This touch volume control circuit has two touch pads which enable the user to increase or decrease the volume of an audio amplifier simply by touching the relevant touch pads.
The advantages of this solid-state volume control are: very long life due to the absence of any wear and tear, quick and easy finger touch control, and low distortion.
How the Circuit Works
The circuit works like an electronic attenuator, configured to sense and respond to finger touch on alternate touch pads. The FET T1 is wired to simulate a variable resistor, across a resistive divider network T1, R1.
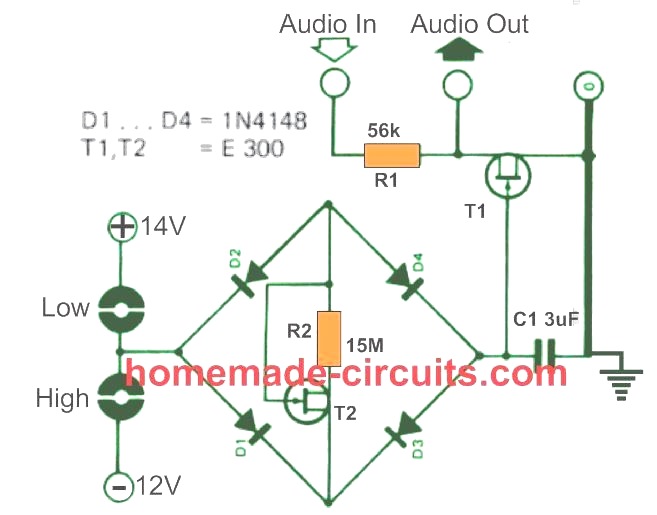
The resistance formed across T1 is determined by the negative voltage created across capacitor C1.
When the touch pads associated with the negative supply line is contacted with finger, a current via D2, R2 and D3 charges the capacitor C1, with a delay time decided by the values of C1, R2.
When the negative charge developed across C1 is sufficiently high, T1 is inhibited from conducting anymore, which allows an un-attenuated audio signal to pass through. This enables the volume to be increased
In order to reduce the volume of the audio, the user simply has to touch the pair of pads connected with the positive side of the supply.
This causes C1 to begin discharging, so that T1 again gets more conductive, and diverts the audio towards the ground line. This causes a corresponding amount of attenuation on the audio signal, and the volume gets reduced proportionately.
The amount of volume to be attenuated or increased will depend on the time for how long the touch pads are kept contacted with the finger.
The FET T1 simply behaves like a linear resistor whose gate bias is modulated by the audio signal input.
The output distortion is reasonably low as long as the input audio signal is not exceeded 30 mV level.




Comments
Hello!
What sort of pads do you use for the touch pads in the circuit? I’m planning to try and replicate it for fun and need to buy parts for it.
Hi, they are simple copper pads, or copper tinned with solder pads
Alright, thank you!
Hi Swag,
I have a pair of wireless headphones that have the volume control kind of broken.
When I roll it to increase or decrease the volume it some times faills to reproduce the sound in one of the sides and produces scratch sound.
If I replace the volume with this circuit, will it work?
Will I have a kind of a digital volume control?
Best Regards.
Nelio
Hi Nelio, yes definitely you can replace the electro-mechanical one with the solid state type as explained above.
It will provide a fully digital control without any losses.
Hi Swag,
Thanks.
There’s only one catch with this circuit….
The Voltage…. 12 and 14…
The headphones are 3V (2×1.5V AAA Batteries)
Best Regards.
Nélio
Hi Nelio, that’s correct, so this circuit cannot be used for low voltage applications.