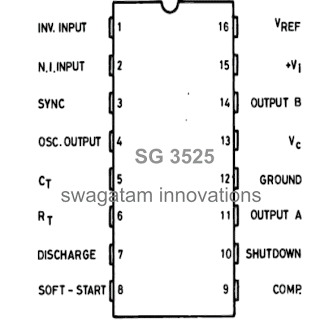
In this article I have explained the pinout functions of the IC SG3525 which is a regulating pulse width modulator IC. So I have explained in details: Main Technical Features The main features of the IC SG3525 may be understood with the following points: Pinout Diagram of the IC SG3525 PinOut Description A practical implementation […]
Electronics Theory
DPDT Relay Working, Pinouts, Testing Explained
In this post we are going to understand about how this DPDT relay actually works, how we identify its pinouts, and how we can use it in our projects. We shall go step by step so that you can feel confident with every small thing about it. Introduction We know that a DPDT relay means […]
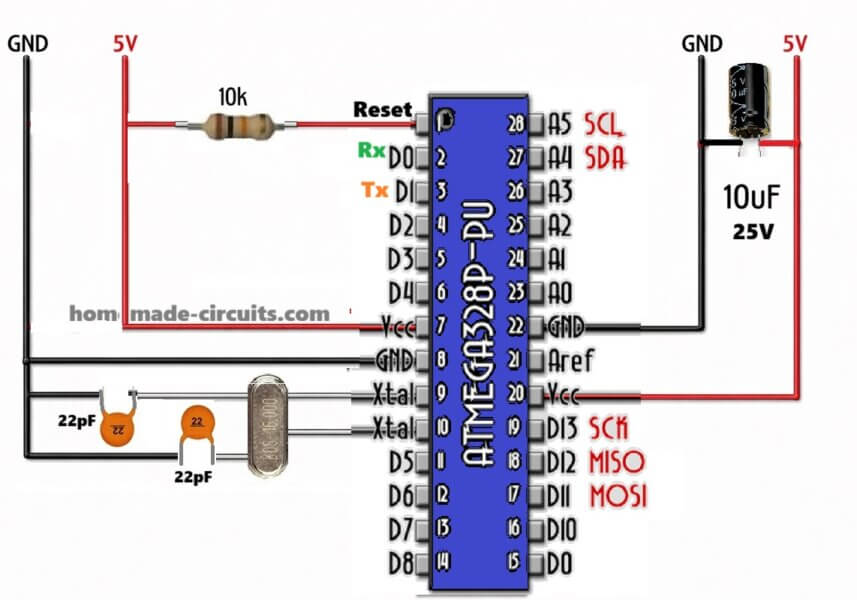
How To Use And Program ATmega Microcontrollers From Scratch Without Arduino
ATmega microcontrollers, they are coming from the AVR family which Atmel developed long back, and later this Atmel company was taken by Microchip. So now officially Microchip owns it but still people say Atmel AVR only. These MCUs became very popular slowly because they are easy to understand, quite affordable, stable in long run and […]
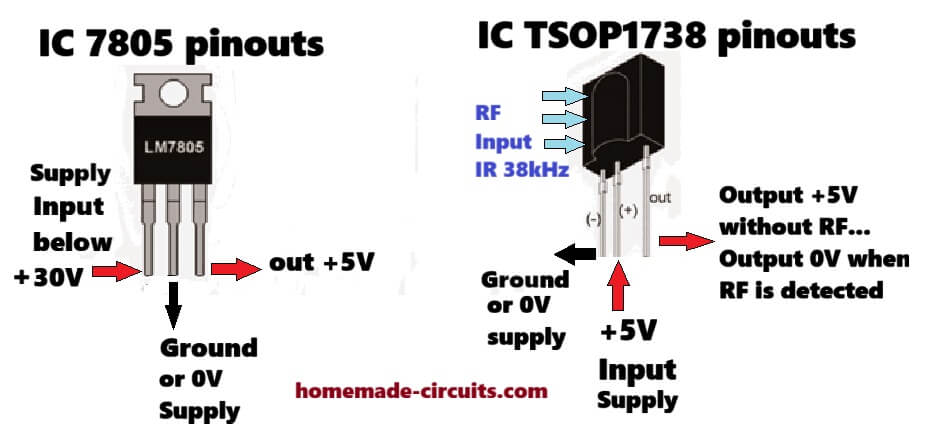
How to Connect a TSOP1738 IR Sensor
TSOP17XX series devices are advanced infrared sensors having a specified center frequency of operation which makes their detection extremely reliable and foolproof. In this post I have explained how to connect a TSOP series infrared sensor and use it for a specified IR remote control operations. TSOP IR Sensor Specifications A TSOP series of IR […]
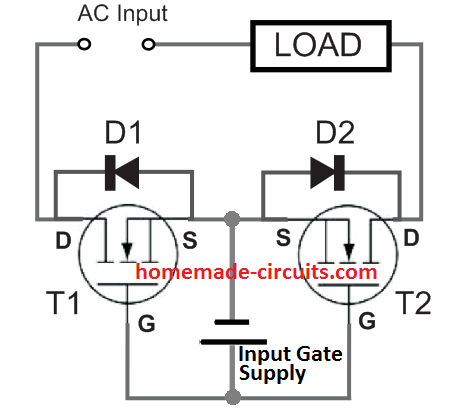
Solid State Relay (SSR) Circuit using Two MOSFETs
SSR or Solid state relays are high power electrical switches that work without involving mechanical contacts, instead they use just a couple of solid state semiconductors like MOSFETs for switching an electrical load, smoothly, and with high efficiency. SSRs can be used for operating high power loads, through a small input trigger voltage with negligible […]
How a Relay Works – How to Connect N/O, N/C Pins
An electrical relay consists of a electromagnet and a spring loaded changeover contacts. When the electromagnet is switched ON/OFF with a DC supply, the spring loaded mechanism is corresponding pulled and released by this electromagnet, enabling a changeover across the end terminals of these contacts. An external electrical load connected across these contacts are subsequently […]