A suddenly dimming and brightening automobile headlamp is usually quite undesirable, since it causes a painful interference with the normal vision of the opposite side driver or the passengers.
In this post we try to design a gradually self-adjusting automobile headlamp brightness circuit, which enables the brightness of the vehicle headlamp to vary proportionately in response to the ambient light conditions, and also to the headlamp intensity of the opposite vehicles.
Dimmer/Dipper vs Auto-Adjusting Headlamp
In a conventional automatic dimmer/dipper types of headlamp controller circuit, the head lights are switched with two different filaments or intensity levels. One of the lamp filaments is a low power filament which provides the dipping/dimming effect, or reduction of the lamp intensity, while the other set of filaments are rated at higher power for providing the normal, high intensity on the headlamp brightness.
Although these circuits work well and fulfill the intended lamp brightness control in response to the light beam from the opposite side vehicle headlamps, the relatively rapid switching of the headlamps causes severe strain on the drivers eyes, which may sometimes lead to a hazardous situation.
In contrast, a self-adjusting headlamp dipper appears to be rather useful, which enables the headlamps to gradually adjust the lamp intensity, depending on the brightness of the lamp of the opposite vehicle, and also the lights from the street lamps and other sources.
This concept utilizes a PWM controlled MOSFET circuit instead of relay switching. I have explained the working in details.
How the Circuit Works

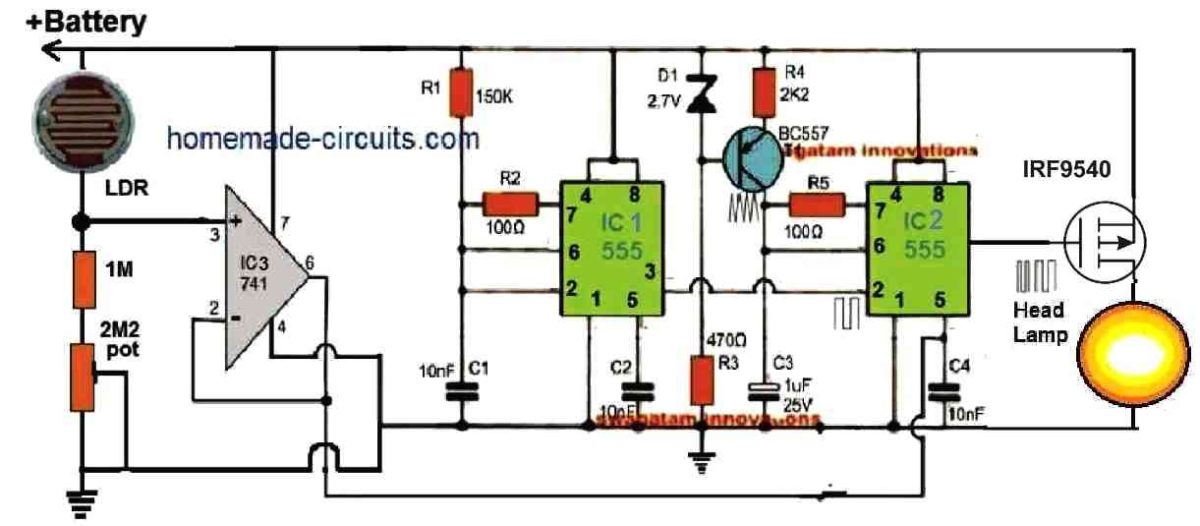
The basic idea is to increase the pulse width at the MOSFET gate and the brightness of the headlamp, when there's lower illumination on the LDR, and vice versa.
The entire circuit could be divided into 4 stages, 1) Light detector, 2) Voltage Follower, 3) Astable Oscillator, 4) PWM Controller.
The left side IC1 555 is configured as a square wave oscillator, which feeds the sample square wave to the pin#2 of the right side IC2 555 circuit which is configured as a PWM generator.
The PWM generator IC 555 transforms the square wave frequency into triangle waves and compares it with the voltage level applied at its pin#5.
The pin#5 of the right side IC2 555 stage is applied with the varying voltage due to the varying light levels on the LDR. This is implemented via the IC3 op amp buffer stage in the following manner.
The potential at the junction of the LDR and the 1M/2M2 resistors increase or decrease depending on the light level on the LDR, coming from the opposite side vehicle.
This varying potential difference is amplified and buffered by the voltage follower circuit using IC 741, whose output is then applied at in#5 of IC2 for the necessary PWM correction.
This instantaneous LDR varying levels applied on pin#5 of IC2 are compared with its triangle waves, which generates a proportionately varying PWM on pin#3 of IC2.
When the light on the LDR gets brighter, it causes the PWMs to become thinner proportionately, and when the light on the LDR gets dimmer, the PWM gets wider proportionately.
This oppositely varying PWM effect in turn causes the headlamp to get dimmer when light on the LDR is brighter, and dimmer when the light on the LDR is brighter.
Thus, depending on the light intensity on the LDR, the headlamp brightness self-adjusts, such that its brightness increases when the light on the LDR is low, and it gradually becomes dimmer as the light intensity on the LDR gets higher.
The 2M2 pot helps the user to set the maximum and the minimum headlight intensities with respect to the LDR illumination levels.

Thanks a lot for circuit! I would like to install this device on my motorcycle. Which LDR resistance do you recommend? thanks
Thanks, and glad you liked the circuit.
You can use any standard LDR available in the market. Please make sure to build the circuit step wise, and with proper understanding.
Thanks a lot sir very nice circuit
Very useful thanks again
You are welcome Mohammed!
hello swagatam.. suggest a circuit to replace common 12V BCU electronics with minimum voltage & minimum wires to operate basic functions of a motorcycle like tuning signals, indicators, multitoned warning sounds, brake light etc
Hello Manojkumar, please explain your requirement in more details, if possible I will try to figure it out….