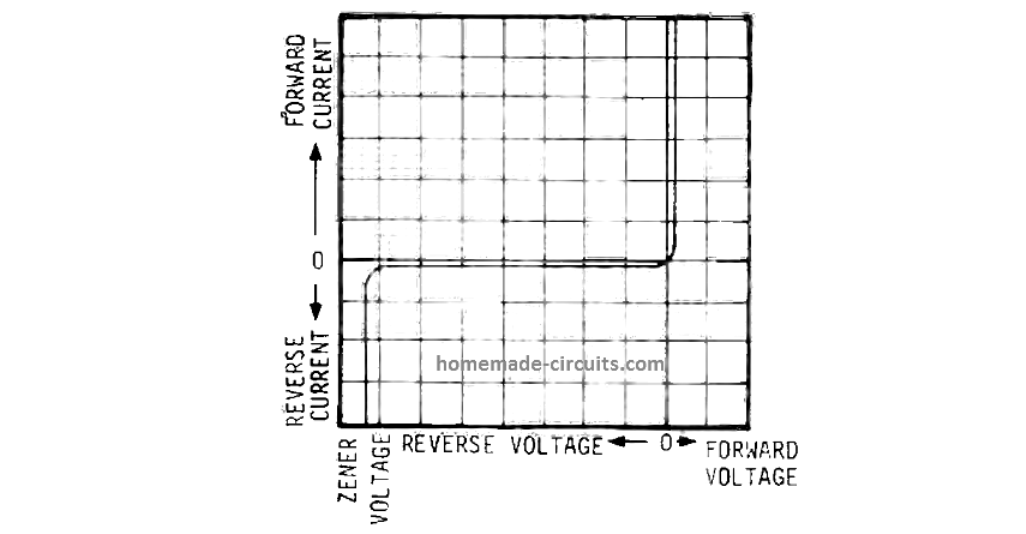
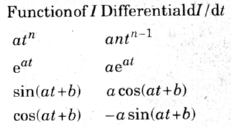Zener diodes – named after its inventor Dr. Carl Zener are fundamentally used in electronic circuits for generating precise voltage references. These are devices that are able to create a practically constant voltage across them regardless of variations in circuit and voltage situations. Externally, you may find zener diodes a lot similar to standard diodes […]
Electronics Theory
Simple Buck-Boost Converter Circuits Explained
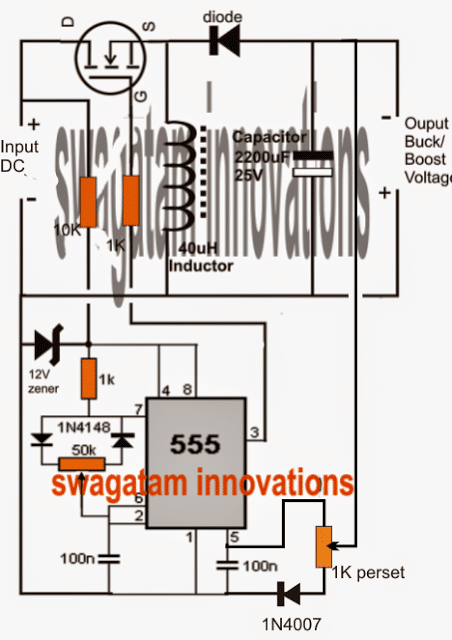
In this post I have explained s few simple DC to DC buck-boost converter circuits which can be used for either stepping up the input DC voltage or stepping down the input DC voltage to specific output DC voltage levels. Since a buck-boost converter allows the input voltage to be either stepped up or stepped […]
Capacitor Inductor Calculations
Inductors can be imagined as the opposite of capacitors. The main difference between a capacitor and an inductor is that a capacitor carries a protective dielectric between its plates, which inhibits the conduction of current across its terminals. Here it acts like an open circuit. On the other hand the inductance of an inductor is […]
Transistor Relay Driver Circuit with Formula and Calculations
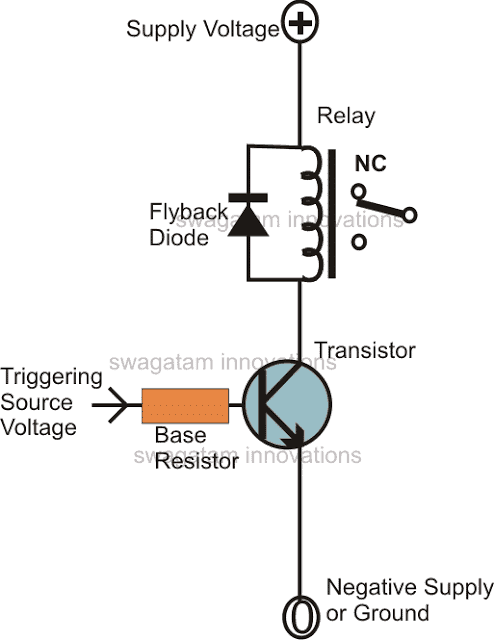
In this article we will comprehensively study a transistor relay driver circuit and learn how to design its configuration by calculating the parameters through formulas. Importance of Relay Relays are one of the most important components in electronic circuits. Especially in circuits where high power transfer or mains AC load switching is involved, relays play […]
How to Make Logic Gates using Transistors
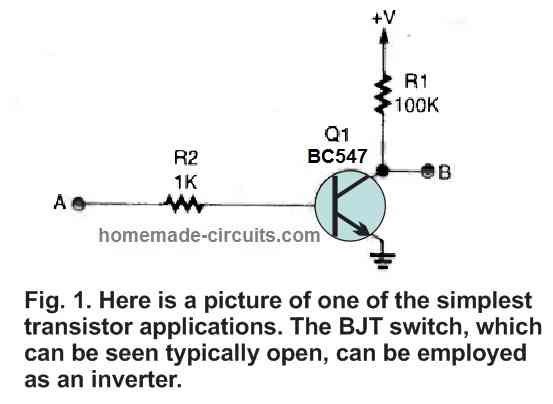
In this post I have explained how to build NOT, AND, NAND, OR, and NOR logic gates using discrete transistors. The main advantage of using transistor logic gates is that they can work even with voltages as low as 1.5 V. In some electronic applications the available voltage may be inadequate to power TTL or […]
Light Emitting Diodes (LED) Explained
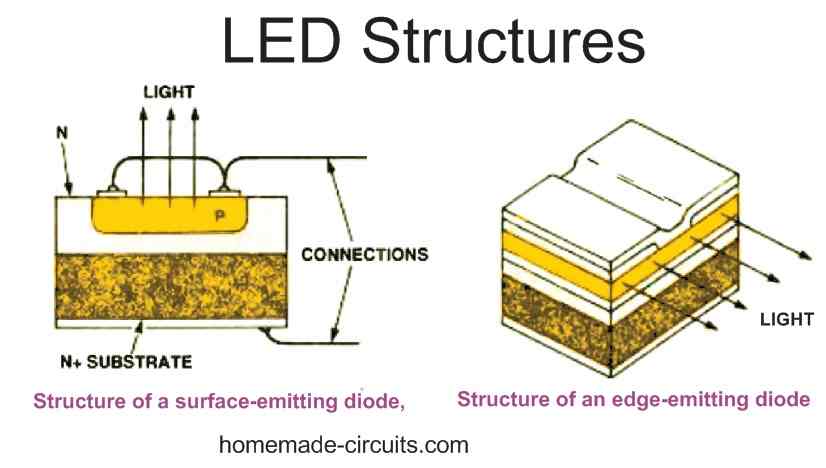
The full form of LED is Light Emitting Diode. LEDs are special type of semiconductor diodes which emit light in response to a potential difference applied across their terminals, hence the name light emitting diode. Just like a normal diode LEDs also have two terminals with polarity, namely anode and cathode. To illuminate an LED […]