In this post we try to investigate the mains differences between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC).
The word AC and DC are pretty common with electronics and we all come across it while developing or dealing electronic circuit designs.
Overview
Though the terms are very ordinary with the field, many noobs become confused with them as far as the technical difference is concerned.
For the newcomers in the field of electronic the following note will prove quite useful, lets learn exactly what;s the difference between alternating and direct current or simply AC and DC.
As the name refers to an alternating current is a current which alternates or fluctuates between a certain positive and negative voltage levels.
The intermediate area of the positive and the negative extremes of the above voltage levels is the zero level or the neutral level.
Before we begin, let me inform the readers that here "current flow" refers to the position of the flowing electrons while passing through a conductor at any particular instance of time.
The level of displacement of the electron depends on the voltage, which is the source responsible for making the electrons move (My Definition of Current).
Difference Between AC and DC
Looking at the diagram, we see at at any instance AC fluctuates between zero to the positive peak, then it returns back to zero and heads for the negative and finally back to zero.
The cycle continues many times per second depending upon the frequency of the signal.
An AC can be sinusoidal or square wave type. A sinusoidal or sine type AC makes the above alterations in an exponential form, meaning the rise and the fall proceeding of the waves vary instantaneously with time and takes the form of the wave as shown in the diagram.
A square wave AC differs with a sine AC as it does not vary its shape with time rather the rise and fall are in the shape of definite square or rectangle waveforms.

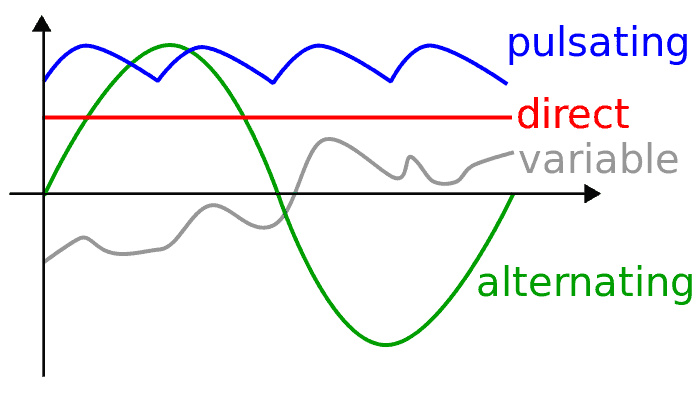
Image courtesy: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Types_of_current.svg
A direct current, again as the name refers to is "direct" by nature, meaning they do not generate oscillations or waves like an AC.
Thus a DC will never have a varying polarity neither a frequency.
A DC will be either a negative with reference to zero or positive with reference to zero but never be simultaneously.
An alternating current can be easily converted to DC with the help of rectifying devices called the diodes which may be configured as bridge networks for implementing the conversions.
Similarly a DC can be also be converted to AC using some special electronic circuits, it's a little complicated than converting AC to DC though.
Need Help? Please Leave a Comment! We value your input—Kindly keep it relevant to the above topic!