The Field-Effect Transistor or the FET is a 3 terminal semiconductor device which is used for switching high power DC loads through negligible power inputs. The FET comes with some unique features such as a high input impedance (in the megohms) and with almost zero loading on a signal source or the attached preceding stage. […]
Circuits
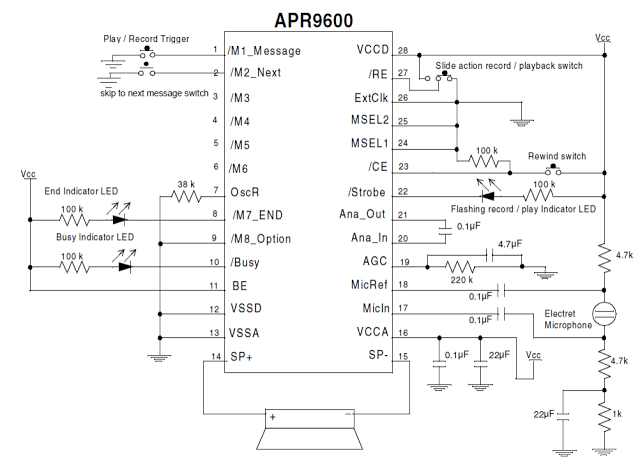
Voice/Audio Recorder Playback Circuits
In this article I have explained a single chip circuit which can be used for recording and playing back short voice clips or any audio clip ranging from 20 to 60 seconds. About the IC APR9600 The incorporated IC APR9600 is a programmable voice recorder chip which facilitates infinite number of recording/erase of audio files […]
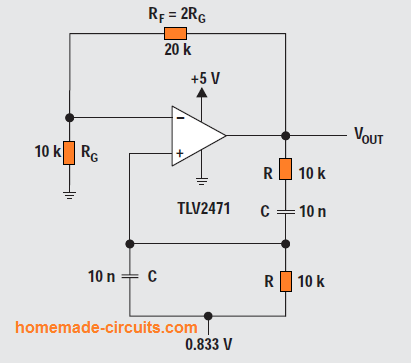
Phase Shift Oscillator Circuits – Wien-Bridge, Buffered, Quadrature, Bubba
A phase-shift oscillator is an oscillator circuit designed to generate a sinewave output. It operates with a single active element such as a BJT or an op amp configured in an inverting amplifier mode. The circuit arrangement creates a feedback from the output to the input through using an RC (resistor/capacitor) circuit arranged in a […]
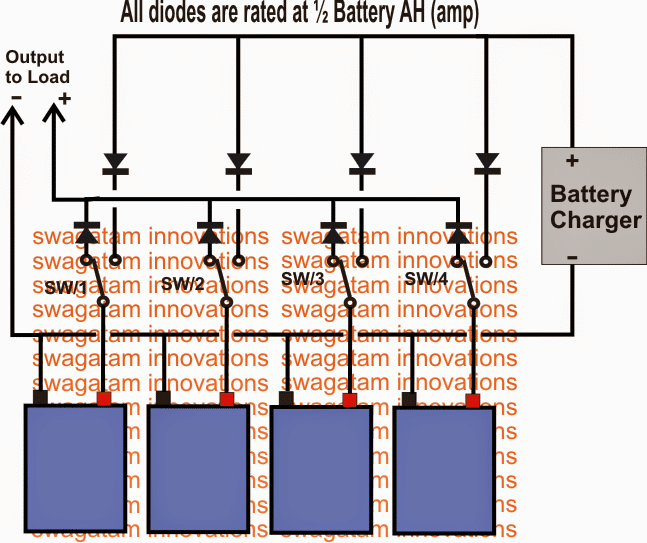
Parallel Battery Charger Circuits Explained
In this post I have explained two methods of connecting batteries in parallel. The first one below deals with changeover circuit using SPDT switches to charge multiple batteries individually or collectively. These may be connected in parallel using a single battery charger and through a manual SPDT changeover switch bank. The seconds design talks about […]
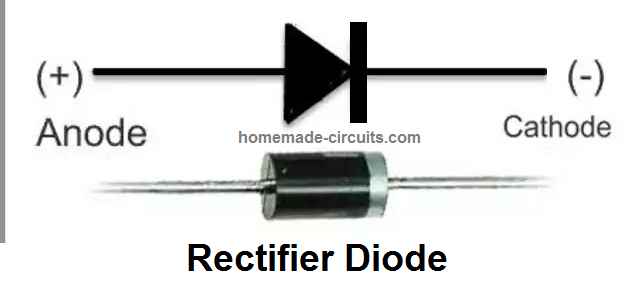
Simple Diode Circuits Explained
In this post I have explained how to use rectifier diodes for building some practical and useful electronic circuits. A diode is the most basic semiconductor electronic component, which is built with a single pn semiconductor junction. It has only two terminals, which are referred to as the anode and the cathode. Diodes can be […]
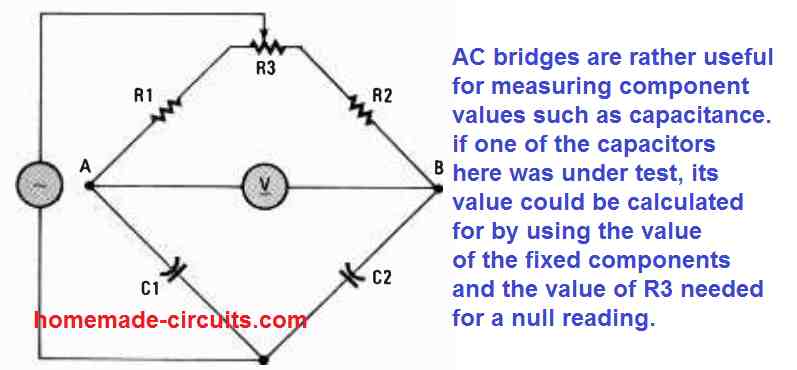
6 Simple AC Bridge Circuits Explained
An AC bridge is a circuit which can be used for measuring parameters like capacitance, resistance, Inductance using differential method, by comparing them with known values of similar components, positioned diagonally across a bridge circuit, and through an analogue meter placed at the center of the bridge. Before we begin talking about the AC bridge […]