White LEDs have become so common nowadays that even school kids today know how to use them for making simple LED projects. LEDs are typically used for illuminating purposes, the discussed circuit is also intended for similar applications. The post talks about how to wire LEDs and battery to make a simple DIY LED flashlight.
White LEDs are Awesome
Before the advent of the efficient white LEDs, incandescent bulbs were the only option which could be used for making flashlights.
Though not as bright as a white LEDs, filament bulb type flashlights served the purpose quite well, until LEDs were invented, which completely transformed the scenario.
White LEDs are so efficient that they produce 4 times more light than a conventional incandescent type flashlight yet consume 60% less power.

No surprise why white LEDs are being considered as the future option for all lighting applications.
The LED flashlight circuit explained here is very simple, and it simply requires to follow the instructions as given for making it successfully.
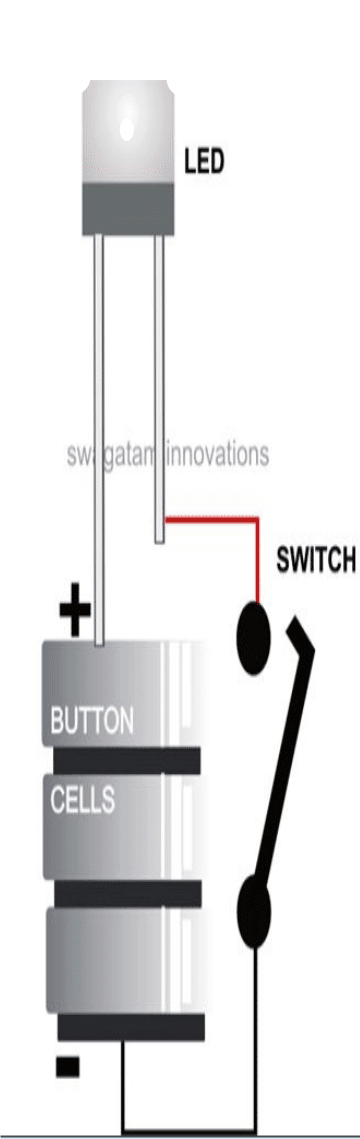
The proposed circuit utilizes just a single high bright white LED, three 1.5 volt button cells and a switch.
White LED Forward Drop Voltage
As we all know, a white LED typically needs a 3.5 volt supply for illuminating directly, without the need of any current limiting resistors.
Therefore here we connect the three 1.5 volt button cell connections directly across the LED terminal for switching it ON and for getting the intended illumination from it.
Being low in current the 4.5 V output from the cells does not produce any damaging effect, rather automatically adjusts to illuminate the LED very brightly.
Now add a switch anywhere in between the above cell and LED connection, it becomes switchable manually, your simple LED flashlight circuit is ready.
The discussed flashlight arrangement will require a proper casing for holding all the parts in place securely so that it can be comfortably operated by hand.
A sample design is shown below, which may be copied for making the enclosure for the above circuit.
Circuit Diagram
Economical Flashlight using Switched Output
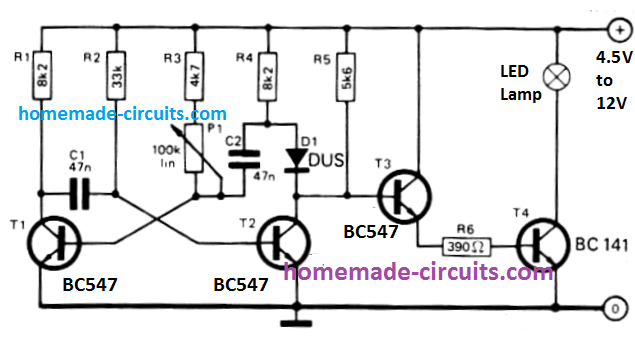
Due to the fact the full illumination of a flashlight is not always required, an appropriate dimmer might be a pleasant power saver.
The device was created around an astable multivibrator whose duty-cycle could be adjusted through potentiometer P1. The diode is included to enhance the rise time. The diode can be a 1N4148.
Through T3 the AMV switches transistor T4, which in turn switches the LED lamp. T4 can work without any heatsink.
The control range is such that the lamp could be tweaked to consume at about one third of its total brightness level; which means the batteries will likely then continue to operate 3 times more than its normal life.
The implementation of the circuit is naturally not restricted to flashlights alone; it could likewise be employed for solar lights, radio dial brightness, etc.
If an LDR is used in place of P1, it might be possible to achieve an automated dimmer that self adjusts the illumination of the lamp depending on the background light conditions.
Flashlight with Charger Circuit
The following, very useful concept of a chargeable flashlight circuit was contributed by a dedicated follower and reader of this site, "Ersa".
The first image below shows the circuit diagram and the parts list of the chargeable flashlight.
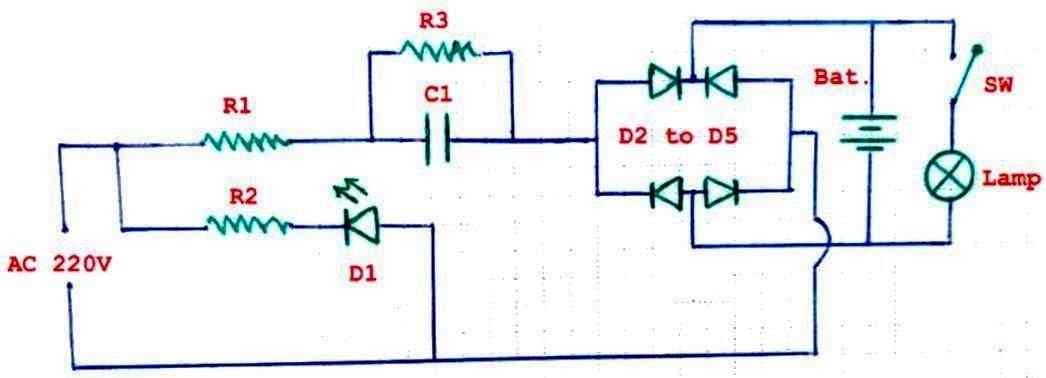
- List of components:
- R1 = 1R5 1/4W
- R2 = 220k 1/4W
- R3 = 270k 1/4w
- C1 = 470nf 400v
- D1 = LED red
- D2 to D5 = 1N4007
- Bat. = 2.4V 700mAh = 2×1.2V NiCd or Lead Acid
- Lamp = 2.5v 300mA
The following images show the specification of the high value capacitor which forms the crucial part in the circuit for charging the battery.

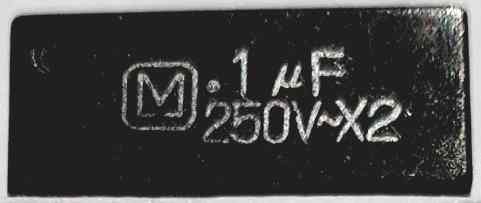
Warning: The circuit is not isolated from mains AC, and therefore is greatly prone to lethal electric shock if touched in an uncovered and switched ON condition. Appropriate precaution is strictly recommended for the user.
Enjoyed article on led flashlight, but having problems with my Nebo led/USB rechargeable light which has dimming feature. Have contacted company on several occasions of light not working or not accepting charge with same reoccurring problem and every time company has replaced light to a total of four times . Trying to understand circuitry and possibly trouble shoot. Realize a little off topic but would appreciate suggestions, thx Tom
Glad you enjoyed the post, and I understand your problem, however the circuit configuration can be a lot different for different brands, so without seeing the internal wiring and the board it can quite difficult to troubleshoot the unit, or suggest you the tips regarding the troubleshooting
Best info about flashlight apps used in android phones. Thanks for sharing