A very interesting circuit of a RMS controlled modified sine wave inverter is discussed in this article which incorporates just ordinary transistors for the proposed implementations. The use of transistors typically makes the circuit easier to understand and more friendly with the new electronic enthusiasts. The inclusion of a PWM control in the circuit makes […]
BJTs
Understanding Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs)
If we look at the diodes, their internal construction look very simple. They are made by joining two pieces of semiconductor material, and this is called a pn-junction. But when we talk about bipolar junction transistor or bjt, then things get little more complicated. It needs adding one more layer of semiconductor material, and that […]
DC Biasing in Transistors – BJTs
In simple terms, biasing in BJTs may be defined as a process in which a BJT is activated or switched ON by applying a smaller magnitude of DC is across its base/emitter terminals so that its is able to conduct a relatively larger magnitude of DC across its collector emitter terminals. The working of a […]
Understanding Common Base Configuration in BJTs
In this section we are going to analyze BJT common-base configuration, and learn regarding its driving point characteristics, reverse saturation current, base to emitter voltage and evaluate the parameters through a practical solved example. In the later parts we will also analyze how to configure a common-base amplifier circuit Introduction The symbols and annotations utilized […]
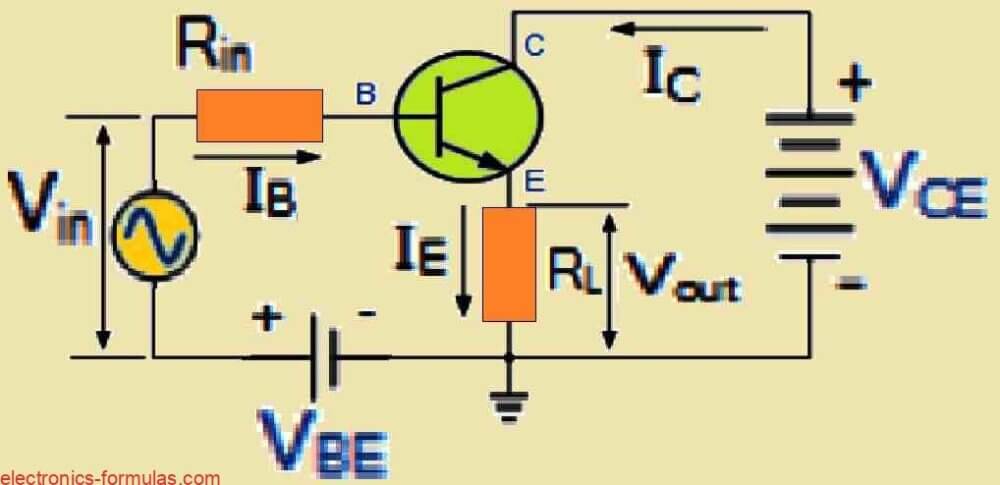
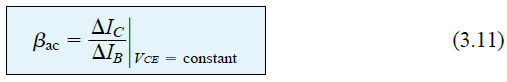
What is beta (β) in BJTs
In bipolar junction transistors the factor that determines the sensitivity level of the device to base current, and the amplification level at its collector is called beta or the hFE. This also determines the gain of the device. In other words, if the BJT uses relatively higher current to switch its collector load optimally then […]