The shock alarm module that we are presenting to you can be used in a house as well as in a car. Given its low manufacturing cost, it can be replicated in several copies and connected to different positions at home. It can be also installed in a vehicle where it will trigger a siren when a strong vibration is detected. By: Ramdas
Main Features of 801S Shock Detector (Learn More)
The shock and position detector, for a more than affordable price, has very interesting characteristics that make it particularly suitable for alarm systems. It only requires a few very common and low-cost components for its implementation.


The photograph above gives an idea of its physical appearance. Its main features are as follows:
- detection of very low amplitude shocks,
- detection of changes in position,
- detection in all directions,
- guaranteed lifespan of at least 60,000,000 detections,
- adjustable detection sensitivity,
- operates without mercury (environmentally friendly!),
- very high sensitivity,
- completely static,
- can be used for alarm, security systems, etc.,
- dimensions: 0.7mm for a length of 9.2mm,
- outputs on 0.5mm pins for printed circuit.
Electrical Characteristics of 801S Shock/Vibration Sensor
The electrical characteristics of the shock sensor 801S are:
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V to 5V DC
- Operating Current: <1mA
- Output Signal: Digital (High or Low)
- Sensitivity: Adjustable
- Detection Angle: 360°
- Detection Range: Up to 3 meters
- Response Time: <15ms
- Operating Temperature: -10°C to 70°C
- Lifespan: 60 million detections
- Dimensions: 9.2mm x 7mm
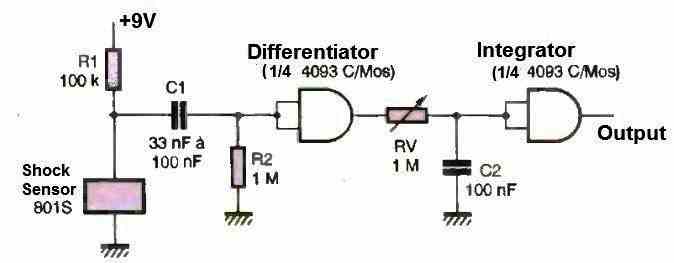
The basic diagram shown in figure above indicates what can be done simply with this 801S shock detector. Note that the output, when the 801S sock detector is triggered, provides a rectangular and unstable signal. The sensitivity is adjustable.
Circuit Description
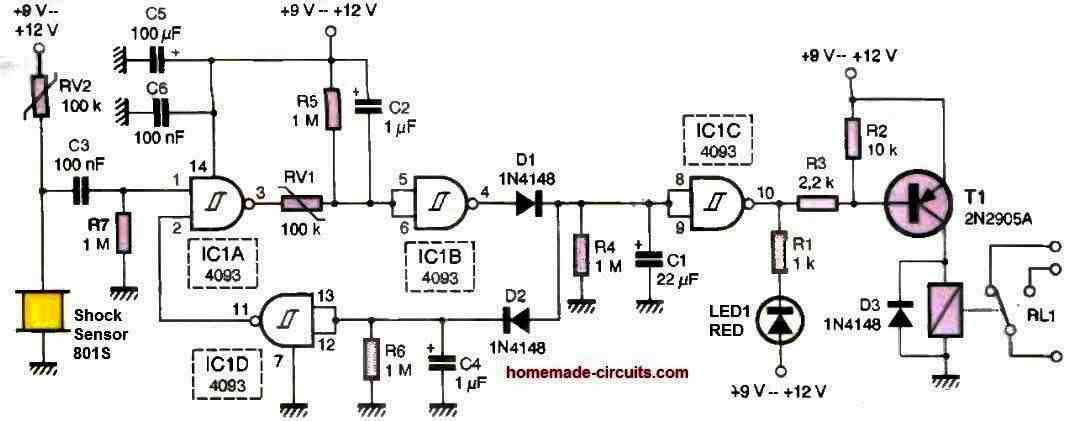
As can be seen in the figure above, shock detector circuit using 801S requires only a few components, in greater numbers than the first diagram, but giving better results.
The adjustable resistor RV2, which also adjusts the sensitivity of the circuit, constitutes a voltage divider with the 801S detector. When the sensor is triggered, the voltage at the input of the NAND gate IC1 (4093) changes and triggers the system.
A negative pulse appears on the output of this gate, which becomes positive at the output of the IC1B gate.
This pulse charges capacitor C1, and, inverted by the IC2C gate, makes transistor T1 conductive, which triggers the electromechanical relay.
On the other hand, it generates a negative pulse at the output of the IC1D gate, which will keep the IC1A gate low until capacitor C1 is discharged.
The relay will be activated for a few seconds, a duration that can be increased by changing the value of capacitor C1. The circuit can be powered by a voltage that can exceed 12V, which is the case in a car and almost all domestic alarm systems.
Construction
The printed circuit board layout and the component placement diagram of this 801S shock sensor is shown in the Figure below.
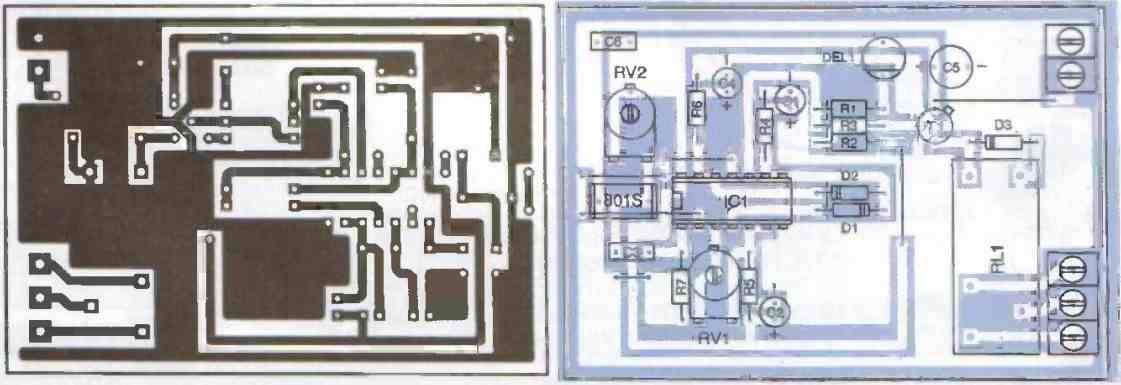
Six straps need to be placed on the board. As usual, start by placing the smallest components and end with the largest ones.
The power input and the three relay outputs (common, normally open, and normally closed) are made respectively on two- and three-point screw terminals.
The 4093 (IC1) will be placed on a socket, which will facilitate its replacement in case of an incident. If the circuit is independent, the power can be supplied by a 9V battery incorporated in the enclosure (in the case of a home alarm system).
After finishing the wiring, check the solder joints and the continuity of the tracks. If the board is used as a car alarm, apply a coat of varnish on the copper side to protect it from moisture.
How to Test
Regarding testing, there is nothing special to mention. Simply power up the board with the adjustable resistors set at mid-position.
By lightly tapping the board, the relay should activate.
Then adjust the potentiometers to achieve the desired sensitivity. For a value of 22 uF (C1), the relay stays activated for about six seconds. Its value can be increased if necessary.
Hi very nice circuirt, nice solution. Can you tell me please whether your simple solution is good enough for a lot and frequent registration of vibrations? Actually I’m seeking for the solution for the gas cannon. You probable know that there is about 20,000 hits by only one LPG 12kg bottle. Can I be sure that this shock sensor can handle such a many vibrations?
Hi, thanks for your feedback.
Yes, the above circuit looks accurate but I don’t think it can handle such intense vibrations.
Instead I would recommend using a piezo based sensor, as explained in the following article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/how-to-make-vibration-detectormeter/
Let me know your opinion on this.
Very nice many thx for sharing