In this post I will show how to construct a battery eliminator / DC variable power supply which will automatically cut-off the supply, if the current flow through the load exceeds the preset threshold level.
By Girish Radhakrishanan
Main Technical Features
The proposed over current cut-off power supply circuit using Arduino has 16 X 2 LCD display, which is used to show case the voltage, current, power consumption and preset threshold current limit in real time.
Being an electronics enthusiast, we test our prototypes on a variable voltage power supply. Most of us own a cheap variable power supply which might don’t sport neither voltage measuring / current measuring feature nor short circuit or over current protection built in.
That’s because power supply with these mentioned features can bomb on your wallet and will be overkilled for hobby usage.
Short circuit and over current flow is a problem for beginners to professionals and beginners are prone to this more often because of their inexperience, they might reverse the power supply’s polarity or connect the components in wrong way, etc.
These things can cause the current flow through the circuit unusually high, resulting in thermal runaway in semiconductor and passive components which results in destruction of valuable electronic components. In these cases ohm’s law turns into an enemy.
If you never made a short circuit or fried circuit, then congrats! You are one of few people who are perfect in electronics or you never try something new in electronics.
The proposed power supply project can protect the electronic components from such frying destruction, which will be cheap enough for an average electronics hobbyist and easy enough to construct one for who is slightly above beginner level.
The Design
The power supply has 3 potentiometers: one for adjusting the LCD display contrast, one for adjusting the output voltage ranging from 1.2 V to 15V and the last potentiometer is used for setting the current limit ranging from 0 to 2000 mA or 2 Ampere.
The LCD display will update you with four parameters every second: the voltage, current consumption, pre-set current limit and power consuming by the load.
The current consumption via load will be displayed in milliamps; the pre-set current limit will be displayed in milliamps and the power consumption will be displayed in milli-watts.
The circuit is divided into 3 parts: the power electronics, the LCD display connection and power measuring circuit.
These 3 stage may help the readers to understand the circuit better. Now let’s see the power electronics section which controls the output voltage.
Schematic diagram:
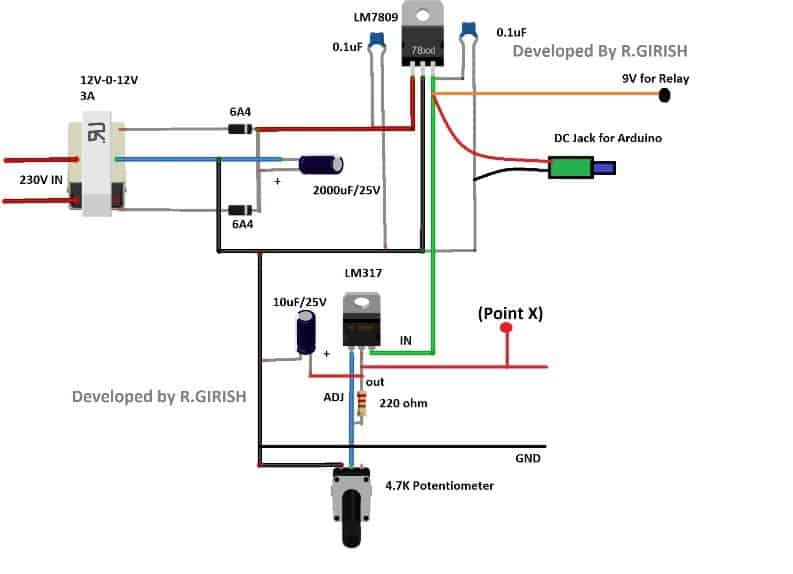
The 12v-0-12v / 3A transformer will be utilized for stepping down the voltage, the 6A4 diodes will convert the AC into DC voltage and the 2000uF capacitor will smooth out the choppy DC supply from diodes.
The LM 7809 fixed 9V regulator will convert the unregulated DC to regulated 9V DC supply.
The 9V supply will power the Arduino and relay. Try to use a DC jack for arduino’s input supply.
Don’t skip those 0.1uF ceramic capacitors which provide good stability for output voltage.
The LM 317 provides variable output voltage for the load which is to be connected.
You can adjust the output voltage by rotating the 4.7K ohm potentiometer.
That concludes the power section.
Now let’s see the display connection:
Connection Details
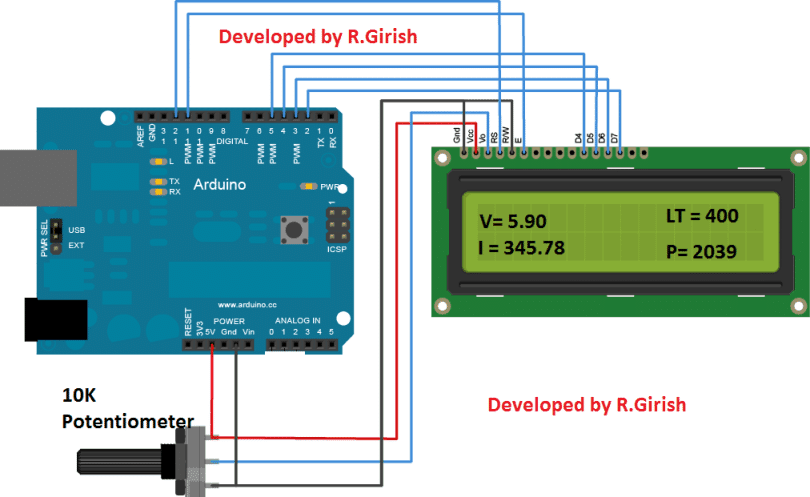
There is nothing to explain here much, just wire up the Arduino and LCD display as per the circuit diagram. Adjust the 10K potentiometer for better viewing contrast.
The above display shows the sample readings for the four parameters mentioned.
Power Measuring Stage
Now, let’s see the power measurement circuit in detail.
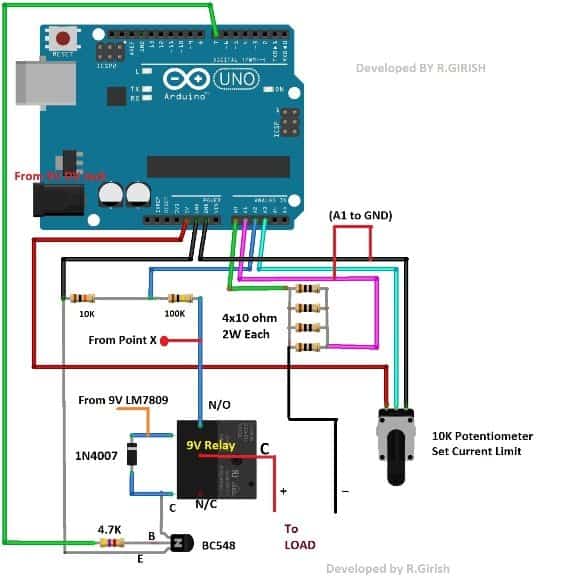
The power measuring circuit comprises of voltmeter and ammeter.
The Arduino can measure voltage and current simultaneously by connecting the network of resistors as per the circuit diagram.
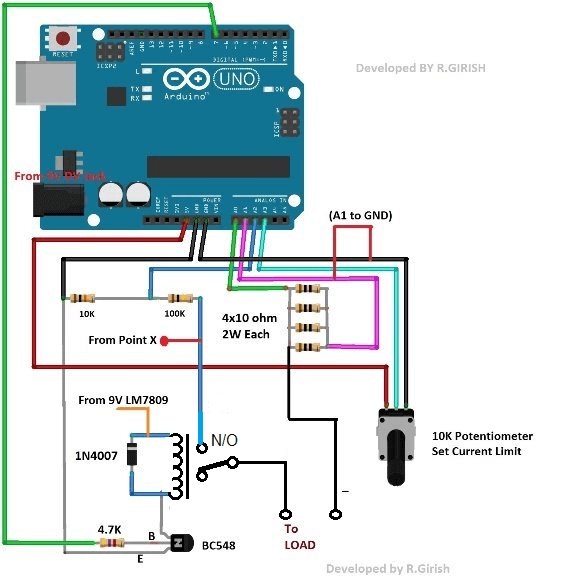
Relay Connection Details for the above Design:
The four 10 ohm resistors in parallel which forms 2.5 ohm shunt resistor which will be utilized for measuring the current flow through the load.
The resistors should be at least 2 watt each.
The 10k ohm and 100k ohm resistors helps the Arduino to measure voltage at the load. These resistor can be one with normal wattage rating.
If you want to know more about the working of Arduino based ammeter and voltmeter check out these two links:
Voltmeter: https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2016/09/how-to-make-dc-voltmeter-using-arduino.html
Ammeter: https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2017/08/arduino-dc-digital-ammeter.html
The 10K ohm potentiometer is provided for adjusting the maximum current level at the output.
If the current flow through the load exceeds the pre-set current the output supply will be disconnected.
You can see the preset level in the display it will be mentioned as “LT” (Limit).
Say for example: if you set the limit as 200, it will gives out current till 199mA. If the current consumption gets equal to 200 mA or above the output will be immediately cut-off.
The output is turned on and off by the Arduino pin #7.
When this pin is high the transistor energizes the relay which connects the common and normally open pins, which conducts the positive supply for the load.
The diode IN4007 absorbs the high voltage back EMF from the relay coil while switching the relay ON and OFF.
Program Code:
//------------------Program Developed by R.GIRISH------------------//
#include <LiquidCrystal.h>
#define input_1 A0
#define input_2 A1
#define input_3 A2
#define pot A3
LiquidCrystal lcd(12, 11, 5, 4, 3, 2);
int Pout = 7;
int AnalogValue = 0;
int potValue = 0;
int PeakVoltage = 0;
int value = 0;
int power = 0;
float AverageVoltage = 0;
float input_A0 = 0;
float input_A1 = 0;
float output = 0;
float Resolution = 0.00488;
float vout = 0.0;
float vin = 0.0;
float R1 = 100000;
float R2 = 10000;
unsigned long sample = 0;
int threshold = 0;
void setup()
{
lcd.begin(16,2);
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(input_3, INPUT);
pinMode(Pout, OUTPUT);
pinMode(pot, INPUT);
digitalWrite(Pout, HIGH);
}
void loop()
{
PeakVoltage = 0;
value = analogRead(input_3);
vout = (value * 5.0) / 1024;
vin = vout / (R2/(R1+R2));
if (vin < 0.10)
{
vin = 0.0;
}
for(sample = 0; sample < 5000; sample ++)
{
AnalogValue = analogRead(input_1);
if(PeakVoltage < AnalogValue)
{
PeakVoltage = AnalogValue;
}
else
{
delayMicroseconds(10);
}
}
input_A0 = PeakVoltage * Resolution;
PeakVoltage = 0;
for(sample = 0; sample < 5000; sample ++)
{
AnalogValue = analogRead(input_2);
if(PeakVoltage < AnalogValue)
{
PeakVoltage = AnalogValue;
}
else
{
delayMicroseconds(10);
}
}
potValue = analogRead(pot);
threshold = map(potValue, 0, 1023, 0, 2000);
input_A1 = PeakVoltage * Resolution;
output = (input_A0 - input_A1) * 100;
output = output * 4;
power = output * vin;
while(output >= threshold || analogRead(input_1) >= 1010)
{
digitalWrite(Pout, LOW);
while(true)
{
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("Power Supply is");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("Disconnected.");
delay(1500);
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("Press Reset the");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("Button.");
delay(1500);
}
}
while(output >= threshold || analogRead(input_2) >= 1010)
{
digitalWrite(Pout, LOW);
while(true)
{
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("Power Supply is");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("Disconnected.");
delay(1500);
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("Press Reset the");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("Button.");
delay(1500);
}
}
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("V=");
lcd.print(vin);
lcd.setCursor(9,0);
lcd.print("LT=");
lcd.print(threshold);
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("I=");
lcd.print(output);
lcd.setCursor(9,1);
lcd.print("P=");
lcd.print(power);
Serial.print("Volatge Level at A0 = ");
Serial.println(analogRead(input_1));
Serial.print("Volatge Level at A1 = ");
Serial.println(analogRead(input_2));
Serial.print("Voltage Level at A2 = ");
Serial.println(analogRead(input_3));
Serial.println("------------------------------");
}
//------------------Program Developed by R.GIRISH------------------//
By now, you would have gained enough knowledge to construct a power supply which protect you valuable electronic components and modules.
If you have any specific question regarding this over current cut-off power supply circuit using Arduino feel free to ask in comment section, you may receive a quick reply.
Hi sir , I have a megger ago meter . which has burnt four resistors connected in series with the voltage connection leads. The reason was I used it to check voltage across diode in a microwave oven. Please can you help find the value of the burnt resistors
Hi Stephen, sorry I do not have any idea about it, you can perhaps try using 4nos 1M resistors and see how it works.
Sir,how can I use a AC load for this project? Beacuse in the diagram I see the load in DC right? Because im planning to use 240V AC light bulb.
Rizal, the above Arduino design can be difficult to modify for an AC current control, however it can very simply done using a transistor based circuit as shown below:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/mains-ac-overload-protection-circuit/
For IN4007,how is the connection with 5v relay module? As the relay 5v have vcc,ground and in,so how to connect the IN4007 with the relay? Thank you.
please see the last diagram.
sir I cant understand for the relay part..I have buy 5v relay module bt I dont know how to connect IN4007 with the relay as the relay has 3 terminal which is vcc,ground and in.Can you explain sir? Im really appreciate it.
Rizal, the above circuit will require an isolated relay without a PCB, so please do not use a relay module, instead buy only a simple relay and wire it as shown in the diagram.
For more help you can refer to the following article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/how-a-relay-works-in-circuits-how-to-connect-it/
Hye..what happen if I dont use transistor in this project? And can I change 4.7k ohm resistor with 10k ohm resistor? Thank you.
Hi, without the transistor you cannot operate the relay. yes 4k7 at the transistor must be changed with a minimum 10K resistor
Sir,I have made the connection accordingly to your schematic diagram but it doesnt work.Can you give a better schematic diagram sir? I mean the connection on the bread board since maybe I have connect wrongly on my bread board.I really need that sir since this is my FYP project. Hope you can consider that. Thank you.
Hi Rizal, the schematic is very clearly presented in the article, please let me know where exactly are you having problems regarding the schematic view?
Initially You can eliminate the first diagram, and instead use a ready made 9V adapter, and use its output to power the Arduino as well as the “point X”
hye sir,what kind of load I can use to show that when over current occur it will turned off? And how to connect them? Thank you.
Hi Rizal, according to me you can add a 9V filament bulb as the load.
I’ll draw the relay diagram properly soon, and update it in the above article.
ok sir..Hope it wont take too much time because Im going to do this for my FYP. Thank you.
Hello, what should I modify for an automotive 12 volt 10 amp battery charger?
Thankful!
Please reply in my email if possible
You can probably experiment with the four 10 ohm resistors for increasing or decreasing the current sensing range
Thankful
Hi Valmir,
The maximum capability is 2 A, you can’t use it for 10 Amps in this project, if modified for 10 A, then codes should also be modified accordingly .
sorry for the previous comment’s misinterpretation.
Regards
Hye sir..can i get the full schematic diagram for this project? and what type of load you use in this project?
Hi Rizal, the connection diagram is already explained in the schematic, if you are having trouble understanding any specific section, you can tell me here I’ll try to clarify
Hye sir..for the program code is it correct? Because i have put the program code in the Arduino software but it says error..
Rizal, the coeds are correct, did you download the necessary files in your Arduino software before uploading the codes? Anyway I’ll forward this message to Mr. GR for further clarification.
Hi Rizal,
There is no error in the code, we’ve double checked, Just the code is enough. No need to download any additional library files.
Regards
can we make 19v 5a=A laptop dc power supply
discrete components
I have a voltmeter circuit published in this blog:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2013/05/make-this-simple-digital-voltmeter.html
the same can be modified to measure current by suitably configuring a current sensing resistor
Hello sir,
I am start new project & required one digital display circuit
Input voltage – 54 volt DC
Show voltage – as for actual for 54 volt dc
Show load currant – as for actual dc load
Show A/C current as for actual
So please provide this circuit
Hello Rohit, do you want this in Arduino or using discrete components??
Sir,
This is only read for A/D voltage but my quiry one single display read DC voltage, Dc load & Ac voltage
Rohit, you can use the suggested circuit for all the 3 functions.. but through a selector switch.
Sir,
Please provide complete circuit diagram with connection can’t understand connection
great article loved it
thankx