In this article I will explain a couple of very easy to build RF detector circuits, which can be used to sense or detect or sorts of Rf electrical noise that may be floating in the surrounding atmosphere.
What is RF
RF stands for radio frequency, which is a kind of electrical interference transmitted in the atmosphere, whenever there is a voltage/current fluctuations across an electrical system.
Whether it is a static electricity (DC) or a capacitively linked AC from neighboring overhead wires, noise spikes from engines, or a radio-frequency waves from a cellphone, all contribute to the world's electromagnetic interference and noise.
A RF noise can be a high level noise such as during thunderstorm lightning, welding, or very tiny such as when you click a gas lighter.
How can Electronic Circuits Detect RF
RF noise or RF signal can interfere with an electronic circuit working if it has a semiconductor with a high impedance end unconnected. Noise is picked up whenever such a high-impedance input is left open and disconnected.
This is actually a problem that an electronic can face due to RF interference, and this can cause its output to amplify the RF interference and cause a correspondingly fluctuating output voltage.
However, the above problem becomes the advantage of our RF detector circuits, and we used this to illuminate an LED whenever an RF interference is detected our circuit.
Using Transistors
As shown below a Darlington connection is used in our first RF detector circuit, using transistors in a super-high gain mode with a rather high input impedance.
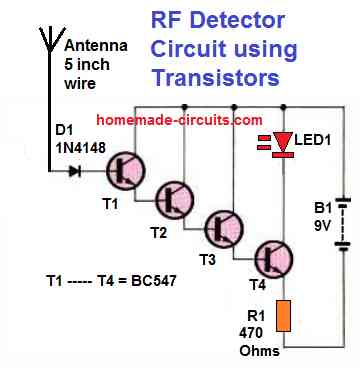
If each of the transistor in the diagram is assumed to have a current gain (β) of 150, the total β becomes 150 x 150 x 150 x 150 = 506250000 and the input impedance is potentially 506250000 x 470 ohms, or almost 237937500000 ohms or 237937.5 Mega Ohms.
Due to leakage, the above mentioned result might actually not be as high as it appears. In essence, the circuit's difficulty is that any RF signal in or near the first couple of transistors is substantially boosted. That's most likely why just a handful of your transistors can work effectively.
However, for this simple transistor RF detector to work a super clean, alcohol-washed veroboard would be required, under reduced humidity circumstances.
Temperature variations, light beaming on the transistor, and other inbound signals would almost certainly still trigger the circuit and could make it unstable.
CMOS Circuit using IC 4001
The next diagram below depicts another simplified RF detector circuit based on an IC that you might enjoy playing with.
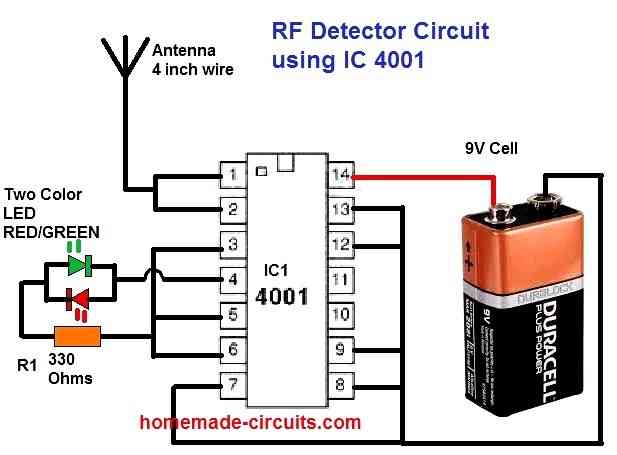
Touching or keeping your hand on top the antenna will flip the LED red to green, or opposite; it could also become yellow or orange, or even switch off completely.
All sorts of RF interference such as RF from mobile phones, thunder lightening, AC hum all can cause the LEDs to flicker in response to these interference.
The extraordinarily high input impedance of CMOS integrated circuits is used in this design. It also demonstrates why such a CMOS inputs must never be left disconnected; electrical noise can trigger highly unpredictable performance.
On dry seasons with an abundance of static electricity in the surrounding, you might expect to obtain the most fascinating results.
100 MHz RF Detector
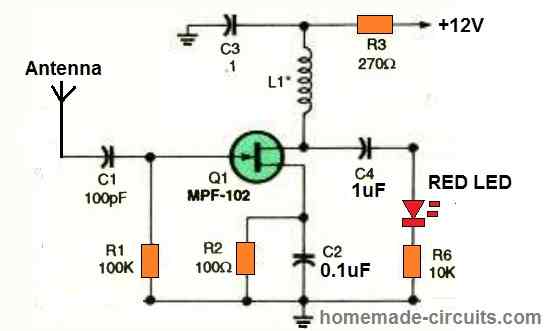
This circuit is capable of detecting signals up to 100 MHz, depending on the value of L1. Use a 100 µH choke for signals between 30 and 100 MHz, a 1000 µH choke for frequencies between 2 and 30 MHz, and a 2.5 µH choke for signals below 3 MHz. In the circuit, the FET serves as a wideband amplifier.
There is something I don’t understand. In the 1st circuit, only electrons are allowed to pass from T1 to the antenna. It seems impossible for electrons to come back from the antenna to the circuit. When the electrons gather in the antenna over time, is there no problem for the circuit to work and detect the radio waves? Where do the electrons accumulated in the antenna go? Shouldn’t the electrons be able to exit as easily as they enter the antenna? I did not understand how the circuit could work, since the electrons coming to the antenna had no place to exit. I would be glad if you help.
When electromagnetic frequency in the form of RF hits the antenna, the electrons inside the antenna metal are agitated which creates a forward pressure on the base/emitter junction of the transistor T1, causing it to conduct. When T1 conducts it amplifies the antenna signal slightly and supplies it to T2. T2 amplifies it further and carries it forward to T3 for even greater amplification and so on.