The TIP150, TIP151, TIP152 series are high voltage, high current Darlington transistors which can be used for applications involving voltages at mains 120V or 220V levels. The datasheet and other related details can be read in the following article.
The typical applications of this transistor could be for high voltage motor control, automotive ignition, inverter converter switching, SMPS and in many other similar areas.
Main Specifications
The main datasheet, specifications and features are as follows:
Collector to Emitter Continuous Voltage:
VCEO(sustained) = 300V minimum for (TIP150)
VCEO(sustained) = 350V minimum for (TIP151)
VCEO(sustained) = 400V minimum for (TIP152)
Collector−Emitter Saturation Voltage: VCE(sat) = 2V maximum at I current of 5A
The maximum current for the above voltages is 7 amps (continuous) and 10 amps for instantaneous peaks.
The base/emitter saturation voltage for TIP150, 151, 152 is 1.5V at 100mA for a typical 2 amp collector load, while it could be around 250mA at 2.3V for a 5amp collector load.

Pinout Details
In the shown image above the pinouts of the transistor can be identified as follows:
The center lead is the collector, it's connected with the metal tab of the device therefore the back steel tab also becomes the collector.
The right side lead is the emitter.
The left side lead is the base of the transistor.
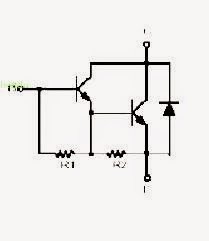
Internal schematic of the transistor TIP150/TIP151/TIP152
The above figure shows the internal Darlington structure of the transistor. A typical paired transistors could be seen here which forms the Darlington configuration.
This configuration helps to provide the device with extremely high gain and sensitivity even at the specified high power inputs.
How?, Can you provide me with accurate circuit diagram and specifications.
You can try the circuits explained in the following article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/simple-high-voltage-generator-circuit/
How do i connect the TIP152 for an amplifier to amplify 7.2volt,2amps DC to 400 volt?
You will need a boost converter circuit for that…a transistor alone cannot be used for boosting a voltage level.
The inductor is about 330uH. The battery is 3.7v 1200mah. I used the concept of the 1.5v to 12v converter i found in your site here. The two transistors are BC548-558(complementary). But i want to use 4×1.5v in parallel.
the 330uH coil should be rated at 1 amp, meaning the wires guage should be at least 0.8mm and the transistors should also be rated equally, 2N2222/2N2907 could work.
Alternatively you can try the following design if the previous circuit does not give appropriate results:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2012/10/1-watt-led-driver-using-joule-thief.html
Ok. The joule thief cellphone charger i produced was discharging instead of charging the phone. Please what could be the problem. And if i use L7805 with it, the current output will drop to 10mA. My phone needs atleast 800ma to charge. Please help
provide me with all the details about the circuit, only then i would be able to suggest correctly.
provide the coil details and the battery details
Please sir, i have a 650VA UPS that is powered with a 12v, 7AH rechargeable battery. Is it possible to charge 50 cellphones at once with this UPS? If not, how many cellphones can it charge at once?
50 cell phones would consume 0.2 x 50 = 5amps of current while charging, your battery would get discharged within half an hour so it's not feasible in my opinion.
….oops sorry 0.2 x 50 = 10amps, now it looks impossible…