The electronic 2 tone door bell circuit is designed around the popular IC 555. The IC 555 is extensively applied in numerous varieties of timers and also as a basic oscillator circuit. In this particular project both the timer and the oscillator functions of the IC are utilized.
As soon as the indicated push-button is pushed with our finger, the IC 555 begins oscillating with a specific frequency (tone), and as soon as the push-button is released, the frequency changes, modifying the sound of the tone, and the IC now continues generating this second tone for a specific amount of time period, as determined by the RC time constant of the IC.
Hence, when the bell button is pressed once, we get a two-tone doorbell sound from the speaker which is directly attached to the IC pin#3, and operated directly by the IC 555 output.
How the Circuit Works
Referring to the diagram below, the working of this two tone doorbell circuit can be understood with the help of the following points:
The capacitor C2 gets charged at the start, and the charge reaches the supply level of +9V through resistors R2, R3 and R4.
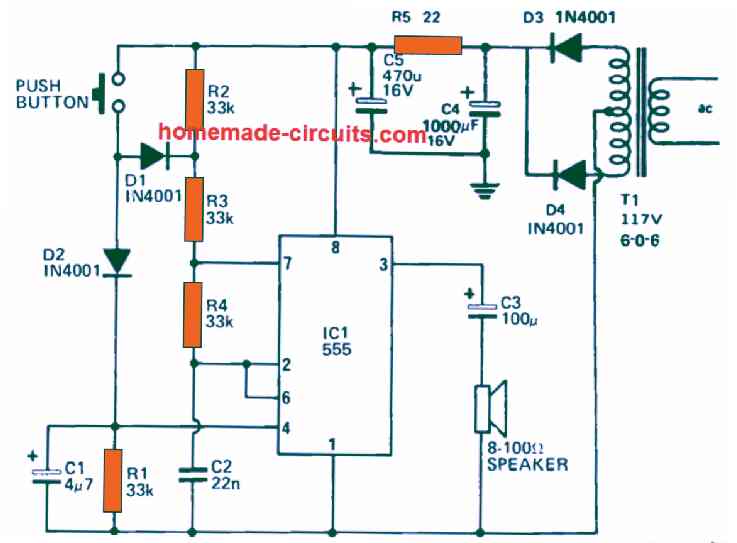
However, because the upper end of the capacitor is linked with both pin#2 and pin#6 of the IC.
Therefore, as soon as the voltage across the capacitor tends to reach 6V level, the two internal comparators of the IC gets above their threshold level, causing the IC 555 at pin#3 to go low, which in turn results in the internal transistor of the IC to switch on.
The action short circuits the pin#7 of the IC to ground.
But, since pin#7 is hooked up with the junction of the resistors R3 and R4 and C2, now begins getting discharged by means of the resistor R4.
During this process as soon as the voltage stored inside C2 tends to drop below 3 V, causes the output of the IC to yet again go high, switching OFF the internal transistor of the IC.
This in turn immediately causes C2 to start charging again by means of the resistor R2, R3 and R4.
This sequence of action goes on repeating continuously, which causes the generation of triangular waveform across C2, creating a train of pulses at the IC output pin#3.
This train of pulses coming out from the pin#3 of the IC can be seen configured with a loudspeaker by means of the capacitor C3.
The C3 capacitor ensures that the dc component present in the pin#3 output voltage does not reach the loudspeaker and thus prevents the loudspeaker from burning.
The capacitor C2 generates the triangular waveform as it charges through 3 V to 6 V and while discharging from 6V to 3V.
If you desire to change the pitch tone of the two tone door bell circuit, to a different tone you just have to tweak the values of the resistors R2, R3, R4 or simply the change the value of C2 appropriately until the desired tone output is achieved.
Parts List

Post your comments here and get guaranteed replies. Comments must be related to the above article.