The TIP122 is an NPN Darlington pair transistor that is commonly used in power switching applications. It has a high current gain and can handle up to 5A of continuous current.
Here is the complete datasheet for the TIP122 transistor:
Electrical Characteristics (Do not exceed these specifications):
- Collector-Base Voltage (VCBO): 100V
- Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO): 100V
- Emitter-Base Voltage (VEBO): 5V
- Collector Current (IC): 5A
- Base Current (IB): 5A
- Power Dissipation (PD): 65W
- DC Current Gain (hFE): 1000 (min) at IC=3A, VCE=4V
- Switching Speed: 3MHz (typical)
Package Type:
The TIP122 transistor is available in a TO-220 package, which is a standard three-lead package with a metal tab for heat dissipation.
Pin Configuration:
As shown in the diagram, the TIP122 transistor has the following three pins:

- Pin 1: Base
- Pin 2: Collector
- Pin 3: Emitter
The internal Darlington configuration of the transistor is as shown below:
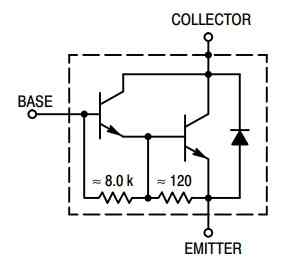
Applications:
The TIP122 transistor is commonly used in power switching applications such as:
- DC motor control
- Solenoid control
- Lamp control
- Relay control
Simplest Solar Charger Application Circuit
The following image shows how TIP122 transistor can be used to build a simplest solar charger circuit:
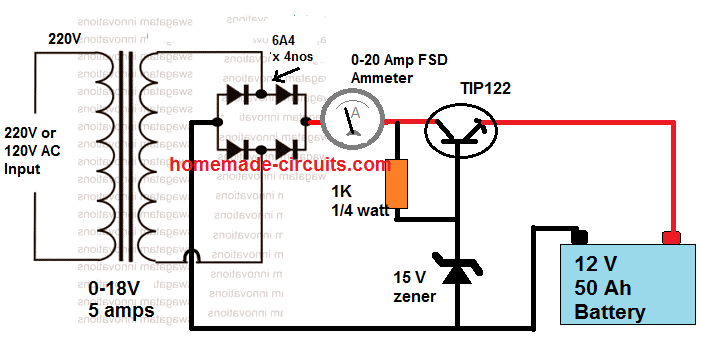
The output voltage is calculated using the following formula:
Vout = zener value - TIP122 forward drop
= 15 - 1 = 14 V
The TIP122 here is configured as an emitter follower, therefore its forward voltage drop will be approximately equal to 0.6 + 0.6 = 1.2 V. The double 0.6 V is due to the Darlington transistor, each dropping around 0.6 V.
Note: This datasheet is for reference only. Please refer to the manufacturer's datasheet for complete specifications and characteristics of the device.
Post your comments here and get guaranteed replies. Comments must be related to the above article.