In this article I will explain a battery status indicator circuit which can be also used as a battery charging fault indicator circuit. The idea was requested by Mr. Faizan.
The Design
The idea presented here takes care of all the parameters required for charging a battery ideally and safely.
Referring to the shown battery charging fault indicator circuit, the design may be understood with the help of the following points:
The IC LM3915 which is a dot/bar LED display driver IC forms the main charging indicator module of the circuit.It's pin5 is the sensing input, the rising battery voltage is sensed at this pin and the IC responds to it by producing a proportionately sequencing LED illumination across its 10 outputs, as shown with the 10 connected LEDs.
A LM317 IC can also be seen attached at the input of the circuit, it's wired as a constant current generator so that the circuit is able to produce error free indications and operations regardless of the input current level. Rx is selected suitably in order to enable this correctly.
Circuit Diagram
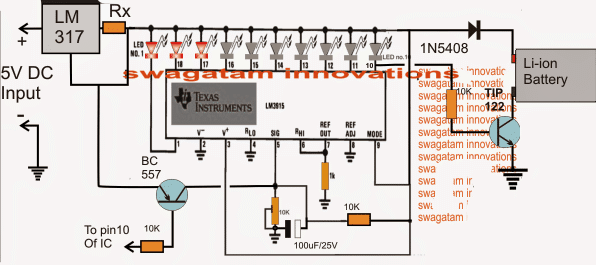
When power is switched ON, the 100uF/25V capacitor across the pin5 preset of the IC momentarily grounds pin5 so that all the outputs of the IC begin by staying shut off.
This is important to make sure that the TIP122 is able to initiate the charging process and the BC557 is inhibited from an accidental switch ON due to the initial surge transients.
As soon as the 100uF is charged up, pin5 is allowed to sense the actual voltage that's been utilized by the battery while it's been charged, which should be normally anywhere around 3 to 3.3V for a fully discharged 3.7V Li-ion battery.
Here each LED may be set to indicate an increment of 0.42V, which implies that the illumination of the 10th LED indicates 4.2V which may be assumed to be the battery full charge level indication.
This also implies that during power ON, 7 LEDs must be illuminated to indicate a correct battery discharge level and charging process.
Less that 7 LEDs illuminated would indicate a badly discharged battery or a damaged battery consuming excess current than the specified range.
With all the LEDs lighting up during power switch ON would imply either the battery is fully charged or the battery is not accepting charge and is faulty.
Under normal conditions, around 7/8 LEDs should be illuminated at power switch ON and as the battery voltage increases due to charging, the LEDs should also sequence by illuminating the 8th, 9th and the 10th LED sequentially.
Once the 10th LED is illuminated, a low logic is sent to the base of the TIP122 which is now inhibited from a base bias and the charging voltage to the battery is thus cut off, switching off the charging voltage to the battery.
The low logic from the 10th pin is also sent to the base of the shown BC557 which conducts and connects pin5 of the IC directly to the 5V supply making sure that the 10th LED becomes latched and the situation is locked until power is switched OFF and ON for further actions.
How to the set up the circuit
It's the simplest part in the design.
Initially do no connect any battery across the shown points.
Apply a precise 4.2V at the input.
Now begin adjusting the pin5 preset such that the LEDs light up sequentially and the 10th LED just illuminates brightly.
Seal the peset once this is confirmed.
Your battery charging fault indicator circuit is all set now for the proposed battery fault indications and also charge level indications.
Battery Fault indicator Circuit using a Flashing LED.
The following update shows a simpler design that may be used for indicating a battery charging malfunction through a flashing LED
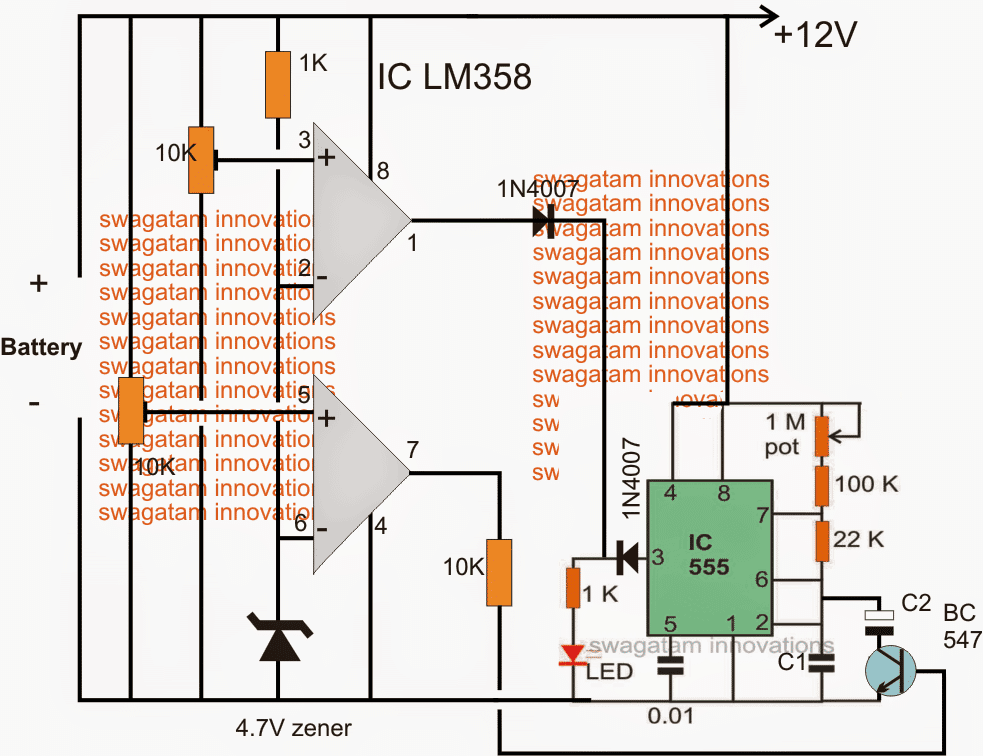
Initially both the opamp outputs may be assumed to be low, if the battery is discharged below 11V, this will be indicated with a fast blinking of the LED. C1 must be set for achieving this fast blinking.
The lower opamps is set using pin5 preset such that when the connected 12V battery reaches around 12.5V, its output pin goes high, once this happens the BC547 triggers and adds a high value capacitor C2 in parallel with C1 slowing down the flashing rate significantly and indicating that the battery has entered the next upper charging phase and also that the battery is good and is accepting the charge well.
As the battery continues to get charged and acquires a voltage level of around 14V, the upper opamp which is set using pin3 preset to trigger at this point triggers and renders a high across the connected LED stopping its flashing and illuminating it to solid.
Once this happens the user may assume the battery to have reached the optimal charging level and may remove it from the charger.
How the Battery fault is Indicated
1) If the LED blink rapidly would initially indicate that the connected battery is over discharged, however this condition should improve and the LED should transit into a slow flashing after an hour or so depending upon the sate of the battery. If this does not happen, the battery may be assumed not accepting the charge due to internal damage or short circuit.
2) If the LED lights up solid when power is switched ON would clearly indicate a faulty battery which may be completely inactive internally and unable to accept any current.
The above explained battery charging fault indicator circuit can be upgraded for an automatic over charge cut off through some modification as shown in the following diagram:
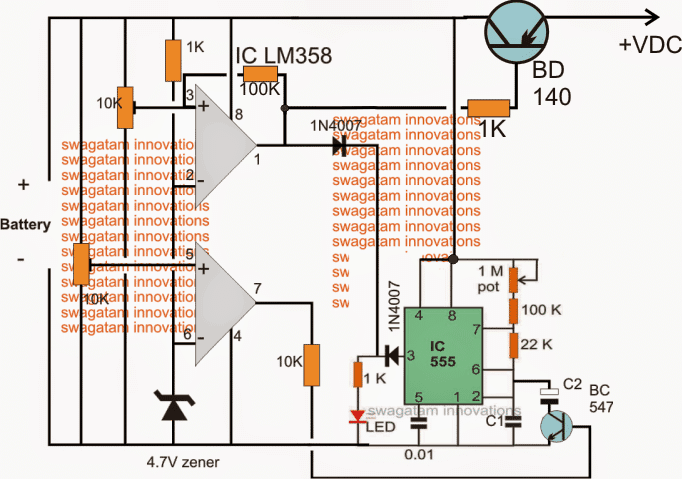
While setting up the two presets make sure the 100K link remains disconnected in the upper opamp.
After setting up the thresholds, the 100k link can be reconnected into position.
The circuit will not initiate until a battery is connected, so make sure the battery to be charged is first connected and then power is switched ON.
For a 3.7V battery, the 4.7V zener must be replaced with two
A little in-depth investigation shows that in the above circuit C2 will not have a discharge path through the connected BC547 and therefore it won't help to slow down the oscillations while the lower opamp is in the activated state.
The correct implementation of the above concept could probably be done by using an optocoupler as shown in the following figure.
Here instead of targeting the frequency determining capacitor C2 the resistor counterpart is selected for the intended control of the frequency and LED blinking rate:
Schematic for Blinking LED Fault Indicator
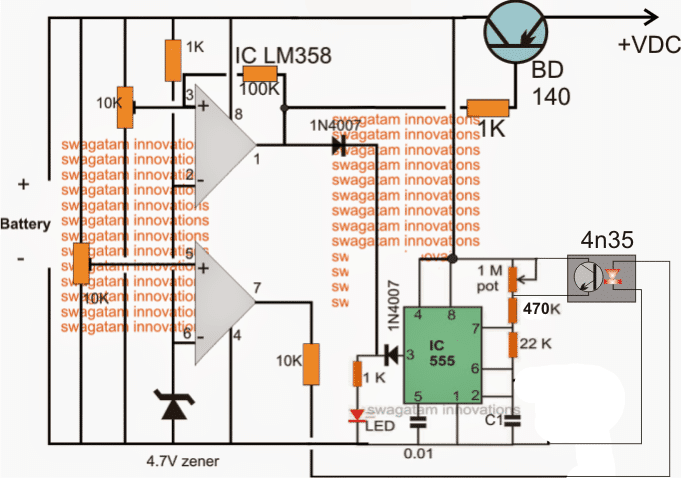
Now it looks much better.
What is Battery reversal when charging start-
Please Sir I saw Schematics diagram online for automatic lithium ion battery charger using lm358 and 8550 transistor. The Circuit employs three led indicators,one is used to indicate the charging status of the battery,the other blinks to indicate the charging and the other is used to Indicate w hen the battery is fully However many viewers including me who tried the Schematics didn’t work as expected or successful done in the video. The channel name was Creative Science. Please Sir could you review the diagram for any Corrections?
Because I tried it several times no success. The led does not blind and the others stay on
Hi Lawal, the schematic in the video looks OK to me. The left side op amp IC1B is designed to work like a square wave oscillator. While the battery is charging the output of the right side op amp IC1A is low, which allows the D4 to get the low signal from the right side opamp IC1A and it starts blinking. D1 remains shut off because there’s no high output from the right side op amp IC1A. When the battery is full charged, the output of the right side op amp IC1A becomes high illuminating the D1 and shutting off D4. Try increasing the value of C1 and see if that helps to blink the D4 LED or not. Remember the right side op amp IC1A output must be low while the battery is charging, this can happen only if the battery is discharged so that the pin3 voltage of IC1A is lower than its pin2.
Thank you Sir. Please Sir I assembled the diagram again on breadboard. However when I connected a lithium ion battery at the output,the power led and the charging status led (Red and green) both lighted.But the charging led or the blinking led (yellow led) stayed off. I disconnected and measured the output of the charger .It read 3.78 v on my multimeter. I measured the voltage of the battery and it reads 3.8 volts.
I connected a different battery with a low voltage of 2.4 volts.The power indicator led (red) only lighted after connecting the battery .After connecting the charger to the power supply 5volts,the charging status led only lighted without blinking. However when I touched the 1megaohm resistor pin connected to the output or pin7 ,the charging status led or the blinking led started to blinking.when I removed my hands it stays on.
Lawal, LED D4 will blink only when IC1A output is low. Output of IC1A will low when its pin3 voltage is lower than its pin2 voltage. Pin3 voltage will be lower than pin2 when a discharged battery is connected at the output and the battery low voltage drags and drops the supply DC to a level which causes pin3 voltage to become lower than pin2.
Connect the blinking LED D4 directly to ground and check whether it is blinking or not, if not then the left side square wave oscillator may have problems, you can try increasing the value of the C1 and check the response.
Remember breadboard assembly can have loose contacts, so it is not good, build the circuit over a PCB or a strip board by soldering.
good evening sir,in the lm3915 circuit,if you said “the transistor tip122 will inhibit charging process and bc557 will latch the the the charging” and don’t the basic rule of operation of transistor that says npn operate with >0.7v at the base and pnp operate with <0.7v at the base hold anymore?
Hello Yusuf, I did not understand your question. Actually when pin#10 activates it becomes low, causing the NPN to switch OFF and PNP to switch ON. When PNP switches ON it latches by supplying the full input supply to pin#5 of the IC.
thanks for your patience and response I really appreciate it all
you are welcome!
thanks sir .but u didn’t tell me any side effects of connecting different rated battery. like. please sir I will be very grateful if u can design a circuit that can monitor d current capacity of li ion battery maybe with lm3914.
Hello Tina, I think the negative factor is already known to you, the lower Ah batts will be charged at a faster rate and will continue to get charged until the other higher rated batts are fully charged, this will create an adverse effect on the low Ah batteries.
One easy wayout could be to restrict the full charge level to slightly lower than the actual full charge level of the batteries….for example instead of 4.2V you can set the charging voltage to 4V…then you can keep the charger connected indefinitely until all the batts are charged, without having to worry about any issues.
sorry, LM3914 cannot be used for controlling current, LM317 is the easiest option in hand
I need your knowledge .am confused. I have some set of li ion 4.2v 18650 of different current capacity. I want to connect them together in parallel to increase d current. my question is after using d battery,so I start charging it I guess those with small current capacity will first full ? and leaving all batteries to full hope it will not affect the those with small current capacity that have reached full level. or every battery will wait for each other to full… thanks in advance
If you intend connect different rated batts in parallel that would require a current limiter stage in between each of the batteries, this is to ensure that all of them are charged at the the same rate….ideally at 0.5C rate….for this you can use LM317 current limiter circuits in series with each of the batteries.
Under where can I find d ATS, changeover etc? I see one of out of “3 phase circuit”( single phase from three phase supply ) but no place to comment under the article sir I have build it but no good response and use battery to power it but something surprise me is it compulsory to use the transformerless Power for the circuit to make it work? but I see possibilities that the format of circuit ll work well and i believe in you. thanks for everytime…may you live long in good health amen more grace ahead of you in Jesus name. thanks in advance
Jesubiyi,
You can refer to the following links
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/?s=ATS
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/?s=changeover
And please try to use correct English while commenting, and do not use short forms for the words 🙂
alright noted
pls I want to build without microcontroller if possible (construction of auto power supply of 4 different sources ie solar mains gen and inverter to ensure no break of power to d load . pls share me d link/ knowledge. thanks
similar circuits are already present with names ATS, changeover etc…you can use the search box to find them..
sir can this circiut work for my 350v 1200amps lithium battery or what are the changes i need to make to the circuit and thank sir for the high voltage charger circuit it worked like charm
Abioye, you can try it, but you will have to scale it down appropriately to match the circuit’s voltage parameters, use potential divider network to scale down the battery voltage down to 15V, and then you can feed this to the battery input of the circuit
I'm trying to find a diode that rated to 7 amps. can you please suggest one?
thank you.
please search it on Google you'll surely find it
thanks for responding,
first and for most i would like to thank you for your patient and help.
also, do i need to replace the diode in the above circuit 1N5408 to one that is rated above 7 amps.
and im getting a little confused between the first and second circuit you mention in the last post. isn't all included in the same circuit mentioned above in this post.
the TIP142 is replacing the TIP122 to the far right, right before the battery.
the LM317 is replacing LM338 to the far left, right after the external power supply.
thank you, your an awesome man!!!!!!!!
Mamdouh, Actually I was referring to the following circuit:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2013/03/simple-dc-ups-circuit-for-modemrouter.html
since I had linked the above article and we were discussing this one in our earlier comment above.
If you are referring to the first circuit on this page, well yes it would also operate with 24V….and the LM317 would need to be replaced with LM338, the TIP122 with TIP142, and the 1N5408 with a 7 amp diode….coincidentally all the specs are matching perfectly with this design too as suggested by me for the other designs in the linked article. you are most welcome dear…keep up the good work
oh i forget one more thing. the LM318 i found LM318 and LM318T is there any different ?
Hi Mamdouh, the connections should be exactly as shown in the design, and all the parts are standard parts.
yes the resistor calculations correct.
the 100uF is electrolytic
your two theory is OK, you can go ahead with it.
You have put a few ebay links in your comments, so I have to delete the comments…but don't worry in the circuit article I'll post your comments without the links
your two diode theory is OK, you can go ahead with it.
LM318T or LM318 it doesn't make a difference for a comparator application, you can use any of them…
Great, is the circuit showing above would operate on 24v with 4~6 amps. And i should use only 2 diods from the suggested circuit, correct!
If so, what kind of diods would it be?
Thanks,
Mamdouh Mikhail.
yes it will work with 24V also and two diodes would be needed at the indicated positions which must be rated at above 7 amps as per the specs.
for the first circuit the transistor will need to be replaced with a TIP142, and in the second circuit the LM317 replaced with a LM338
in the transistor circuit, the zener value determines its output voltage for the battery
hi MR. Swagatam,
i was wondering if i connect my load ( the circuit i'm trying to supply)in parallel with the battery, so in this case will starts with main power adapter then the circuit followed by the battery then my load.
In this case if i applied higher voltage thru the power adapter the battery will become the load with my circuit, therefore i can charge the battery and supply my circuit in the same time ?
i'm not sure if what i'm saying make since, but I've done many researcher and that's what i came across to put the power adapter with the battery and my circuit in parallel, so when i disconnect the external power then my battery will supply: And if i connect the external power at higher voltage my battery will become a load with my circuit. so that i can charge the battery and supply my system.
thank you.
sincerely,
Mamdouh mikhail.
Hi Mr. Mamdouh,
you can definitely do that, but by adding a few diodes with the outputs, as discussed in the following article, this will allow you to successfully implement the desired application:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2013/03/simple-dc-ups-circuit-for-modemrouter.html
When u are trying practically ?
no need of checking, I am 100% sure that the circuit is fine and will work if done correctly as per the instructions and the "setting-up" procedures
Please suggest the fix values because with 5 volt given at input and threshold set at 4.2V the LED's blinks at no battery connect but suddenly gets solid when a discharged battery is attached to it.
without practical checking it would be difficult to suggest fixed values, not possible without knowing what voltage you are getting across the collector/ground of BD140
I have explained the procedures many times, I can't repeat the same thing again and gain.
OK.Can we achieve fixed values in this circuit for 4.2V output?is it necessary to add LED's more then one with one we can no achieve the flashing and solid?
If your input is a fixed 5V then we can remove the presets and have fixed resistor instead.
only one LED will be present in the final circuit, I suggested more LEDs only for testing and confirming the results which may be removed after the testing is finished.
One more thing to know is when battery is fully charged their will be a slow flashing still going on which is very minute but it is.Thecollector to ground is 3.8V.If circuit is set on 4.2V and a rectifier is attached.
At full charge pin1 is supposed to become high and stop the LED from flashing.
feed the 5V directly at the emitter of the transistor, don't use any diode or resistor.
make sure pin1 is set to become at 4.2V as explained previously.
I told you to connect LEDs on the different areas for the indications.
correction:
….make sure pin1 is set to become high at 4.2V as explained previously.
5v through a diode 1N4007 to the emitter of the TIP127 gives output of 3.85V maximum.As a result the battery charges to 3.85v not beyond that point and flashing continues.
a rectifier will drop around 0.6V nothing more than that, so I am sure how you are checking it. a BJT will not drop 0V across C/E
It may be due to the battery which is still getting charged, let it charge for sometime you'll find it reach the 4.3V level.
I meant
a rectifier will drop around 0.6V nothing more than that, so I am not sure how you are checking it.
a BJT will drop 0V across C/E
With TIP127 the input should be 5V so that the output will becomes 4.4V then i use resistor to drop it to 4.2V.
When setting up should the resistor connected at pin1 of LM358 also disconnected?
How to check a fault condition for fast flashing?
that's completely wrong.
feed the 5v through a diode 1N4007 to the emitter of the TIP127 that will take care of the output to the battery.
while setting just remove the 100k link from pin3 of the IC and reconnect it after the setting is complete.
connect a red LED in series with base of BC547, base of the TIP127, and between the cathodes of the pin1 diode and the IC 555 pin3 diode all these will tell you how the circuit is responding while setting it up
I have tried it but the current remains the same.
not sure why? according to me if the transistor gets a positive voltage from pin1 of the upper IC it has to conduct and will provide the battery with full current input.
It is conducting 0.45A while connecting directly and 0.2A while connecting at Collector of transistor.
Also i have noticed that if 1k connecting to base of BD140 is reduced to 500ohms the current increases.What to do?
Also how to check circuit if their is a fault what will be the procedure to check that fast blinking.?
I told you to use TIP127, so try this transistor.
set up the preset in the following manner:
initially keep both the presets slider arm to ground level
next disconnect the 100 link associated with the upper opamp
then connect a variable power supply FROM THE BATTERY SIDE. set it to 3.3V
The LED should show a fast blinking at this stage
now slowly adjust the lower preset such that the LED speed reduces to a slow flash.
Now increase the input voltage to 4.2V an slowly move the upper preset such that the LED just becomes solid.
that's it now the circuit is all set
My input supply is capable of providing 4.2V 5A but the battery is taking only 0.3A while it is at 3V.How to increase the charging current.And in place of variable can we achieve fix values of resistors?
connect the source directly with the battery and check the current using an ammeter, if it shows much higher amp reading would indicate that the BD140 was not conducting properly in the circuit… in that case you can try changing the BD140 with a TIP127 for an enhanced current gain
Also for flashing the on time is more then the off time how this can manage?
use 1M for adjusting flashing speed, and adjust 22k for getting different ON/OFF periods
And how charging current can be increased?
by increasing the input current
OK in case of damaged battery (dead battery) or battery is short what will be the status of LED?.
Also the green LED light output is less so i have replace 1k with 100ohms and still it is dim.
What is the function of 1 mega pot with 555?
for a short battery, the LED will not light up or will blink very fast.
use a red LED for more brightness. 100 ohm is OK
Yes i have recheck the connections are reverse now it is OK.The solid is very difficult to achieve.why?
when the upper opamp's output will turn positive it will make the LED solid so it cannot be so difficult
By that transistor pin settings the with supplied input of 4.2V the output goes to zero.
check online the image of BD140…see whether or not you have selected the correct pins with reference to the above diagram.
emitter must go to the supply input
And does it cut-off the battery after fully charge?charge termination?.The connection of Bd140 has some issue i have swap the collector with emitter then gets output by giving 5v input the output i get is 4.3v
yes it'll cut off after the battery is fully charged…the BD140 connections in the diagram is correct, if you modify anything in the diagram it'll not work.
I have explained the setting procedures above, you must follow them exactly as given.
a battery should be connected to the shown position before power switch ON for initiating the circuit.
Zener of 4.7v is used or 2x1n4148?
2×4148 back to back, cathode towards ground
And how much the Vcc will be now?
Vcc = 4.2V as before
Many thanks.Some questions are as:
How to set up the thresholds?.How to set threshold for 4.2v battery?.
The circuit will not initiate until a battery is connected, so make sure the battery to be charged is first connected and then power is switched ON.
If battery is charged and switching will be done later On then what will happen?
For a 3.7V battery, the 4.7V zener must be replaced with two ??
initially keep both the presets slider arm to ground level
next disconnect the 100 link associated with the upper opamp
then connect a variable power supply FROM THE BATTERY SIDE. set it to 3.3V
The LED should show a fast blinking at this stage
now slowly adjust the lower preset such that the LED speed reduces to a slow flash.
Now increase the input voltage to 4.2V an slowly move the upper preset such that the LED just becomes solid.
that's it now the circuit is all set
battery should not be allowed to remain connected while the circuit is not powered otherwise the batt will slowly get discharged through the 10k presets and the zener
Waiting for the updated circuit diagram.
It has been updated
OK i will wait for the updated circuit.Thanks
In place of LM358 can LM393,LM339 or LM324 be used?
you can use two 741 instead
….sorry 741 will not work at 3V so LM358 is more appropriate
OK can i remove the status LED from this circuit?.
My battery charging current is 400mA.
Voltage is 4.1 +- 0.5volts
SO what will be the value of 3ohms resistor to change to? 1.5ohms 1watt?
Supply voltage is 5V,2A.
Any other change in value of components?
yes it can removed and replaced with a link.
1.5 ohms is correct although thsi stage is not crucial and can be removed.
no other changes would be required.
actually the above LM358 circuit can be also modified for an auto cut off, no need of using another external circuit.
LM358 can be replaced with any other opamp example two 741 ICs but using LM339 or LM324 would mean two idle or unused opamps which will need to be terminated correctly for maintaining stability, so not recommended.
I'll update the above circuit for an auto cut off, possibly soon.
OK what circuit is best suitable for charging lithium ion battery 4.2v,1200mah? with cut-off,over charging protection.In this case the battery is attached to a charging circuit?.
you can refer the last circuit from this article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2013/12/usb-automatic-li-ion-battery-charger.html
What will be the value of zener for 4.2Volt case?
you can two 1N4007 diodes in series with cathode to ground.
any change in value of zener?.
C1=1uf multilayer or ceramic ?
C1, C2 both can be electrolytic
OK what will be the input voltage in this case?
it'll be 4.2V
SO how this can be used for charging a lithium ion battery?.
What is the value of C1,C2?
Does it will work for slow flashing and for fast flashing?
yes it will work as per your mentioned specifications
for a li-Ion feed a 4.2V input, adjust the 10k preset such that at 3.5V, the lower opamp output just switches ON (become high).
Use a 7555 instead of 555 because 555 may not work below 4.5V
C1 = 1uF, C2 = 2.2uF
so that means the circuit can be little smaller.I will wait for the whole circuit diagram.Thanks.
OK!
still working on it, possibly I'll finish it by tomorrow
diagram updated check it out
Can the flashing can be done with 2 transistor multivibrator?
yes, and the following can also be used
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2011/12/how-to-make-single-transistor-led.html
Solid need for charge completion only.
i'll try to do it, but the circuit will be quite lengthy and bulky.
you'll get it tomorrow
First of all a proper charger needed with cut-off,secondly a multivariate can be connected to have charging status?.For fault indication that is tricky to have fast flash may be with 555 timer?
introducing two 555 stages for just flashing an LED could make the design so much lengthy and bulky,
using 4 separate solid LEDs makes more sense according to me. which will light up individually (not together) for indicating the various conditions of the battery
Oh that's sad.Please let me know other options? if not working with LM3914.
For status LED i need to have some changes like:
1:Green LED fast flashing indicates fault i-e 1 flash per 2 seconds agreed.
2:Green LED slow indicates charging condition agreed.
3:Green LED solid ON indicates battery is full charge please check.
sorry it's not working out.
with 4 static LEDs it may be possible but not with a single flashing LED
OK i am waiting because i have to do in this week.Thanks,
fast flashing for fault,
slow flashing for charging
and very slow flashing may be at 1 flash per 2 seconds
this much can be provided.
Any updates i am waiting anxiously?
I have the idea, but unable to update it due to the lack of time….will do it soon for sure.
Yes surely it needs a new one
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2013/12/usb-automatic-li-ion-battery-charger.html can this be modified?
the above design is based on a different principle so it cannot create flashing indications,
for flashing indication a different circuit will be required having the caapcbility to sense the battery condition and change the flashing rate.
Any updates?
I tried but couldn't figure out a proper design till now…
Sure i will wait for this.Thanks
For status LED i need to have some changes like:
1:Green LED fast flashing indicates fault
2:Green LED slow indicates charging condition
3:Green LED solid ON indicates battery is full charge.
in the above design it would be difficult to add these enhancements, if possible i'll try to design a new circuit.
this is not working as the output across TIp122 is below 2v which is low when input is 5V.
change the position of the battery as shown in the updated diagram…
Very strange behavior from circuit when only +ve terminal of battery connected to the TIP122 all of bar graph ON as battery is not connected to GND and not fully charge this happens every time and no current charging current is sensed.My battery is OK i have test with another charger.
connect a diode in between the battery positive and the TIP122 emitter, this will solve the issue.
anode to emitter, cathode to the battery positive.
Hello;
As the LM317 drops 1.25volts so the output is less then we need to charge up the battery so what should be done in order to get correct output at TIP122?
Are you sure the 317 will drop 1.25V? If it is so, then you may have to use a 6V input instead of the shown 5V
One more question about setting up LM3914 does the input 4.2V means by providing input at pin 9 by removing the LM317 to tune it up?
input should be applied across the points where 5V is indicated, that is at the input of LM317, it should not be removed.
once the IC is set, then the 4.2V can be removed and replaced with 5v
Can it tell the short circuiting of battery or reverse polarity as well?
battery cannot get short circuited in the above design.
for reverse indication polarity simply add a LED with a 1k series resistor across the emitter and ground of TIP122 but in reverse polarity that is anode to ground and cathode to the emitter.
By mistake i put the BC557 question i got it,it is PNP.
Can i use LM3914 in place of LM3915?
yes 3914 will do.
Thanks for circuit.I want to know about Rx value i have selected it 2ohm 5watt for 0.6A charging current is it OK?
Also tell me about BC557 transistor which is PNP not NPN should it be 547? or 577?.
I am using switching power supply of 5v,3A is it OK to use ?
Rx = 1.25/charging current,
for a 1000mAh Li-ion batt the charging current should be 1amp, therefore
Rx can be = 1.25 ohms
BC557 is PNP
5V/3amp input is OK