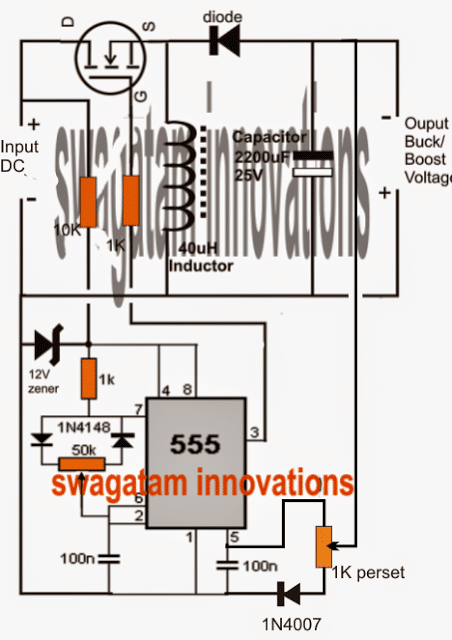
In this post I have explained s few simple DC to DC buck-boost converter circuits which can be used for either stepping up the input DC voltage or stepping down the input DC voltage to specific output DC voltage levels. Since a buck-boost converter allows the input voltage to be either stepped up or stepped […]
Explained
Light Emitting Diodes (LED) Explained
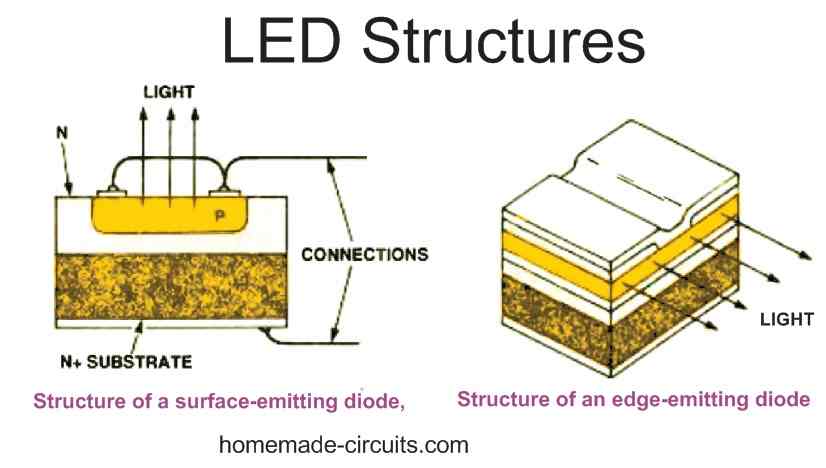
The full form of LED is Light Emitting Diode. LEDs are special type of semiconductor diodes which emit light in response to a potential difference applied across their terminals, hence the name light emitting diode. Just like a normal diode LEDs also have two terminals with polarity, namely anode and cathode. To illuminate an LED […]
CMOS Astable, Bistable, Monostable Circuits Explained
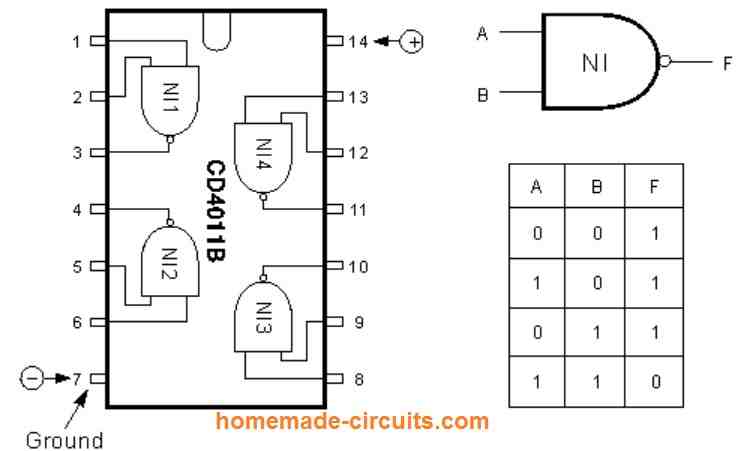
In this article I have explained how to use the low-cost CD4001 and CD4011 quad 2-input gate CMOS integrated circuits in bistable, astable, and monostable multivibrator applications through forty different manners. We also learn how to enhance and modify these configurations to produce highly improved outputs from these multivibrators. When CMOS logic gates are configured […]
OCL Amplifier Explained
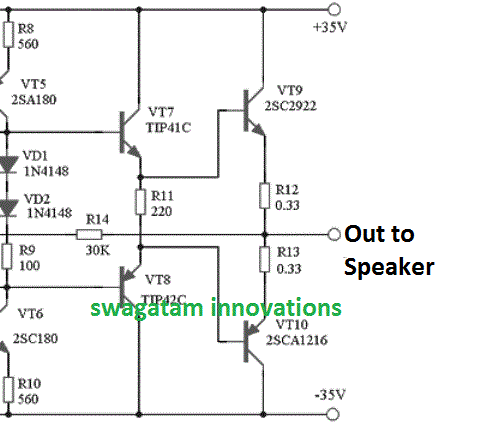
In the field of audio amplifiers OCL stands for Output Capacitor-Less Amplifier design. How it Works In this OCL type of amplifier topology or configuration, the power output stage is directly coupled to its preceding driver stage without coupling capacitors. The following figure shows a typical OCL amplifier output stage, as can be seen, the […]
Types of Batteries Explained [NiCd, NiMH, Lead Acid, Li-Ion]
In this post I have explained the main types of batteries that are widely used in today’s world for almost all important applications, ranging from cars, automobiles mobile phones, airplanes, industries, satellites to name a few. The Nickel Cadmium (NiCd) Battery Fundamentally, the NiCd battery adopts fast charging as opposed to slow charging and employs […]
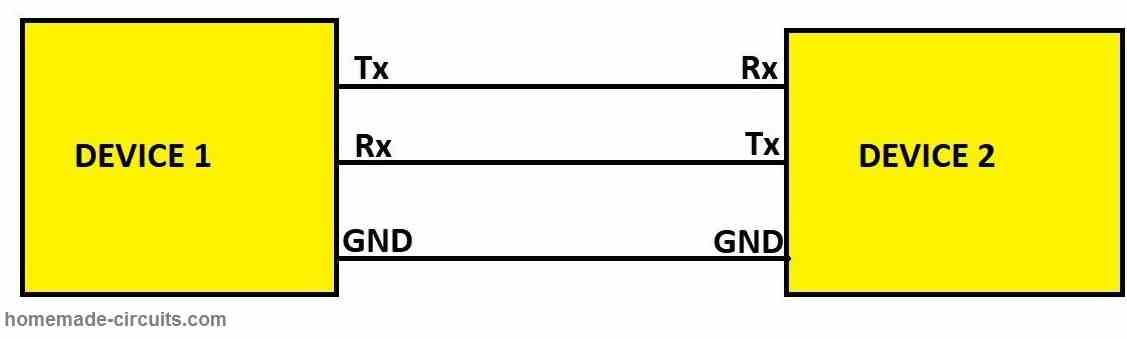
Communication Protocols in Microcontrollers Explained
In this post I am going to explain various communication protocols that are used by microcontrollers, microprocessors and ICs for communicating with various sensors, electronic drivers, input and output devices. We will see: Why do communication protocols exist in electronics? UART protocol. I2C or IIC or “I squared C” protocol. SPI or Serial Peripheral Interface […]