In this post I have explained a simple configuration which can be added with all SG 3525/3524 inverter circuits for implementing automatic PWM output voltage regulation by the IC. The solution was requested by Mr. Felix Anthony.
The Circuit Problem:
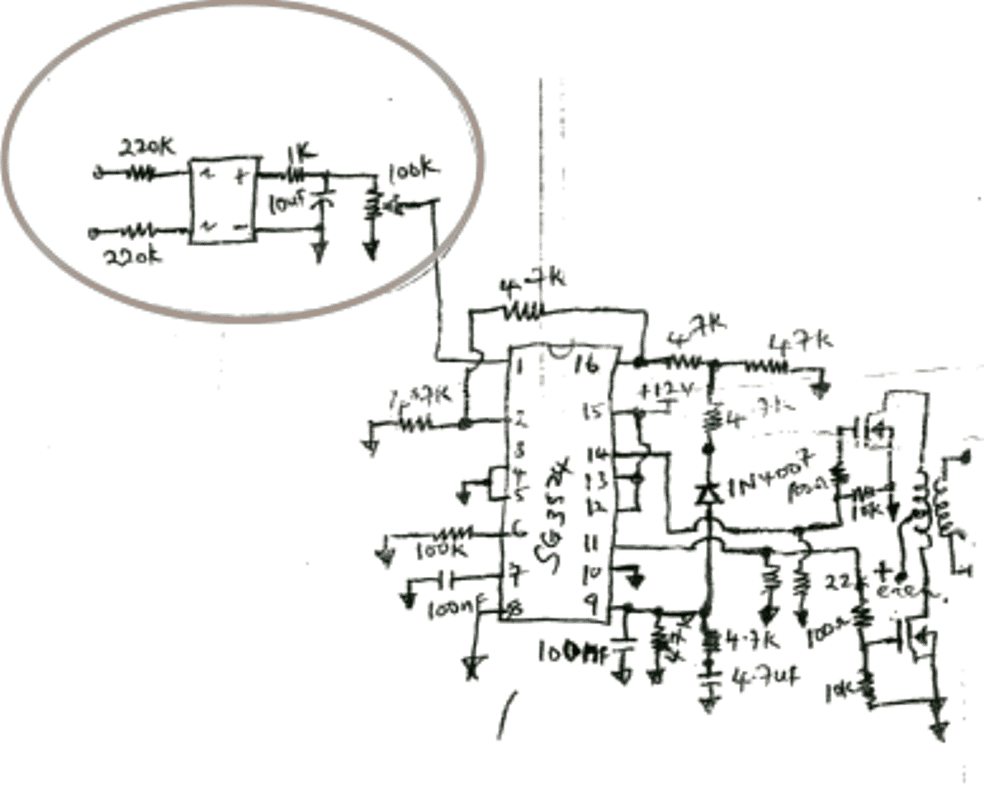
Sir, I would need your help on a project about a schematic that I do not understand a particular section. Our Lecturer gave us the schematic on a printed sheet to build the circuit on our own. He listed the parts but building the circuit is not easy for me as there is one section I do not really understand what that IC represents. Can you help me please The section I circled with a pen is the part of the circuit I do not really understand anything about it. The drawing of the circuit was turned upside down by the computer operators I gave it to. Thanks so much for your upcoming review.
Please use this online calculator to calculate the SG3525 parameters.
Solving the Circuit Problem
The section that's circled is a simple bridge rectifier with a potential divider stage in the form of a 100k pot. It rectifies and sends a sample feedback voltage from the inverter mains output to pin1 of the IC which identifies this feedback and accordingly controls the PWM of the IC and regulates it so that the output from the inverter never exceeds a predetermined limit as set by the 100k preset.
pin1 is the sensing input of the IC which responds and makes the PWMs narrower whenever the fed voltage from the 100k pot exceeds a certain predetermined limit.
Pin1 of IC SG3525/3524 actually forms one of the pinouts of the internal error amplifier opamp. The term error amplifier itself suggests that the opamp is assigned to sense and check a feedback sample voltage (error signal) from the inverter output and correct the output PWM width accordingly. This voltage is sensed with reference to the other pin of the IC (pin16) which is internally fixed at a reference voltage of 5.1V.
In case a rising feedback is detected, the potential at pin1 of the IC which is the sensing input of the error amplifier proportionately goes higher than the other complementing pin16 of the opamp creating a high at the output of the internal error opamp.
This high is utilized internally to modify or slim down the PWM frequency which in turn forces the mosfets to conduct with proportionately lower current, thus correcting the output voltage of the inverter automatically with respect to the feedback signal.
Parts list for the above shown SG 3525 inverter circuit with auto PWM voltage control feature





Comments
Sir
please explain beter your answer to chidubem.So if i need a 1000w inverter with a irf150N, the number of mosfet in parallel will be 1000 divided by 42A.,which is around 23 mosfets , its much.
That is correct. If you want to reduce the number of mosfets then use something like IRF3205
Thanks once again for your help . The charger circuit you referred me to is a 48v charger with 56v input. Please how can I modify it to give me 24v at 30amp
The same circuit can be used for charging a 24V battery also, make sure to use 28V as the input
Sir please you can retry to make the diagram of this circuit ? I see anything in this circuit…
Matt, I have enlarged the diagram please check it out…..
Sir
please can explain to me how to choose a MOSFET for an inverter
for example choosing IRF540 for 1000W inverter how will I know the number of this MOSFET I will connect in parallel to govet me 1000w at the transformer output
Chiduben, first find the maximum current handling capacity of the mosfet…then divide 1000 by this value. This will provide the number of mosfets that needs to be connected in parallel…
keep a 20% +/- margin for safety
Well done Swagatam,how can i calculate the efficiency of a built inverter and its power rating especially transformer based ones. i have several formulas but how to get the Pin and Pout is the issue.
thanks atinuke, the easiest way is by practically connecting a known load at the inverter output, then by measuring the current through the load and through the battery separately.
after that the battery side current could be multiplied by the battery voltage to get the input wattage.
and similarly the output side current could be multiplied with the output voltage for verifying the output wattage.
finally dividing the output result with input result and multiplying by 100 would fetch you the efficiency of the inverter with the given load.
Hi sir, help & design for me an inverter driver circuit using a multivibrator system of two transistors
Then design for me the suitable power stage to be used, thanks.
Hi Kakooza, you may refer to the following posts:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2012/07/simplest-and-best-100-watt-inverter.html
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2012/02/how-to-make-simple-200-va-homemade.html