The circuit described here can be built and used in your vehicle for an automatic dipping and dimming operation of the vehicle headlamps, in response to the intense lights coming from an opposite vehicle headlamps.
What's a Dimmer/Dipper in Automobiles
An automobile headlight dimmer/dipper is a circuit which automatically switches the headlight intensities of vehicles arriving from opposite directions in a controlled manner.
This prevents the drivers from the blinding glares of the opposite side headlights, and allows the drivers to have proper control of their vehicles, and avoid serious accidents.
Why an Automatic Headlight Dimmer/Dipper is so Important in Vehicles
You must have come across this irritating situation while driving at night when you find the headlight lamp focus from an opposite vehicle coming straight to your eyes, making things difficult to assess, and giving rise to a situation of a collision or a possible accident.
Incidentally, the driver of the opposite vehicle might be going through the same situation due to the headlight focus from your vehicle.
Such situations are normally tackled by using manual dipper switch mechanism, where the driver is prompted to "dip" the focus of his headlight, thus giving the opposite vehicle a chance to adjust his vehicle and also an indication that he too needs to "dip" his vehicle lamps.
However, doing the above operation manually, every now and then can become horribly laborious and troublesome, therefore if some kind of automatic system is Incorporated, can help to save this headache of the driver, especially while he is driving in stressful conditions and on dangerous highways.
You maybe also interested in reading a PWM based self-adjusting dimmer/dipper circuit
Circuit Operation
The following diagram describes a simple yet effective auto head lamp dipper or dimmer circuit.
The transistor is used as a comparator, which compares the preset resistance level and the LDR resistance level with reference to ground.
Circuit Diagram
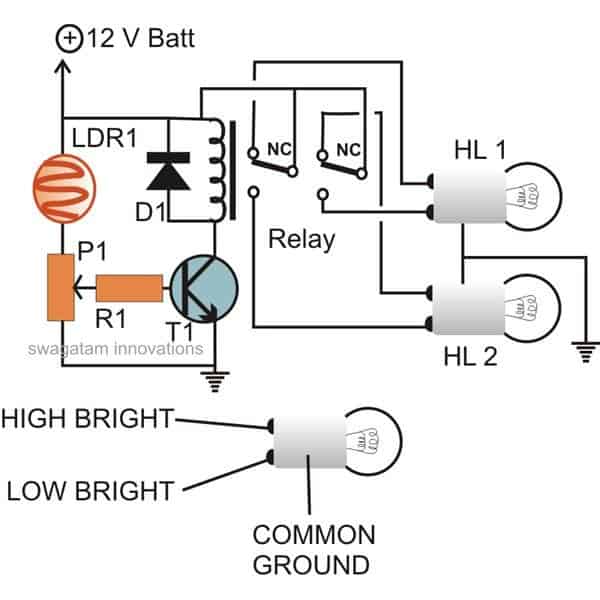
DPDT Relay Connection Diagram with Dipper Bulb
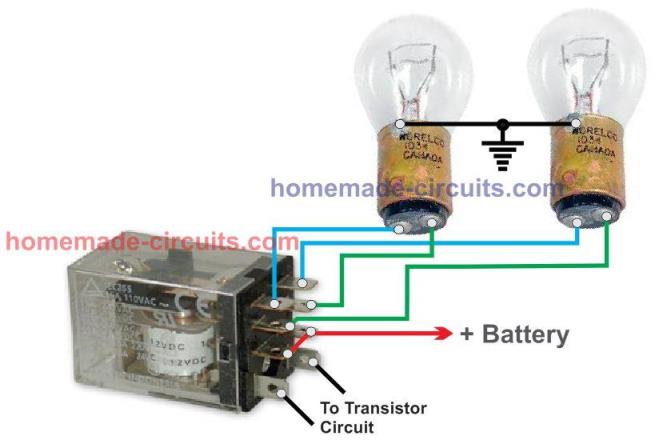
How the LDR Operates
Light falling over the LDR from the headlight of the vehicle coming from the front instantly lowers its resistance and allows more current to flow to the base of the transistor.
The transistor conducts and activates the relay, which in turn flips the contacts such that the host vehicle's headlamps gets connected with the dipper filament, changing its intensity.
The whole circuit may be enclosed in a small box and installed somewhere near the driver's dashboard area, however the LDR needs to be wired and placed out of the enclosure, in some corner of the wind shield, so that it is able to "see' the light from the opposite vehicles just as the driver would see them.
Parts List
R1 = 1K,
P1 = 10 K,
LDR = With resistance @ around 10 to 50 K when illuminated in daylight (under shade).
T1 = BC547,
D1 = 1N4007
Relay = coil 400 Ohms, DPDT, 12 volts
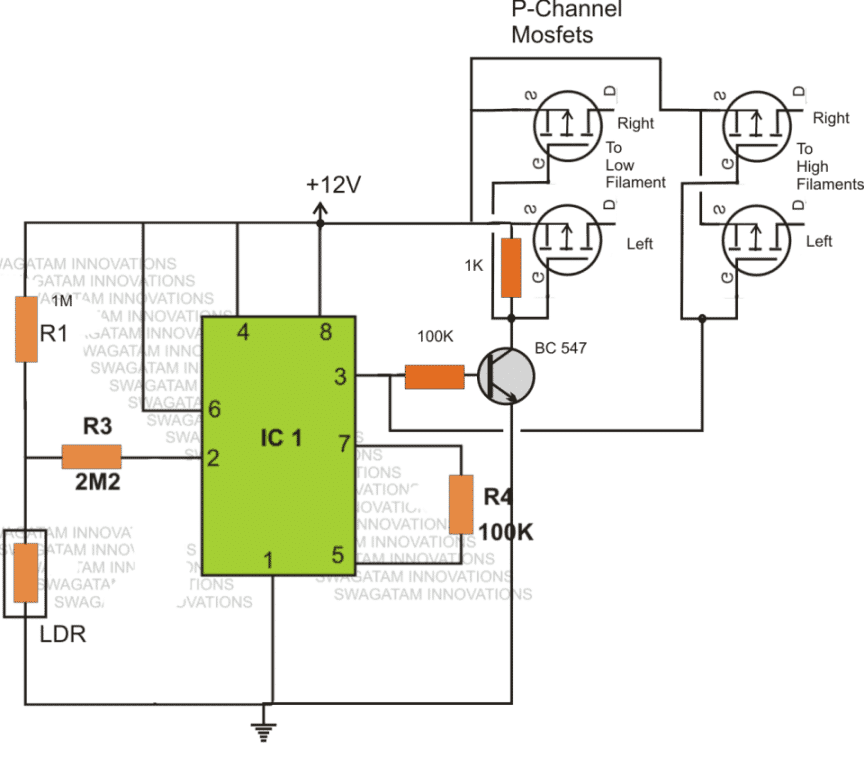
Making a vehicle dimmer/dipper without Relay
The above automatic dipper circuit can be modified for operating with mosfets:
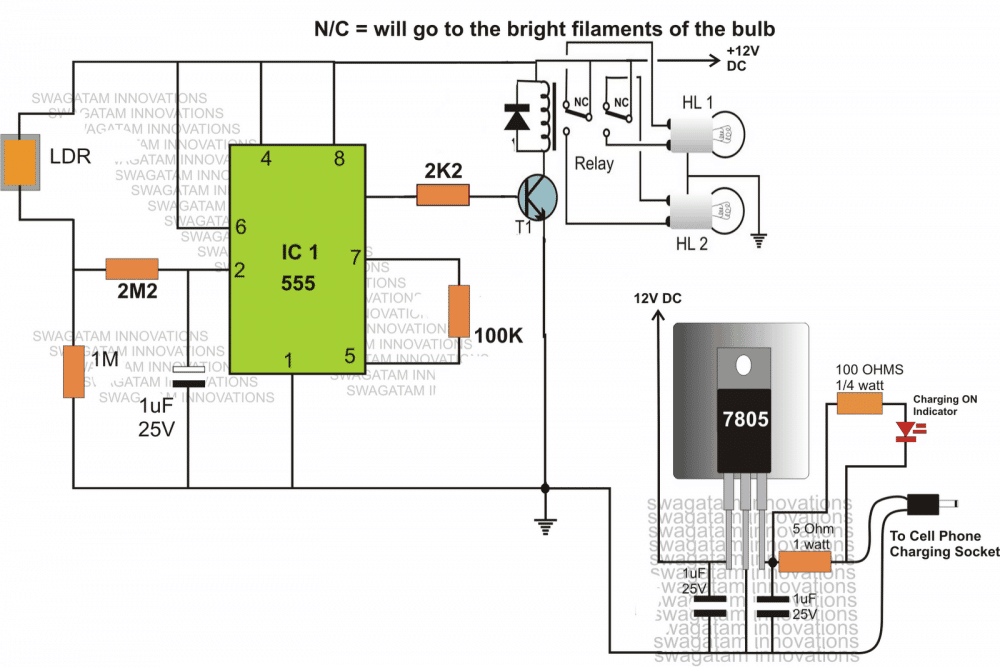
Dimmer Dipper with Cellphone Charger
The following brief explanation was provided by Miss Surya for getting a better view of the proposed circuit design of an automobile dimmer/dipper head light switch circuit with an optional cell phone charger circuit for facilitating the charging of a cell phone also on board.
Circuit Operation
Here the IC 555 has been used not as a charging indicator rather as a comparator for controlling the dipping action of the head lamps.
The use if IC 555 as a charging indicator would have made the circuit unnecessarily complicated, therefore a novel and simpler way is selected for the charging ON indication.
The LED connected across the 5 Ohm watt current limiting resistor effectively indicates the charging status of the cell phone and switches OFF the moment the charging process stops.
The IC 555 works like a comprartor here, when light falls on the LDR, voltage at PIN#2 rises above the set internal threshold which prompts the IC to change its output PIN#3 voltage from 0 to 12, triggering the connected relay.
The relay contacts immediately transfer the positive supply from the "high" filament to the "low" filament of the head lamps, resulting in an instant dipping of the lamp intensity.
The LDR must be positioned in such a way that it only receives light rays coming from front of the vehicle, which will be mostly the lights from another vehicle's head lamps.
When we are using the IC 555 in comparator mode, it depends on the two important reference voltages to change its output:
- Trigger Voltage (Vtrigger): This is the voltage at pin 2, which is the inverting input. When this voltage drops below a certain level then it causes the output to switch from high to low.
- Threshold Voltage (Vthreshold): This is the voltage at pin 6 known as the threshold pin. When this voltage goes above a specific level then it makes the output switch from low to high.
Key Voltage Thresholds:
Trigger Voltage (Vtrigger): The output will switch from high to low when the voltage at pin 2 (the inverting input) falls below one-third of the supply voltage (VCC). We can express this as:
Vtrigger = (1/3) × VCC
Threshold Voltage (Vthreshold): On the other hand, when the voltage at pin 6 (the threshold pin) rises above two-thirds of the supply voltage (VCC), that’s when the output changes from low to high. We can write this as:
Vthreshold = (2/3) × VCC
Hysteresis in Comparator Mode
When we use the 555 timer with hysteresis, which is usually done by adding some positive feedback to pin 5, then the way the comparator switches becomes a bit less sensitive to tiny changes in the input signal.
This is really helpful because it helps prevent any noisy or erratic switching making everything run smoother.
So how does this hysteresis effect work? We create it by connecting a resistor between the pin 5 and the threshold pin (which is pin 7), in the above diagram it is 100k.
This setup forms a feedback loop that shifts both the trigger and threshold voltages. As a result we end up with two different voltage levels for switching the output which makes the comparator much more stable.
Here is what exactly happens in this case:
- Vtrigger (with hysteresis): When the input voltage at pin 2 drops below the level set by the hysteresis feedback, that is when the output will switch from high to low.
- Vthreshold (with hysteresis): Conversely when the input voltage at pin 2 goes above the level determined by the hysteresis feedback, the output will switch from low to high.
The feedback voltage which we call Vfeedback is given by the ratio of the resistors in that feedback network.
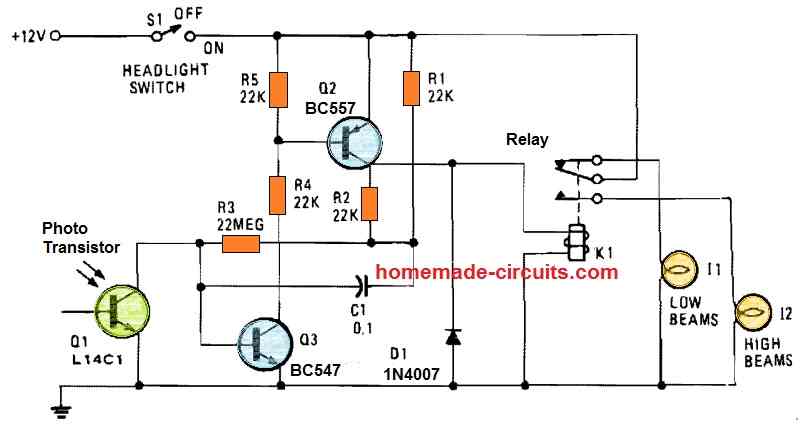
Using Photo Transistor
When photo-transistor Q1 detects the headlights of an approaching vehicle, the circuit gets operational and starts executing the dimming/dipping function.
The 22 M resistor, R5, sets the sensitivity to approximately half a foot-candle. A 12 V, 0.3A coil is utilized for the relay.
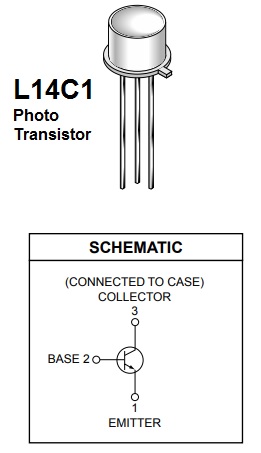
The photo transistor L14C1 comes with an one-inch lens with a 10° angle of view and a 1 inch diameter.




Comments
sir i just want to make the model of an autommatic dimming system in a dummy car. how could this be possible?
we have connected potentiometer in the 1st circuit,so how much of resistance to be applied
R1 can be replaced with a 1M pot.
what is the use of potentiometer in auto dipper circuit
hi sir ,
can you send me the circuit diagram for automatic head lamp control using micro controller please
Sir will u tell us how to make connections