Although transistors (BJTs) are popularly used for making amplifier circuits, these can be also effectively used for switching applications. A transistor switch is a circuit in which the collector of the transistor is switched ON/OFF with relatively larger current in response to a correspondingly switching low current ON/OFF signal at its base emitter. As an […]
Newly Updated Circuit Projects:
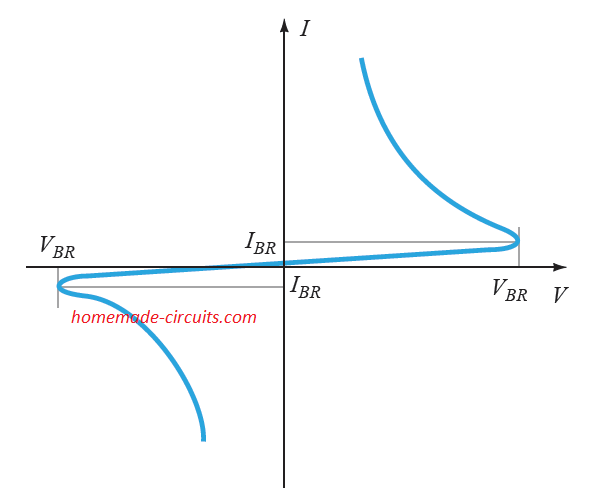
Diac – Working and Application Circuits
The diac is a two-terminal device having a combination of parallel-inverse semiconductor layers, which allows the device to be triggered through both directions regardless of the supply polarity. Diac Characteristics The characteristics of a typical diac can be seen in the following Figure, which distinctly reveals the presence of a breakover voltage in across both […]
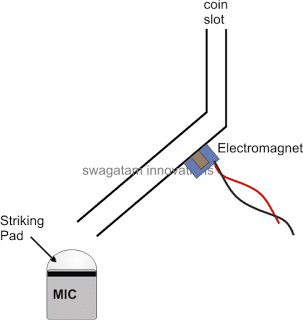
Simple Tea Coffee Vending Machine Circuit
A simple tea, coffee vending machine circuit idea is explained here which allows a customer to access the beverage with a press of a button and by inserting a genuine 5 rupee coin. The idea was requested by Mr. Ramesh. Circuit Objective and Requirement I need the water puling mechanism like coffee vending machine if […]
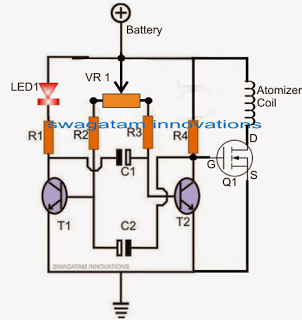
Atomizer Circuit for E Cigarettes
In this post I have explained a simple transistorized PWM controlled atomizer circuit for E-Cigarettes which may be used for controlling the filament heat levels of an atomizer. The idea was requested by Mr. Dave. Technical Specifications My name is Dave. Found your site searching for a driver circuit for a mosfet gate. I like […]
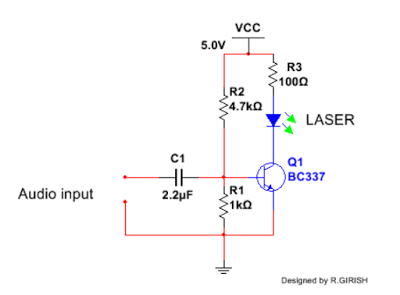
Laser Communicator Circuit – Send, Receive Data with Laser
In this article I have explained how to make a simple laser communicator circuit for sending and receiving data through laser beam. Laser has been a boon since its invention. Laser is used in wide variety of applications, from Blu-ray driver to high powered cutting torch. There are also many classifications of laser technologies. Here […]
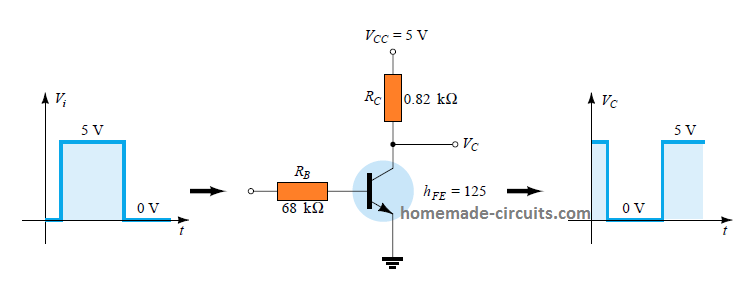
DC Biasing in Transistors – BJTs
In simple terms, biasing in BJTs may be defined as a process in which a BJT is activated or switched ON by applying a smaller magnitude of DC is across its base/emitter terminals so that its is able to conduct a relatively larger magnitude of DC across its collector emitter terminals. The working of a […]