The article below presents a comprehensive know how regarding how buck converters work. As the name suggests, a buck converter is designed to oppose or restrict an input current causing an output that may be much lower than the supplied input. In other words it can be considered a step down converter which could be […]
Work
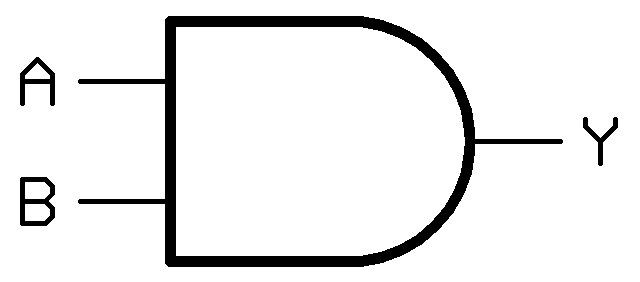
How Logic Gates Work
In this post I will comprehensively explain what logic gates are and its working. We will be taking a look at the basic definition, symbol, truth table, Multi input gates, we will be also constructing transistor based gate equivalents and finally we will take an overview on various relevant CMOS ICs. What are Logic Gates […]
How Contactless Infrared Thermometers Work – How to Make One
In this post I have explained the basic working concept of thermal scanners or contactless IR thermometers, and also learn how to make a practical DIY prototype of the unit without Arduino. In the post COVID-19 era, witnessing doctors holding a contactless temperature gun and pointing toward the forehead of a COVID-19 suspect is a […]
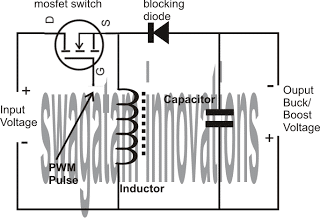
How Buck-Boost Circuits Work
We all have heard a lot about buck and boost circuits and know that basically these circuits are used in SMPS designs for stepping up or stepping down a given voltage at the input. The interesting thing about this technology is that it allows the above functions with negligible heat generation which results in a […]
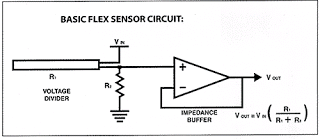
How Flex Resistors Work and how to Interface it with Arduino for Practical Implementation
As electronics enthusiasts we may come across many kinds of resistors, from small fixed resistor to high current bulk rheostat. There are humongous classifications among resistors, but here we will focus on a particular kind of resistor called “flex resistor” and learn how it works. As the name signifies a flex resistor is flexible and […]
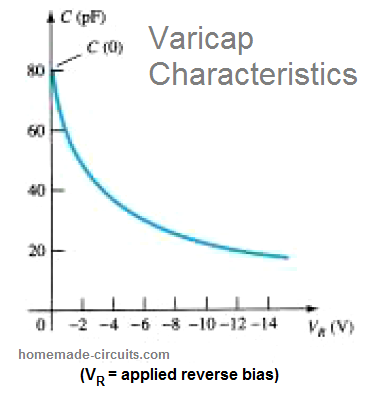
How Varactor (Varicap) Diodes Work
A varactor diode, also called varicap, VVC (voltage-variable capacitance, or tuning diode, is a type of semiconductor diode which features a variable voltage-dependent capacitance on its p-n junction when the device is reversed biased. Reverse bias basically means when the diode is subjected to an opposite voltage, meaning a positive voltage at the cathode, and […]