In this post I will explain what a supercapacitor is, how closely similar or different to an ordinary capacitor, where it is used and we will be doing comparison between batteries and super-capacitors to find out which one of them is superior.
Let’s understand the basics of an ordinary capacitor.
How Ordinary Capacitor Works
A capacitor is a passive electronic component which can store small amount of electrostatic energy between the interleaved conductive and dielectric material.
We can charge and discharge the capacitor at rapid rate; due to this property we use them as voltage smoothers in all power supply circuits.
All the capacitors have some specification coated on the body, such as operating temperature, operating voltage, and value of the capacitor which is usually range from few pico-farads to few thousand micro-farads.
The capacitors which we find usually on consumer grade electronics are ceramic, polyester, paper, etc. These types of capacitor usually have low capacitance in the range of few pico-farads to less than a micro-farad.
The one with higher capacitance are electrolytic type, which has capacitance ranging from 0.1uF to several thousand microfarads.
The electrolytic capacitor increases its charge storage capacity by adding a tissue soaked with some chemical electrolyte as dielectric and either of the side with aluminium foil, as shown in figure.
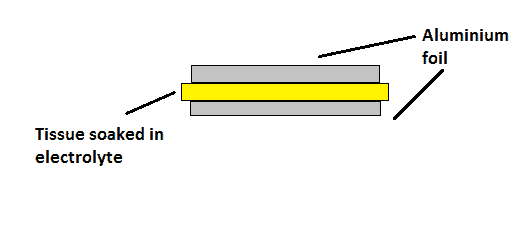
The stack of aluminium and tissue is rolled into cylinder form and housed into aluminium chassis. The diameter of the roll, height and thickness of the tissue determines the various parameters of the capacitor.
The electrolytic capacitors are polarized, which means it has anode and cathode terminal and we should not be interchanged the input supply polarity to the capacitor as we do on other type of capacitors.
How Supercapacitors Work
Supercapacitor is also called as Ultracapacitor or double layered capacitor. The supercapacitor has humongous charge storing capacity and it is usually measured in Farad (without micro or pico or nano prefixes).
A supercapacitor can range from few Farads to few thousand Farads. Unlike ordinary capacitors, the supercapacitor has lower operating voltage, which is usually between 2.5V to 2.7V.
They are connected in series and parallel configuration to increase the throughput from the capacitor bank.
The supercapacitors are utilized where batteries can’t handle the given task efficiently, for instant regenerative braking in vehicles. The kinetic energy is converted to electrical energy and stored for a while and reused to accelerate the vehicle.
This mechanism improves overall efficiency of vehicle. But using batteries alone, the energy capture is not efficient. Many car manufactures are experimenting with supercapacitor in combination with batteries and reportedly improved overall efficiency of the system.
Supercapacitor has better charge and discharge cycles compare to batteries. A typical lithium-ion battery found in our smartphones has roughly 1000 charge and discharge cycles, where as a supercapacitor has over 1 million charge and discharge cycles.
Batteries deteriorate its effective capacity when the battery is discharged below certain voltage for prolong time. A supercapacitor has no such limits; it can go all the way to zero volts.
But leaving any capacitor over prolong period of time like a year or so without charging can also deteriorate its charge holding capacity due to some chemical reaction between plates of the capacitor.
Construction of Supercapacitor:
The construction of supercapacitors are fundamentally same as ordinary capacitor only the difference is the type of material used and some method is utilized to increase the energy storing capacity.
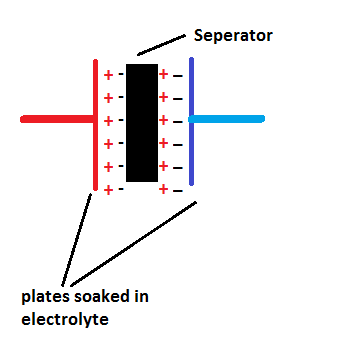
Supercapacitors have conductive plates on either side of the separator soaked in electrolyte and the separator is a very thin dielectric materiel made from plastic or carbon or paper.
The separator is made very thin compare to ordinary capacitor to increase efficiency of ion transfer between plates.
The supercapacitors are sometimes referred as double-layer; this is because when the plates on either sides charge up it produces charge on either side of the separator as shown in figure.
By now you would have an idea about supercapacitor and its fundamental functioning.
Battery vs Supercapacitor:
Let’s compare energy density and weight in batteries and supercaps.
Lithium-ion and lithium-polymer has the highest energy density compare to any other battery technology available commercially. This is the reason why our smartphones and other portable electronics are built with li-ion/polymer.
The energy density of supercaps is pretty low compare to lithium batteries thus making it ideal only for non-portable devices.
Supercaps are very good at rapid charging and discharging. This cannot be achieved with battery due to higher internal resistance in all kinds of batteries.
If we try to discharge the battery beyond its safer current limit, we might damage the battery. This is because the batteries possesses internal resistance and generate heat. The generated thermal energy is enough to create irreversible damage to battery capacity.
In supercaps, internal resistance is very small, even smaller than internal resistance in some automobile batteries which is designed to provide high current. The chance of supercapacitor getting damaged due to thermal is pretty low.
The batteries can hold the charge for very long period of time, but for supercaps self-discharge is a problem and not suitable for storing energy for long period of time.
Now its conclusion time,
So which one of them is superior? Probably none of them are superior to each other. Batteries have great portability but, supercaps have very high charging and discharging rate. At end of the day it depends on the application what we use and this decides which one of them is most suitable.
Let us know in the comment section, do you think one day supercapacitors will replace batteries due to rapid development in technology.
Hi Mr Swagatam;
I am intented to make an AC voltage meter. I will use bridge rectifier and voltage divider loop after AC input. However I will also use a capacitor 0,1 uF or 1 uF and thermistor and fuse serial before bridge rectifier since the current is not issue . Please advise that will make safer to protect the whole circuit and which capacitor value is better for me? Thanks
Hi Suat, since current is not important you can use 0.1uF capacitor for minimum current and maximum safety.
hi Swagatam
please would you show me a supercapacitor dump charger circuit with transistors which can charge a supercapacitor to a voltage level then discharge it to a 5 v relay for seconds and the process goes on again and again .
thank you
Hi Khorshid,
You can try the following concept:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/super-capacitor-dump-charger-circuit-1.jpg
that was very helpful . i don’t know how to thank you . keep going sir your are doing good job .
No problem, khorshid! It is my pleasure!
A marvellous weblog that helped a lot to understand about supercapacitor. Electrolytic capacitors can be used in a broad range of applications because they bridge the gap between batteries and capacitors. The future of these ultracapacitors is very promising. Keep sharing such an informative piece of knowledge.
Thank you for sharing your feedback!
Hi Swagatam
Thanks for the informative post, it has helped my fledgling supercapacitor understanding move forward a big step.
I know it’s a little old now but I was hoping you’d help me with a small repair before I blow something up. I have to replace a 0.1F Supercapacitor in an AV receiver but accidentally ordered a 1F. It has the same voltage rating as the original. Would this be safe to use as a replacement?
The SC is to activate a power supply relay or similar on start up.
I really enjoy your site, many thanks.
Thanks Rohan, the Farad represents the current storing and supplying capacity of the capacitor, therefore the current capacity will not affect your application as long as the voltage rating is not increased. If the voltage spec is the same as the original, then you can use the 1F in place of the 0.1F without any issues.
Thanks sir for this piece. Is it possible to parallel large uF capacitors to make a 1F supercapacitor
Hi Seun, that may be possible!
Thankyou very much for your nice information as usual.How can we use supercap.for emergency light?and how to build a charger for it?
you will require many capacitors in parallel for making a an emergency light from it, and select an LED whose consumption allows the backup to last for the required amount of time.
charger controller is not required, but make sure that the supply input voltage to the super capacitors is not higher than its breakdown voltage limit.