Audio amplifiers which are designed to work with a 5 V supply from a USB socket such as from a computer USB are called an USB amplifiers.
In this article I have explained how to build a simple 3 watt amplifier circuit which can be powered directly from a computer 5V USB port for driving an 8 ohm 3 watt speaker. You can build a couple of such circuits and use them for creating a stereo output into a pair of 8 Ohm speakers.
Please note that TDA2822 IC is obsolete now therefore opting a circuit using this IC for the discussed project may not be a good idea. However the present design is based on the IC LM4871, which is abundantly available I have explained the main features and working of this IC

Main Features
- The IC works without involving any sort of coupling capacitors, or bootstrap capacitors, or snubber capacitors
- It exhibits extreme stability through Unity Gain .
- Comes with WSON, VSSOP, SOIC, or PDIP Packaging
- Allows to Set an external Gain control network
Important Specifications:
- The IC LM4871D is designed to handle loudspeakers rated at 3 ohms or 4 ohms at 3 watts
- All the remaining versions in the series are specified to handle 1.5 watt with 8 Ohm speaker.
- The ICs have shutdown current internally set at 0.6uA typically
- The working voltage range is between 2.0V to 5.5V, perfectly suited to work with PC USB power.
- Maximum Total Harmonic Distortion with a 8 Ohm speaker load at 1kHz is around 0.5%
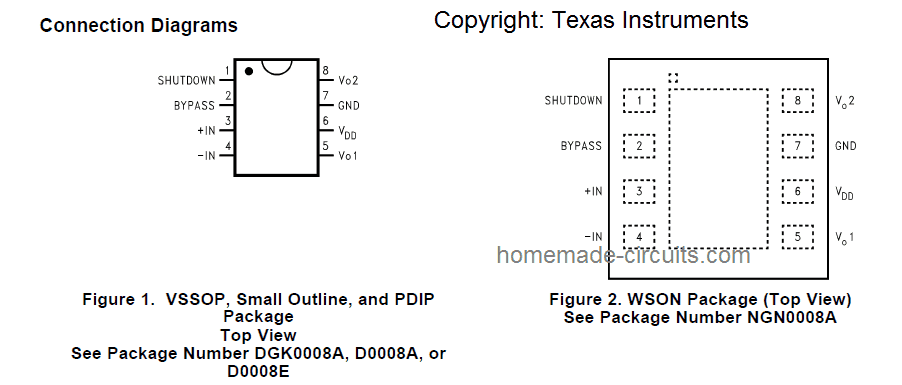
Pinout Specifications and Package
The following image shows the pinout details of the IC and the available package models, and layouts:
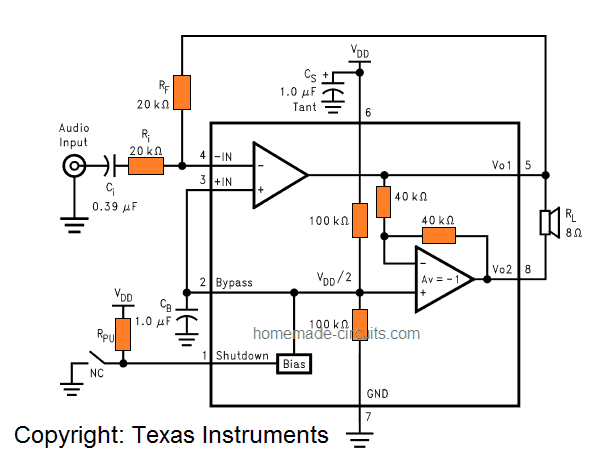
5V USB Amplifier Circuit Operation
Parts List
All resistors 1/4 watt or 1/8 watt, 1% MFR or SMD
- 20 K = 2 nos
- 100 K = 1 no (Rpu)
Capacitors
- 0.39uF ceramic = 1 no
- 1uF / 16V Tantalum = 2 nos
Semiconductor
IC LM4871 = 1 no
As can be seen in the above schematic, the LM4871 includes a couple of operational amplifiers internally, providing the user the option of configuring the amplifier through a few specified ways.
The gain of the first amplifier can be managed externally, while the second amplifier has been wired up internally with an inverting unity gain.
The closed loop gain for the first amplifier can be determined by appropriately selecting the values of the ratio Rf/Ri, whereas the same has been fixed for the second amplifier internally through a couple of 40K resistors.
We can see that the output of the amplifier#1 is configured to be the input of amplifier#2, allowing both the amplifiers to generate signals with identical values, although these may be 180 degrees out of phase.
This results in the IC’s differential gain to be AVD= 2 *(Rf /Ri ) .
Typically, for any amplifier a “bridged mode” set up can be implemented by driving the connected load deferentially via a couple of outputs Vo1 and Vo2.
An amplifier configured in the bridged mode will have a different operating principle in contrast to the traditional single ended amplifiers which have one end of the load wired with the ground line.
A bridged mode circuit works with better efficiency compared to a single ended amplifier since the load or the loudspeaker is switched in a push-pull manner, enabling a double voltage swing for each alternate frequency pulse.
This actually allows the loudspeaker to produce 4 times more power than a single ended version under identical circumstances or specifications.
The ability to achieve such increased power allows the amplifier to work without a current limiter stage and hence without undesirable clipping.
An added benefit of differential bridged output is the absence of net DC across the connected loudspeaker. This happens since VO1 and VO1 are biased at identical voltage levels, that is VDD/2 in the present case. This allows the amplifier to work without an output coupling capacitor, which otherwise becomes mandatory in single ended amplifiers.
Understanding Component Working and Specifications
Ri is the inverting input resistor which is employed to set the closed loop gain along with Rf. Additionally this resistor also implements a high pass filter function with Ci at fC= 1/(2π RiCi).
Ci forms the input coupling capacitor positioned to block DC and allow audio AC frequency across the input pins. This capacitor also enables a high pass filter in conjunction with Ri at fC= 1/(2π RiCi).
Rf becomes the feedback resistance that fixes the closed loop gain with the help of Ri.
Cs acts like supply bypass capacitor and provides ripple filtering for the power supply.
Cb is positioned as the bypass pin capacitor and this capacitor enforces filtering for half-supply
Absolute Maximum Ratings
The maximum tolerable rating for this circuit are I have explained below:
- Maximum supply voltage is 6V, typical working voltage is 5V
- The minimum and maximum tolerable temperature levels are -65 and 150 degrees Celsius respectively.
- The input music signal from the USB could be anywhere between -0.3V and 5.3 V
- Maximum power dissipation is internally limited so no need to worry about this issue.
Electrical Characteristics:
Vdd signifies the supply voltage which is within 2V and 5.5V typically.
Idd is the quiescent current consumed from the input power supply by the IC and this may lie between 6.5mA to 10mA
Isd is the symbol for shutdown current, when pin#1 potential becomes equal to Vdd, the shutdown is initiated causing the consumption to drop to 0.6uA
Vos refers to output offset voltage, and is initiated when Vin = 0V, and could be 5V typically, and 50mV in the limited mode.
P0 is the output power and is around 3 watts when the load is an 3 or 4 Ohm speaker
THD+N indicates the total harmonic distortion which is within 0.13 to 0.25% with a frequency range of 20Hz to 20kHz.
PSRR gives us the power supply rejection ratio for Vdd at 5V typical, and this is around 60dB.
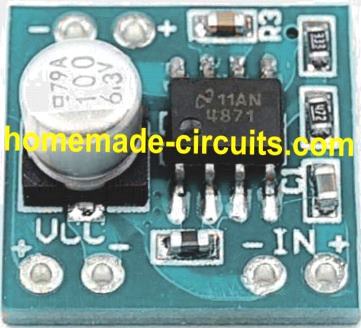
Prototype Image of the 5V USB amplifier:
PCB Layout Recommendation:
Original article: www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/lm4871.pdf


Comments
I HAVE CONNECTED 20W 4 OHM SPEAKER TO 5V POWER SUPPLY, THE SOUND IS LOW IF I CONNECT 1OW 4 OHM SPEAKER INSTEAD, THE SOUND WILL BE LOUDER. I DONT HAVE ANY ELECTRONICS KNOWLEDGE.
Which amplifier circuit did you use?
SG FLASH BLUETOOTH FM USB AUX CARD MP3 STEREO AUDIO AMPLIFIER SOUND CIRCUIT ELECTRONIC HOBBY KIT
I WANTED TO AMPLIFY TV SOUND THE BLUETOOTH WAY IS IT POSSIBLE SIR
Yes it is possible, you can buy readymade bluetooth transmitter/receiver modules. Connect the transmitter module with your TV, and receiver module with your amplifier, that’s all…
I am confused. RE: LM4871 Important specs says 3 or 4ohm speakers=3watts & 8 ohms= 1.5 watts. Electrical characteristics says 8 ohm = 3 watts. Please explain the difference. I have Basic electronics knowledge so please simplify. Thankyou.
Hi, It seems like a typo, I will fix it soon…thanks for pointing it out..
Tks. I am looking for an audio amp schematic/project that will give me 3-5watts from a 5 volt DC power bank. Also would like to incorporate ability to use 6vdc power adapter from 110ac mains. This is for a practice guitar amp combo that I am working on. Would you happen to have anything like that?
You can try the following circuit with 6V, I think it should be able o provide upto 3 to 5 watts on a 4 ohm speaker:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/small-5-watt-amplifier-circuit-compressed.jpg
Hi Swagatam;
There are 2 seperate pins of sockets about the audio input or audio output on my pc mainboard.(P5QL SE)
One is called as SPDIF digital audio connector interface port which consists of 3 pins (+/- 5 V and SPDIF)
And other is front panel audio connector which consists of the pins of MIC-L, MIC-R, HP-L, HP-R and Jack_Sense. This is also referred as both “Azalia compliant” and / or “legacy AC97 compliant”.
Please advise if that works when I use the usb amplifier circuit shown on your page to one of the connector on my pc mainboard since my embedded sound card is out of order. Best Regards
Hi Suat,
Sorry, I am not well-versed with these parameters of audio systems so I won’t be able to help you in this regard. I think you may have to check it through practical testing.
No problem Swagatam;
Today I have tried at first the SPDIF side and I used the amplifier circuit with 555 IC since it was easy for me input voltage 12 V. I initially tested on my laptop and output quality and loudness were good. And then I used SPDIF pins; 5 volts was empty gnd was common and spdif out was to 555 circuit sound input. The result was like;
Also I will check the AC Compliant side today. Regards
Thank you Suat, for updating the info. I hope you will be able to solve the problem soon.
Thank you for kind reply
A question arose while designing the board on my own based on the schematic and BOM you suggested.
In the prototype image, I saw the Aluminium capacity(79A,100, 6.3v).
But I didn’t find this capacitor in the list of the BOM you attached in this article as parts list.
(0.39uF ceramic = 1 no
1uF / 16V Tantalum = 2 nos)
Could you help me to understand about the circuit?
I think that’s an extra capacitor 100uF/6.3V connected across the supply lines to provide improved filtration of the DC and for eliminating any residual ripple current. This capacitor is provided by the manufacturer of the prototype which is not shown in the datasheet diagram.
Hi,
Thanks for sharing.
I’ll try building it.
I have juste a question : what is “Bias” ? Point test ?
Thanks for response.
Best regards.
biasing of an electronic component is providing the minimum necessary supply voltage to enable it to operate normally
hi swag.please watch TROUBLESHOOT ELECTRONICS FAST WITH A SUPER PROBE by Mr.Carlson’s lab and help me redraw the connections and parts lists.please explain in details operation you used to.thanx
thank you for clarification of parts.i ‘ll try building it.
Hi Dennis, the schematic is already available online…you just have to copy the parts from the schematic. All the stages are basically cascaded transistor amplifier stages (common emitter). The transistors can be all BC547, all resistors are 1/4 watt and capacitors are ceramic type.
Thanks. I assumed that was the case. Do you have a a BOM and where you got the components? I want to share this with some high school students.
Sure! I have updated the parts list under the circuit diagram.
It looks like you may have modified the original TI circuit. Can you post your circuit diagram? It may also be that I am just not very good at reading the values of surface mount caps. Also, this looks identical to a circuit for sale on Amazon, eBay and elsewhere. Is that the case?
Nothings’s modified here, it’s the original TI design, and it cannot be modified since it’s a perfect design already. The copyrights marks have been put me.
yes anybody can manufacture such modules and sell them anywhere they wish to.
Hi. Swagatam
I have some questions
In the BOM
20 K = 2 nos
40 K = 2 nos
100 K = 3 nos (including Rpu)
Capacitors
0.39uF ceramic = 1 no
1uF / 16V Tantalum = 2 nos
So total components are the 7 pcs of the resistor and 3 pcs of the cap. Totally 10 pcs.
But in the image of the module board I saw the 5 SMD components and 1 dip cap. Then totally 6 pcs.
Where did I have a mistake?
Hi, Xuel, sorry I am not sure if I understood your question, because I can see all the 10 components in the circuit diagram.
In “5V USB Amplifier Circuit Operation”, I thought that 2pcs of 100kohm and 2pcs of the 40kohm is the internal components in the LM4871 and the other 6 components are the external components that should be mounted around the LM4871.
And I think that the pcb board of this circuit is like the image of the “Prototype Image of the 5V USB amplifier”
mentioned above.
But I don’t know well if my thought is right.
Thank you, Xuel, I think you are right, those 4 resistors inside the square boundary are internal to the IC, and they can be ignored. Only 6 components are actually required externally for completing the project, 3 resistors and 3 capacitors.
I will correct the parts list accordingly.
Hi. Swagatam.
Sorry for less explanation.
Let me explane in detail