A very interesting circuit of a RMS controlled modified sine wave inverter is discussed in this article which incorporates just ordinary transistors for the proposed implementations.
The use of transistors typically makes the circuit easier to understand and more friendly with the new electronic enthusiasts. The inclusion of a PWM control in the circuit makes the design very efficient and desirable as far as operations of sophisticated appliances are concerned at the inverter output.
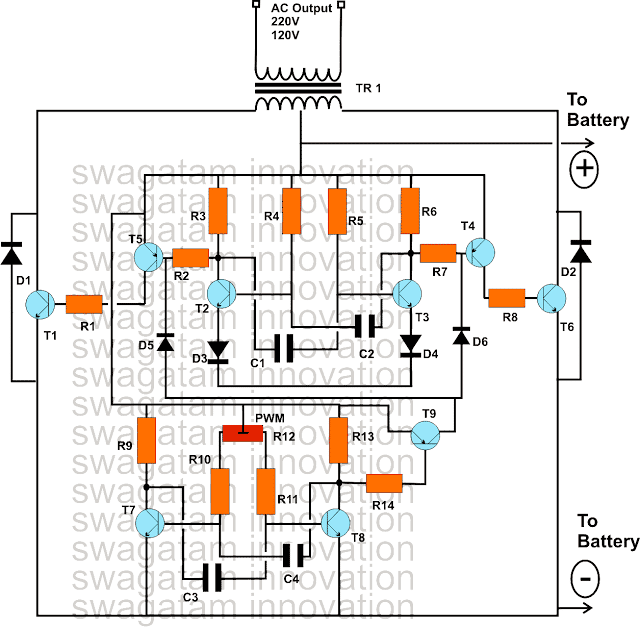
The circuit diagram shows how the entire circuit is laid down. We can clearly see that only transistors have been involved and yet the circuit can be made to produce well-dimensioned PWM controlled waveform for generating the required modified sinew waveforms or rather modified square waves to be more precise.
The whole concept may be understood by studying the circuit with the help of the following points:
Astable as the Oscillators
Basically we can witness two identical stages which are wired up in the standard astable multivibrator configuration.
Being astable in nature the configurations are specifically intended for generating free running pulses or square wave at their respective outputs.
However the upper AMV stage is positioned for generating the normal 50 Hz (or 60 Hz) square waves which are used for operating the transformer and for the required inverter actions, in order to get the desired AC mains power at the output.
Therefore there’s nothing too serious or interesting about the upper stage, typically it consists a central AMV stage consisting of T2, T3, next comes the driver stage consisting of the transistors T4, T5 and finally the receiving output stages consisting of the T1 and T6.
How the Output Stage Works
The output stage drives the transformer via the battery power for the desired inverter actions.
The above stage is only responsible for carrying out the generation of the square wave pulses that’s imperatively required for the intended normal inverting actions.
The PWM Chopper AMV Stage
The circuit at the lower half is the section which actually does the sine wave modifications by switching the upper AMV according to its PWM settings.
Precisely, the upper AMV stage’s pulse shape is controlled by the lower AMV circuit and it implements the square wave modification by chopping the basic square inverter square waves from the upper AMV into discrete sections.
The above chopping or dimensioning is executed and defined by the setting of the preset R12.
R12 is used for adjusting the mark space ratio of the pulses generated by the lower AMV.
According to these PWM pulses, the basic square wave from the upper AMV is chopped into sections and the average RMS value of the generated waveform is optimized as close as possible to a standard sine waveform.
The remaining explanation regarding the circuit is pretty ordinary and may be done by following the standard practice that’s normally employed while building invertes, or for that matter, my other related article may be referred for acquiring the relevant information.
Parts List
- R1, R8 = 15 Ohms, 10 WATTS,
- R2, R7 = 330 OHMS, 1 WATT,
- R3, R6, R9, R13, R14 = 470 OHMS ½ WATTS,
- R4, R5 = 39K
- R10, R11 = 10K,
- R12 = 10K PRESET,
- C1-----C4 = 0.33Uf,
- D1, D2 =1N5402,
- D3, D4 = 1N40007
- T2, T3, T7, T8= 8050,
- T9 = 8550
- T5, T4 = TIP 127
- T1, T6 = BDY29
- TRANSFORMER = 12-0-12V, 20 AMP.
- T1, T6, T5, T4 SHOULD BE MOUNTED OVER SUITABLE HEATSINK.
- BATTERY = 12V, 30AH



Need Help? Please Leave a Comment! We value your input—Kindly keep it relevant to the above topic!