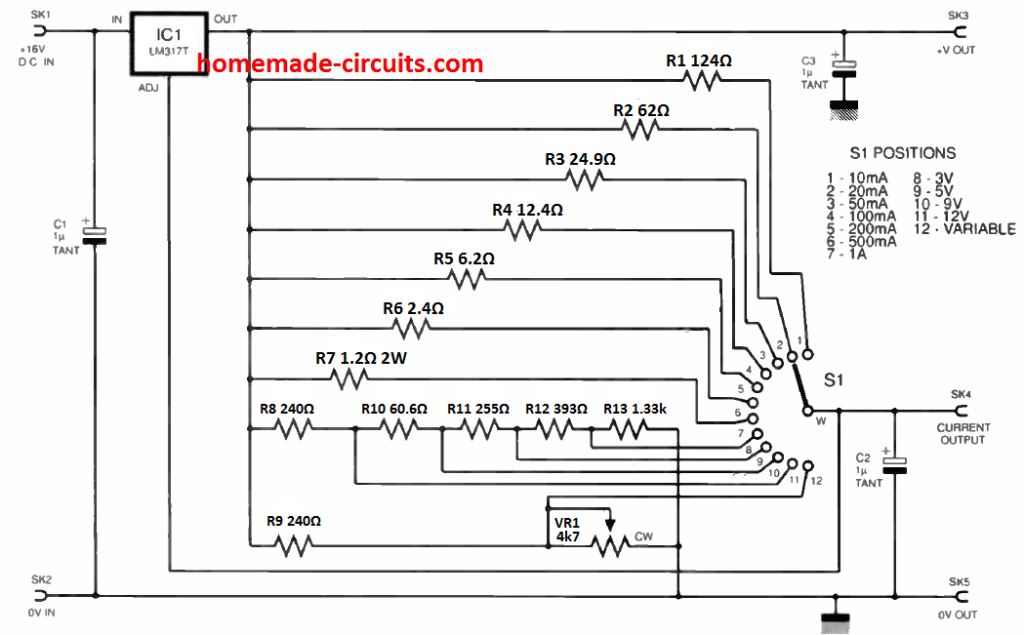
It is an uncomplicated venture for the newbie to construct, and is meant to be utilized with a plug-in mains adaptor providing an unregulated d.c. output. IC1 is actually a adjustable regulator type LM317T.
The rotary switch S1 chooses the setting (constant current or constant voltage) along with the current or voltage value. The regulated voltage can be obtained at SK3 and the current is in SK4.
Observe that a adjustable setting (position 12) is incorporated that enables a variable voltage to be tailored through potentiometer VR1.
The resistor values must be manufactured from the closest obtainable fixed values, positioned in series as necessary.
Resistor R6 is rated at 1W and R7 at 2W although the remaining could be 0.25W. Voltage regulator IC1 317 must he installed to some heatsink the size of which is determined by the input and output voltages and currents necessary.


Getting 5 Amps from a 7812 IC
If you are wondering how to get 5 amp or higher current from a 7812 regulator IC, then the following circuit might be the one you are looking for.
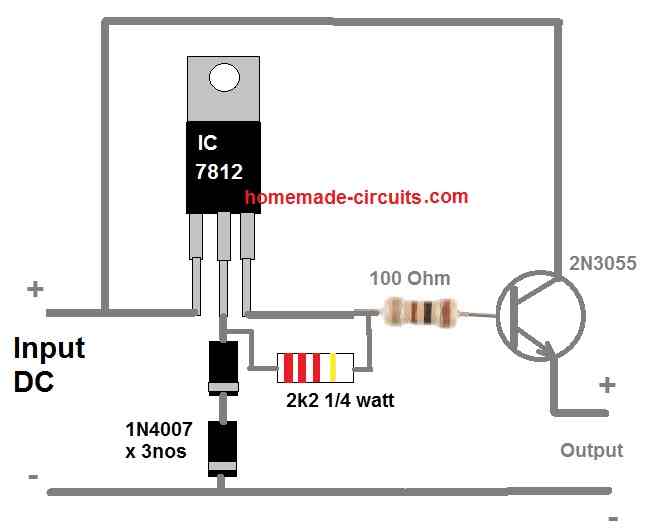
As you can see a power transistor 2N3055 is configured with the 7812 output as an emitter follower for transforming the 1 amp current from the 7812 output into a massive 5 amp current at the emitter of the transistor.
However, there's a drawback of using an emitter follower configuration. It reduces the output voltage by 0.7 V or 1 V due to the base-emitter forward voltage drop specification of the BJT.
To compensate this we raise the 7812 output by around 1 V by adding a couple of series diodes at the GND terminal of the IC.
The 100 ohm resistor at the base of the transistor determines the output current. The 100 ohm value is arbitrarily chosen.
If you find 100 ohms not delivering the intended 5 amps then you can try reducing this value. Just make sure the wattage of the resistor is also appropriately increased so that the resistor does not heat up and burn.
Designing a Basic 741 based Regulator Circuit
Presented below is an exclusive depiction of a dual-stage voltage regulator setup, proficient in delivering approximately 3 Amps at its output.
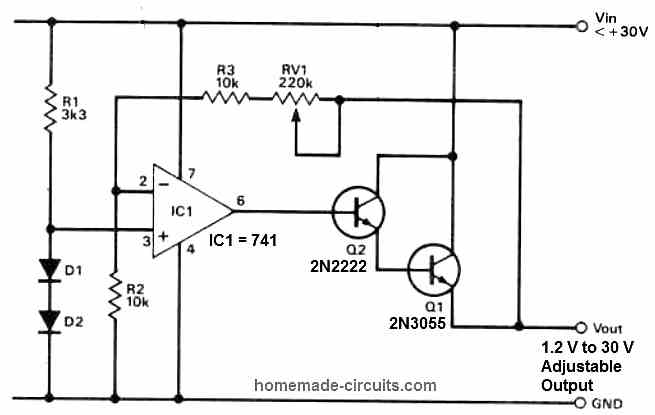
The primary stage incorporates an op-amp IC 741, functioning as a DC voltage amplifier.
An adjustable amplification factor allows a wide array of output voltage options, achieved by employing a reference voltage derived from a stack of diodes as the input signal.
The subsequent stage serves as a current amplifier, efficiently converting the available 10 mA from the op-amp output into a usable 3 A supply current.
Using a Feedback
An intriguing aspect of this configuration is that the current gain stage is integrated into the feedback loop of the system.
Consequently, the regulator's output voltage is determined by the product of the reference voltage and the op-amp gain, where the op-amp gain is calculated from the expression:
A: (Rf + Rin)/Rin.
To obtain this gain value, a potential divider is formed using the total value of the feedback resistors Rf and the input resistor Rin.
This well-engineered setup ensures optimal voltage regulation with high precision, catering to a variety of practical applications.
Sir,
I need help for my 3D printer power supply, it’s 24 volt 240 watt but it’s giving only 12 volt, I have replaced the transistors and feedback ic but still 12 volt output, the local supply don’t work. Original is too expensive.
Hi Ajay, did you check the output by removing or disconnecting the feedback link entirely?
Hi Swagatam, I am failing at finding a simple circuit to invert a +5v to -5V from a usb source.
I have some encoders that are 2 channel A+ and B+ but apparently the driver board requires a A- and B- as well so I figured I could just invert the pulse from both channels but I’m not smart enough to locate a circuit to accomplish this that is not huge and far to cumbersome.
Hi Shawn,
Yes, I find it difficult too..
An easy method is shown in the following article. Please see the first diagram on top.
However, for this you will have to buy the IC LM2664.
https://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/lm2664.pdf?ts=1711337251116&ref_url=https%253A%252F%252Fwww.google.com%252F
Thank you so much for the quick reply!
My pleasure!
Hi again Swagatam, I’ve really been struggling with this. I’m trying to invert a pulse signal from an encoder and I finally got the circuit functional but the driver board errors out after about a revolution of the encoder. I think the cap is not discharging fast enough and is too large. I went all the way down to .1uf poly (the green ones) and have ordered ceramic at 10,100pf and .1 and 3,3uf as I am guessing that i don’t want a high value and a quick discharge. But I am wondering if maybe I should be using a discharge resistor and if so what value or if I am totally off track here? Thanks in advance for any help. BTW I soldered the SOT-23 (6) package directly (NIGHTMARE TERRITORY!) and the first 3 broke the legs while i tried to connect leads lol I cant believe they only sell them in that micro package! I ended up getting breakout boards and boy did that make my life easier! 😀 Oh and I eliminated the output cap as It was not discharging fast enough and I think its not really needed in this application.
Thanks for the update Shawn,
I guess you are referring to the circuit from the following datasheet:
https://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/lm2664.pdf?ts=1711337251116&ref_url=https%253A%252F%252Fwww.google.com%252F
Here, C1 and C2 are supposed to be 3.3uF, low ESR capacitors. I would recommend using tantalum capacitors for these caps.
I am not actually sure about the significance of output capacitor C2.
If you think C2 is causing the problem due to slow discharging, you can try adding a resistor parallel to C2 as shown on page 7 of the datasheet.
I can see a formula given to calculate the resistor Rout, but it looks too daunting.
So i would recommend you to try the Rout resistor value with some trial and error. You can start with a 1k resistor first and see how it goes.
However, if eliminating C2 still works for you, then i think there’s nothing more we can do, because the other cap C1 is crucial and cannot be removed and it cannot be modified with any external components either.
Let me know if you have any further doubts.
Thx, I’m going to try the ceramics when they come in as the datasheet notes “Capacitors with higher ESR will increase output resistance, reduce output voltage and efficiency” which is really fine by me as its only a reference point for a differential circuit. If the ceramics don’t work then I will look for tantalum with a quick discharge rate. I’ll update again when they show up. I was looking up discharge rate and from the formula it looks like the lowest esr value will discharge the quickest, do I understand that correctly? It seems to make since that the lower the resistance the quicker it would discharge.also the 3.3 value I think is for a continuous supply and I could not get a trailing edge so I tried various resistors on cap 2 to no avail and then removed c2 to some success and then lowered the value to 2.2 and then .1 and then the trailing edge was more defined and I think the driver board needs that or it will detect the differential as being an error if the values fall out of tolerance. that is my guess as I have no clue how that circuit functions, it is a black box.
You are right, A capacitor with a lower ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) will discharge quicker than one with a higher ESR.
If your current modifications are working for you then you can continue with them.
Let us know how it goes.
Can’t edit last post, I’m trying to get tanalums I can’t find esr values! I have been looking t data sheets but they don’t list them and using the simsurfing tool is not showing them either. I think I’ve fallen down the rabbit hole. 🙂
The quickest I cant get them shipped looks like walmart in 3 days but i don’t know what ones to order. I orginally order ceramic because I gave up trying to find esr values and read somewhere ceramic had the lowest.
Ceramic may have the lowest esr, you are right. I suggested tantalums since the diagram showed polarized capacitors, however there’s no need of using polarized caps, so even ceramic caps can be used…
Thank you for the information you’ve provided. I already have a Altech corp. dr-120-24 power supply. I want to take the existing output of 24v 5a and split it into two 9v 2.5a circuits. I’ve been reading online and watching lectures and believe knocking the voltage down to 9v then splitting the 5a between two circuits should be pretty straight forward but can’t seem to find a solution. *or* more likely I’m just missing what they are already explaining to me. Would this be a simple circuit to design or is it a complex design. Thank you in advance for your time.
Hi, thanks for the question.
I don’t think it is possible to split current. Current can be limited or restricted and controlled, it cannot be divided. Voltage can be split, and the current through each channel could be limited to 2.5 amps.
Is it true if a device requires 2.5a it doesn’t have a negative impact, if the circuit has 5a available? My latest understanding is if the circuit has equal to or greater than the current required all is good. Of course the voltages need to match.
If I can create two circuits at 9v then i should not care if 5a available on both circuits. Each circuit or branch will have a end device which requires 9v 2.5a. so two 9v 5a branches should work? Or is this grossly frowned upon?
Hope this gets closer to filling in the variables for you.
-Daniel
Yes, that’s right, if the voltage specifications is matched as per the load specifications the current becomes immaterial, it can be of any level, doesn’t matter. If you are supplying two separate 9V 5A sources to your 9V/2.5 amps devices then it is perfectly fine.
Well done Swagatam. Mine is, how do I register in your tutorial lesson for more knowledge. I am interested in knowing electronic configuration, design and troubleshooting. I want a full lesson from you. How do I go about that with you pls?
Thank you Femi, learning electronics can be a long process involving a lot of theoretical and practical courses. You can start by building transistor based circuits, and learn how the configurations are designed to work. If you have any issues you can ask your questions under any relevant article here, I will try to sort them out for you.
The design diagram and the outlines must be in a simple way so that any hobbiest having not enough practice must follow easily so that his thrust of gaining and seeking knowledge about the goining on SMPS be satisfied and enjoybl…….
..
You can always feel free to ask through comments if you you have any doubts, I’ll be most happy to help!
Really what I need is to remove a relay switch on my circuit, I have a relay for cut-off when the battery gets to full charge and a relay for transition when the main supply is off, I want to remove the relay for cut-off.
Without a relay how will you implement the cut off action?
I want to use a 14V zener diode to simply clamp the circuit sir.
Where do you want to connect the zener diode?
I sent you the link to the schematic sir did you see it?. but effectively that is exactly the help I need from you, where can I connect the zener to simplify the circuit cause really I just want to simplify it.
Jack, external website links cannot be published. If possible I will extract the circuit diagram from your link and post it here to continue the discussion…but it might take some time for that. I will let you know once it is done.
alright sir thank you.
Can you please tell me what change exactly do you want in the following circuit, or simply tell me your requirements, I will give a new circuit:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/power-supply-with-battery-backup-and-relay.jpg
I want to use a zener to protect the battery from overcharge, I also want to use only one relay for transition. I also want to protect the battery from over discharge. Can you help with that sir?
OK, I think you can try the last diagram from the following article. The MOSFET can be replaced with any PNP power transistor.
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/battery-deep-discharge-protection-circuit/
Thank you very much sir.
You are welcome Jack!
Hello Sir. I hope you are well. I need your help with a schematic, it’s a 12V power supply with a back up battery I have the schematic how can I send it to you for help.
Hello Jack,
You can upload the link to any free online image hosting site and provide me the link here…I will check it out.
Bro can you kindly help me to build a 0-30v and 0-20a variable SMPS?
I have already made an linear power supply from your suggestions but I heard that SMPS has greater efficiency to willing to make one too.
So please help to build a complete variable SMPS from scrap
Sorry Bivash, I do not have a 30 V, 20 amp SMPS circuit with me. I will try to look for it, if I find, i will let you know.
Ok bro
I love this, it definitely helps me in my projects. Thank you sir and keep up the good work ????
You are welcome Victor!
Hello sir, how can I make a full wave rectifier with a 12 and 24 Voltsdesired output DC from 12 and 24 AC. Can you help me in designing it.
Hello Khina, I am sure you know how to make a bridge rectifier using rectifier diodes. If not then you can refer to the following article. You can make two of these bridge rectifiers, and connect one bridge across the 12 V wires and connect the second bridge across the 24 V wires. This configuration will be enough to convert the AC voltage into unfiltered DC outputs.
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/how-to-understand-diodes-and-build/
I’m building a 120Vac to 24Vdc power supply using a 100va step down transformer incorporating a 25amp full wave bridge rectifier.
My question is “what type and size of filter capacitor should I use on the output side of the bridge to clean up the final DC output”
Thanks
Any values between 2200uF / 50 V to 6800uF / 50 V will be sufficient according to me.
Dear Sir,
I need some assistance in designing a variable power supply for a 90volt 2amp brush motor. Will you please help me?
Kind regards,
Jaap
Hi Jaap,
I would recommend using a transformer based power supply or a ready made SMPS. If you are using a transformer then I can show you how to build the 90 V regulator.
If you want to control speed then you may have to employ a PWM controller circuit also.
I intend to use a transformer based power supply.
If you use a variable power supply for controlling motor speed, then the associated power transistor can heat up a lot. Instead you can use a PWM controller with a fixed 90V power supply.
You can use a bridge rectifier using 6A4 diodes, and a 1000uF/140V filter capacitor with a 0-65V/2amp transformer.
The output will be around 90 V 2 amps DC. You can connect this 90V with the following PWM circuit for controlling the motor speed.
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/DC-pwm-motor-control.jpg
Make sure to replace the R3 with a 4.7K 1 watt resistor.
Thank you very much for the speedy response. I notice that according to your circuit that the supply voltage to the PWM is 12volt while the motor is 90volt?.
You can use 90V instead of 12V, just make sure to replace R3 with 4.7 K 2 watt or 5 watt resistor
Thank you very much for the the time you took to respond to my request, I appreciate it a lot.
It’s my pleasure Jaap!
Good day sir
Thank you for your speedily response. Just to confirm I have my own 16.5V 5A entering as DC. I was under the impression the IC would regulate to 12V and pass the same current 5A. postsI use the updated diagram at the end of the post then.
Thank you
Greg
You are right, the last circuit in the above article will regulate the 16 V to 12 V and pass the 5 amp current to the output.
Thank you sir.
Good day Sir.
How would I design a 12v 5A Regulator using L7812? I can see there are designs above, however I was concerned which type and exact micro-pharid capacitors to use in order to be precise to power a 12v DC 5A TFT LCD/LED MONITOR.
I have a 16.5VAC 5A
An exact design would really put my mind at ease.
Greg
(South Africa)
Hi Greg,
I have the updated the required design at the end of the above post. You can check it out.
Design a power supply for XMC1404 MCU from 12V power. The power supply should be able
to output at least 100mA of current.
I wanted to design a fixed 1.8v 1A power supply do you have any ideas regarding that?
You can build an LM317 based power supply, it will give a minimum output of 1.25V, you can easily adjust the output to 1.8V.
Hello sir,
In rectification circuit if I need 5v output how can I calculate the size of capacitor and resistor which I will need.
For getting 5V the easiest way is to use a 7805 IC….using resistors will restrict current which will be not suitable for most circuits.
Hi engineer, iam student and I want to be designer, I saw almost your circuit designed, and it is very nice.
Engineer, I want ask question about circuit design, if I want to design circuit how can I calculate which size of resistor and capacitor I need?
Hello Najib, resistors basically decide how much voltage and current must be restricted or supplied to the various semiconductors in a circuit, capacitor block DC and pass and also provide time delays. Designing circuits might require a lot of studying and learning, along with many practical experiments.
Hi can i ask on how i can design a dcsp with one fixed voltage output either positive or negative, and the other one being a variable, also being either positive or negative
Hi, sorry I have no idea about this concept!
Hi sir Swagatam thanks for your very interesting circuit diagrams.I want to use the circuit – How to Get 9 V Variable Voltage from IC 7805 – in a way that to have suitable 5 to 12 v variable voltage for changing the speed of my 12V 300mA PC fan which I use to cool me at nights when I am asleep. a friend of mine told a resistor between ground and output terminals does that but I do not know how. I have all components at home. would you help me sir?
thanks in advance
Thank you Ersa, you can also refer to the following article for more details:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/ic-7805-variable-power-supply-circuit-5v-to-15v/
You can ask me if you have specific questions.
Hi Sir Swagatam! I appreciate your nice feedback. I made the first circuit in your link using 18 V DC input with the variable 1.5K option only. There is great problem in it, for me of course. I receive 12 v only when the value of 1.5K vol is set on 550 ohm and at 1.5K I have more than 15 V output which will unwillingly damage the fan, think when I wake up at midnight and am sleepy, I do not know where is the exact place of vol head for 12 V voltage.
I wish the circuit was not dependent to the input voltage. May be there is a solution. I did not do the second circuit and do not know how is it.
Thank you Sir Swagatam
Bye
Thank you Ersa, yes the output will be dependent on the input voltage. In that case you must use an LM317 based circuit instead of the 7805. Or try using a zener diode in series with the 7805 ground, instead of the resistive divider.
Hi Sir Swagatam! Thanks for your guidance. If you mean that I can connect a 12v Zener diode between R1 and ground; without removing variable R2 it would be ideal and most appreciated.
Good bye dear Swagatam
Hi Ersa, yes that’s correct, I am assuming this will not allow the output voltage to go beyond 12 V.
Dear Sir Swagatam
Hello. You are right Sir. Not only the output voltage did not go beyond 12 and remained steady as per the value of zener diode, but also the 1.5k variable resistor did not decrease or increase the voltage range.
Thank you anyway for taking your time for me.
Best wishes for you and your dear family
Ersa
Thank you Ersa for updating the results, however decreasing 1.5k value should cause the output voltage to drop, because then the 12V zener is bypassed by the resistive divider, forcing a lower voltage drop at the 7805 ground pin….this is my assumption though.
Hello dear Swagatam
Thank you for your response. I assure you that decreasing 1.5k value did not drop the output voltage, just a bit, say around 0.5 V.
Thank you again and good bye for now
Wish you healthy
No problem Ersa, when you decrease the 1.5k potential divider, the voltage across 12V zener will become less than 12V, therefore the zener will switch OFF, as a result the 7805 output will follow the 1.5k adjustment.
It is difficult to guess why it is not working for you!
Dear Sir Swagatam
Thank you very much for your valuable information on how the circuit(s) works. your site is really a university and you are the kind and generous (in teaching) instructor of it. I will try it once more and will update the results with you dear Engineer.
Wish you all good things
Bye for now
Thank you Ersa, appreciate your feedback!
hello ! in (12V, 5V Regulated Power supply) is it not better to get the input voltage for 7805 from source rather than get it from the output of 7812 , i think we will have a current problem here if for example you need 1A from 5V and the same from 12V , as the 78XX has a 1A limit ,, what do u thing about it ?
Yes that’s correct, getting 1 amp current from both the ICs can become a problem. Even better idea is to have a 6-0-6V transformer, and use two bridge rectifiers across the 0-6V and 0-12V taps for supplying the respective ICs.
Hi , I think if you do that you will not be able to common the -ves as they will be at different potentials?? I tried something similar in a high current power supply and initially connected the 2 negatives with a resistor to limit current flow and found a significant potential difference.
According to me the negatives of different supply sources can be safely joined in common, and that’s the standard practice which is followed in all electrical and electronic networks whenever there are more than one supply source that needs to be used with several common elements.
I need a simple power supply where the incoming power is 24VAC (think HVAC) and I need 5VDC out with roughly 2A. This would be used to power a micro-controller, so good DC is important. Thanks!
You can try this
PWM Solar Battery Charger Circuit
Hi I want to make a power supply that uses batteries as its power source. I need to have a 10 v DC and and a 10 v AC signal at the output. The device has to be small, preferably no bigger than a large band-aid. The device needs to be disposable, flexible, and we will need to sterilize it.
Can you give me your thoughts on this,
Thanks
Jeffrey Owen
Hi, if the current is below 30 mA then you can use the IC 4047, which will give you 10 V AC across its pin 10 and pin11.
how to design power supply for 6.2V output and Rl of 5k ohm
try this software
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/lm317-lm338-lm396-calculator-software/
Sir i want to build that 5volts 5 apms output power supply circuit. But i want all formula and calculations for it and full detail of design upto doing into practical. Will u please help me with regarding this sir.
Hi Mayur, 5 amp is too high for a capacitive power supply, and it will wastes a lot of energy through heat dissipation. It idea does not look practicable
…sorry I mistakenly thought it to be a capacitive power supply. You can go ahead and use the LM338 design for getting 5V at 5 amps. Use a 0-6V transformer, along with bridge rectifier and filter capacitor
sir i built this 4th circuit but the maximum output i could get is 12v at the output. i used lm317, ik preset instead of 4.7, i used 270 resistor because 240 ohm is not in the market, now what could be the problem for not getting 30v at the output. this is how i connected the preset, one leg of the preset is connected to the ground and the other two which is the wiper/middle and the r remining were tie together to the adjustment pin of the ic lm317
Youngking, the output range depends on the pot value, since you have used 1K pot so the maximum range has been reduced to 12V. Please use a 4k7 pot or a 10K pot.
so is 10k pot higher preset to be put in place for the job
you can calculate the ranges by suing this software:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/lm317-lm338-lm396-calculator-software/
sir the voltage can be reduce to lower level but I can’t get higher voltage let say 14 and above but I will still use 10k pot to see the changes , thank you for your reply
higher pot value will allow higher output voltage selection, provided the input has the required maximum voltage.
sir i replace 4k7 preset with 100k potentiometer I forgot to add it at the previous comment.
hello sir I build this forth variable power supply circuit but the output is 12.54 I later change the 4k7preset the out was increase to 14.53 but it later drop to 13.52. I tried everything but the out remain the same.but apart from this other is working fine so what could be the issue here I use ic lm317 .
youngking, if the voltage is not reducing to lower levels with the pot rotation then either there’s something wrong with your connections or the IC itself is faulty.
100k will not work. you can try a 10K pot instead.
Hi Swagatam! My question relates to using two 12vdc 1A power supplies in series to produce 24vdc. I recently received two a 5m reel of 24v 2835 strip LEDs by mistake. I am trying to figure out how I may use these as I only have 12v power supplies. It may be worth the money to purchase a 24v power supply, rather than discarding the two 5m reels. I may use these in small strips so as to not require large power supplies. If you have any ideas as to how I can use these 24v LED reels, please share them with me. Thanks!
Hi Norman, the only easy option is to make a boost converter circuit and use the LED with it.
you can try the last circuit from this link
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2014/11/12v-car-laptop-charger-circuit-using.html
the T1 feedback is not crucial, it can be eliminated….
E-Mail sent for you.
Sir,
Hoping you maybe able to assist with an issue with a power supply on a pre-amp.
The pre-amp has been upgraded several times and along with it the power supply, originally it had 4 small capacitors each 1000 uf then they were replaced with 1,000uf x 100v and the toroid was replaced with a 600va x 71/0/71…every thing worked well for 8 years until last weekend until I decided to upgrade the capacitors to 6,800uf each (two each feed), they slotted in just perfect and when switched on was just excellent, every thing was just spot on i.e. 71/0/71 ac in and 90/0/90dc to the main board on the board sits 4 little Nu-Vista valves hence the 90volt output…….I then connected the power supply to the main board and switched on and BANG..the tracks from the A/C input on both had been taken out thro the 3 filter caps (104j x 250v) and only up to the rectifier (W04M 1.5amp) everything else was fine…put the P/S back as it was and the pre-amp works just fine…….Question, what went wrong?…too much capacitance or as I feel the rectifier needs beefing up as the other was small and only 1.5amp…oh and between the main caps are two resistors 330 ohm 2 watts metal film +/- 1%
Your input with this would be greatly appreciated
Mick
Hi Mick, It can be difficult to judge precisely without seeing the damaged area practically, yes increasing the capacitor value could have caused this due to an increase in the current level, and if the tracks got burnt then certainly something across these tracks could not handle the current generated from the 6800uF cap.
the 330 ohms are no match for 91V, even though these are rated at 2 watt still these would begin smoking at 91V….but tracks getting burnt is strange unless something shorted them across the supply rails…you will need to find the weak link between these tracks which might have triggered the issue.
Hi, again…I could send you images, the tracks destroyed go from AC in to the rectifier and no further….getting a bigger rectifier tomorrow so we shall see, nothing has changed over the past 8 years apart from these new caps, the only thing that was between the rectifier and AC in were three 104J x 250 volt caps for I assume smoothing…..will get back to you in a few days and let you know which part of my house wall is still standing….many thanks for your time
Mick
Hi, you can send it to my email admin @ http://www.homemade-circuits.com
the bridge might have caused the issue only if it was loaded, otherwise not
Hi, send an email for you
Mick
I have seen the images, according to me the bridge rectifier is the culprit, may be it was not rated to handle 91V and the increased current and as a result it burnt….because rest of the components look OK, so that clearly indicates that the issue is with the bridge.
Sir, I want to build a sterio amplifier using IC LM3886 two no. Purchase power supply ready board low ESR using 4700×8 cap in dual rail.( I.e. + and – ). I am getting a 50hz noise. Transformer using 18-0-18 3A. I deside to use a load resistance, but the value how to calculate? Will u suggest to replace the transformer? (As the transformer become very hot within short period.) Circuit I have purchased from eightaudio.com. they suggest to use 22-0-22 4A transformer. Please help me.
Jyotirmoy, you will need to install the entire amplifier board and the power supply transformer inside a good metal cabinet, once this is done the 50Hz ripple will be significantly reduced.
Make sure to connect your amplifier negative line with the metal box, and also make sure the transformer is tightly clamped with the box using nuts and bolts.
If your transformer is becoming HOT then it's not rated correctly or is of bad quality, replace it with a new one as per the recommended specifications of the amplifier and use a good quality transformer from a standard manufacturer.
What pot value did you use? Increase its value and you will be able to acquire the whole range. try a 22K pot that will be enough
Sorry sir pls what do you mean by 'reparable'
sorry, i meant to say "replace"
Good day thanks so much for your kindness in sending us the circuit. But please I have some questions first can we design the power supply of the sound decibel meter circuit using a centre tapped transformer, secondly we want to use buzzers and incandescent lamps for the design instead using only LEDs. Reason is that we want to draw students attention with buzzer and lamp when the noise level in the classroom is high. Regards
you can use a center tap transformer for powering the circuit, as shown in the second circuit above.
and you can easily reparable the LEDs with 12V piezo buzzers for the relevant indications.
I am a teacher and want to build a classroom noise monitor with my students. So we need a circuit diagram of classroom noise monitor, if you can help us.
you can try the following circuit:
/blog/2016/02/sound-decibel-meter-circuit.html
Sir you use voltage regulator circuit with ic LM338 can i replace it with just the ic of voltage regulator e.g. 78XX05 or anyother else?
Zunair, No, it's not possible in the LM338 circuit, you can use it with a different configuration if you intend to achieve a fixed 5V from it.
Hello swagatam,i'm using 7805 regulator in my power supply. Which diodes should i use, and how to decide the specifications of capacitor that need to be used for getting 5V output.
Hello Sumit, you can use 1N4007 diodes for the bridge rectifier, and filter capacitor can be anything above 1000uF/25V, it's not critical.
Good day, sir.
It was mentioned that, in PS circuit designs without ICs, the outputs have “ordinary regulation” and “fail to provide ideal DC output”. Can you please elaborate? Also, does this mean that, when viewed using an oscilloscope, the output voltage is not linear (specifically, horizontal)?
I have been wondering about this for hours and my teacher won't answer me. It would be great to know about some enlightenment. 🙂
Good day Chritian,
regulation refers to voltage and current being constant, but the level of pureness of the DC is governed by the filter capacitor not by the IC….therefore the cleaning the DC is done by the filter cap while the ICs make sure that the voltage and the current remain steady all throughout regardless of the input fluctuations.
the straightness of the DC horizontal line is essentially controlled by the filter capacitor
Thank you so much, sir! Have a good day.
Namaste Swagatam,
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2012/03/how-to-design-power-supply-simplest-to.html
In the first diagram in above article, you show a HALF WAVE rectifier, yet the diagram says FULL WAVE.
You need to fix that if you want to teach and not confuse!
Have a nice day!
Jeff
how to calculate capacitor rating for 5 volt power supply??
you can try the details presented in this article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2015/11/calculating-filter-capacitor-for.html
Hello sir,
I would like to ask that what is the use of bridge rectifier in power supply
Hello Ashok, it's to channelize both positive and the negative half cycles of the AC into only positive cycles….thus the negative and the positive cycles both are converted to positive cycles.
Dear sir,
I have made one development board of Pic18f4520 Microcontroller. And now i need to provide it exact 5 volt dc power supply. Please help me in designing power supply. What should i do?
Dear Vicky, you can use a 7805 IC circuit for getting a regulated 5V. check the datasheet of the IC you'll get the required diagram there.
Hello sir,
Thank you for providing this blog. Its very useful.
it's my pleasure Vicky.
Dear sir i need a power supply constant 0.9V and at least 20mA of current can you give me a circuit because i am newer to this things please help me
Dear Suresh, why do you need a constant 0.9V, and for what application, please let me know so that I can configure a proper design for you.
Hello Sir ,
you are running an excellent block….
can u tell me how can i design a 15v 1A power supply ???
Thanks Sayli,
If you want to build an SMPS type of power supply then you can try the following design:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2012/03/how-to-make-simple-12-v-1-amp-switch.html
for a transformer power supply you can simply use a 0-12V transformer and join a bridge rectifier with a filter capacitor, as shown in the third diagram above for getting a 15V output
Sir can you tell me how do we decide the value of capacitor used as a filter ??
there is a formula for it, however practically it's never required because most electronic circuits will work nicely even if there's a slight ripple….but as a rule of thumb it's recommended to use a value that may be as high as possible from the user, because the degree of filtration is directly proportional to the value of the cap (uF)
RC time constant has no relevance to a power supply, if you are referring to the filter capacitor formula you can easily find it online, just type: "power supply filter capacitor formula" you'll find many related sources
can i get 1.8v and 2.2amos by using this circuit??
the last circuit using LM338 IC will give you this.
Hello sir,
what do you think about adding non-polar caps in parallel to each diode in the bridge network configuration? do these guys provide better stability??
Do you suggest me connecting a resistor at the output after the electrolytic cap?
does connecting resistor reduce hum on the DC output.
Please help in such thoughts.
Hello Sherwin, such enhancements are not crucial and may be ignored, because the circuits which would be operated using these supplies would be already sophisticated enough to tackle such small inefficiencies from the power supply.
Thanks for the article.
I need to step-up 8V(p-p) 1MHz AC signal,which type of transformer should I use?
you will need a ferrite ring type of transformer for this.
Sir please can u give more details on this? and is it easily available? I require it on urgent basis.
you can try a joule thief circuit kind of configuration for your application.
you will find plenty of such designs on the web.
Thank you sir for the reply.
Sir,on the receiver side I'm getting enough voltage but very low current.I need to amplify current but at the same time voltage should not drop more than 1V.How can I do that?
which circuit you have used, pls provide me the link.
thank you for everything sir.
but I developed a 5v power supply, it works well but my worry is that the output current is to small so, how can I increase it thank you.
The output current will depend on the transformer rating….if you have used a 7805 IC the transformer could be rated at 1 ampere.
Hello Sir,
Day's Greet.
I find this site is is very interesting and I like it very much.
Sir,I am using LM2576 to get 5V.
Input to the LM2576 should be minimum 7V.
Max current handling capacity of LM2576 is 3A
My transformer is 9V,1A.
Load is 0.70A.
What should be the value of capacitor.
I got the value of load from DC power supply by providing 9V at the input of Bridge rectifier.
Please, suggest the solution and its formula.
Please reply me this here as well as on my email-id n_nogaja@yahoo.co.in
You can refer to the following post, it explains the entire procedure of calculating filter capacitors in power supplies.
http://www.tpub.com/neets/book7/27e.htm
Thanks you!
you mean by using discrete transistors or mosfets??