The circuit presented here is a tester circuit for testing CDIs for motorcycles and three-wheelers.
Designed and Written By: Abu-Hafss Basically there are 2 types of CDIs:
Technical Specifications
a) AC CDI, in which the HVAC (about 180V) is obtained from the source coil inside the magneto housing.
b) DC CDI, in which the HVAC is generated by circuitry inside the CDI, from 12VDC.
Then there are further 2 types in AC-CDI and CD-CDI which are usually used in performance bikes or heavy bikes.
They are equipped with microprocessor to provide advance ignition curve for better burning of fuel inside the cylinder head. The captioned tester circuit is designed to test the CDIs without microprocessors.
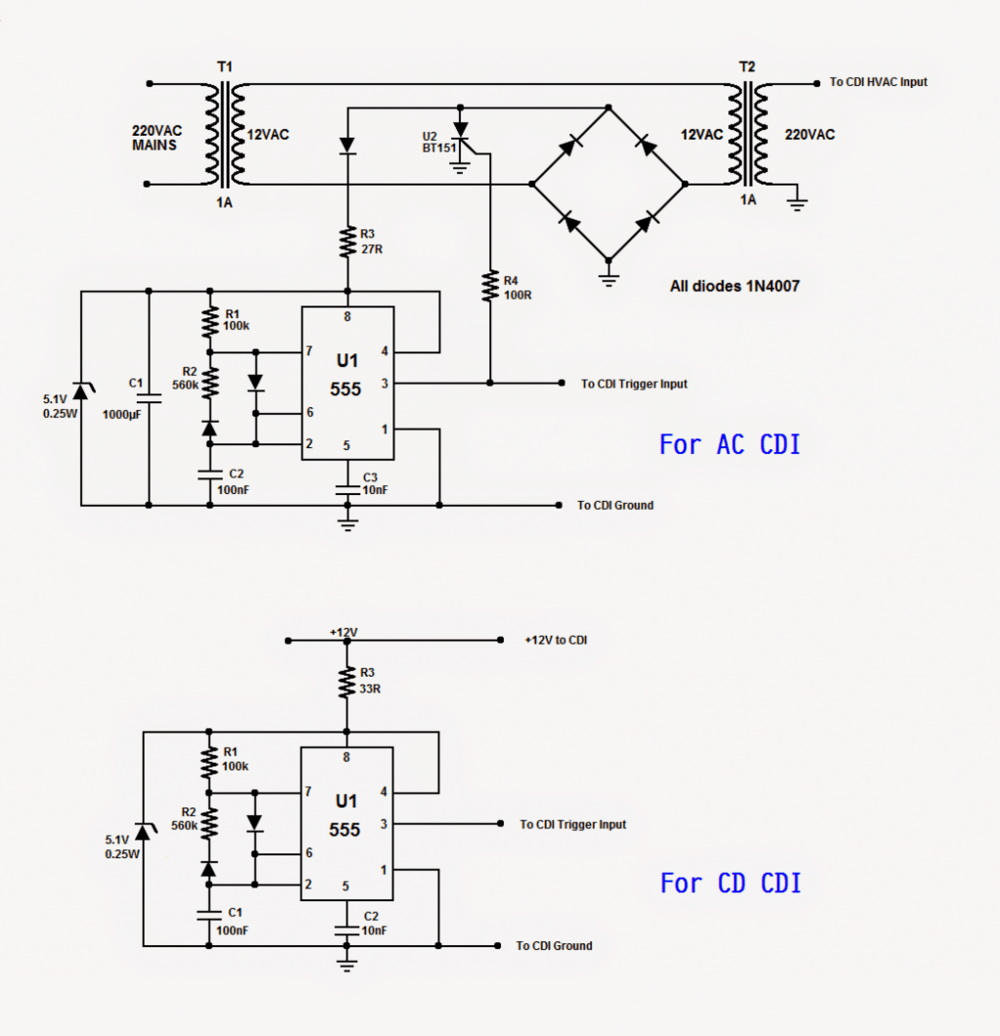
Studying both the circuits will reveal that the lower circuit is the portion of the first circuit. The first circuit is to test AC-CDIs.
Circuit Operation
The transformer T1 converts 220VAC from mains to 12VAC and then T2 re-converts 12VAC to 220VAC.
This set-up is to isolate the rest of the circuit from grid mains. This 220VAC is fed into the CDI's HV Input, replacing the HVAC which is obtained from bike's source coil.
The rectifier bridge converts 12VAC into 12VDC and C1 smoothes it. The SCR U2 is used to stop the 12VAC supply to T2, which will be discussed shortly.
The IC U1 is 555 timer configured as an astable multivibrator with duty cycle about 20% and frequency about 17Hz.
The generated pulse train will replace the triggering coil pulse at fixed rate of (17 x 60 =) 1020 RPM.
The output is fed into the CDI's Trigger Input and the ground is connected to the (-)ve rail. The output is also connected to the gate of the SCR via R4.
Whenever there is a positive pulse, the SCR will temporarily cut-off the 12VAC supply to T2. Hence, 220VAC supply to CDI will be paused. This is necessary to avoid a shorted path when the SCR inside the CDI is dumping the charge of the main capacitor.
The CDI's output is connected to one end of the primary of an ignition coil. The other end is connected to the (-)ve rail.
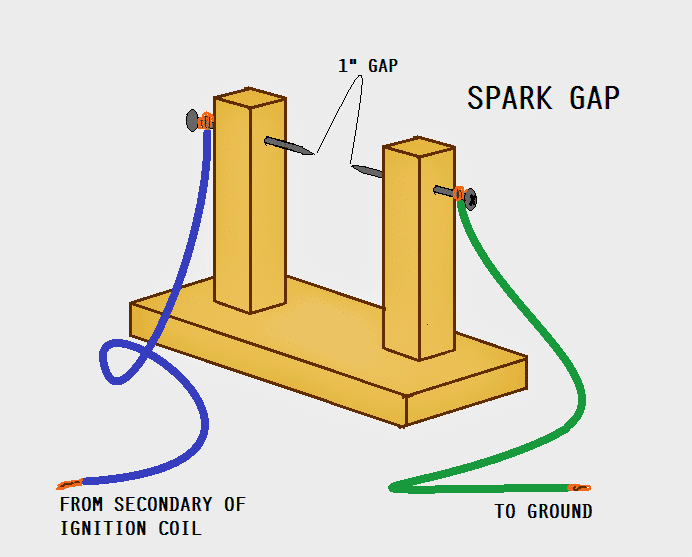
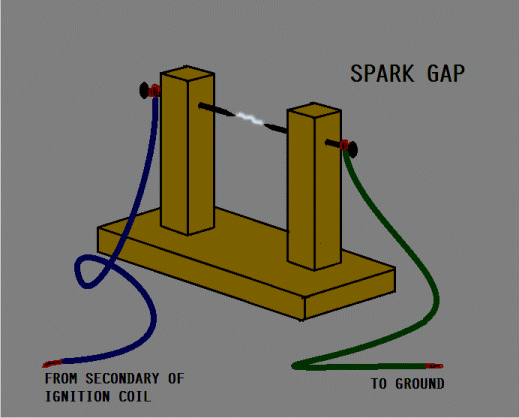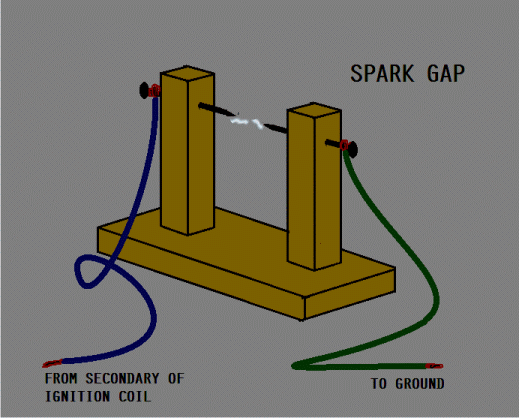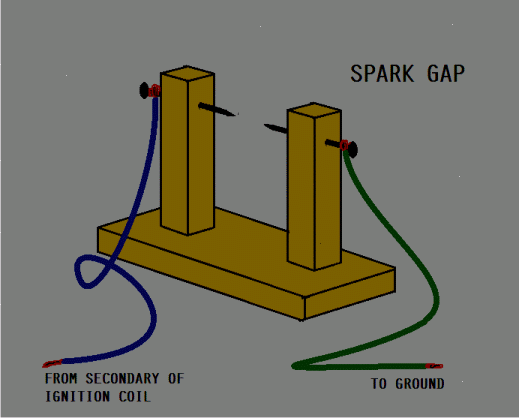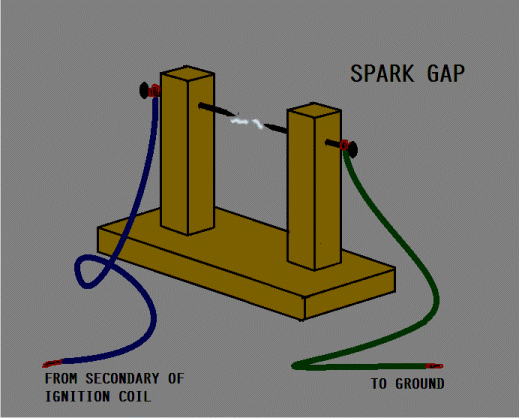
One end of the secondary of the ignition coil is connected to a spark gap and the other end is connected to the (-)ve rail.
The second end of the spark gap is also connected to the (-)ve rail. A strong spark across the gap will indicate that the CDI is good.
If the CDI under test is DC-CDI, the lower circuit will be used. The connections will be the same except the power supply will be 12VDC. The HVAC supply is built-in inside the CDI. A good CDI will fire strong spark across the gap.
Dear friend, I want to build this project since I am a motorcycle mechanic and it would be very useful for me but I have a doubt, does the tyristor interrupt shorting the bridge rectifier, does not cause heating or damage to it or the transformer? I was about to put it together but that doubt arises, thank you very much and greetings.
Dear Carlos, yes it does short circuit the transformer/bridge, you can use a low current transformer to avoid damage to the diodes or the SCR.
Alternatively you could try the last design from the following article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/make-this-enhanced-capacitive-discharge/
Thank you very much, that was my doubt, I will arm it anyway to check the operation of the CDI at least at low revolutions, since I can not find any circuit that works simulating higher revolutions, since that is where they tend to fail, but this circuit It will be useful, thank you.
OK, no problems!
congratulations for the super project for a chance could be adapted a potentiometer to simulate the engine rpm in this project and where you could put thanks in advance
Thanks, Glad you liked it, yes that may be possible by replacing the lower diagram’s R1 with a 100K pot, but make sure to connect a 1K resistor in series with it
Thank you for responding and in the ac cdi it would be possible
yes, it is possible with both the designs
Unless i missanderstood the schematic, the AC CDI gets his power at 50/60Hz, so it will work only for 3000~3600 rmp max. I’m rigth?
According to me it seems the SCR will fire only 50 times per second, the high frequency from the IC 555 might not help to chop the SCR conduction, because the SCR will be latched until every zero crossing which will force it to work at max 50Hz frequency or less.
Esta interesante el circuito
gracias
Dear Swagatam
Would you mind letting me know the wattage of all the resisters used in this model?
Regards
Hi Ibtihaj,
All the resistors can be 1/4 watt, CFR 5% resistors.
Dear Swagatam,
R3 & Zener Diode are getting hot where R3 is getting too hot to touch, in just few seconds. Please advise what to do?
Regards
Dear Ibtihaj, increase R3 to 1K and check the response
Okay. Thanks
Can we use ignition coil itself instead of using this wooden model?
the wooden model is used for spark generation just like a spark plug does…
Thank you very much sir
Please I want to know the difference between ups and Inverter, after that can I replace the 7ah ups battery with 200ah?
Thanks Basiru,
UPS has an automatic changeover and is normally suitable for all appliances whereas an inverter may lack both of these features.
yes you can replace a 7ah ups battery with 200ah battery provided the voltage is not altered