In this post I have explained how to make a simple yet efficient transistor/diode tester circuit, that will not only test the quality of a BJT, but will also help to identify whether it is is an NPN or a PNP. The circuit was designed and contributed by Mr. Henry Bowman.
Circuit Operation
Referring to the transistor tester circuit diagram, when the 555 timer on the left puts out a positive pulse, it triggers the timer on the right to put out a negative pulse and vice-versa.
Meaning, when the output on pin 3 of the left side 555 goes high, the output pin 3 of the right 555 goes low.
When the output pin 3 of the left side 555 goes low, the right side 555 pin 3 goes high. The right side 555 output will always be opposite polarity from the left side 555 pulse.
It’s similar to a flip-flop circuit. You have a positive and negative continuing reversal that is applied directly to the emitter and to the collector via the center tap of the transformer.
The first 555 sets the pulse rate to be about 1.5 seconds width in position 2. Some transistors testers require the use of a DPDT switch to reverse the polarity depending on NPN, or PNP type transistors.
My design eliminates the switch. The base receives a portion of the collector voltage through VR2 and resistor R7. Oscillations will occur if the transistor is good and the appropriate led will light.
If the transistor is shorted, both led2 and led3 will light and oscillations will not occur. To test a diode connect it across the E and C leads. Place selector switch in position 1. The polarity reversals occur much faster in position 1. It doesn’t matter which way you connect the diode.
If the diode is good only led 2, or led 3 will light, but not both. If the diode is shorted, but leds will light.
I have tested some power transistors with this circuit, like the 2N3055. Some power transistors have an internal clamping diode, such as the ones used in tv flyback transformers.
These transistors will light both leds, when they are actually good. Avoid using any voltage higher than 9 volts in this circuit. Using 12 volts can cause some transistors to have the “avalanche effect” and appear shorted.
You can select position 3 while the transistor is oscillation and it will stop the polarity reversals, so you can adjust oscillation pitch and gain settings. S3 selects speaker or meter output. D1 allows only dc to pass through the meter.
Also depending upon what type of meter is used, it may require a potentiometer in series to prevent full scale deflection. I actually used a 50 millivolt full scale meter instead of a millamp meter, but either one will work.
Circuit Diagram of Transistor Diode Tester Circuit
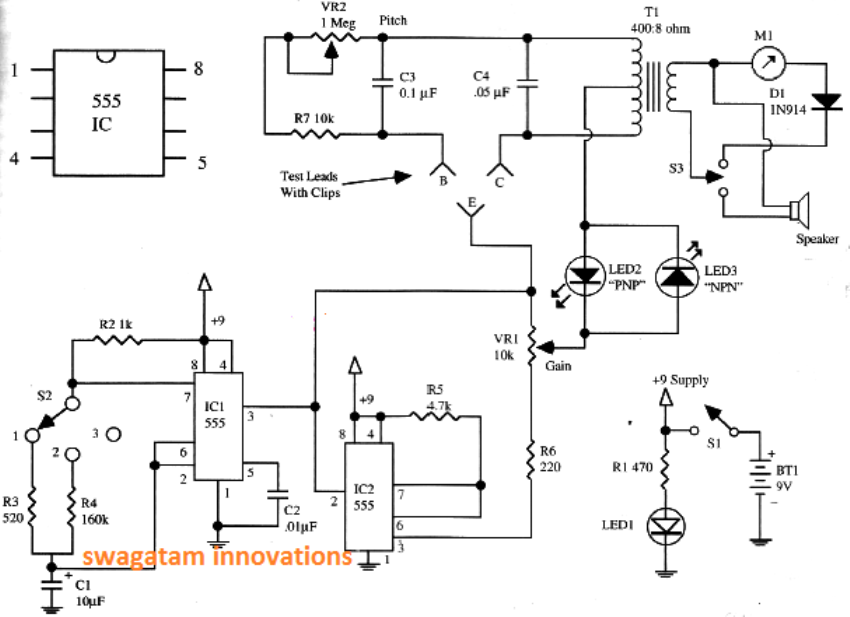
Designed By : Mr. Henry Bowman
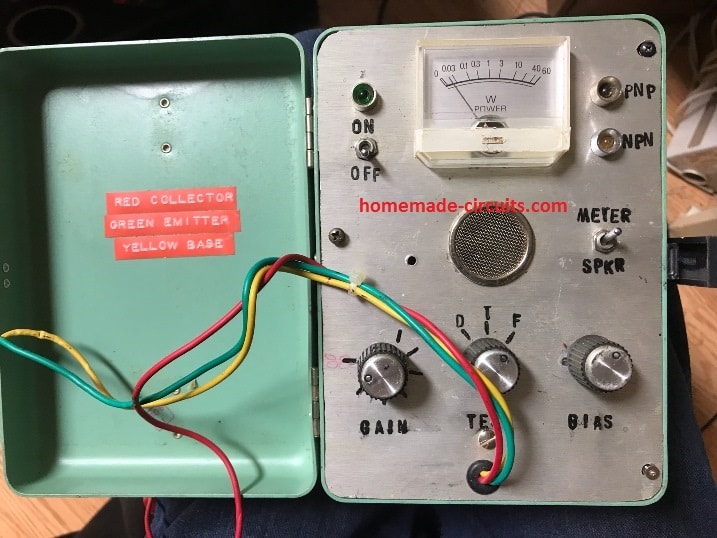
The following image shows the completed prototype of the transistor diode tester circuit by Mr. Henry.



Comments
Swagatam, I think that there would be a S2A and a S2B selector switch for the second monostable oscillator to select two different capacitors that would match the astable oscillator.
That’s right Clair, or maybe we can add a pot in series with R5.
Swagatam, what’s the value of the capacitor in the monostable oscillator circuit IC2, it looks like it’s missing
You are right Clair, it seems Mr. Henry forgot to insert the capacitor between pin6/7 of IC2 and ground.
Unfortunately, I am not sure about the value since I have not yet studied the working of the circuit fully.
You can try random values between 0.1uF and 1uF and check which one produces a valid result.