A sine wave generator is actually a sine wave oscillator circuit which generates an exponentially rising and falling sinusoidal waveform.
The 9 simple sine wave generator circuits presented in the following article are easy to build, since they incorporate a small number of ordinary electronic components, and can be used for generating an exponentially varying waveform with a specified frequency.
The frequency is determined by an RC feedback network between the input and output of the circuits.
The kind of sine waveform that can be achieved from the following circuits can be witnessed in the following diagram:

1) High Quality Sine Wave Oscillator
The below indicated sine wave generator circuit is not only easy to build, it also provides an exceptionally pure output having a total noise and distortion level that is effectively under 0.1%.
The design is a simple Wien Bridge oscillator configured around an operational amplifier.
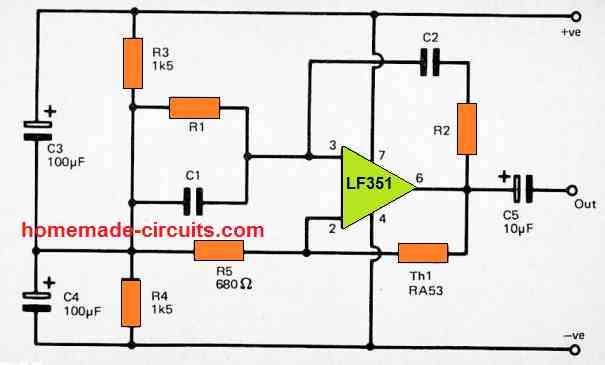
However, the circuit consists of thermistor Th1 used for stabilizing the closed loop gain of the circuit with a magnitude which can generate a very good quality output sine wave signal with an amplitude of around 2 volts peak to peak.
The one downside of this circuit is the presence of RA53 thermistor which has a useful property of self heating. This type of thermistor can be much costlier compared to the normal thermistors.
Nevertheless, the easy design of this sine wave generator and the an excellent sine wave output from this stabilization technique probably justifies the high cost.
Alternatively, you can replace the thermistor with a small 6 V incandescent bulb for getting the same effect
Capacitors C1, C2 and resistors R1, R2 are used for fixing the operating frequency of the output sine wave. Here, the resistor R1 value can be same as R2, and likewise C1 and C2 can also have the identical values.
The frequency of sine wave could be determined through the following formula
Frequency = 1/2πCR
This implies that, if the operating frequency is approximately 1 kHz, then C1 and C2 could be around 4n7, and R1 and R2 could be set at 33k. Modifying either the resistors or the capacitors allows an oppositely proportional variation in the frequency value.
It is recommended to have the values of the two resistors between a few kilohms and many Megohms. For the capacitors any value in the range of a few pFs or higher can be just fine.
Having said that, you cannot use polarized type of capacitors like electrolytic or tantalum elements, and practically speaking this condition restricts the value of the capacitor to around 2.2uF maximum.
It is possible to make the output frequency of the sine wave adjustable by replacing the R1 and R2 with fixed resistors and by putting a potentiometer in series, and it is certainly essential to utilize a twin gang potentiometer to ensure that R1 and R2 series values could be altered in a combined way.
The circuit works with a least supply voltage of around 6 volts, and the the circuit can tolerate a absolute maximum 36 volts.
This simple sine wave generator circuit can be efficiently driven through a dual balanced power supply using the center tapped 0V supply being generated by the resistors R3, and R4.
If the circuit is powered through genuine dual supplies, then obviously, R3 + R4 tend to be unnecessary and could be eliminated.
Hi Swagatam,
Question about the second circuit in section 8 . I have a simple rail splitter circuit consisting of a resistor (100k) and a capacitor (10uF) divider in parallel across the positive and ground rails taking a virtual ground from the centre rail . I’ve sent you the circuit via email. How would I apply this correctly, including power supply to the op amp, to the circuit I mentioned?
Kind regards,
Alasdair
Hi Alasdair,
I saw the diagram, it should work as intended. You can consider reducing the resistor values to 10k, or use a 10k preset as shown below:
" rel="ugc">
Is there a practical (and safe) way to rectify the sawtooth wave form from a generator to a pure sine wave? Obviously, the biggest hurdle being the big power requirements for the average home (120v and around 10kw).
If you are referring to AC voltages at 10kW then you might need to do it through an inverter, by converting the sawtooth into SPWM, through transformers.
There is a small issue with the 8th circuit, C2 and R2 are connected parallel on the schematic, but they should be in series. After this fix the circuit works well and the frequency is quite stable, i’m using it for a self-test board.
Thank you so much Zoltan, for the important correction.
I have modified the 8th diagram accordingly, please check it and let me know if it is alright or not.
Many thanks….
With this circuit can used to that is 50Hz as inverter oscilator
These circuits will not help to create a sine wave inverter.
I used circuit #4.
Change the bias resistor to 330k and T resistor to 5k6, that I have in my spare, give me ~1080Hz @400mVpp
It is sufficient for test purpose .
Thank you
Yes, 400mV should be enough for most test applications
Sir, i want to know if these sine wave oscillators can be used as an oscillator stage in an inverter to build a sine wave inverter circuit
Hi Alimon, sine wave cannot be applied directly to the gate or base of transistors for driving the transformer with sine wave, so it is not possible.
Hi I have bread boarded the Variable Sine Wave Generator Circuit and it works BUT that is to the scope when I try and connect to a audio amp it kills the signal Have tried a resistor / cap / elec non allow the siganl to come through the amp your comment
Hi, you can probably try using a transistor buffer stage in the middle and check if that helps. You can use a BC547 in emitter follower mode. Connect the base to the sine wave signal through a 100K resistor, connect the collector to a DC supply such as +5V or +12V, connect the emitter to the amplifier input.
I made your “Single Transistor Sine Wave Generator” variable by replacing R1+R2 with a double gang 10k pot wired in series with a 3.3k resistor on each side. Thank you!
Glad you could make it successfully!
What I can see is LF351 nothing else the rest is resistors and capacitors
Good evening swagatam
I can see in your write up about this circuit you mentioned thermistor but I can’t find one in it and why is’t so or is’t that you made a mistake in the circuit diagram?
Emmanuel, please see the first diagram carefully, the Th1 RA53 is the thermister