In this post I have explained a simple lithium polymer (Lipo )battery with over charge cut off feature. The idea was requested by Mr. Arun Prashan.
Charging a Single Lipo Cell with CC and CV
I came across your work on “Bicycle Dynamo Battery Charger Circuit” in Homemade circuit design blog. It was really informative.
I would like to ask something regarding that article. I am working on a hexapedal robot with battery switching mechanism. Once the primary battery gets beyond a preset voltage, secondary battery will power up the robot’s system. My concern is not regarding the switching circuit.
Together with this, I am working on energy generation by attaching a generator to each motor. The current generated is intended to be used to recharge 30C 11.1V 2200mAh 3 cell LiPo battery.
I am aware that the circuit mentioned in “Bicycle Dynamo Battery Charger Circuit” will not be useful for my purpose. Can you give me any other option pertaining my issue. I just need to know on how to modify the circuit to make it LiPo compatible with constant voltage and constant current or CC and CV rates. Thanks, looking forward for a reply.
Regards,
Arun Prashan
Malaysia
The Design
A Lithium polymer battery or simply a lipo battery is an advanced breed of the more popular lithium ion battery, and just like it's older counterpart is specified with stringent charging and discharging parameters.
However if look at the these specifications in detail we find it to be rather lenient as far as the rates are concerned, to be more precise a Lipo battery can be charged at the rate of 5C and discharged even at much higher rates, here "C" is the AH rating of the battery.
The above specs actually gives us the liberty of using much higher current inputs without worrying about an over current situation for the battery, which is normally the case when lead acid batteries are involved.
It means the amp rating of the input could be ignored in most cases since the rating may not exceed the 5 x AH spec of the battery, in most cases. Having said that, it's always a better and a safe idea to charge such critical devices with a rate that may be lower than the max specified level, a C x 1 could be the taken as the optimum and the safest rate of charging.
Since here we are interested in designing a lithium polymer (Lipo) battery charger circuit, we'll concentrate more on this and see how a lipo battery may be charged safely yet optimally using components that might be already sitting in your electronic junk box.
Referring to the shown Lipo battery charger circuit diagram, the entire design could be seen configured around the IC LM317 which is basically a versatile voltage regulator chip and has all the protection features built in. It will not allow more than 1.5 amps across it's outputs and ensures a safe amp level for the battery.
The IC here is basically used for setting up the exact required charging voltage level for the lipo battery. This may be accomplished by adjusting the accompanied 10k pot or a preset.
Circuit Diagram
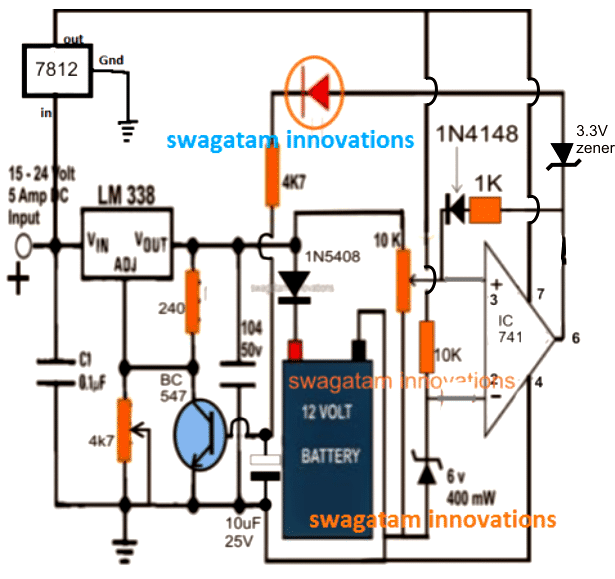
The section at the extreme right which incorporates an opamp is the over charge cut off stage and makes sure that the battery is never allowed to overcharge, and cuts off the supply to the battery as soon as the over charge threshold is reached.
Circuit Operation
The 10 k preset positioned at pin3 of the opamp is used for setting the over charge level, for a 3.7 V li-polymer battery this may be set such that the output of the opamp goes high as soon as the battery is charged to 4.2 V (for a single cell). Since a diode is positioned at the positive of the battery, the LM 317 output must be set to about 4.2 + 0.6 = 4.8 V (for a single cell) for compensating the accompanied diode forward voltage drop. For 3 cells in series, this value will need to be adjusted to 4.2 x 3 + 0.6 = 13.2 V
When power is first switched ON (this must be done after connecting the battery across the shown position), the battery being in a discharged state pulls the supply from the LM317 to the existing level of its voltage level, let's assume it to be 3.6 V.
The above situation keeps pin3 of the opamp well below the reference voltage level fixed at pin2 of the IC , creating a low logic at pin6 or the output of the IC.
Now as the battery begins accumulating charge its voltage level starts rising until it reaches the 4.2 V mark which pulls pin3 potential of the opamp just above pin2 forcing the IC's output to go instantly high or at the supply level.
The above prompts the indicator LED to light up switch ON the BC547 transistor connected across the ADJ pin pf the LM 317.
Once this happens the ADJ pin of the LM 317 gets grounded forcing it to shut off its output supply to the lipo battery.
However at this point the entire circuit gets latched in this cut off position due to the feedback voltage to pin3 of the opamp via the 1K resistor. This operation makes sure that the battery under no circumstance is allowed to receive the charging voltage once the over charge limit is reached.
The situation stays locked until the system is switched OFF and reset for possibly initiating a new charging cycle.
Adding a Constant Current CC
In the above design we can see a constant voltage control facility using LM338 IC, however a constant current seems to be missing here. In order to enable a CC in this circuit, a small tweak might be enough to get this feature included, as shown in the following figure.
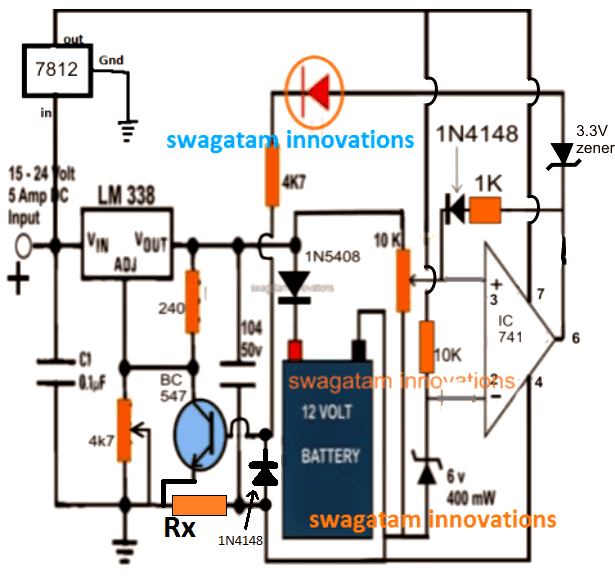
As can be seen, a simple addition of a current limiting resistor and a diode link transforms the design into an effective CC or constant current Lipo cell charger. Now when the output tries to draw current above the specified CC limit, a calculated potential is developed across Rx, which passes through the 1N4148 diode triggering the BC547 base, which in turn conducts and grounds the ADJ pin of the IC LM338, forcing the IC to switch OFF the supply to charger.
Rx may be calculated with the following formula:
Rx = Forward voltage limit of BC547 and 1N41448 / Max battery current limit
Therefore Rx = 0.6 + 0.6 / Max battery current limit
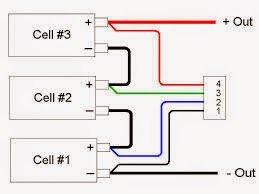
Lipo Battery with 3 Series Cells
In the above proposed 11.1V battery pack, there are 3 cells in series and the battery poles are terminated separately through a connector.
It's recommended to charge the individual batteries separately by locating the poles correctly from the connector. The diagram shows the basic wiring details of the cells with the connector:
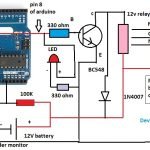
UPDATE: In order to achieve a continuous automatic charging of a multi-cell Lipo battery, you may refer to the following article, which may be used for charging all types of Lipo batteries regardless of the number of cells included in it. The circuit is designed to monitor and automatically transfer the charging voltage to the cells which might be discharged and needs to be charged:


Comments
..
Pls sir,I need 12v 200ah battery over charge cut off
iyiola, you can try the following circuit:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2011/12/high-current-10-to-20-amp-automatic.html
Hi, I've started to construct the above circuit and I would like to clarify one condition. 3V zener diode after the output of LM324 is in reverse polarity. Does this indicate the diode's breakdown/knee voltage? Correct me if I'm wrong. Thanks.
sorry i did not understand your first question….
the 741 pinouts are correct and can be used in the above circuit
In terms of 741, how would the pin connections differ?
2= -Vin
3= +Vin
4= -Vcc (ground?)
6= o/p (to 3V zener)
7= Vcc (positive)
Am I correct with the flow?
I would like to try with LM324. Correct me if I'm wrong, the negative input will be after 1K feedback resistor while the positive input will be from 10K resistor. In the diagram its shown the other way.
yes, but the unused opamps must be used as "followers" with the one that's used for the above application for ensuring stability of the IC.
Alternatively you can use a single opamp such as a 741
So I am free to choose the op amp 324 inputs?
Pin 2&3 or 5&6?
The negative feedback will be in either pin 2 or 6, I am correct?
Yes the zener is positioned so that it conducts only when the output of the opamp has crossed the knee voltage of the zener, ensuring a legitimate full charge signal from the opamp
Hi Mr Swagatam, sorry for disturbing you everyday. I was checking on an appropriate generator coupled with a high torque DC motor. Then I checked that the above diagram where it states 15-24V 5A input. 5A rated generator seems to be hard to get. Can you advice on the minimum current needed to run the charging circuit or am I left with using a current booster circuit?
Hi Mr. Arun, the input amp rating should be according to the Lipo battery rating, in your case since the cells are rated at 2200mAH, a 2 to 3amp input could be used, the diagram was taken from some other application in this blog so the 5 amp was mistakenly printed, is not crucial and may be replaced as per the present situation.
Is the component in the circled region is a potentiometer? If not how shall I modify it?
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B3p3Sae8pVavTzZFR0Rfc3NTNzg/edit?usp=sharing
correction
…adjust the preset until the LED just lights up….
you surely did not do the way I suggested in the above comments.
I told you to disconnect the LED 4k7 from the transistor base and connect it to ground, and also to keep the 1K across pin6 and (+) of the opamp disconnected during the setting up procedure….after this you will need to adjust the preset carefully until the LED just shuts off…seal of the preset in this position and restore the 4k7 and 1k to their original positions.
I did the above setup and adjusted the output of LM317 to 4.8V without Lipo battery connected. What I found weird is that the LED light up once I connect the circuit with external supply (dynamo/24V lead acid battery-4A). Where did I go wrong? I tried the setup again and noticed that the LM317's output is 1.2V no matter how I tune the potentiometer.
while doing the above also make sure that the 1K feedback from the opamp pin6 is kept disconnected…restore it back to its indicated state after the setting-up procedure is completed.
it should be a preset ideally, because we want to set it only once.
Adjust the voltage at the output of LM317 to 4.8V (without any battery connected) now set the opamp 10k preset such that the LED just comes ON.
In the above process connect the LED 4k7 resistor to ground and NOT with the base of the BC547….once the setting is complete you may restore the position to the base of the BC547.
Now your circuit is ready and can be used for the intended results.
Hi Mr.Swagatam,
I went through “Lithium Polymer Battery Charger Circuit” as I request few days back. Impressive explanation. But I have a question, turns out to be rather a silly one. The LiPo battery I have has a separate charging pins. It has 4 pins in total. What are the modifications required for that particular battery. Together I’ve attached the power terminal and charging terminal of my battery.
Thank you.
Appreciate it, thank you.
Hi Arun thank you, I have the updated the required info in the above article, please check it out…you may have to charge the cells individually using the above charger circuit after locating the poles correctly inside the connector.