In this post I am going to explain different types of uninterruptible power supply (UPS) that are available in the market and how they are classified according to the consumer’s requirement. We will also explore the different types of UPS’s block diagram to understand their technical difference between them.
UPS systems are a type of power supply that is designed to provide an uninterrupted AC mains power supply to the connected load, regardless of whether the grid AC is present or absent.
- The loads can be critical where interruption of power is unacceptable like data center’s servers, patient lifesaving equipment on hospitals etc.
- The loads can also be semi-critical like, desktop computers where interruption in power will lead to data loss, network devices like modems and routers at offices / homes.
- The loads can also be non-critical like lighting, fans, refrigerator etc. at home and offices.
There are three major types of UPS available:
- Online UPS.
- Line interactive UPS.
- Standby UPS / Offline UPS.
Online UPS:
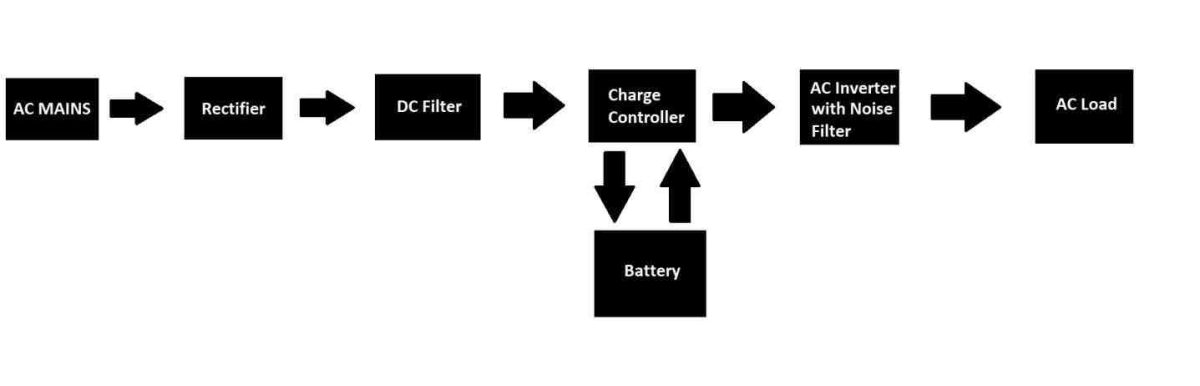
An online UPS system provides a very high quality power output for critical loads where power surge or interruption is not acceptable.
A feature that makes this UPS system outstanding is “zero millisecond” transfer time between AC mains to backup battery during a power outage. The input and outputs are noise filtered to a great extent so that no spike or surge will appear at the output. Let’s try to understand how an online UPS works.
An online UPS system consists of the above illustrated blocks, the AC supply from the utility grid is converted to DC using rectifiers (may also sport power factor correction) and filtered using banks of capacitors to provide as pure DC as possible.
The next block is a charge controller where the backup batteries get charged and also powers the DC to AC inverter block.
The charger manages the charging process of the battery properly and when it detects a power outage or power surge, the battery is discharged immediately and provides the power to the inverter uninterruptedly.
The way online UPS manages to achieve zero millisecond transfer time is too technical and is subject for another article.
The inverter block is the one which actually converts the DC to AC from either during mains input or with backup batteries.
You would have noticed that the inverter circuit is powered ON all the time and also the AC mains is converted to DC first and again back to AC, this is called double conversion.
Double conversion is important to achieve superior noise immunity from the utility grid and also for zero transfer time.
An online UPS is NOT something that is connected to the internet, it is called online because the inverter circuitry that is present in the UPS system powers the connected load all the time whereas other types of UPS’s inverter circuit come to life only after a power interruption.
Advantages of online UPS:
- No power interruption due to zero millisecond transfer time.
- High reliability.
- Isolation between noisy AC mains and loads.
Disadvantages of online UPS:
- Due to double conversion of input supply, heat losses are more compare to other type of inverters.
- Expensive, only business or commercial entities usually purchase it.
- If the inverter fails, there will be a catastrophic power failure on critical loads.
This concludes about the online UPS system.
Line Interactive UPS System:
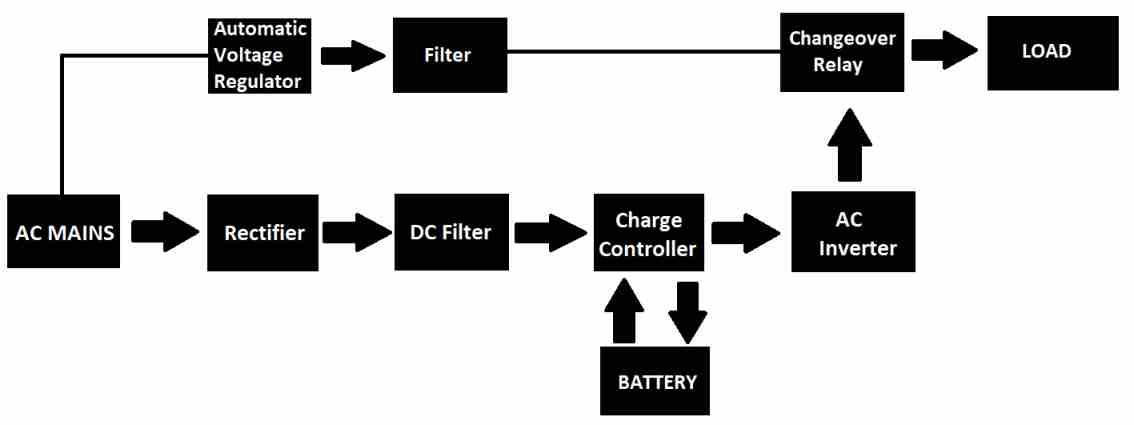
Line interactive UPS system as the name suggests it interacts with AC main lines for automatic voltage control (for stabilizing the output during AC mains) and for noise filtering and as well as to provide backup for the connected load.
This type of UPS is also best for loads which are voltage sensitive.
In this type of UPS there will be a small interruption in power when the UPS changes over from AC mains to battery during a power outage.
The changeover (transfer) time for an average line interactive UPS is under 10 milliseconds and this is enough for semi-critical loads like desktop computer, routers and modem without any restart or interruption in their operation.
Let’s try to understand the block diagram. The AC main is rectified and filtered and applied to a charge controller which keeps the battery charged full.
When the UPS detects AC mains power failure, the inverter is turned ON and the changeover relay quickly connects to DC to AC inverter, thus providing power to the load in a matter of few milliseconds after power outage.
During AC mains the line interactive UPS will regulate AC output using its transformer and few relays. Usually a line interactive UPS system utilizes the same transformer for charging the battery, to stabilize the AC mains, as well as to work like a step-up transformer when power outage occurs.
Typically a line interactive UPS doesn't have the quality of the AC output as online UPS possesses, because most of the cheap line interactive UPS don’t output a pure sine wave AC during a power failure, instead it outputs modified sine wave which is inferior to pure sine wave.
However, loads like computers and modems don't care about the wave form as these loads consist of switching power supplies for converting the AC to DC.
Please note that when AC mains exist, the output will be a sine wave which is the same as from the utility grid.
Advantages of Line Interactive UPS:
- Cheaper than the online UPS system.
- The UPS can act like a stabilizer.
- An AC noise filter system exists.
Disadvantages of Line Interactive system:
- There is a small power interruption under 10 milliseconds.
- Output is not a pure sine-wave in most of the cases.
This concludes the line interactive UPS.
Standby UPS system:
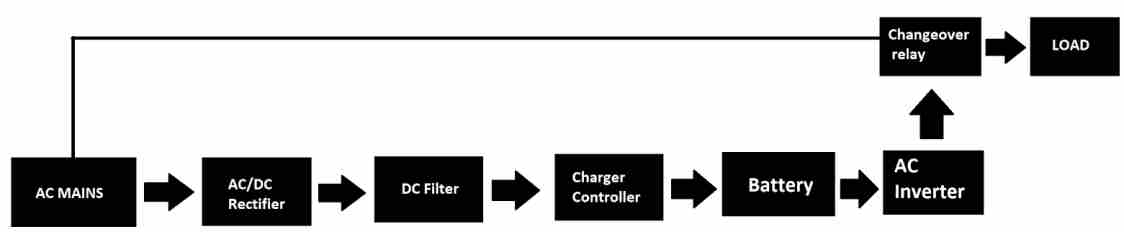
A typical standby UPS or an offline UPS waits for a power outage or power surge to kick its inverter ON. There will be no interaction with the AC mains, but there may be a basic AC noise filtering system for spike suppression.
Let’s understand the block diagram. The AC mains is converted to DC using rectifiers and filtered using capacitors and fed to the charge controller and this will charge the battery properly.
When a power outage is detected the changeover relay is switched from AC mains to inverter’s output, thus powering the connected loads uninterruptedly.
The transfer time of standby UPS are usually more than line interactive type, but fast enough to keep non-critical loads like lights, fans, toasters, refrigerators going.
Some standby UPS have transfer time as high as 300 milliseconds where the UPS waits for AC mains to go off completely before inverter kicks in. The output can be a pure sine wave or modified sine wave, depending on the cost.
Advantages of Standby UPS:
- Cheaper than other types.
Disadvantages of Standby UPS:
- The cheaper types of standby UPS outputs modified sine wave where it can be noisy on inductive loads.
- Transfer time is longer than other types.
This concludes about standby UPS.
hi,sir can i get a 24v battery charger that can charge a 200ah battery while also powering an inverter
Hi Vincent, you can try the following circuit:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/current-sensed-battery-chager-circuit.jpg
Full explanation is given in the following article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/high-current-10-to-20-amp-automatic/
Sir,
Good evening,
Can I use an old APC 600VA UPS as extension box by removing old battery and transformer.
Thanking you for your time,
Hi Vishwa,
Yes, you can make an extension box from an empty UPS cabinet.
Sir,
Good morning,
Thanks for your prompt help.
Regards,
You are welcome Vishwa!
I was hoping for success in connecting the inputs of the three-phase inverter to a single phase. Thank you
hello swagatam. I have a three-phase inverter with an output of 15 kva.Can I run it on one phase, for example? thank you.
Hello Abu, Do you want to convert your 3 phase output into a single phase output? That looks quite complex.