This calculator helps estimate resonant frequency or compensation capacitor for a wireless EV charging primary coil. It is for first-step design and learning, not final tuning...
EV Wireless LC Resonance Calculator
1) What You Are Actually Calculating
In wireless charging, primary coil is always used with a resonance capacitor, together forming an LC tank. This calculator finds one unknown when two others are already known.
- Coil inductance (L).
- Resonant capacitor (C).
- Target operating frequency (f).
You must already know at least two, otherwise nothing works.
2) Measure Coil Inductance First (Very Important)
Before using the calculator, let us be clear.
- Build the actual primary coil.
- Mount ferrite backing if used.
- Measure inductance using an LCR meter.
Always measure inductance in microhenry (µH). Do not rely only on online coil formulas. This measured value is what you enter as Primary Inductance.
3) Choose What You Want To Calculate
At the top, select Calculate.
- Resonant Frequency: when L and C are known.
- Capacitance: when L and frequency are known.
- Inductance: when C and frequency are known.
For beginners, mostly you will use Capacitance (µF), that is common case.
4) Enter The Two Known Values
Typical example.
You measured:
Primary inductance = 110 µH.
You want:
Operating frequency = 85,000 Hz.
So enter:
One field: 110 and select Primary Inductance µH.
Other field: 85000 and select Frequency Hz.
Order does not matter, calculator will handle it.
5) Enter The Coupling Coefficient (k)
This shows how well primary and secondary coils couple magnetically.
If unsure, use safe beginner values.
- Coils very close and aligned: k = 0.3 to 0.4.
- Moderate air gap or slight misalignment: k = 0.2 to 0.3.
- Poor alignment: k = 0.15.
For first designs, 0.25 is a good starting value. This matters since coupling changes effective inductance. Ignoring k gives wrong resonance prediction.
6) Click CALCULATE
Calculator will show either:
Estimated resonant frequency or required resonance capacitor value.
This is starting design value we can use....
7) Choosing Nearest Standard Capacitor Value
Exact capacitor value never exists in real life.
Example:
Calculated value = 0.148 µF.
Use:
0.15 µF, or combine capacitors in parallel.
Always use polypropylene film capacitors, high voltage rating, low ESR. Electrolytic capacitors are not suitable.
8) Important Check
This calculator gives theoretical resonant point only.
- In real wireless EV charging:
- Vehicle position changes
- Coupling changes
- Load changes
- Frequency shifts slightly
So expect fine-tuning, expect small frequency or capacitor adjustment, this is normal and unavoidable. All commercial systems do this.
9) Recommended Oscillator Or Driver Setup (Wireless Charge Transmitter)
Once resonance values are known, use one of these.
Best option, industry standard.
Phase-shifted full H-bridge
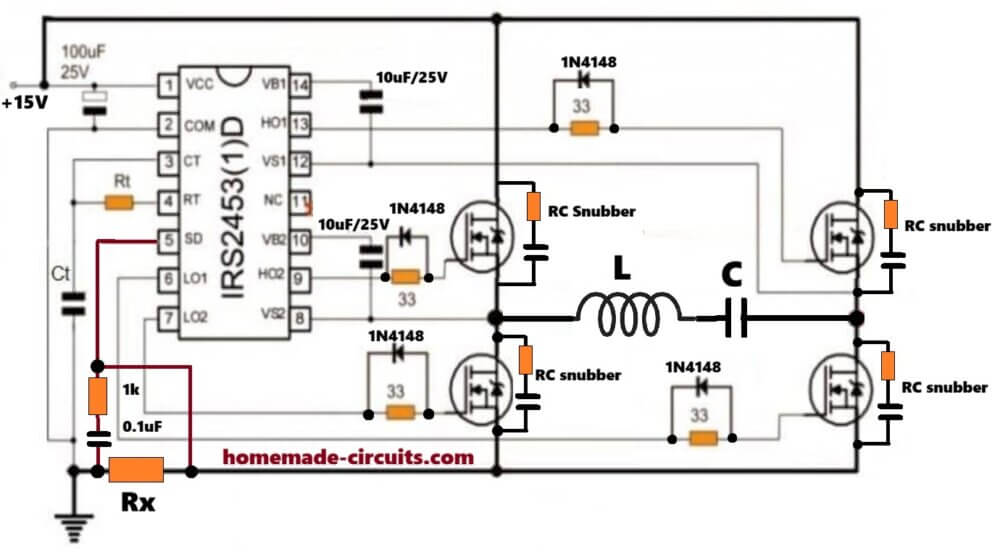
- Fixed frequency
- Controlled power
- ZVS Control through deadtime control
- Suitable as EV chargers
Medium power option.
Half-bridge resonant inverter
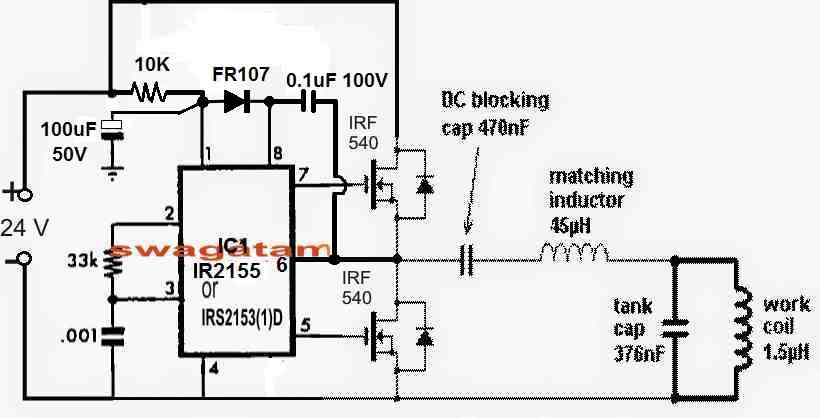
- Simpler
- Good efficiency
- Still controllable
Learning only.
Self-oscillating ZVS (Royer/Mazzilli)
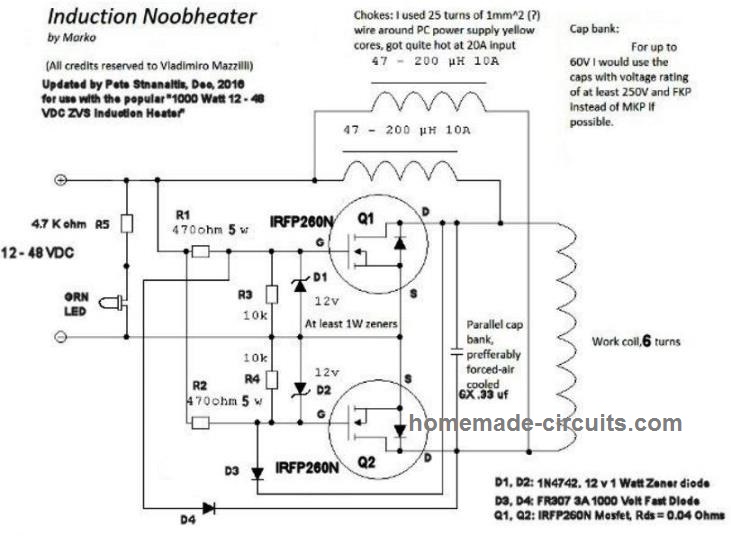
- Easy to build
- Frequency drifts
- Not suitable for professional EV systems