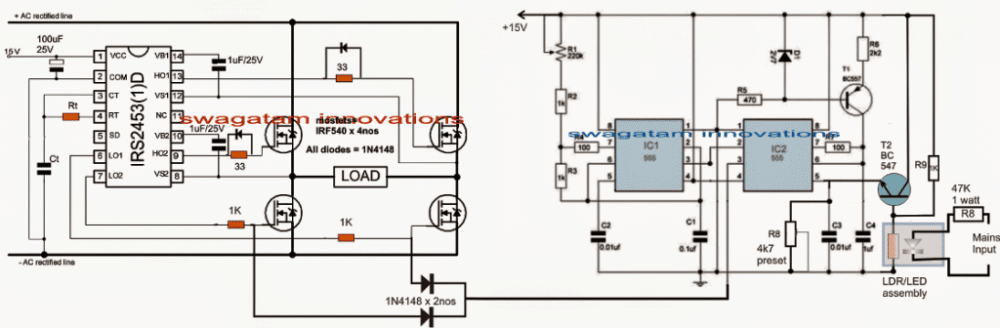
In this post I have explained a simple circuit design which ensures a perfectly stabilized 220 V or 120 V mains voltage across the connected load, without using relays or transformers, rather by the use of accurately dimensioned and self adjusting PWM pulses. The idea was requested by Mr. Mathew. Warning: Circuits I have explained […]
Voltage Control and Protection
Simple Refrigerator Protector Circuit
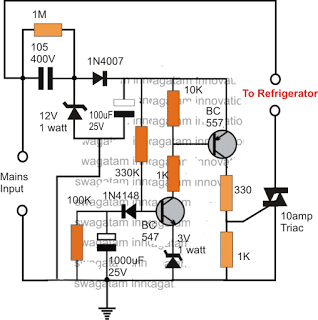
This simple refrigerator protector circuit is actually a delay ON timer circuit which makes sure that whenever a power failure occurs or in case abrupt power fluctuations take place, the refrigerator is never allowed to switch ON instantly, rather after a delay of a few moments. Conventional Protection Features Today most modern refrigerators are equipped […]
Triac Phase Control using PWM Time Proportional
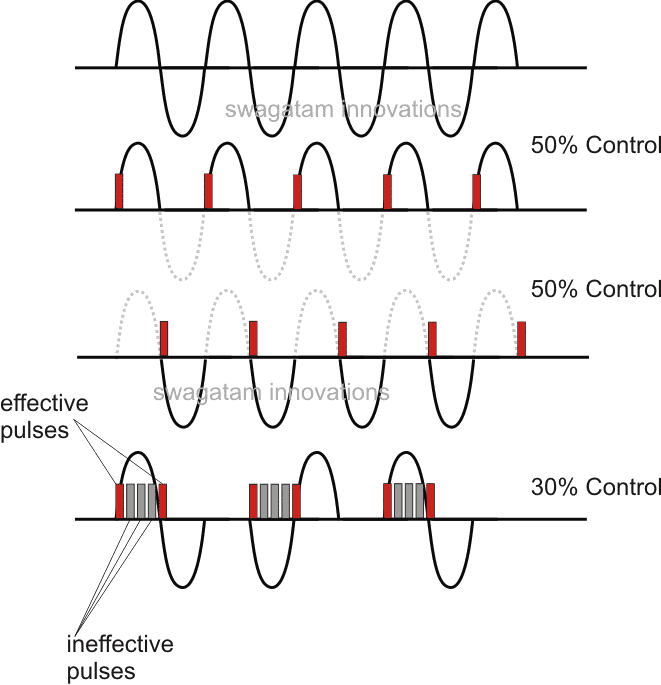
A triac phase control using a PWM circuit can be useful only if it’s implemented using a time-proportional format, otherwise the response could be haphazard and inefficient. In a few of of my earlier articles as given below: Simple Remote Controlled Fan Regulator Circuit Push Button Fan Regulator with Display Circuit Dimmer Circuit for LED […]
Surge Arrestor Circuit with Measuring Facility
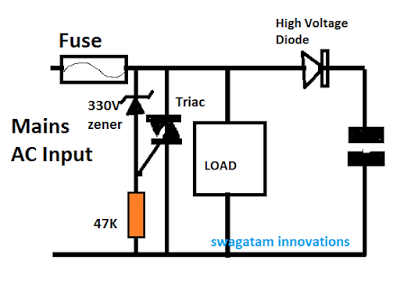
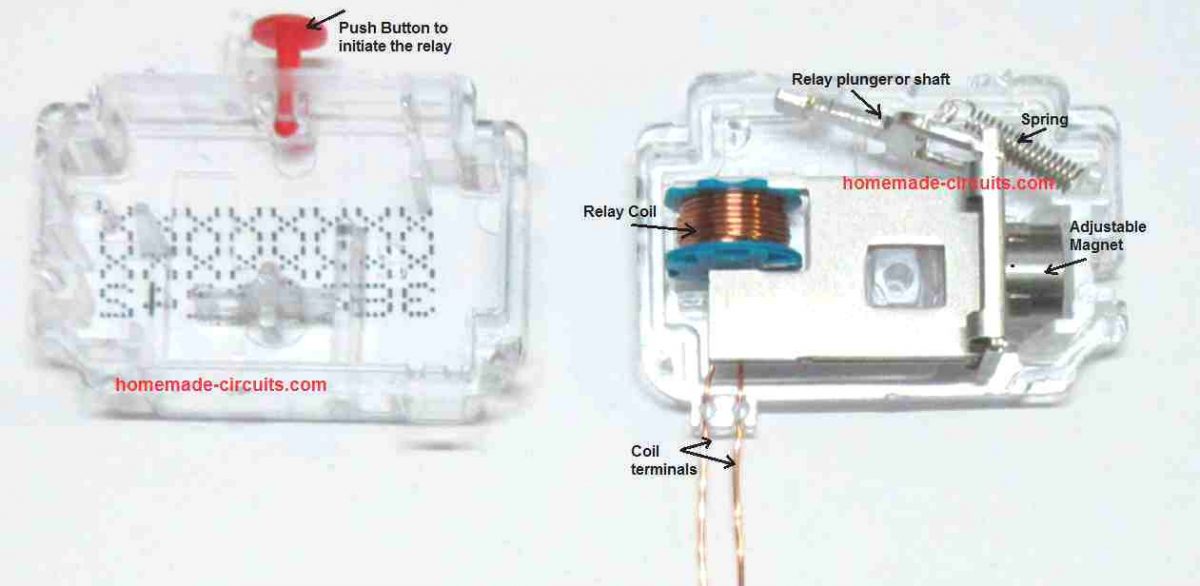
In this post I have explained about a simple surge voltage protector circuit using a fuse and a triac crowbar circuit and also learn the method to record and measure the last maximum surge that could have destroyed the specified load in case the protection was not introduced. The idea was requested by Mr. Akram. […]
How RCCB Works [with Circuit Diagram]
A Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB) or a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI), is a form of circuit breaker which will shut down mains AC power as soon as it detects an discrepancy between the incoming current and the outgoing current, through it. The primary objective of an RCCB device is to cut-off main AC […]
Using an NTC Thermistor as a Surge Suppressor
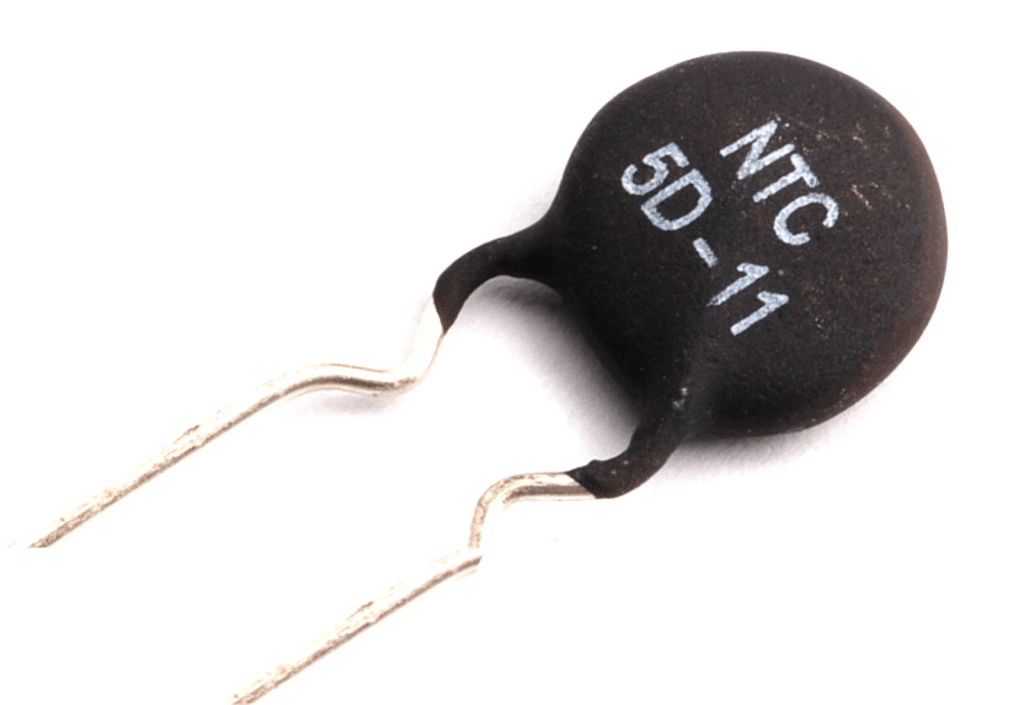
A Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) thermistor is a device which is able to suppress switch ON current surge due to its initial higher resistance at room temperature. However, as the NTC suppresses the initial surge current, it warms up causing its resistance to drop to nominal levels and this in turns allows the current to […]