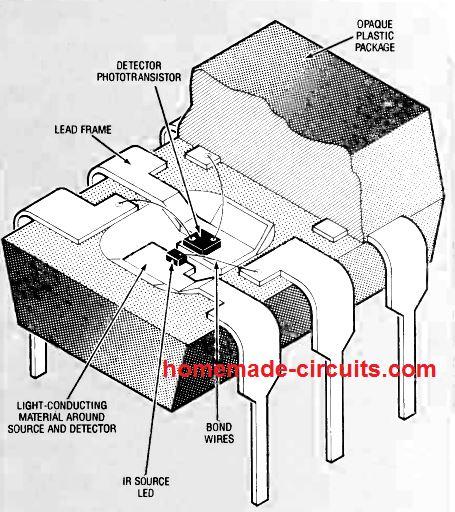
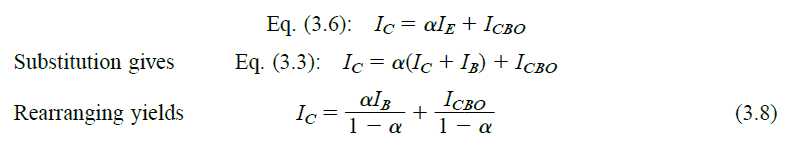OPTOCOUPLERS OR OPTOISOLATORS are devices that enable efficient transmission of DC signal and other data across two circuit stages, and also simultaneously maintain an excellent level of electrical isolation between them. Optocouplers become specifically useful where an electrical signal is required to be sent across two circuit stages, but with an extreme degree of electrical […]
Characteristics
Schottky Diodes – Working, Characteristics, Application
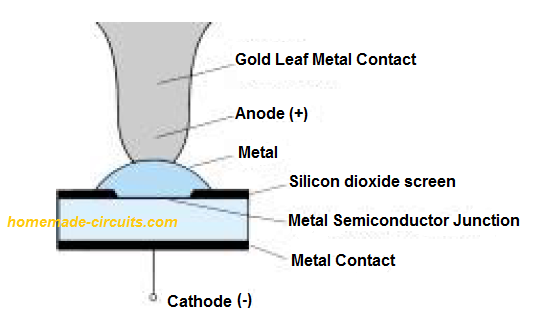
Schottky barrier diodes are semiconductor diodes designed with minimal forward voltage and fast switching speeds which may be as low as 10 ns. These are manufactured in current ranges of 500 mA to 5 amps and up to 40 V. Due to these features they become specifically suitable in low voltage, high frequency applications such […]
Common Emitter Amplifier – Characteristics, Biasing, Solved Examples
This configuration is known as common-emitter configuration because here the emitter is used as the common negative terminal for the input base signal and the output load. In other words, the emitter terminal becomes the reference terminal to both the input and output stages (meaning common to both the base and collector terminals). Common emitter […]
What is IGBT: Working, Switching Characteristics, SOA, Gate Resistor, Formulas
IGBT stands for Insulated-gate-Bipolar-Transistor, a power semiconductor which includes the features of a MOSFET’s high speed, voltage dependent gate switching, and the minimal ON resistance (low saturation voltage) properties of a BJT. Figure 1 exhibits IGBT equivalent circuit, where a bipolar transistor works with a MOS gate architect, while the similar IGBT circuit is actually […]
Zener Diode Circuits, Characteristics, Calculations
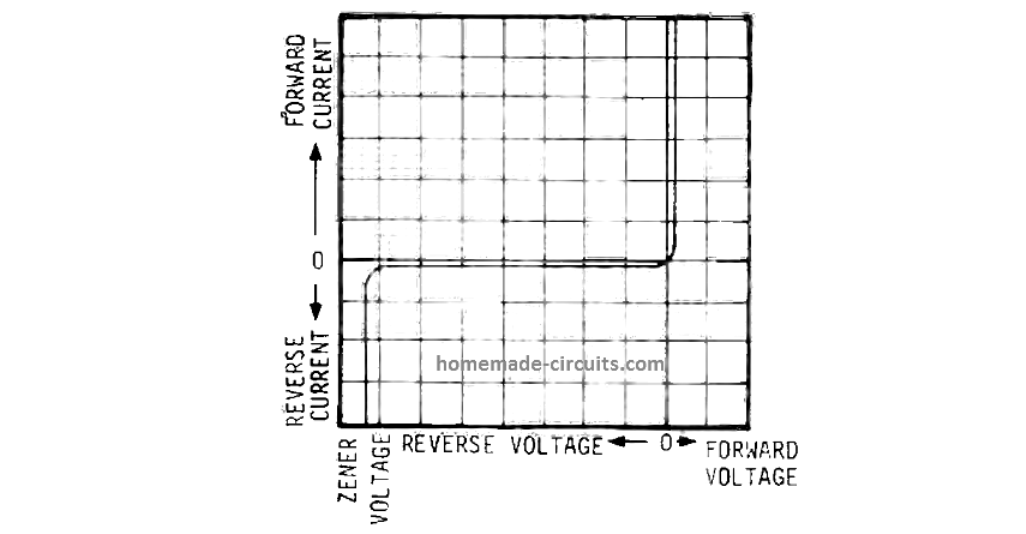
Zener diodes – named after its inventor Dr. Carl Zener are fundamentally used in electronic circuits for generating precise voltage references. These are devices that are able to create a practically constant voltage across them regardless of variations in circuit and voltage situations. Externally, you may find zener diodes a lot similar to standard diodes […]
BJT Transfer Characteristics
In BJTs or bipolar transistors, transfer characteristics can be understood as plotting of an output current against an input-controlling magnitude, which consequently exhibits a direct “transfer” of variables from input to output in the curve represented in the graph. We know that for a bipolar junction transistor (BJT), the output collector current IC and the […]