In this article I will explain a simple mains failure backup circuit for providing Arduino boards an uninterruptible supply during such situations. The idea was requested by Mr. Fredrik.
Technical Specifications
This blog gave me a lot of interesting information. Especially the power supply circuit with battery backup part.
The reason for this is that I am working on a Arduino based system for monitoring and controlling heating cables at my summer place.
This system will eventually be gsm controlled so I quickly can get an update on for example the temperature in the bathroom.
The part that I am stuck on is that I would like to have the Arduino to have a battery backup of some sort so it can still monitor the temperature around vulnerable waterpipes, and possible notify me if mains power goes out. I'm thinking of using a car battery so it can last for ages if power goes out.
What changes will I have to make to the "Power Supply Circuit with Emergency Backup" circuit to make it work with a 12V car battery and still have it trickle charge slowly?
Thank you in advance for any advice.
Sincerely
- Fredrik
Circuit Diagram
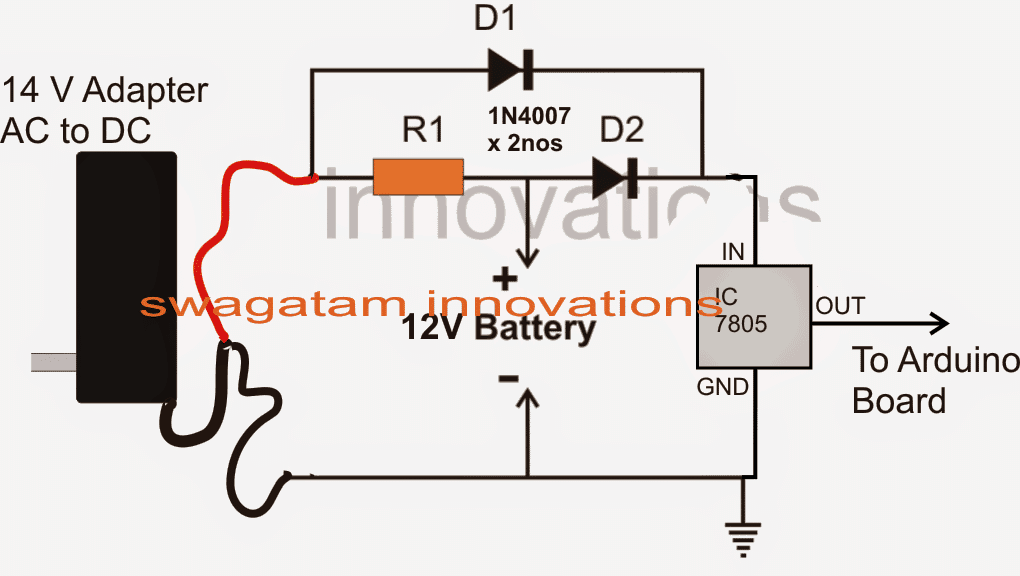
The Design
The simplest way to implement the proposed application is by using two diodes as shown in the above diagram.
The design shows two diodes with their cathodes connected together and anodes terminated to a 14 V source and anodes to the positive of a 12 V battery source respectively.
The common cathodes of the diodes are further connected to a IC 7805 IC whose output is finally applied to the Arduino board.
When mains is present the 14 V supply ensures s constant trickle charge supply to the attached battery via R1 and also feeds the Arduino borad through D1 and the 7805 IC.
In this situation D1 cathode experiences a much higher potential than the cathode of D2 due a relatively lower battery potential at D2 cathode.
The above situation keeps D2 reverse biased allowing the battery charge to stay blocked and pass only the adapter voltage to the Arduino board.
But as soon as the mains supply fails, D1 instantly stops conducting and enables D2 to get forward biased so that now the battery instantly takes over and begins supplying the Arduino via the 7805 IC.
Another 1 doubt sir….
This circuit i'm using for CD4017
D2 output shall i connect resistor…..
To limit the current…bcs i'm using 4v 1A ….sometimes in my area continuously power cut may be 7 hrs….
So when i use resistor..The backup time will be high…
How much current will required for cd4017
even without a resistor the IC will not consume more than 5mA….but you can use a resistor in the backup mode to reduce this 5mA to a lower value may be 2mA to just keep the IC "alive" during that period
V/I
Input 5v
Current 800ma…
5/800ma =6.25 ohms sir
Wattage of resistor is 1.28 watts…
Is it correct sir
Thank u sir
Hai sir…
I'm using this circuit without 7805.
Battery voltage is 4v 1A lead acid batteries….
Backup power supply for IC…
Kindly tell the resistor value for charging the battery….
Daily night 10 hrs i will use this circuit in the between of 10hrs the power supply failure.in that it will work….
So i need slow charging method…
Main input dc voltage i'm using 7805 output voltage and 1ampere diode….
…
Resistor value and watts i need sir..
Hi kesava, you can use ohms law for this
R = V/I…
V is the input supply voltage, I is the charging voltage which is 100mA or 0.1Amp in your case
wattage = I^2 x R