In this post I have explained the fundamental methods of triggering a triac, and also discuss the right way to connect the terminals of a triac.
Triacs are solid-state bidirectional thyristors that can switch across both the AC half cycles on a 120-volt or 240-volt Ac power system.
A triac could be activated (switched on and latched) with the AC line both synchronously or asynchronously.
However, if the triac's gate terminal current drops just below its lowest holding threshold, it will be switched off instantly at the completion of each AC half-cycle (180 electrical degrees).
WARNING: ALL THE CIRCUITS DISCUSSED IN THE FOLLOWING ARTICLE INVOLVE LETHAL 220 V MAINS AC. THEREFORE YOU MUST BE EXTREMELY CAREFUL WHILE USING AND TESTING THESE CIRCUITS, MAKING SURE THAT YOU APPLY ALL THE NECESSARY PRECAUTIONS DURING THE PROCEDURES. ALL THESE CIRCUITS ARE STRICTLY RECOMMENDED ONLY FOR THE EXPERTS.
Synchronous vs Asynchronous Switching
In an asynchronous switching, the triac is triggered ON randomly at any point of the phase cycle.
Due to this, asynchronous switching of triacs can produce substantial radio-frequency interference (RFI), especially at the first switching cycle.
In a synchronous triac switching, the switching periods consistently arrive on at the same moment for each AC half-cycle (typically right after the zero-crossing period) and therefore produce negligible RFI.
All the circuits I have I have explained in this article use asynchronous power switching. Figures 1–8 depict a number of asynchronous triac power-switching circuits for elementary ON/OFF AC line switching.
How to Connect a Triac
A triac has 3 terminals, which are MT1, MT2, and the Gate. The MT stands for main terminal.
Therefore, the main terminals MT1 and MT2 are used for switching heavy AC mains operated loads, through 220V or 120V AC mains supply.
This switching happens in response to a small DC voltage applied to the gate terminal of the triac.
New hobbyists often get confused and ask the question how the MT1 and MT2 terminals should be configured with the AC load and through a DC at the gate?
Remember, the correct method to connect the triac MT1 amd MT2 terminals is by ensuring that the AC load is always connected in series with the MT2 terminal, and the MT1 is connected directly with the other AC line of the mains supply.
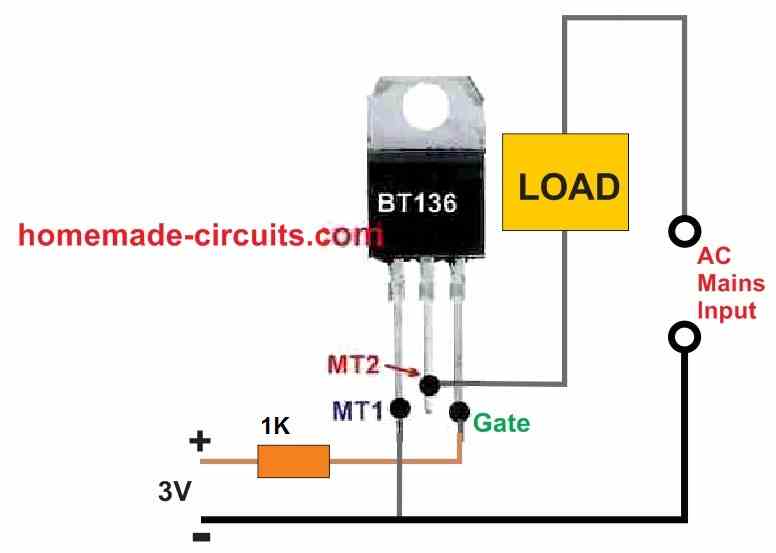
Also, it is extremely important to note that the AC line associated with the MT1 terminal must be also linked with the negative or the ground line of the DC supply, which is being used for triggering the triac gate.
Failing to do this will not allow the triac to respond to the gate signals.
Triac Switching
A basic AC power switch using a triac is shown in Figure 1.
This triac circuit can be used to control the flow of AC power to lamps, heaters, motors, and a variety of other appliances and devices.
However, the triac for this circuit should have the appropriate power handling capacity to reliably switch AC power for the particular application.
All of the components in this article's schematics were chosen to switch only 120 volts, 50/60 Hz AC.
During the time the switch S1 is open, the triac is turned off and functions as an open switch.
However, when switch S1 is closed, it operates as a closed switch which is powered from the mains AC line via the load and R1 right at the start of each AC half-cycle.
When the triac is turned on, its main terminal voltage decreases to just a few hundred millivolts, thus R1 and S1 draw relatively negligible current.
Please remember that as soon as S1 is initially closed, the triac's turn ON threshold is not synchronized with the AC line, but it gets synchronized with the successive AC half-cycles.
The snubber network formed by resistor R1 and capacitor C1 reduces voltage spikes which develop whenever inductive loads are switched and when current and voltage are out of phase.
Most of the triac circuits discussed in this article incorporate snubber connections.
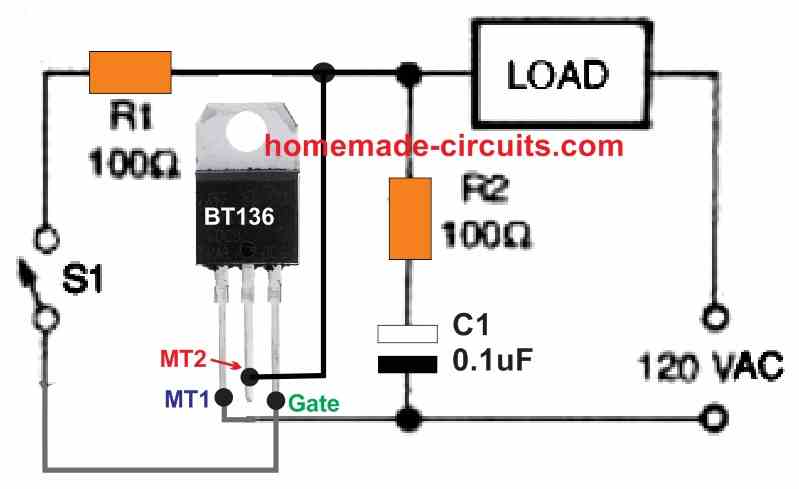
The triac works like a power switch that may be actuated by DC supply derived from AC supply, as shown in Figure 2 below.
Each positive line half-cycle charges capacitor C1 to +10 volts via resistor R1 and Zener diode D1.
When S1 is turned ON, the charge from C1 initiates the triac. Here the resistor R1 always gets exposed to approximately to the whole AC line voltage.
As a result, it demands a significant power rating (5 watts in ous case).
Due to the fact that all portions of this circuit are "active," it can create a fatal electrical-shock hazard.
Furthermore, since it lacks an isolator or complementing mechanism, this circuit is impossible to integrate with outer control circuitry.
Isolated Triac Control using Opto-Couplers
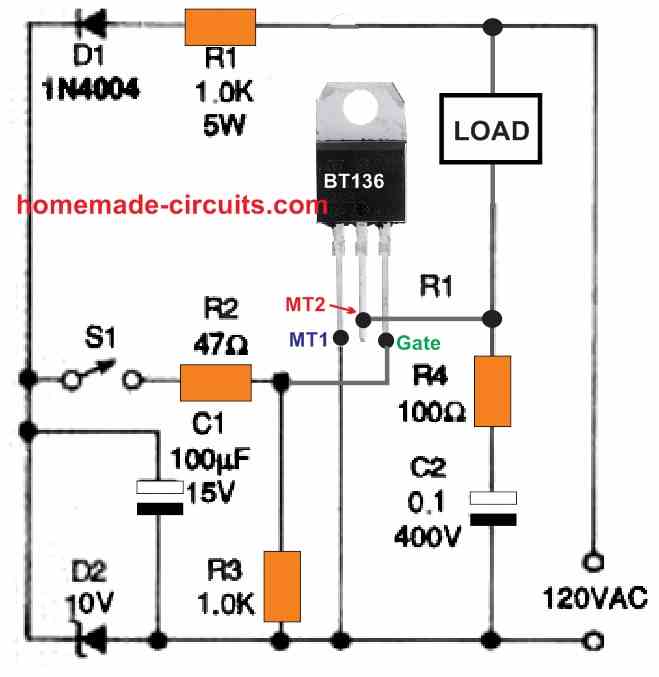
The next Figure 3 below demonstrates how to modify the circuit in Figure 2 to make it easier to connect with external control circuits.
Bipolar junction transistor Q1 is used in instead of switch S1 and is operated by the output stage of an optocoupler (or optoisolator) IC1.
An infrared light-emitting diode (IRED) is optically linked to a phototransistor in this system. Any of the commercially available transistor-output optoisolators can be implemented in these application.
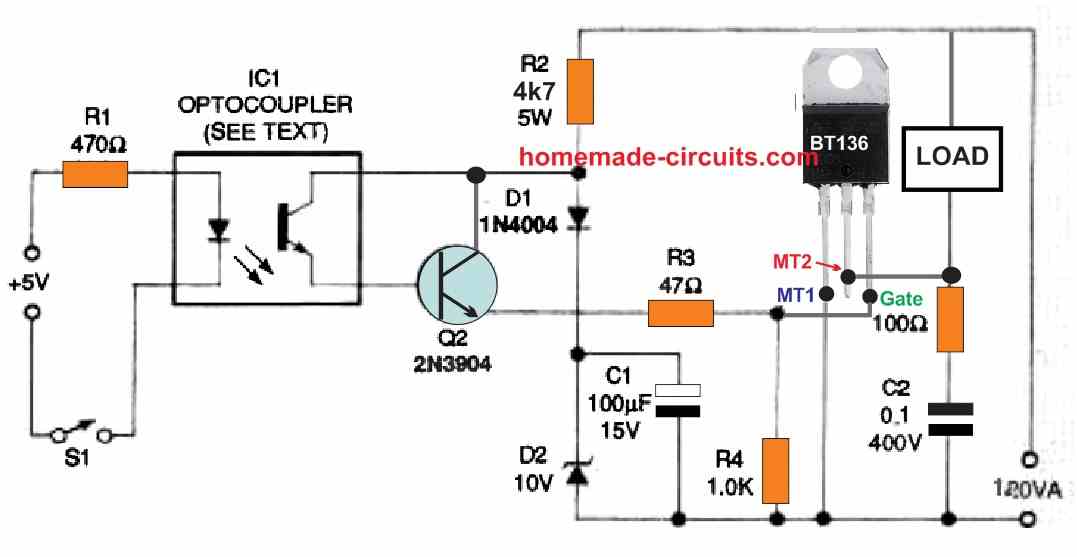
The opto couplers like TIL111, TIL 112, 4N27, and 4N28 are among the several. Using resistor R1, a 5 volt or larger DC source could be used to power the optocoupler.
Only after switch S1 connects the input circuit supply to a 5 volt or larger power source, the triac is switched on.
Typical isolation values (Viso) for optocouplers are 5000 volts AC, with some having ratings as large as 7500 volts AC.
This implies that the DC input circuit is completely isolated from the triac output side circuit powered by the AC line.
By substituting S1 with an appropriate electronic detector, this fundamental triac switching circuit may be modified to provide any desired type of automated "remote" triac switching.
Figure 4 below shows a modification of the circuit seen in Figure 3.
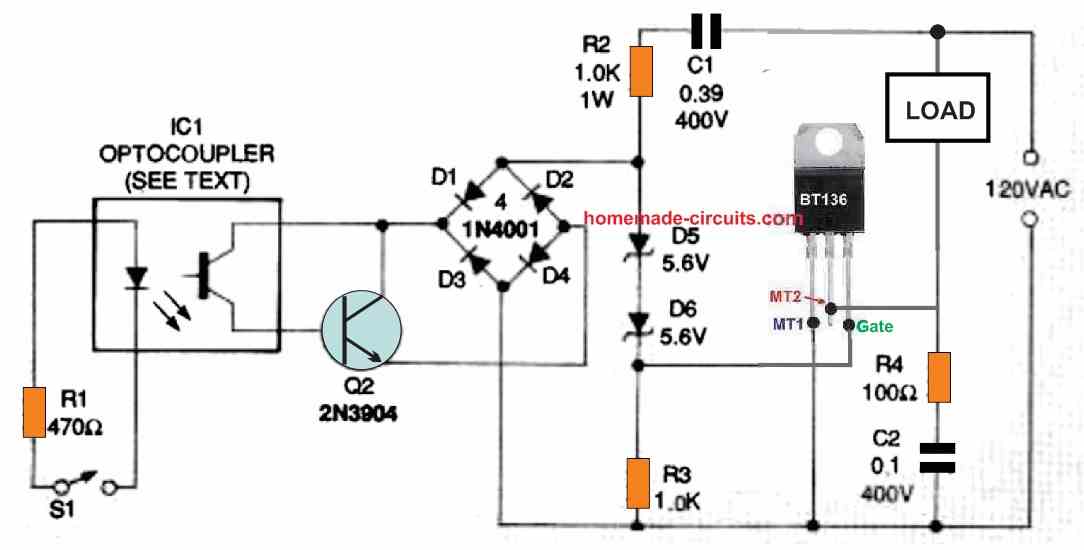
Using capacitor C1 and the series resistor R1, along with the back-to-back Zener diodes D5 and D6, the triac is AC actuated on each line half-cycle in this design.
The amount of the triac gate current is determined by C1's AC line impedance, while the power dissipation of the capacitor C1's is almost around zero.
The series connection of Zener diodes D5, D6, and R3, that is loaded by transistor Q1, is coupled across the bridge rectifier built using diodes D1, D2, D3, and D4.
The bridge is essentially open while transistor Q1 is off, and triac TR1 switches on following the onset of each AC half-cycle.
As soon as transistor Q1 is turned on, an almost a short circuit like condition is developed across D5, D6, and R3, which shuts off the Triac gate current, eventually turning off the triac TR1.
The optocoupler from the isolated external input stage drives transistor Q1, thus the triac is typically on, but it switches off as soon as the switch S1 is closed.
Using DC for Triggering a Triac
Figures 5 and 6 as given below, illustrate how to use a DC power source from a transformer power supply and a transistorized switch to activate a triac AC power switch.
When S1 is closed, both the transistor and the triac are both turned on, and as soon as S1 is open, both the devices are turned off.
In Figure 5, switch S1 can be substituted by a sensor device that can detect and respond to physical changes.
Transistor Q1 can be a BC557 transistor, not shown in the diagram.
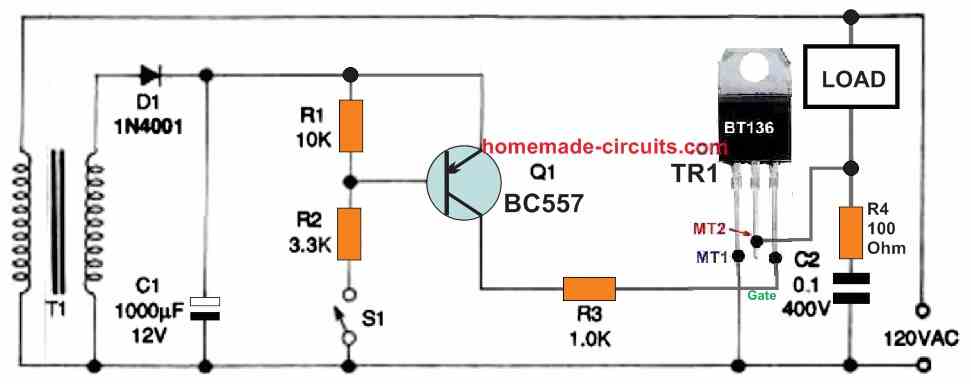
For example, If the ambient temperature decreases below a predetermined level, a thermistor, can be incorporated to activate the triac circuit.
Similarly, photoconductive cell can be installed to detect light levels, a pressure sensor may detect changes in air or liquid pressure, and a flow metre can react to variations in liquid or air flow rate.
Please be cautioned that the Fig. 5 circuit, is "live" and poses a lethal shock threat.
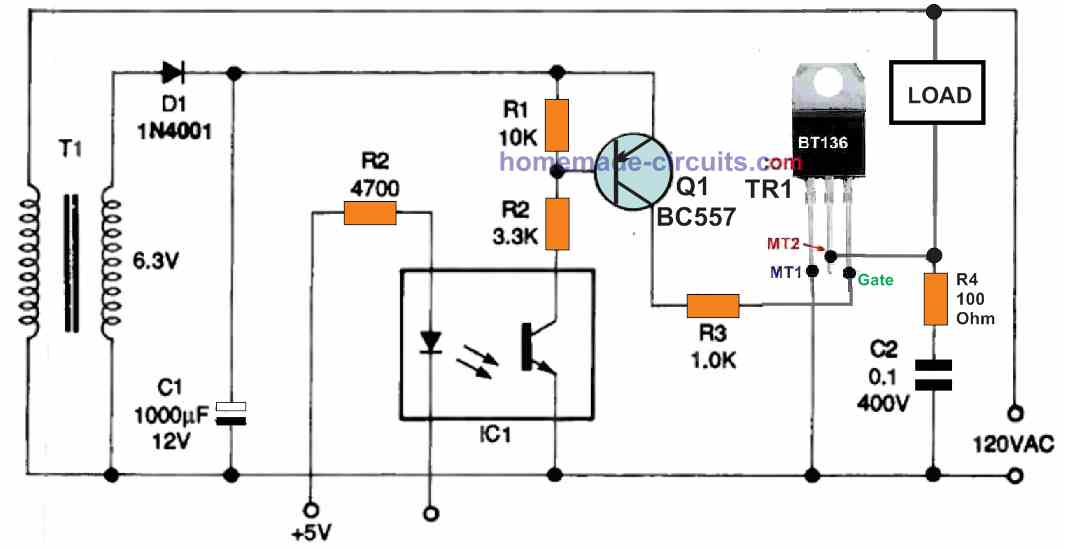
Figure 6 below demonstrates how to adapt the Fig. 5 circuit to use an optocoupler for its control.
This circuit could be actuated through a completely independent and isolated external circuit due to the presence of the optocoupler.
Triggering through Unijunction Transistor
Figures 7 and 8 as shown below, depict many different methods for triggering a triac through a completely isolated external circuit.
A unijunction transistor (UJT) placed in a pulse-generating relaxation oscillator provides the triggering operation in both of these circuits.
The oscillator circuit, which contains UJT Q2, provides the triggering pulses in these two circuits.
It works with a frequency of many kHz and feeds its output pulses to triac's gate via the pulse transformer T1, that ensures the intended isolation.
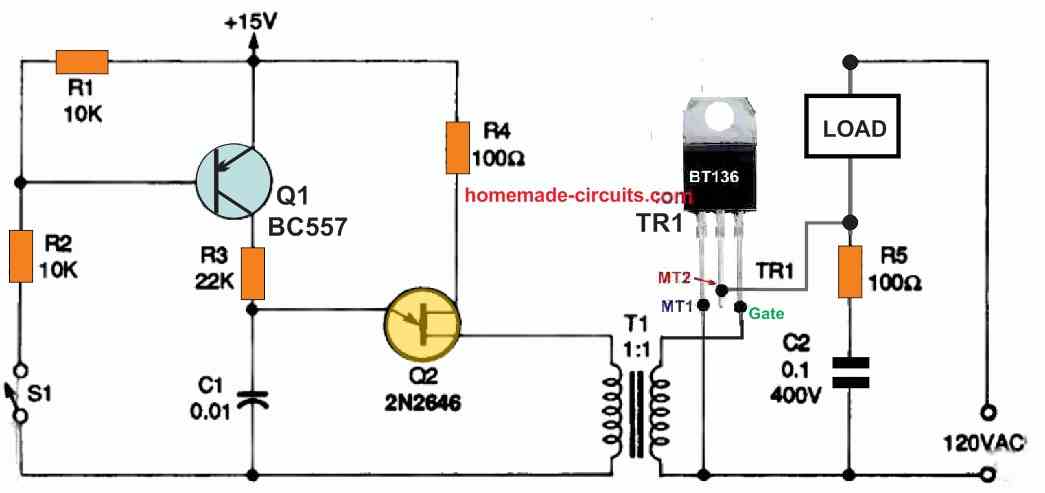
During the ON periods of the oscillator, the triac is turned on immediately at the start of each AC half-cycle due to the UJT device's relatively high working frequency.
With a resistor R3 is connected between the emitter and the base B2 of the UJT Q2, and a capacitor C1 hooked up between the emitter and the base B1, the UJT Q2 now works like a relaxation oscillator.
In this configuration UJT is able to switch rapidly to charge/discharge the capacitor at high speeds, as soon as the capacitor voltage reaches a certain threshold.
The time consumed by the capacitor to discharge could be evaluated, using the sawtooth's frequency calculations which is around 1/ time.
Since Q1 is in series with the UJT's primary timing resistor R3 in the Fig. 7 circuit, the UJT and the triac only switch on when S1 is closed.
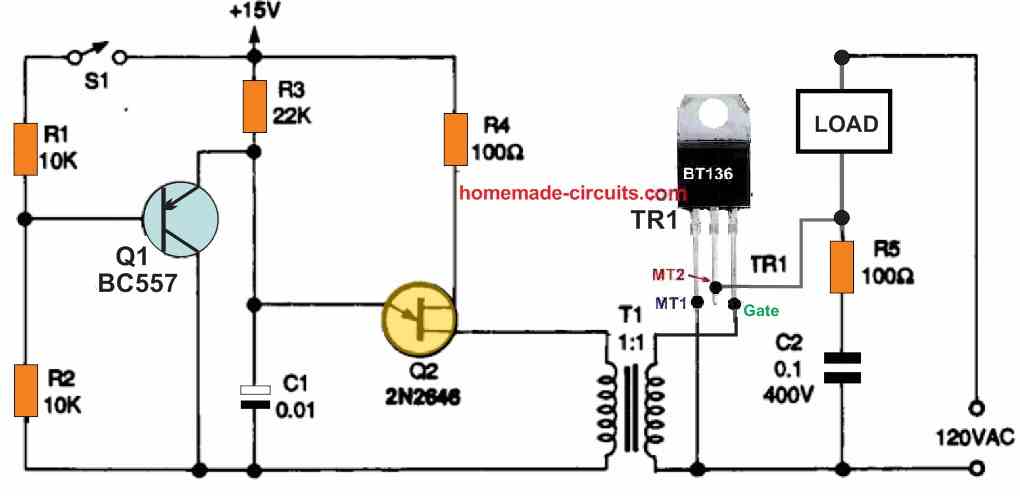
On the other hand, in Figure 8 above since Q1 is in parallel with the UJT's primary timing capacitor C1 in the Fig. 8 circuit, the UJT and triac only switch on when S1 is open.
S1 could be substituted by a sensor or transducer in each of these circuits to provide an automated power-switching operation as mentioned previously.
The Q1 in the above figure should be an NPN transistor, such as a BC547.

Comments
sir
i want to drive Triac BT131 600 with mcu without MOC 3021 & capacitive reactance . kindly check my schematics & guide me it is ok ? gate resistance value proper? suppose mcu pin source 20 ma current then how can i count gate current .give me idea by maths .
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/regarding-triac-triggering-with-bridge-rectifier.jpg
Noted
Thanks
Nitesh, I don’t think your circuit is correct.
According to me the following configuration is better and might work correctly…however a capacitive transformerless power supply is NEVER recommended for Arduinos or MCUs:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/triac-triggering-correct-way-from-220V-AC-capacitive-power-supply.jpg
Dear
i change my thought & now fix it for isolated type so i add MOC 3021 & NTC with 1w zener ,kindly request for check & now it ok ?
what happened if we replace 1000 mfd by 470mfd/25v bcz i have my old one ckt in which i run it with only 100mfd/16v with same mcu & same type load connect with negative side. & it work ok with bride ,, Due to size concern i revised same project so 1000/35 is little big in diameter for me & less adjust on kit
Looks ok to me, but the MOC IC must be configured as per the datasheet diagram:
https://www.farnell.com/datasheets/97984.pdf
470uF is also work.
dear sir
my load is Liquid Vaporizer 3W – 6W Indoor mosquito repellent ( heater coil) , now finely inform me may i connect this heater coil ( as load ) in series with phase & BT MT2 TERMINAL OR or in series with nutural & mt1 terminal side. which one better for long ckt life & less stress on trial .And also explain why ?
i will fix either moc type or whiteout moc bcz it going under thought for price.
mu ic has IOH = -18 ma @5v & IOL = 20ma @ 5v
Nitesh, for standard configurations without MOC IC, you an put the load in series with the MT2 pin, but if MOC is used then please do it as per the datasheet diagram.
Thanks
check this last one & say does it ok ? 5v1 zener 1/2 w not sufficient ? bcz my mood is to sell ckt too cheap & i am fear now days by clone also. so say zener 1/2 w work or heat?
also pl inform may i choose 5D 5 ntc instead of 5d11 bcz it has 4amp steady current while my ckt operate with very few miliamp .so 5D5 has 1amp current .so it work ?
You did not connect the VSS to the other AC line?
It should be like this:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/Arduino-capacitive-power-supply.jpg
Dear
it already connected but due to schematics drawling i give lable & it name is N . so it not shown But anyway thanks for guide.
may i choose finally 1/2 w zener & NTC 5dD5?
request for give answer for finial this two part. so my project will move ahead.
Dear
ok thanks.
i will add led +4.7k &10k between gate to mt1
Dear sir
Thanks for attend.
so i finalized 1w Zener & 5D5. i make both type moc & without & give 2 different price to market .
second after lot of depth think again for moc less circuit ,, when ac & BT off while negative voltage at end of MT2 at that time does my mcu pin get damage or not due to high spike pass from MT2 to gate to MCU pin ? so may i connect 4007 diode in series from mcu pin to resistor & resistor to gate ? so after this last answer i will give design for make pcb sir.
Nitesh, It is not recommended to use a capacitive mains power supply with any sensitive electronic circuits like MCU. But technically your circuit will mostly not cause any harm to the circuit, since one of the phases is protected by series 0.39uF capacitor, and NTC. Also the zener diode ensures the MCU does not get any initial surge current.
If you are worried about the triac gate connection with the MCU output, you can put an LED + 4.7k resistor in series with the triac gate and MCU output, also put a 10k between the triac gate and the ground line (MT1).
OK, no problem, but do not use 1/2 watt zener, use 1 watt or higher rated zener diode for better safety.
NTC can be 5dD5, that is ok…
hi… very helpful article
so, i tried to build electronic controller using arduino + some relay and electronic circuit for my washing machine
currently, i can say, it almost working perfectly , specially for the washing process, it can turn clock wise and counter clock wise, also i can control the speed
what i did is, i control speed using PWM,
the only problem, i’ve found the motor often produce a weird sound
i though it because i dont implement zero cross
another problem, i believe the original circuit (from the manufacturer) dont use pwm to control the speed, so i think it control the triac like using variable resistor but, controlled electronically
i’ve tried to figure out how it will looks like
can we use transistor to control current as replacement of variable resistor?
Hi, thanks for your question. Glad you liked the post.
If you are using PWM with a triac then yes it might have problems due to incorrect zero switching timing.
A MOSFET or a BJT can be used to control the motor with PWM, that is definitely feasible without the zero crossing issue.
using BJT it means using DC
currently the motor using AC,
from googling , since it is a universal motor, it can work well with DC
thank you for the answer
AC motor can be also used by appropriately configuring a bridge rectifier circuit for the BJT. You can see the following example PWM design in which an AC bulb is controlled through a PWM circuit:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/09/elc2Bcircuit.png
Sorry that is not a correct example because the load is getting DC, the AC load must be connected in series with the AC line of the bridge rectifier.
HI .I have Triac operated ( max load < 2w ) ckt & my load is connect in series with Line Nutural of MT1 terminal & MT2 terminal in direct connect with phase & gate is drive from MOC3021 &its works well. Now problem is that without connect load no current pass from gate to MT1. Now i need little bit change inside that is whiteout connect load may i see that Triac is operate or not ? I mean my i give direct Line Nutural to MT1 & give load in series with MT2 ? i want to see on board that triac is work or not? what extra very low consumption load i will place inside ?
Hi, you can connect the load with the MT2 terminal, and connect MT1 directly with the common ground, this will allow the triac to work regardless whether the load is connected or not. For the triac to switch ON, the gate current must flow to the ground via the MT1 terminal, otherwise the triac will not conduct.
as per your suggest if i do not connect load then voltmeter shows ac 220v across load? and what about series resistor from phase to MOC transistor ? i mean i connect 1k series resistor from phase to moc pin 6 ?
Yes that’s correct. However, as per the datasheet if an MOC opto coupler is used then the load should be connected to the MT1 side of the external triac. I am not sure how the circuit will behave if the load is connected to the MT2 pin of the triac. The series resistor must be as per the datasheet diagram.
Please check the last circuit on this pdf datasheet
https://www.farnell.com/datasheets/97984.pdf
Dear
i am looking for Triac (BT131-600v) control circuit with direct MCU with non isolated & capacitive reactance method, my inductive load is < 5w & output voltage of power supply is +5v dc. Kindly see attached file & guide atleast for correction.
Hi, my Arduino knowledge is not good, so solving your request can be difficult for me. Also, the link you sent is not opening.
ok
freeimage.host/i/HT2E114
Removed htttps link of remote schamatics
Thanks
just ask why u said for remove htttp ? i am not able to understand from link why it will be remove?
If you put https it goes to trash folder, and then I have to retrieve the comment from the trash folder….if https is removed then it lands normally in the comment moderation section.
Dear Sir
ok thanks
You are welcome Nil
Dear Sir
When i am trying to see waveform for Zero Crossing Circuit with 4n35 + 2N2222 it failed. Can u please inform me all parts value of it & what exact zero crossing sharp voltage level.( DC level ), i mean how much time period & rising edge & falling edge of zero level value.?
Hi Nil,
In a 50 Hz AC cycle, the zero crossing appears every after 10 ms. The time period of this zero crossing could be hardly 0.1 ms
Which schematic are you referring to?
Dear
ibb.co/710MfGY
i used attached link’s type zero crossing. i know that zero crossing appear every 10ms . Thanks.
But when i try to check simulation with Porteous it did not shown. What change it need ? Mean it require to change in series resistor of Bridge or Opto’s led ?
Actually I do not use software to simulate my circuits, instead I use my knowledge to judge the circuits, so I would be unable to solve the Proteus query.
The LED resistor decides how bright and strong the internal LED will illuminate to trigger the opto transistor.
You have used 110K + 110K which is too high for the opto coupler to operate. You must use only one 10K 5 watt instead.
Sir
My Simulation start to work.
My past observation shows that suppose our load becomes led driver then there is a bridge and one cap of 450v inside that. so if we connect this with Triac + snubber then even after remove moc 3021 led pulse this led chowk becomes operate for min 3 to 4 sec & then slowly off due to 450v cap charge & this was effect gate for on . & if we remove snubber ckt with Triac then it work as normal. So what can i do ? because in some case that types of load also connect with my remote kit.
Also in past u said there is a inside snubber came with opto coupler of 3040 series then why u said this time to connect exeternal snubber also ?
Nil,
The MOC IC does not have internal snubber, it has external snubber connected parallel to the triac MT1 and MT2 pins. Please refer to the following diagram, the 39 ohm and the 10nF, 400V are the snubber components.
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/MOC3040-SSR-circuit-compressed.jpg
Dear
ok .
Hi Nil,
I have already replied to your previous question.
https://freeimage.host/i/HT2E114
Dear
In Snubber circuit what is a wattage of 39 Ohms resistor & which type ( metal oxide or any other ) i used?
You can try 1 watt MFR 1% resistor.
Hi Nil, Yes I have seen your schematic. For the triac and load configuration you can try the following design, according to me:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/MOC3040-SSR-circuit-compressed.jpg
Dear Sir
have u seen my schematics? it’s ok ?
i am using +5v dc generate from Isolated SMPS for optocoupler’s transistor .Is it safe ?
Also in your Triac artical u suggest to connect load with in series with MT2 terminal , but while in my application i need phase out from Triac Circuit because in house hold switch board nuturual direct goes with load & phase goes to load VIA OFF WIRE, So i connect load in series with MT1.
Does it ok ?
Dear Sir
please say which optocoupler i am using in your image .jpg ? It help full for me..i want to uoload my finial schamatics to you. Please give me guidlines because in past i done hevay loss with prodcutio. Second my interest is to fitting this kit it inside house hold’s board instead of seperate board..So while this kit goes inside exiting board ,does we calculate some other parameters like mechinical switch spikes or any other spike inside baord will damage our remote kit ?
I will plan to fit remote kit in one ABS enclosure & then install it in existing house hold normal switch board and insode modular switch board ..So once i shows to finial schamtics & then print sample prototype .i have good grip on kicad pcb design and idea of track width with rule .
please help me sir
OK, +5V will be perfect on the transistor side.
Yes, you can try connecting the load in series with the MT1, I think it should still work.
Hi Nil,
The opto coupler can be a 4n35. If a zero crossing circuit is included then I don’t think any other parameter will be required to be considered. However as you see that the opto coupler requires an external DC on the transistor side….so from where will you get this DC from? Do you want the entire to be transformerless (with zero crossing facility)?
Another alternative is using a high watt resistor instead of a capacitor for the transformerless power supply, this will eliminate the need of the zero crossing detector, but the resistor will heat up significantly.
You can upload your image to any online “free image hosting site” and provide the link here.
Remember to remove the https while submitting the link here.
Hi Nil,
without seeing your schematic it can difficult for me to suggest a circuit diagram. However I think you can try the following design for powering your PIC circuit through a zero crossing circuit. Let me know if it helps or not:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/improved-zero-crossing-circuit.jpg
Dear Sir
i am redesign old remote circuit with 5v smps ( LNK switch of powerint) with isolated , but i have one confusion that it becomes isolated with PIC 16F series ic Vdd , but in my circuit i am also using zero crossing detector of fan speed synchronous, & for that i used one Polyprelene cap of 400v & current limiting resistor is in series with Bridge & output +ve voltage goes to 4n35 opto’s led via also one resistor & finialy opto’s transistor is connect with +5v generate from smps & that opto’s collector direct goes to as a zero-crossing signal via one resistor to PIC 16 ic. Is this safe ? kindly suggest zero-crossing method use for PIC16 ? Is this fully isolated now Or may be Bridge -ve terminal which are connected to the Opto led Cathode create problem to enter line nutural into secondary side of 4n35 ?