In this post I have explained a basic Arduino function where I have explained the process of fading an LED ON/OFF through some basic code implementations.
Creating a Fading Effect
We see how to use an analogwrite() function in order to implement a fading ON/OFF of an LED. The function incorporates PWM pulses across a pinout for accomplishing the suggested fading action over the connected LED.
Hardware Needed
Along with your Arduino, other materials such as a breadboard, an LED and a 220 ohm, 1/4 wat resistor would be required for the experiment.
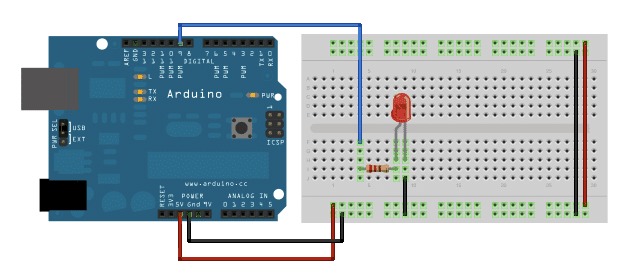
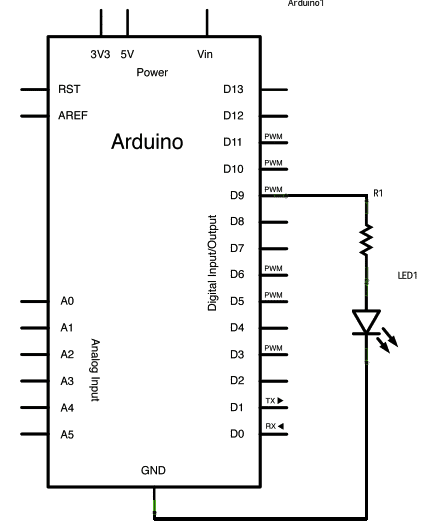
The Circuit
The steps involved for the proposed LED ON/OFF fading with an Arduino are as follows:
1. Attach the longer terminal of the LED to the digital output pin#9 via the 220 ohm resistor in series, while the cathode or the shorter terminal of the LED with the ground directly or the negative supply rail.
The Code
Once pin#9 of the board is integrated as the LED positive pin, the setup() function could be simply left alone and would'nt need any further operations.
The main loop code component in the form of analogwrite() needs a couple of acknowledgments: The first being addressing the function regarding which pin to be used for writing, and the second being the value of the PWM to be determined.
For initiating a fading ON/OFF effect on the connected LED, the PWM could be consistently varied from zero to maximum or to 255 and vice versa, completing the entire single cycle of operation.
The code below shows the PWM magnitude being determined through a variable named as brightness. Also the it increments by variable fadeAmount in the loop.
In a situation where brightness is at the extreme values (either 0 or 255), prompts fade
amount to become negative.
Meaning if suppose the fadeAmount is 5, it changes to -5, and 5 in case it's set a 55. In the later periods in the loop these changes results brightness to vary course of the action as well.
The function analoguewrite() causes quick alterations in the PWM values, such that the delay at the conclusion of the sketch controls the fading speed.
You may experiment with the delay values to investigate the changes produced in the program.
/*
Fade
This example shows how to fade an LED on pin 9
using the analogWrite() function.
This example code is in the public domain.
*/
int led = 9; // the pin that the LED is attached to
int brightness = 0; // how bright the LED is
int fadeAmount = 5; // how many points to fade the LED by
// the setup routine runs once when you press reset:
void setup() {
// declare pin 9 to be an output:
pinMode(led, OUTPUT);
}
// the loop routine runs over and over again forever:
void loop() {
// set the brightness of pin 9:
analogWrite(led, brightness);
// change the brightness for next time through the loop:
brightness = brightness + fadeAmount;
// reverse the direction of the fading at the ends of the fade:
if (brightness == 0 || brightness == 255) {
fadeAmount = -fadeAmount ;
}
// wait for 30 milliseconds to see the dimming effect
delay(30);
}



Comments
Good Day Mr. Majumdar. We were hoping if you could give us tips on how to build a 8×8 dot matrix with RGB leds. For our project. We have MPLABX IDE v1.85 for C language, PICkit2 as emulator. Looking to use PIC12Fxxx or PIC16Fxxx IC's. We wanna use only Red-Green-Blue colors to display desired characters. We really have nothing to start with. I mean, what IC do we use? what other components do we need? Hoping for your reply. Thank You in advance.
Good day Blitz, frankly speaking, I am not expert with MCU circuits and stuffs, so I am as blank as you are right now, hopefully soon I'll get this field too in my area of expertise.